干旱气象 ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 607-615.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-04-0607
内蒙古东南部一次伴冻雨的极端暴雪天气特征
- 内蒙古自治区气象台,内蒙古 呼和浩特 010051
-
收稿日期:2025-01-16修回日期:2025-03-06出版日期:2025-08-31发布日期:2025-09-08 -
通讯作者:张桂莲(1966—),女,内蒙古呼和浩特人,正高级工程师,主要从事各种灾害性天气预报研究。E-mail: 2561750566@qq.com。
-
作者简介:赵睿峰(1994—),男,内蒙古包头人,工程师,主要从事灾害性天气预报研究。E-mail: rfzhao@163.com。 -
基金资助:内蒙古自治区自然科学基金项目(2023QN04008);内蒙古自治区自然科学基金项目(2024LHMS04022);内蒙古自治区自然科学基金项目(2025QN04043);内蒙古自治区自然科学基金项目(2025MS04044);中国气象局复盘总结专项项目(FPZJ2025-020);中国气象局复盘总结专项项目(FPZJ2025-021)
Characteristics of an extreme snowstorm with freezing rain in southeastern Inner Mongolia
ZHAO Ruifeng( ), ZHANG Guilian(
), ZHANG Guilian( ), HUANG Xiaolu, HUO Zhili, JIANG Jing
), HUANG Xiaolu, HUO Zhili, JIANG Jing
- Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Meteorological Observatory, Hohhot 010051, China
-
Received:2025-01-16Revised:2025-03-06Online:2025-08-31Published:2025-09-08
摘要:
伴冻雨的极端暴雪在内蒙古较少出现,研究此类天气对预报预警和灾害防御有重要意义。利用常规气象观测资料、欧洲中期天气预报中心ERA5再分析资料和内蒙古通辽多普勒天气雷达资料,针对2023年11月5—6日内蒙古东南部一次伴冻雨的极端暴雪天气过程,深入分析其发生的环境条件和成因。 结果表明:500 hPa高空冷涡、700 hPa暖式切变线、850 hPa偏东风急流以及北上的地面江淮气旋是此次过程的主要影响系统。冻雨发生时,垂直方向呈现“冷、暖、冷”的层结结构,925~875 hPa存在融化层,雷达基本反射率图中出现零度层亮带;过冷却水粒子和冰晶经零度层亮带进入融化层,之后降落到地面,这一过程符合融化型冻雨的特征。中层西南暖湿气流在低层偏东风形成的冷垫上爬升,产生强烈的动力锋生作用,为极端降雪提供了强劲的动力抬升条件,而强上升运动的存在和长时间维持,是导致极端暴雪天气发生的重要因素。暴雪区低层比湿最大达4~6 g·kg-1,且低层强水汽辐合维持时间长,为极端暴雪提供了充足的水汽供应。综合来看,此次内蒙古东南部伴随冻雨的极端暴雪天气,是高低空系统相互作用、动力锋生触发的垂直抬升以及持续水汽输送共同作用的结果。
中图分类号:
引用本文
赵睿峰, 张桂莲, 黄晓璐, 霍志丽, 江靖. 内蒙古东南部一次伴冻雨的极端暴雪天气特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(4): 607-615.
ZHAO Ruifeng, ZHANG Guilian, HUANG Xiaolu, HUO Zhili, JIANG Jing. Characteristics of an extreme snowstorm with freezing rain in southeastern Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(4): 607-615.
