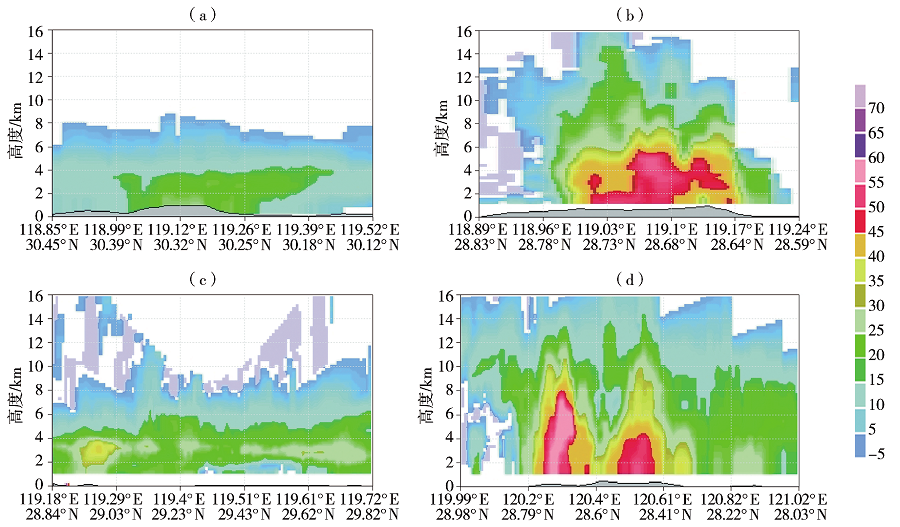
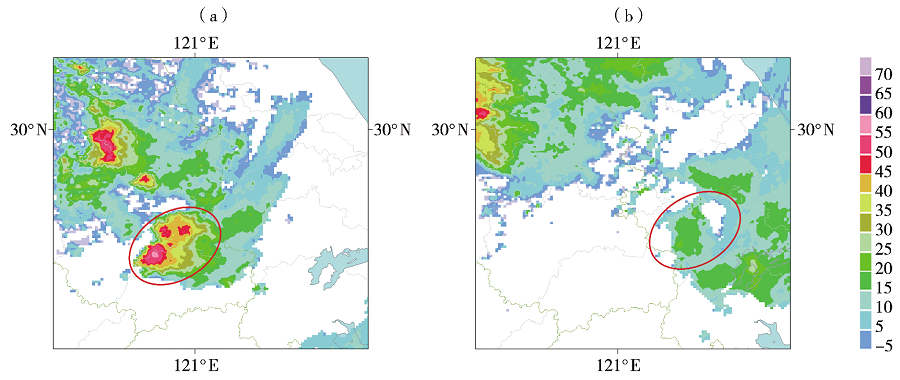
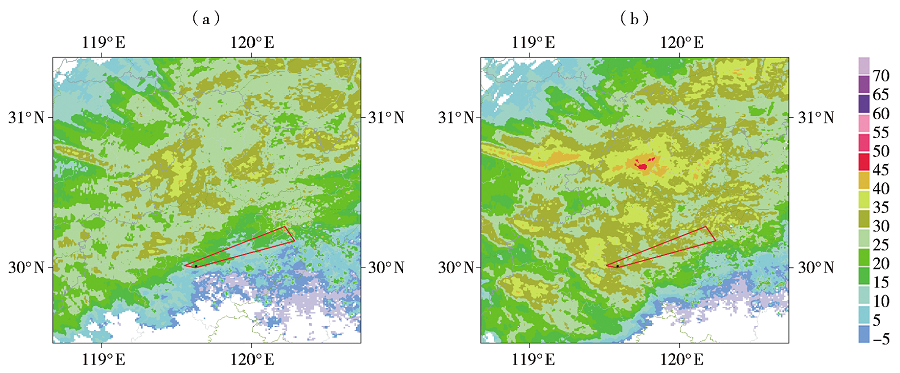
| [1] |
王镇铭, 杜惠良, 杨诗芳. 浙江省天气预报手册[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2013:387-393.
|
| [2] |
肖卉, 白卡娃, 王可法, 等. 江苏省火箭人工增雨作业指标研究[J]. 气象科学, 2008, 28(4):440-443.
|
| [3] |
尚博, 蔡淼, 霍也, 等. 吉林省春季人工增雨潜力及指标的数值模拟研究[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2020, 36(1):74-81.
|
| [4] |
翟菁, 黄勇, 胡雯, 等. 一次积层混合云降水过程增雨条件分析[J]. 气象, 2010, 36(11):59-67.
|
| [5] |
GRANT L O, ELLIOTT R E. The cloud seeding temperature window[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 1974, 13(3): 355-363.
