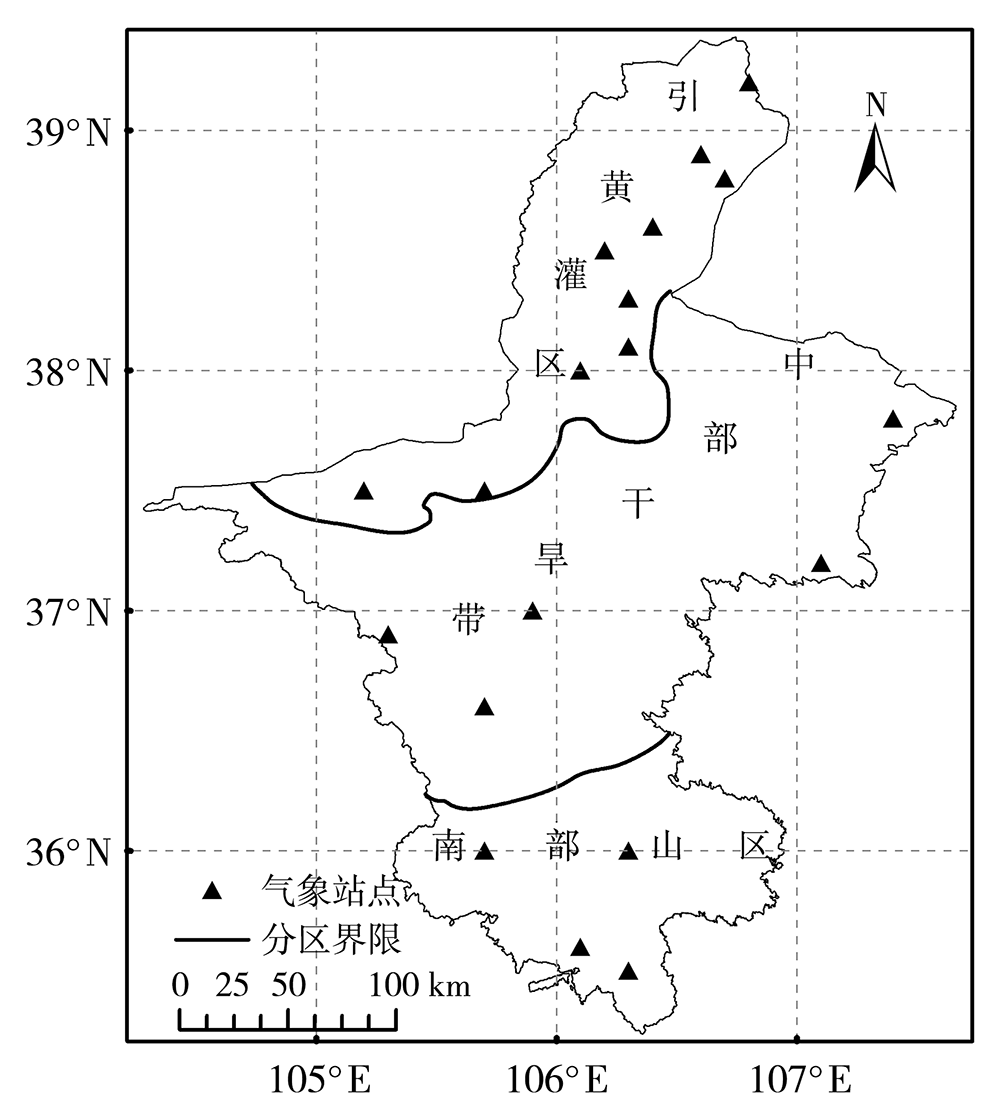
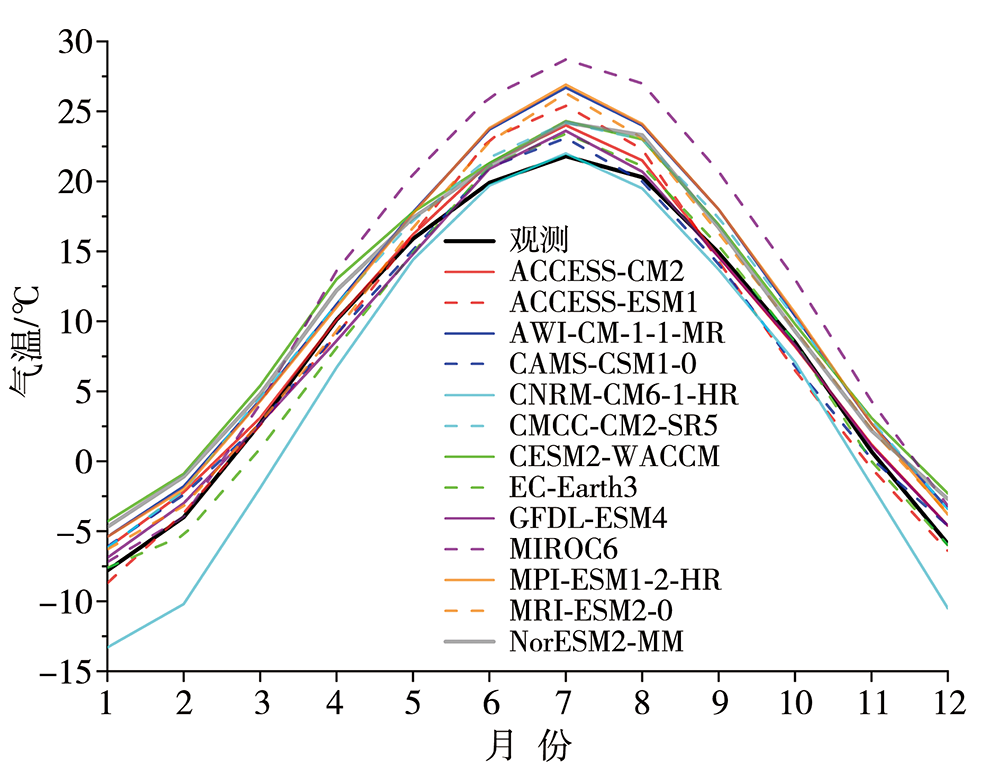
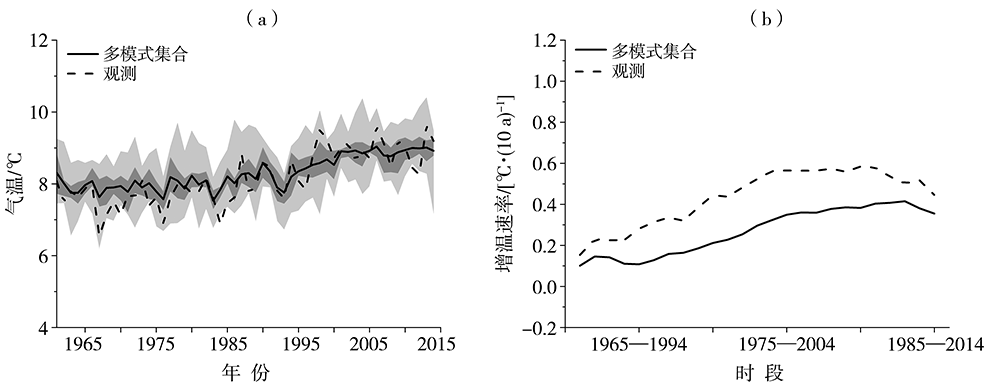
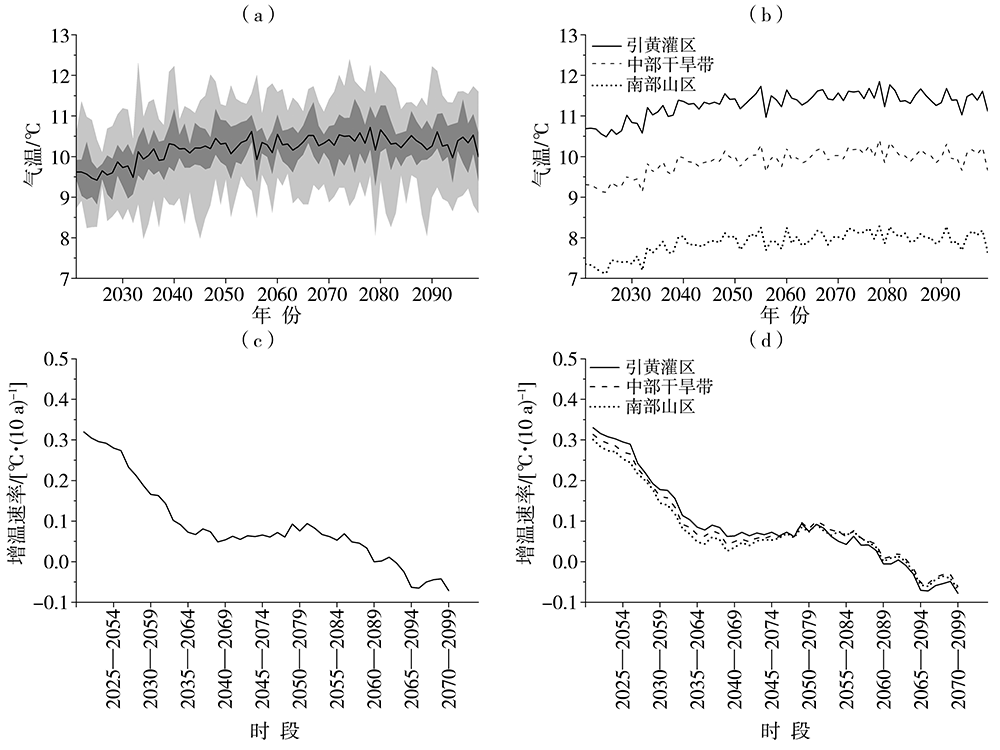
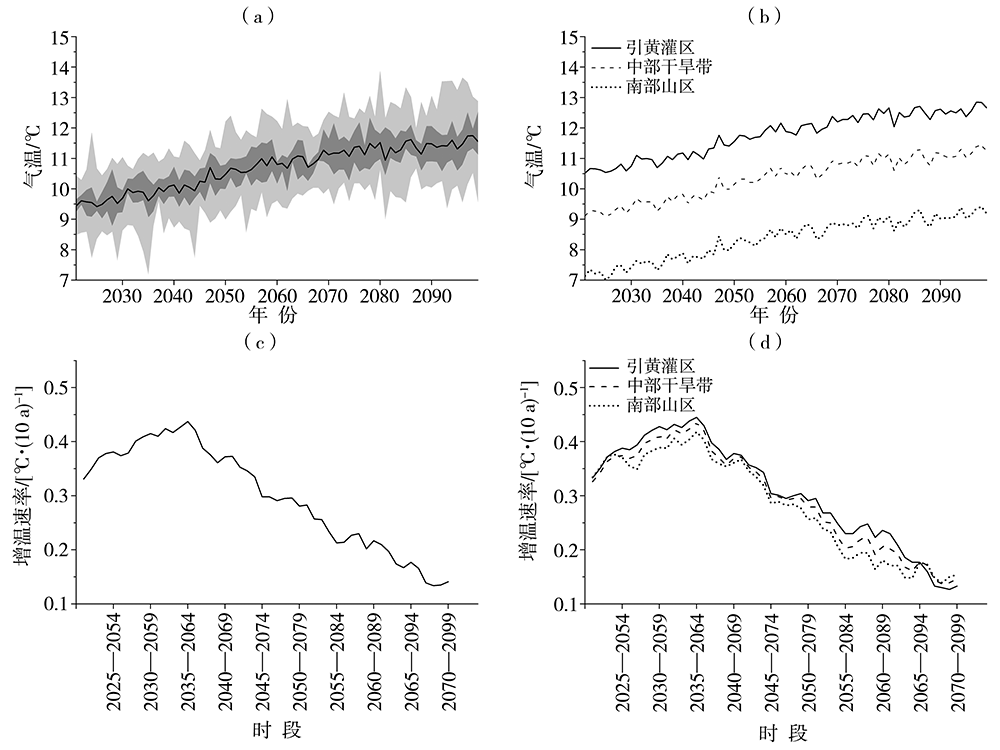
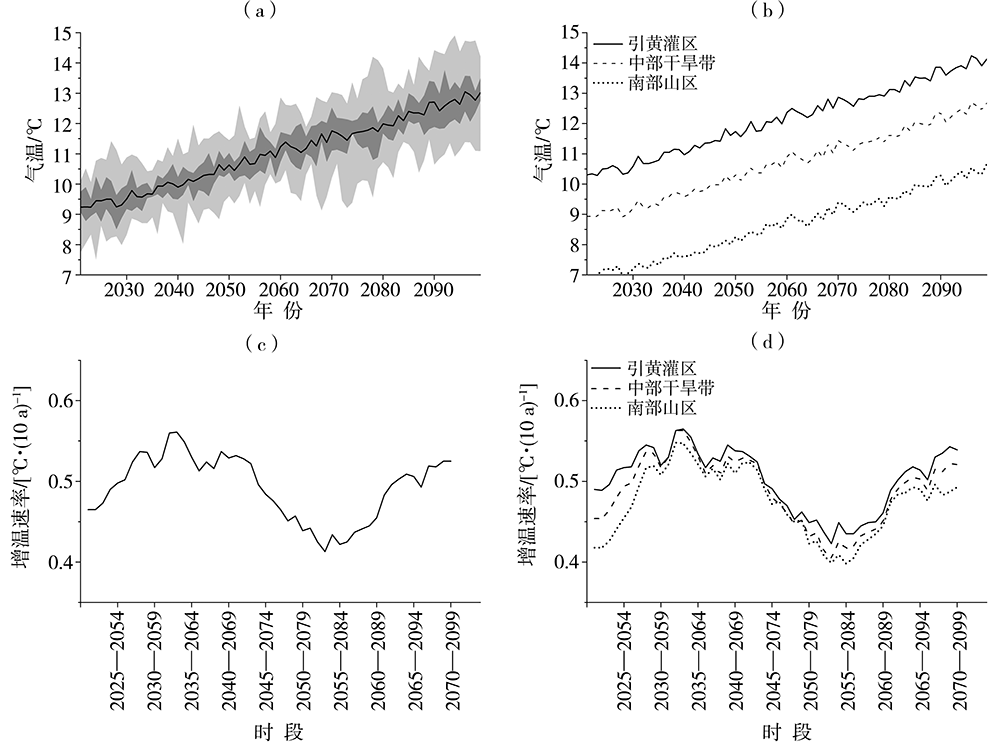
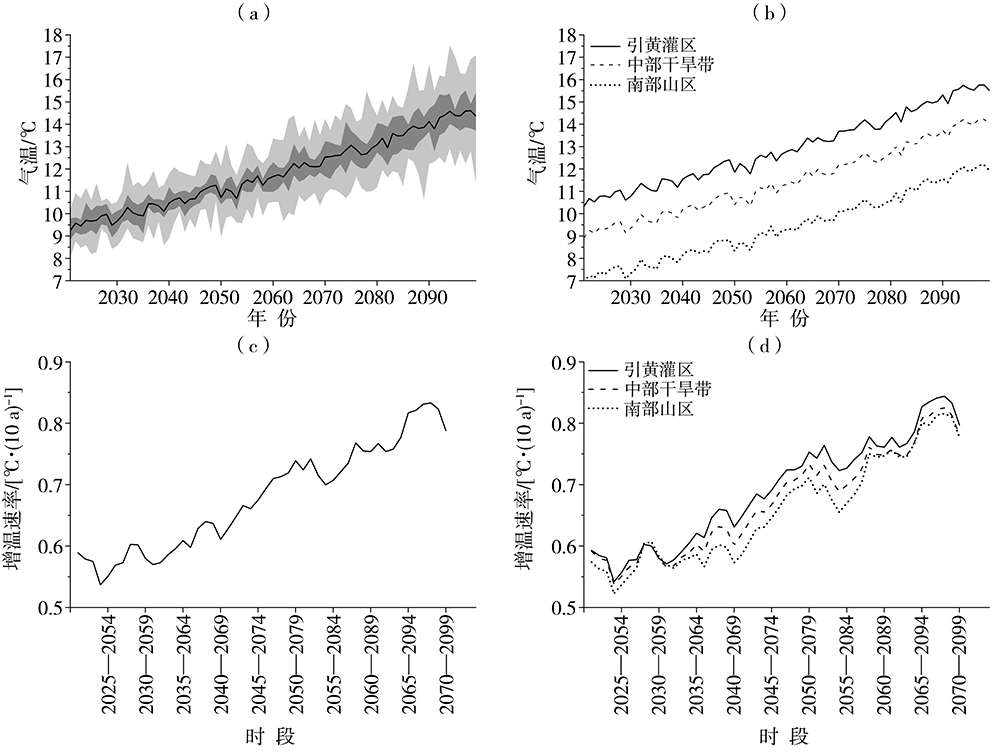
