干旱气象 ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (5): 811-819.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-05-0811
CLDAS气温和降水产品在内蒙古地区适用性分析
- 内蒙古自治区气候中心,内蒙古 呼和浩特 010000
-
收稿日期:2023-02-01修回日期:2023-08-31出版日期:2023-10-31发布日期:2023-11-03 -
通讯作者:赵艳丽(1969—),女,内蒙古满洲里人,正高级工程师,主要从事气象灾害监测、预报预警和评估及气候变化、气候应用服务等研究。E-mail:861952609@qq.com 。 -
作者简介:董祝雷(1989—),男,江苏灌云人,工程师,主要从事气候变化和气候应用服务研究。E-mail: dongzhl89@163.com。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(41965003);内蒙古自治区科技重大专项(2020ZD0013);内蒙古自治区科技计划项目(2020GG0017);内蒙古自治区自然科学基金项目(2021MS04026);内蒙古自治区自然科学基金项目(2022MS04018);内蒙古自治区气象局科技创新项目(nmqxkjcx202211)
Applicability assessment of CLDAS temperature and precipitation products in Inner Mongolia
DONG Zhulei( ), ZHAO Yanli(
), ZHAO Yanli( ), FENG Xiaojing, LIU Shimeng
), FENG Xiaojing, LIU Shimeng
- Inner Mongolia Climate Center, Hohhot 010000, China
-
Received:2023-02-01Revised:2023-08-31Online:2023-10-31Published:2023-11-03
摘要:
中国气象局陆面数据同化系统(CMA Land Data Assimilation System,CLDAS)提供了高时空分辨率的陆面融合数据集,为精细化气象服务提供了重要的数据支撑,而数据的适用性评估是开展数据应用的重要基础。基于国家气象信息中心CN05.1格点观测数据和内蒙古119个国家级气象站观测资料,对CLDAS的2 m平均气温和降水产品在内蒙古地区的适用性进行检验评估,并与欧洲中期天气预报中心的ERA5(The Fifth Generation European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts Re-Analysis)和英国的CRU TS(Climatic Research Unit gridded Time Series)再分析资料进行对比分析。结果表明:三种数据集均能很好地反映内蒙古年降水量和年平均气温空间分布特征,但对内蒙古大部地区降水量存在低估、平均气温存在高估现象,且CLDAS数据集还能够反映地形变化对气温和降水的影响。CLDAS和CRU TS的降水变率空间分布优于ERA5;CRU TS和ERA5的气温线性趋势与CN05.1观测结果相似,但增温率高于观测,而CLDAS气温产品还能反映局地降温趋势。无论是月尺度还是季节尺度,CLDAS数据集与站点观测值的相关系数均高于CRU TS和ERA5,平均绝对误差小于CRU TS和ERA5,CLDAS气温和降水产品误差最大的区域在河套地区。
中图分类号:
引用本文
董祝雷, 赵艳丽, 冯晓晶, 刘诗梦. CLDAS气温和降水产品在内蒙古地区适用性分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(5): 811-819.
DONG Zhulei, ZHAO Yanli, FENG Xiaojing, LIU Shimeng. Applicability assessment of CLDAS temperature and precipitation products in Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(5): 811-819.