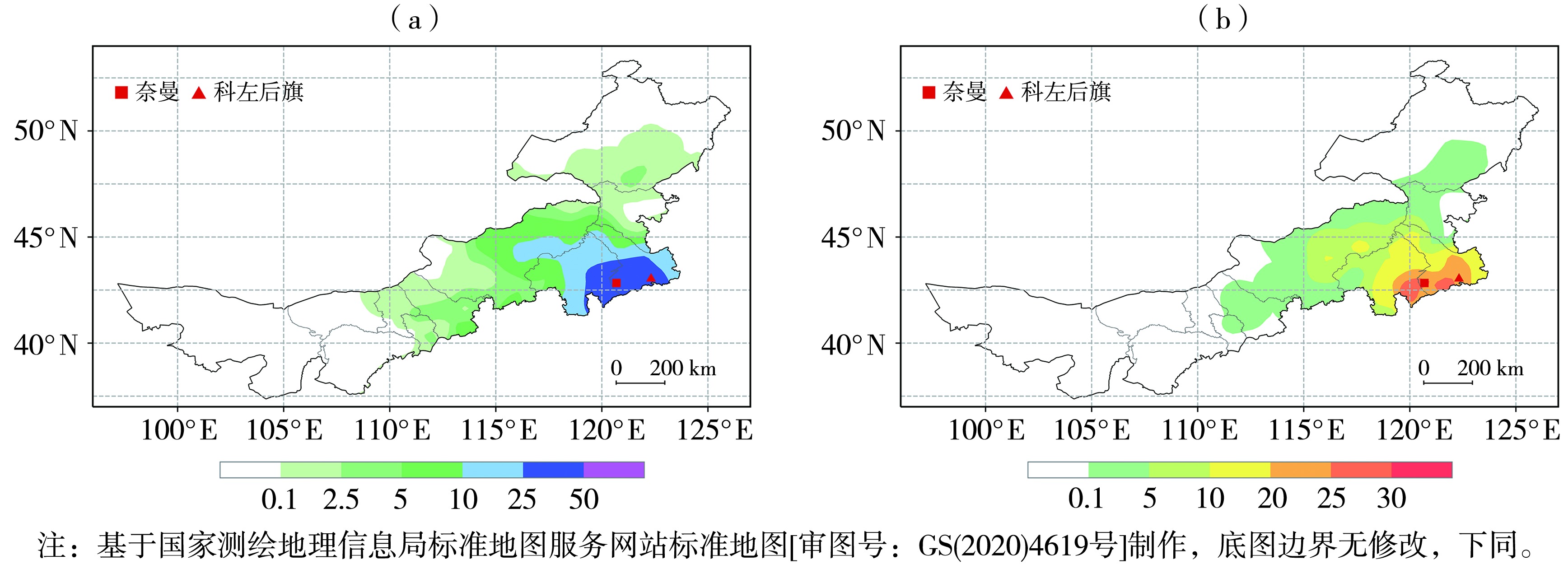
图1 2023年11月5日08:00—6日20:00内蒙古累计降水量(a,单位:mm)和新增积雪深度(b,单位:cm)
Fig.1 Accumulated precipitation (a, Unit: mm) and newly added snow depth (b, Unit: cm) in Inner Mongolia from 08:00 on 5 to 20:00 on 6 November 2023

图2 2023年11月5日20:00(a、b)和6日08:00(c、d)500 hPa位势高度场(蓝色实线,单位:dagpm)和700 hPa风场(风矢,单位:m·s-1)(a、c)、海平面气压场(蓝色实线,单位:hPa)和850 hPa风场(风矢,单位:m·s-1)(b、d)
Fig.2 The 500 hPa geopotential height field (blue solid lines, Unit: dagpm) and 700 hPa wind field (wind vectors, Unit: m·s-1) (a, c), sea level pressure field (blue solid lines, Unit: hPa) and 850 hPa wind field (wind vectors, Unit: m·s-1) (b, d) at 20:00 on 5 (a, b) and 08:00 on 6 (c, d) November 2023

图3 2023年11月5日08:00—6日20:00科左后旗(a)和奈曼旗(b)逐小时降水量、2 m气温和相对湿度演变 (蓝色方框为出现冻雨的时段)
Fig.3 The evolution of hourly precipitation, 2 m air temperature and relative humidity of Kezuohouqi (a) and Naimanqi (b) from 08:00 on 5 to 20:00 on 6 November 2023 (The blue box shows the period of freezing rain)
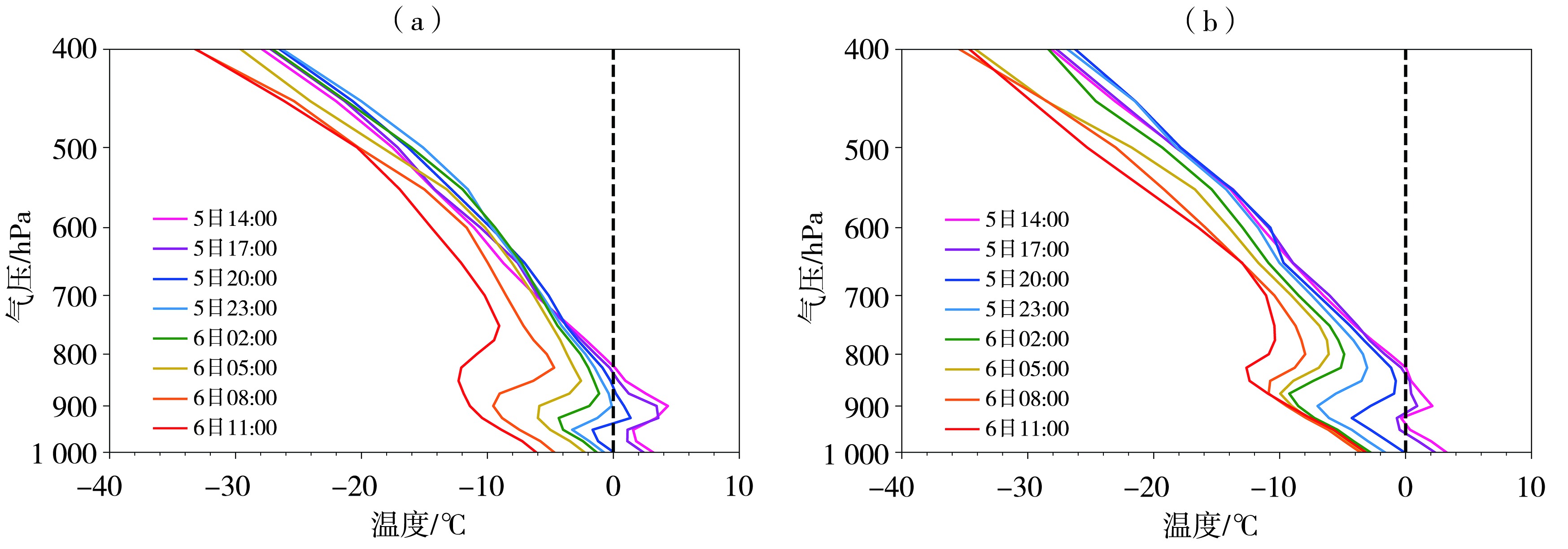