DOI
URL
|
| [6] |
HUDAK D R, LIST R. Precipitation development in natural and seeded cumulus clouds in southern Africa[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 1988, 27(6):734-756.
|
| [7] |
LONG A B, CARTER E J. Australian winter mountain storm clouds: precipitation augmentation potential[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 1996, 35(9):1457-1464.
|
| [8] |
VALI G, KOENIG L R, YOKSAS T C. Estimate of precipitation enhancement potential for the Duero basin of Spain[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 1988, 27(7):829-850.
|
| [9] |
王黎俊, 孙安平, 刘彩红, 等. 地基微波辐射计探测在黄河上游人工增雨中的应用[J]. 气象, 2007, 33(11):28-33.
|
| [10] |
李红斌, 何玉科, 姚展予, 等. 多普勒雷达速度场特征在人工增雨作业中的判据指标应用[J]. 气象, 2008, 34(6):102-106.
|
| [11] |
刘万杰, 朱麟. 多普勒雷达在人工增雨作业中的应用[J]. 气象研究与应用, 2019, 39(增刊2):102-104.
|
| [12] |
李德俊, 唐仁茂, 江鸿, 等. 武汉一次对流云火箭人工增雨作业的综合观测分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2016, 34(2):362-369.
|
| [13] |
林长城, 陈彬彬, 隋平, 等. 闽西北地区降水回波特征和人工增雨作业条件分析[J]. 气象科技, 2011, 39(6):697-702.
|
| [14] |
郭艳, 蔡哲, 杨建超, 等. 江西人工增雨作业条件的雷达回波参数指标分析[J]. 气象与减灾研究, 2010, 33(4):67-71.
|
| [15] |
林娜, 施春华. 利用新一代多普勒雷达产品判别重庆市人工增雨作业指标[J]. 黑龙江气象, 2013, 30(1):40-43.
|
| [16] |
唐林, 魏鸣, 王治平. 湖南人工增雨云型的分析判别与多普勒天气雷达指挥系统的研制应用[J]. 气象科学, 2007, 27(1):95-100.
|
| [17] |
陈羿辰, 何晖. 基于偏振雷达的积层混合云降水增雨潜力识别方法研究[J]. 大气科学, 2017, 41(3):578-592.
|
| [18] |
孙莉娟, 徐阳, 鲁德金, 等. 雷达和GPS水汽资料在人工增雨指标中的应用[J]. 现代农业科技, 2020(16):160-162.
|
| [19] |
王以琳, 刘文, 王广河. 冷云人工增雨催化区的探空判据[J]. 气象学报, 2002, 60(1):116-121.
|
| [20] |
刘贵华, 余兴, 岳治国, 等. 卫星遥感人工增雨作业条件Ⅱ:层状云[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2012, 17(6):758-766.
|
| [21] |
李宝东, 孙玉稳, 孙霞, 等. 河北春季一次飞机人工增雪的综合分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2014, 32(5):819-829.
|
| [22] |
白婷, 黄毅梅, 樊奇. 河南一次降水天气过程人工增雨作业条件综合分析[J]. 气象, 2020, 46(12):1633-1640.
|
| [23] |
李红斌, 胡志群, 张家伟, 等. 多普勒天气雷达速度场特征及在人工增雨中的应用[J]. 气象科学, 2009, 29(4):564-568.
|
| [24] |
王丽莉, 陈真, 季芬琴, 等. 新一代天气雷达速度场特征在人工增雨中的应用[J]. 山西农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 32(3):285-288.
|
| [25] |
郭红艳, 李春光, 刘强, 等. 山东济宁地区人工增雨效果检验[J]. 干旱气象, 2014, 32(3):454-459.
|
| [26] |
张元, 刘建西, 刘晓璐, 等. 2013年四川省飞机增雨作业典型个例分析[J]. 成都信息工程学院学报, 2015, 30(2):192-198.
|
| [27] |
廖向花, 张逸轩, 陈小敏, 等. 重庆一次典型飞机人工增雨作业的效果分析[J]. 西南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 39(9):156-163.
|
| [28] |
王婉, 姚展予. 人工增雨统计检验结果准确度分析[J]. 气象科技, 2009, 37(2):209-215.
|
| [29] |
周毓荃, 朱冰. 高炮、火箭和飞机催化扩散规律和作业设计的研究[J]. 气象, 2014, 40(8):965-980.
|
| [30] |
余芳, 刘东升, 何奇瑾, 等. 2009年飞机人工增雨作业抗春旱效益评估[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 2010, 30(1):72-75.
|
| [31] |
王晓立, 马劲松, 王恬茹, 等. 2016-04-16潍坊市人工增雨效果检验分析[J]. 气象水文海洋仪器, 2018, 35(1):27-33.
|
| [32] |
章澄昌. 当前国外人工增雨防雹作业的效果评估[J]. 气象, 1998, 24(10):3-8.
|
| [33] |
潘多, 侯正俊, 次珍. 基于雷达资料人工增雨潜势预判方法的研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2015, 43(32):360-362.
|
| [34] |
俞小鼎, 姚秀萍, 熊廷南, 等. 多普勒天气雷达原理与业务应用[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2006:181-185.
|
| [35] |
林长城, 姚展予, 林文, 等. 福建省古田试验区云系回波特征与人工增雨作业条件分析[J]. 大气科学学报, 2017, 40(1):138-144.
|
| [36] |
唐佐阳, 吕巍伟, 吕校华, 等. 衡邵盆地7—8月对流云特征与人工增雨作业效果分析[J]. 气象研究与应用, 2018, 39(1):51-54,69.
|
| [37] |
王吉宏, 张维全, 班显秀, 等. 积层混合云人工增雨作业条件分析[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2009, 37(10):4560-4562.
|
 ), SONG Zhe1, XU Cheng1, HUANG Xuanxuan2
), SONG Zhe1, XU Cheng1, HUANG Xuanxuan2