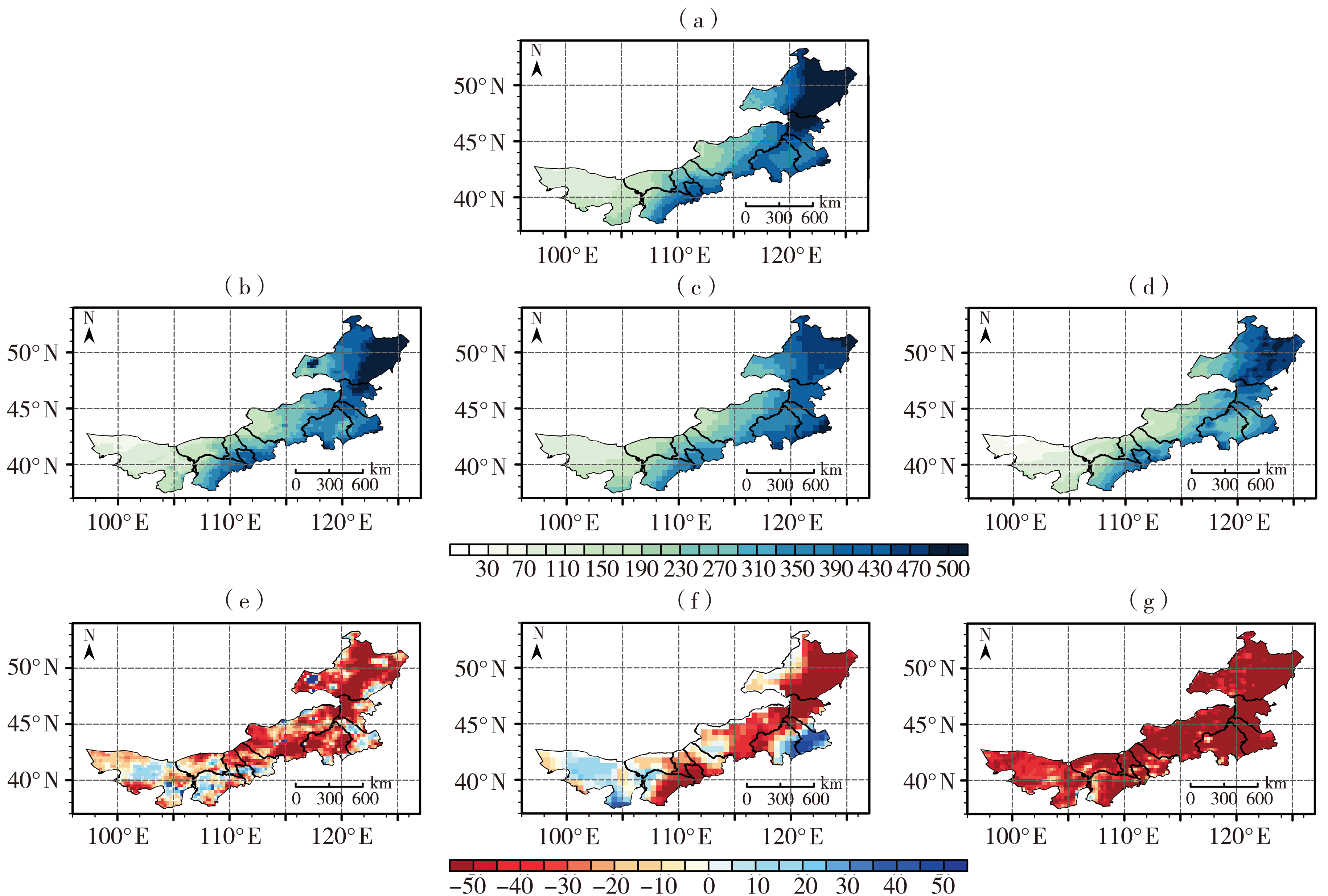
图2 2008—2019年内蒙古地区平均年降水量观测值(a)、三种数据集的平均年降水量(b、c、d)及其与观测值的差值(e、f、g)空间分布(单位:mm) (a)CN05.1,(b、e)CLDAS,(c、f)CRU TS,(d、g)ERA5
Fig.2 The spatial distribution of average annual precipitation from the observation (a) and three datasets (b, c, d), and difference between them and observation values (e, f, g) in Inner Mongolia during 2008-2019 (Unit: mm) (a) CN05.1, (b, e) CLDAS, (c, f) CRU TS, (d, g) ERA5

图3 2008—2019年内蒙古地区年平均气温观测值(a)、三种数据集的年平均气温(b、c、d)及其与观测值的差值(e、f、g)空间分布(单位:℃) (a)CN05.1,(b、e)CLDAS,(c、f)CRU TS,(d、g)ERA5
Fig.3 The spatial distribution of annual mean temperature from the observation (a) and three datasets (b, c, d), and difference between them and observation values (e, f, g) in Inner Mongolia during 2008-2019 (Unit: ℃) (a) CN05.1, (b, e) CLDAS, (c, f) CRU TS, (d, g) ERA5

图4 2008—2019年内蒙古地区CN05.1(a)、CLDAS(b)、CRU TS(c)和ERA5(d)年降水量线性趋势(单位:mm·a-1)
Fig.4 The linear trend of annual precipitation from CN05.1 (a), CLDAS (b), CRU TS (c) and ERA5 (d) datasets in Inner Mongolia during 2008-2019 (Unit: mm·a-1)

图5 2008—2019年内蒙古地区CN05.1(a)、CLDAS(b)、CRU TS(c)和ERA5(d)年平均气温线性趋势(单位:℃·a-1)
Fig.5 The linear trend of annual mean temperature from CN05.1 (a), CLDAS (b), CRU TS (c) and ERA5 (d) datasets in Inner Mongolia during 2008-2019 (Unit :℃·a-1)
| 产品 | 平均气温 | 降水量 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 相关 系数 | RMSE/℃ | MAE/℃ | 相关 系数 | RMSE/mm | MAE/mm | |
| CLDAS | 0.999 5 | 0.48 | 0.38 | 0.965 7 | 8.68 | 4.73 |
| CRU TS | 0.998 3 | 1.32 | 1.13 | 0.866 8 | 18.39 | 10.33 |
| ERA5 | 0.998 4 | 1.09 | 0.85 | 0.874 7 | 18.00 | 9.58 |
表1 三种数据集的月平均气温和降水量与内蒙古119站观测值相关系数和误差统计
Tab.1 The statistics of correlation coefficient and error of monthly mean temperature and precipitation between three datasets and observation values at 119 stations in Inner Mongolia
| 产品 | 平均气温 | 降水量 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 相关 系数 | RMSE/℃ | MAE/℃ | 相关 系数 | RMSE/mm | MAE/mm | |
| CLDAS | 0.999 5 | 0.48 | 0.38 | 0.965 7 | 8.68 | 4.73 |
| CRU TS | 0.998 3 | 1.32 | 1.13 | 0.866 8 | 18.39 | 10.33 |
| ERA5 | 0.998 4 | 1.09 | 0.85 | 0.874 7 | 18.00 | 9.58 |
| 产品 | 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 冬季 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均气温/℃ | 降水量/mm | 平均气温/℃ | 降水量/mm | 平均气温/℃ | 降水量/mm | 平均气温/℃ | 降水量/mm | |||||||||