图4 2023年11月5日14:00—6日11:00科左后旗(a)和奈曼旗(b)逐3 h温度廓线 (黑色虚线为0 ℃等温线)
Fig.4 The 3-hour temperatures profiles of Kezuohouqi (a) and Naimanqi (b) from 14:00 on 5 to 11:00 on 6 November 2023 (Black dotted line is 0 ℃ isotherm)
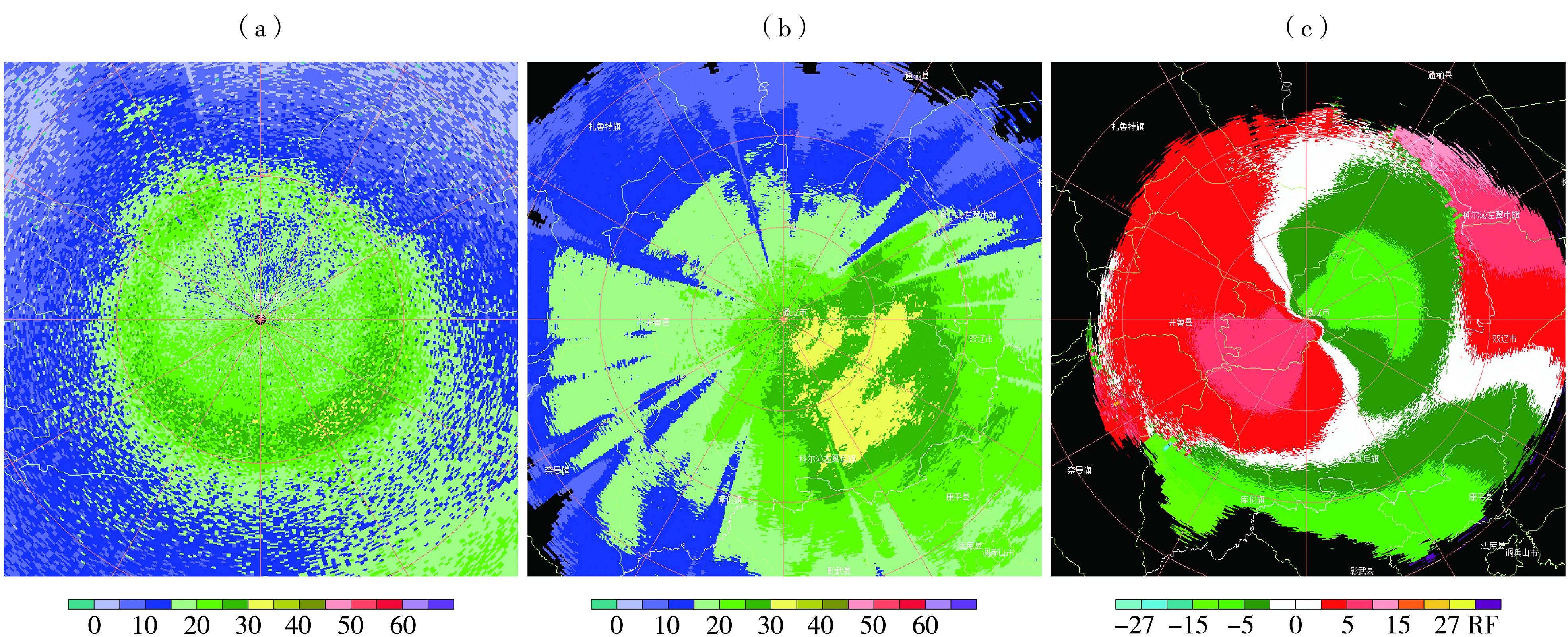
图5 2023年11月5日20:46(a)、6日00:05(b、c)通辽市多普勒雷达6.0°仰角基本反射率因子(a,单位:dBZ)、组合反射率(b,单位:dBZ)和2.4°仰角基本径向速度(c,单位:m·s-1)
Fig.5 The basic reflectivity factor on the elevation of 6.0° (a, Unit: dBZ), the composite reflectivity (b, Unit: dBZ) and radial velocity on the elevation of 2.4° (c, Unit: m·s-1) of Tongliao Doppler radar at 20:46 on 5 (a) and 00:05 on 6 (b, c) November 2023

图6 2023年11月5日08:00—6日20:00奈曼旗特大暴雪中心水汽通量散度(黑线,单位:10-6 g·cm-2·hPa-1·s-1)和水汽通量(填色,单位:g·cm-1·hPa-1·s-1)时间-高度剖面(a)、11月5日20:00大气可降水量(蓝线,单位:mm)和850 hPa比湿(填色,单位:g·kg-1)(b)
Fig.6 The height-time section of vapor flux divergence (black lines, Unit: 10-6 g·cm-2·hPa-1·s-1) and vapor flux (the color shaded, Unit: g·cm-1·hPa-1·s-1) over the severe snowstorm center from 08:00 on 5 to 20:00 on 6 November 