| 偏差 | MAE | 偏差 | MAE | 偏差 | MAE | 偏差 | MAE | 偏差 | MAE | 偏差 | MAE | 偏差 | MAE | 偏差 | MAE | |
| CLDAS | 0.13 | 0.31 | -0.62 | 8.77 | -0.12 | 0.30 | 0.83 | 18.64 | 0.02 | 0.33 | -3.21 | 9.94 | 0.23 | 0.45 | 0.59 | 1.40 |
| CRU TS | -0.52 | 1.07 | -0.46 | 13.90 | -0.59 | 1.01 | 6.99 | 49.32 | -0.08 | 0.87 | -4.00 | 18.97 | 0.19 | 1.19 | -2.40 | 3.43 |
| ERA5 | -0.34 | 0.66 | 2.38 | 12.10 | -0.19 | 0.51 | -40.55 | 51.80 | 0.09 | 0.59 | -1.71 | 14.96 | 0.93 | 1.26 | 2.47 | 3.32 |
表2 三种数据集的季节平均气温和降水量与内蒙古119站观测值偏差和平均绝对误差统计
Tab.2 The statistics of bias and mean absolute error of seasonal mean temperature and precipitation between three datasets and observation values at 119 stations in Inner Mongolia
| 产品 | 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 冬季 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均气温/℃ | 降水量/mm | 平均气温/℃ | 降水量/mm | 平均气温/℃ | 降水量/mm | 平均气温/℃ | 降水量/mm | |||||||||
| 偏差 | MAE | 偏差 | MAE | 偏差 | MAE | 偏差 | MAE | 偏差 | MAE | 偏差 | MAE | 偏差 | MAE | 偏差 | MAE | |
| CLDAS | 0.13 | 0.31 | -0.62 | 8.77 | -0.12 | 0.30 | 0.83 | 18.64 | 0.02 | 0.33 | -3.21 | 9.94 | 0.23 | 0.45 | 0.59 | 1.40 |
| CRU TS | -0.52 | 1.07 | -0.46 | 13.90 | -0.59 | 1.01 | 6.99 | 49.32 | -0.08 | 0.87 | -4.00 | 18.97 | 0.19 | 1.19 | -2.40 | 3.43 |
| ERA5 | -0.34 | 0.66 | 2.38 | 12.10 | -0.19 | 0.51 | -40.55 | 51.80 | 0.09 | 0.59 | -1.71 | 14.96 | 0.93 | 1.26 | 2.47 | 3.32 |

图6 内蒙古119站季节平均气温(a)和降水量(b)与CLDAS、CRU TS和ERA5产品的平均绝对误差分布
Fig.6 The distribution of mean absolute error between seasonal mean temperature (a), precipitation (b) at 119 stations in Inner Mongolia and CLDAS, CRU TS, ERA5 products

图7 CLDAS气温(a、b)和降水(c、d)产品与内蒙古119站观测值的相关系数(a、c)和均方根误差(b、d)空间分布
Fig.7 The spatial distribution of correlation coefficient (a, c) and root mean square error (b, d) between CLDAS temperature (a, b), precipitation (c, d) products and observation values at 119 stations in Inner Mongolia
| [1] | 陈燕丽, 黄思琦, 莫建飞, 等, 2020. 基于CLDAS数据的甘蔗干旱监测评估标准对比——以2011年广西干旱为例[J]. 干旱气象, 38(2): 188-194. |
| [2] | 崔园园, 敬文琪, 覃军, 2018. 基于TIPEX Ⅲ资料对CLDAS-V2.0和GLDAS-NOAH陆面模式产品在青藏高原地区的适用性评估[J]. 高原气象, 37(5): 1 143-1 160. |
| [3] |
崔园园, 张强, 覃军, 等, 2019. CLDAS融合土壤湿度产品在东北地区的适用性评估及订正[J]. 中国农业气象, 40(10): 660-668.
DOI |
| [4] |
董春卿, 郭媛媛, 张磊, 等, 2021. 基于CLDAS的格点温度预报偏差订正方法[J]. 干旱气象, 39(5): 847-856.
DOI |
| [5] | 龚伟伟, 2014. CMA陆面数据同化系统(CLDAS)产品评估[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学. |
| [6] |
郭阳, 师春香, 徐宾, 等, 2023. CLDAS陆面融合实况数据对天津雾和霾判识的准确性分析[J]. 干旱气象, 41(4): 657-665.
DOI |
| [7] | 韩帅, 师春香, 姜立鹏, 等, 2017. CLDAS土壤湿度模拟结果及评估[J]. 应用气象学报, 28(3): 369-378. |
| [8] | 黄嘉佑, 2016. 气象统计分析与预报方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [9] | 季飞, 2015. 北半球中高纬干旱半干旱区强化增温现象研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学. |
| [10] | 刘佩佩, 宋海清, 鲍炜炜, 等, 2021. CLDAS和GLDAS土壤温度数据在陕西省的适用性评估[J]. 气象科技, 49(4): 604-611. |
| [11] | 吕润清, 李响, 2021. ERA-Interim和ERA5再分析数据在江苏区域的适用性对比研究[J]. 海洋预报, 38(4): 27-37. |
| [12] | 单帅, 师春香, 沈润平, 等, 2021. ERA70、 CLDAS和ERA-Interim表层土壤温度在中国地区的评估[J]. 气象科技, 49(6): 830-837. |
| [13] | 师春香, 潘旸, 谷军霞, 等, 2019. 多源气象数据融合格点实况产品研制进展[J]. 气象学报, 77(4): 774-783. |
| [14] | 孙帅, 师春香, 梁晓, 等, 2017. 不同陆面模式对我国地表温度模拟的适用性评估[J]. 应用气象学报, 28(6): 737-749. |
| [15] | 孙小龙, 宋海清, 李平, 等, 2015. 基于CLDAS 资料的内蒙古干旱监测分析[J]. 气象, 41(10): 1 245-1 252. |
| [16] | 闻新宇, 王绍武, 朱锦红, 等, 2006. 英国CRU高分辨率格点资料揭示的20世纪中国气候变化[J]. 大气科学, 30(5): 894-904. |
| [17] | 吴佳, 高学杰, 2013. 一套格点化的中国区域逐日观测资料及与其它资料的对比[J]. 地球物理学报, 56(4): 1 102-1 111. |
| [18] |
武荣盛, 李云鹏, 吴瑞芬, 等, 2021. 内蒙古麦后移栽向日葵精细化气候适宜性区划[J]. 干旱气象, 39(5): 807-815.
DOI |
| [19] |
杨富燕, 彭芳, 于飞, 等, 2023. CLDAS温湿产品在贵州的适用性评估及订正[J]. 高原气象, 42(2): 472-482.
DOI |
| [20] | 杨柳, 师春香, 韩帅, 等, 2023. 两种气温多源数据融合实况产品在新疆地区的评估与对比[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 2023, 17(1): 60-68. |
| [21] | 叶梦姝, 2018. 中国大气再分析资料降水产品在天气和气候中的适用性研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学. |
| [22] | 俞剑蔚, 李聪, 蔡凝昊, 等, 2019. 国家级格点实况分析产品在江苏地区的适用性评估分析[J]. 气象, 45(9): 1 288-1 298. |
| [23] |
张君霞, 黄武斌, 杨秀梅, 等, 2022. 陇东半干旱区一次特大暴雨事件的降水极端性分析[J]. 干旱气象, 40(6): 922-932.