2023 (a), the atmospheric precipitable amount (blue lines, Unit: mm) and 850 hPa specific humidity (the color shaded, Unit: g·kg-1) at 20:00 on 5 November 2023 (b)

图7 2023年11月5日08:00—6日20:00奈曼旗特大暴雪中心散度(黑线,单位:10-6 s-1)和垂直速度(填色,单位:10-1 Pa·s-1)的时间-高度剖面(a),6日02:00假相当位温(填色,单位:K)和风场(风矢,单位:m·s-1)沿42.8°N的经度-高度剖面(b) (红色方框为锋区)
Fig.7 The height-time section of divergence (black lines, Unit: 10-6 s-1) and vertical velocity (the color shaded, Unit: 10-1 Pa·s-1) over the severe snowstorm center from 08:00 on 5 to 20:00 on 6 November 2023 (a), the longitude-height section of pseudo-equivalent potential temperature (the color shaded, Unit: K) and the wind field (wind vectors, Unit: m·s-1) along 42.8°N at 02:00 on 6 November 2023 (b) (The red box shows the frontal area)
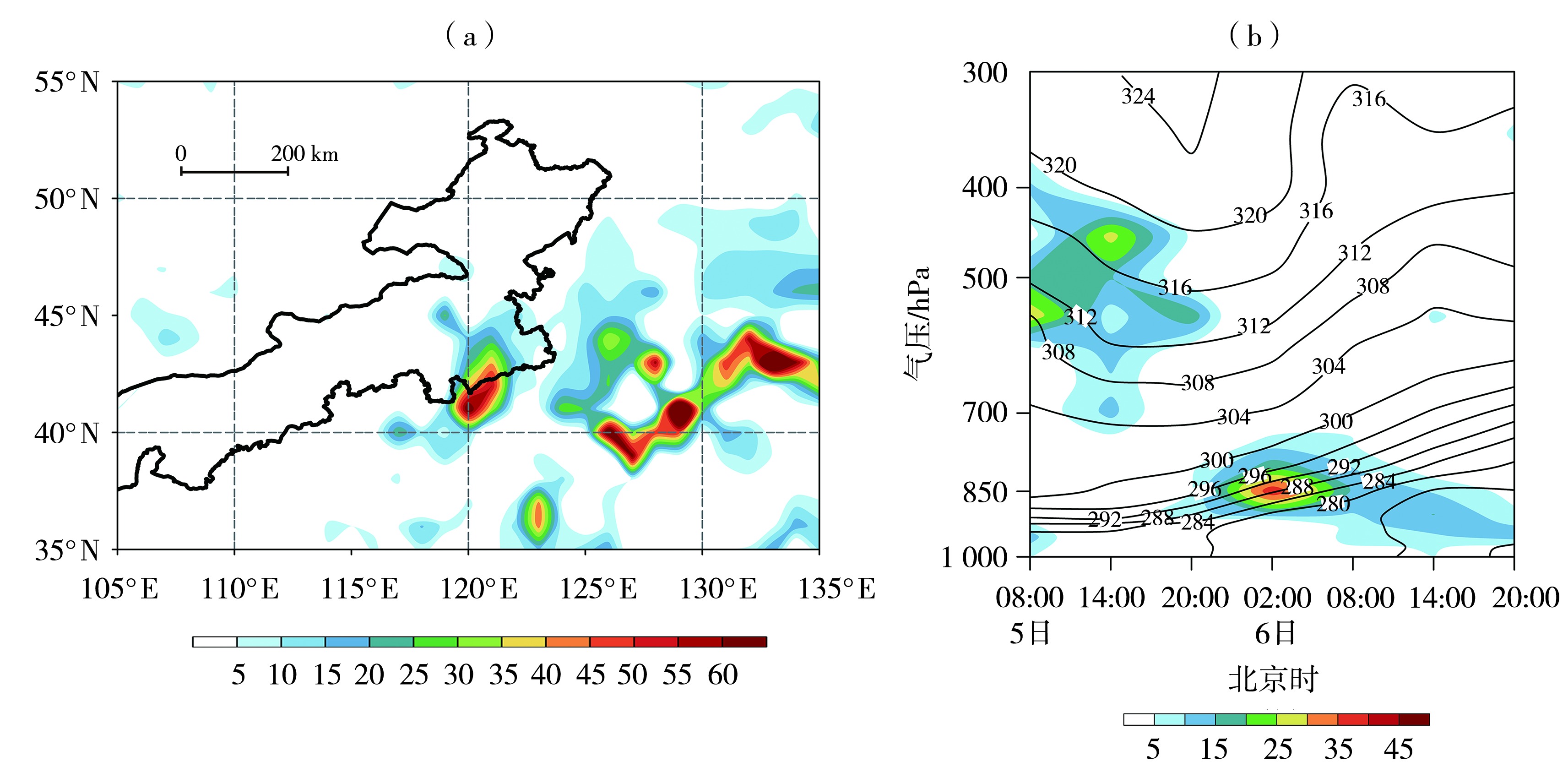
图8 2023年11月6日02:00 850 hPa锋生函数(填色,单位:10-10 K·m-1·s-1)分布(a),5日08:00—6日20:00奈曼旗特大暴雪中心锋生函数(填色,单位:10-10 K·m-1·s-1)和假相当位温(黑线,单位:K)时间-高度剖面(b)