DOI |
| [24] | 张俊兵, 沈润平, 师春香, 等, 2021. 中国大陆地区ERA5下行短波辐射数据适用性评估与对比[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 23(12): 2 261-2 274. |
| [25] | 赵天保, 符淙斌, 2009. 几种再分析地表气温资料在中国区域的适用性评估[J]. 高原气象, 28(3): 594-606. |
| [26] | CHEN Y, YUAN H L, 2020. Evaluation of nine sub-daily soil moisture model products over China using high-resolution in situ observations[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 588, 125054. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125054. |
| [27] |
DEE D P, UPPALA S M, SIMMONS A J, et al, 2011. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: configuration and performance of the data assimilation system[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 137(656): 553-597.
DOI URL |
| [28] | HAN S, LIU B C, SHI C X, et al, 2020. Evaluation of CLDAS and GLDAS datasets for near-surface air temperature over major land areas of China[J]. Sustainability, 12(10), 4311. DOI: 10.3390/su12104311. |
| [29] |
KALNARY E, KANAMITSU M, KISTLER R, et al, 1996. The NCEP/NCAR reanalysis 40-year project[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 77(3): 437-471.
DOI URL |
| [30] | KOBAYASHI C, IWASAKI T, 2016. Brewer-Dobson circulation diagnosed from JRA-55[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 121(4): 1 493-1 510. DOI: 10.1002/2015JD023476. |
| [31] | SIMMONS A J, JONES P D, DA COSTA BECHTOLD V, et al, 2004. Comparison of trends and low-frequency variability in CRU, ERA-40, and NCEP/NCAR analyses of surface air temperature[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 109(D24). DOI: 10.1029/2004JD005306. |
| [1] | 郭阳, 师春香, 徐宾, 司鹏, 徐梅, 王敏, 孙玫玲. CLDAS陆面融合实况数据对天津雾和霾判识的准确性分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(4): 657-665. |
| [2] | 李慧, 郑旭程, 苏立娟, 辛悦, 张杰. 基于毫米波云雷达的黄河流域内蒙古段云宏观特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(3): 434-441. |
| [3] | 苏立娟, 衣娜娜, 郑旭程, 史金丽, 邓晓东. 内蒙古中部干旱半干旱区水汽和液态水特征研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(2): 251-259. |
| [4] | 许志丽, 衣娜娜, 毕立格, 于水燕, 张俊成. 内蒙古中部一次春季透雨过程的云微物理特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(4): 632-639. |
| [5] | 武荣盛,李云鹏,吴瑞芬,郑凤杰,苏玥. 内蒙古麦后移栽向日葵精细化气候适宜性区划[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(5): 807-815. |
| [6] | 杨丽桃,王胜,江像评. 内蒙古马铃薯生育期气候生产潜力时空模拟分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(5): 816-823. |
| [7] | 董春卿,郭媛媛,张磊,胡嘉缨. 基于CLDAS的格点温度预报偏差订正方法[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(5): 847-856. |
| [8] | 衣娜娜, 苏立娟, 郑旭程, 张敏, 弓泓, . 内蒙古西部地区降水云宏观特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(3): 406-414. |
| [9] | 刘炜, 赵艳丽, 冯晓晶. 内蒙古地区夏季旱涝急转环流异常特征及其预测[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(2): 203-214. |
| [10] | 易雪, 杨森, 刘鸣彦, 李涛, 侯依玲, 崔妍. 辽宁省植被覆盖度时空变化特征及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(2): 252-261. |
| [11] | 刘炜, 赵艳丽. 内蒙古中西部地区2018年夏季异常多雨成因[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(5): 709-715. |
| [12] | 刘林春, 刘炜, 孙鑫, 刘新, 董祝雷, 张宇. 内蒙古河套地区极端降水特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(4): 535-542. |
| [13] | 刘昊, 宋海清, 李云鹏. 积雪深度再分析资料在内蒙古的适用性评价[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(4): 639-646. |
| [14] | 陈燕丽, 黄思琦, 莫建飞, 罗永明, 蒙良莉, 匡昭敏. 基于CLDAS数据的甘蔗干旱监测评估标准对比——以2011年广西干旱为例[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(2): 188-194. |
| [15] | 齐铎, 刘松涛, 张天华, 王承伟. 基于格点的中国东北中北部2 m温度数值预报检验及偏差订正[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(1): 81-88. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||