Fig.8 Distribution of frontogenesis function (the color shaded, Unit: 10-10 K·m-1·s-1) at 850 hPa at 02:00 on 6 November 2023 (a), the height-time section of the frontogenesis function (the color shaded, Unit: 10-10 K·m-1·s-1) and pseudo-equivalent potential temperature (black solid lines, Unit: K) over the severe snowstorm center from 08:00 on 5 to 20:00 on 6 November 2023 (b)

图9 2021年11月7日(a)、2023年11月5日(b)不同时刻科左后旗站温度廓线 (黑色虚线为0 ℃等温线)
Fig.9 The temperature profiles at different time at Kezuohouqi Station on November 7, 2021 (a) and on November 5, 2023(b) (The black dotted line is 0 ℃ isotherm)
| [1] | 安晶晶, 王东勇, 李慧敏, 等, 2024. 2024年2月我国两次大范围冻雨过程对比分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 43(4):419-430. |
| [2] | 丁一汇, 王遵娅, 宋亚芳, 等, 2008. 中国南方2008年1月罕见低温雨雪冰冻灾害发生的原因及其与气候变暖的关系[J]. 气象学报, 66(5):808-825. |
| [3] | 冯丽莎, 宋攀, 郑飞, 等, 2020. 2016年初冬河南区域暴雪过程诊断分析[J]. 大气科学, 44(1):13-26. |
| [4] | 顾佳佳, 武威, 2015. 2014年2月4—7日河南暴雪过程的环流特征及其持续原因[J]. 暴雨灾害, 34(2):117-125. |
| [5] |
郭英香, 冯晓莉, 刘畅, 等, 2023. 1961—2021年青藏高原前后冬强降雪特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 41(5):723-733.
DOI |
| [6] |
胡顺起, 曹张驰, 陈滔, 2017. 山东省南部一次极端特大暴雪过程诊断分析[J]. 高原气象, 36(4):984-992.
DOI |
| [7] | 黄小玉, 黎祖贤, 李超, 等, 2008. 2008年湖南极端冰冻特大灾害天气成因分析[J]. 气象, 34(11):47-53. |
| [8] | 黄晓璐, 林弘杰, 李一平, 等, 2021. 2020年初内蒙古一次暴雪天气过程的成因分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 15(6):18-25. |
| [9] | 霍也, 李倩, 尚博, 等, 2023. 2020年11月吉林省罕见冻雨天气成因分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 39(4):25-30. |
| [10] | 靳冰凌, 孙仲毅, 王辛方, 等, 2010. 2009年11月10-12日河南北部暴雪天气诊断分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 33(2):63-67. |
| [11] | 马素艳, 高晶, 李一平, 等, 2022. 2020年内蒙古东南部一次特大暴雪伴冻雨灾害天气特征分析[J]. 气象科技, 50(3):380-389. |
| [12] | 马素艳, 张超, 史金丽, 2017. 回流与倒槽作用引发的内蒙古自治区两次暴雪天气过程分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 33(1):19-25. |
| [13] | 孟雪峰, 孙永刚, 霍志丽, 等, 2022. 内蒙古一次极端暴雪事件中冻雨成因分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 16(4):22-30. |
| [14] | 漆梁波, 2012. 我国冬季冻雨和冰粒天气的形成机制及预报着眼点[J]. 气象, 38(7):769-778. |
| [15] | 钤伟妙, 罗亚丽, 曹越, 等, 2022. 基于多种探测资料对华北中部一次回流暴雪过程的分析[J]. 气象学报, 80(5):732-747. |
| [16] |
任曼琳, 李忠燕, 王博卿, 等, 2023. 2021/2022年冬季贵州凝冻天气阶段性特征及成因[J]. 干旱气象, 41(5):744-752.
DOI |
| [17] | 王瀛, 陈宇, 李姝婷, 等, 2015. 辽宁地区一次罕见冻雨天气分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 31(4):20-25. |
| [18] | 徐娟娟, 郝丽, 刘嘉慧敏, 等, 2020. 2018年1月陕西区域性暴雪过程诊断[J]. 干旱气象, 38(1):117-125. |
| [19] | 许婷婷, 张云惠, 于碧馨, 等, 2017. 2015年12月乌鲁木齐极端暴雪成因分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 11(5):23-29. |
| [20] | 阎访, 孙婧怡, 范俊红, 等, 2021. 石家庄暴雪的时空演变特征[J]. 干旱气象, 39(6):939-947. |
| [21] | 杨晓君, 张楠, 陈宏, 等, 2019. 一次回流型降雪过程的成因和相态判据分析[J]. 气象科技, 47(1):98-105. |
| [22] | 尤凤春, 付桂琴, 刘卓, 等, 2015. 北京地区冻雨时空分布及探空温湿特征分析[J]. 气象, 41(12):1488-1 493. |
| [23] | 于波, 杜佳, 张琳娜, 2016. 1960—2013年北京地区冻雨天气过程特征分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 32(4):113-118. |
| [24] | 张芳华, 陈涛, 杨舒楠, 等, 2014. 一次冬季暴雨过程中的锋生和条件对称不稳定分析[J]. 气象, 40(9): 1 048-1 057. |
| [25] |
张桂莲, 霍志丽, 王学强, 2023. 冷垫背景下冻雨和极端大暴雪成因机制分析[J]. 高原气象, 42(3):725-733.
DOI |
| [26] |
张桂莲, 刘澜波, 孟雪峰, 等, 2022. 冷垫背景下回流暴雪成因与雷达回波特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 40(3):500-506.
DOI |
| [27] |
张入财, 王君, 陈超辉, 等, 2023. 印度双低涡对青藏高原西部一次典型暴雪过程的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 41(3):463-473.
DOI |
| [28] | 张智, 韩永翔, 王瑾, 等, 2016. 高原山地环境下冻雨微物理特征及成因分析[J]. 气象科学, 36(3):389-395. |
| [29] |
赵桂香, 2014. 诊断分析技术在山西强降雪预报中的应用[J]. 高原气象, 33(3):838-847.
DOI |
| [30] | 周雪松, 谈哲敏, 2008. 华北回流暴雪发展机理个例研究[J]. 气象, 34(1):18-26. |
| [31] | CHEN G J, WANG C C, WANG A H, 2007. A case study of subtropical frontogenesis during a blocking event[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 135(7):2588-2 609. |
| [32] | HOBBS P V, RANGNO A L, 1985. Ice particle concentrations in clouds[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 42(23): 2 523-2 549. |
| [33] | ZHUANG H Y, DEGAETANO A T, LEHNER F, 2024. Internal climate variability obscures future freezing rain changes despite global warming trend[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 51(23): e2024GL111741. DOI:10.1029/2024GL111741. |
| [1] | 杨旗, 张海鹏, 吴建蓉, 李昊, 曾华荣, 陆正奇. 对冬季云贵—华南准静止锋上一次多相态降水过程的模拟研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(1): 75-83. |
| [2] | 张桂莲, 刘澜波, 孟雪峰, 张璐, 李林惠. 冷垫背景下回流暴雪成因与雷达回波特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(3): 500-506. |
| [3] | 李美琪, 郭蕊, 贾小卫, 吴丹, 时青格, 刘浩. 冀中南一次持续性大雾过程成因及维持机制[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(4): 591-600. |
| [4] | 尹承美, 焦洋, 何建军, 冯俊杰. 济南地区逆温层特征及其对颗粒物质量浓度的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(4): 622-638. |
| [5] | 吴进,李琛,孙兆彬,王华,马小会. 北京地区两次重污染过程中PM2.5浓度爆发性增长及维持的气象条件[J]. 干旱气象, 2017, 35(5): 830-838. |
| [6] | 陈军,李小兰,喻义军,方标,滕林,胡萍. 贵州铜仁一次大范围高架雷暴降雹天气过程分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2017, 35(4): 649-656. |
| [7] | 卢秉红,杨青,高松影,韩江文,阎琦,梁寒,苏航,刘硕. 两次不同类型暴雪的雷达回波特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2016, 34(5): 836-840. |
| [8] | 郭萍萍1,杨建才2,殷雪莲1,郑学金1. 甘肃省春季一次连续浮尘天气过程分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2015, 33(2): 303-309. |
| [9] | 马 艳,郭丽娜,黄 容. 青岛一次沙尘污染事件的气象条件特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2014, 32(5): 773-780. |
| [10] | 姚蓉, 黎祖贤, 许霖, 唐杰, 陈静静. 湖南冻雨预报关键技术指标及应用[J]. 干旱气象, 2014, 32(3): 366-372. |
| [11] | 郑庆锋,史军. 上海地区大气贴地逆温的气候特征[J]. J4, 2011, 29(2): 195-200. |
| [12] | 丁小剑, 杨 军, 唐明晖, 何正阳, 李象玉. 湖南2次典型的冰冻灾害天气特征及成因分析[J]. J4, 2010, 28(1): 76-80. |
| [13] | 侯瑞钦, 李江波, 赵玉广. 河北平原一次持续大雾天气分析[J]. J4, 2009, 27(3): 263-270. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