| [1] |
陈炜, 姜大膀, 王晓欣, 2021. CMIP6模式对青藏高原气候的模拟能力评估与预估研究[J]. 高原气象, 40(6): 1 455-1 469.
|
| [2] |
冯雷, 李旭东, 2016. 高温热浪对人类健康影响的研究进展[J]. 环境与健康杂志, 33(2): 182-188.
|
| [3] |
姜大膀, 王晓欣, 2021. 对IPCC第六次评估报告中有关干旱变化的解读[J]. 大气科学学报, 44(5): 650-653.
|
| [4] |
姜彤, 吕嫣冉, 黄金龙, 等, 2020. CMIP6模式新情景(SSP-RCP)概述及其在淮河流域的应用[J]. 气象科技进展, 10(5): 102-109.
|
| [5] |
李纯, 姜彤, 王艳君, 等, 2022. 基于CMIP6模式的黄河上游地区未来气温模拟预估[J]. 冰川冻土, 44(1): 171-178.
DOI
|
| [6] |
李佳瑞, 牛自耕, 冯岚, 等, 2020. CMIP5模式对长江和黄河流域极端气温指标的模拟与预估[J]. 地球科学, 45(6): 1 887-1 904.
|
| [7] |
刘倩, 高路, 马苗苗, 等, 2021. 辽宁大凌河流域气温和降水降尺度研究[J]. 水利水电技术(中英文), 52(9): 16-31.
|
| [8] |
马守存, 保广裕, 郭广, 等, 2018. 1982—2013年黄河源区植被变化趋势及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 干旱气象, 36(2): 226-233.
DOI
|
| [9] |
孟雅丽, 段克勤, 尚溦, 等, 2022. 基于CMIP6模式数据的1961—2100年青藏高原地表气温时空变化分析[J]. 冰川冻土, 44(1): 24-33.
DOI
|
| [10] |
孙侦, 贾绍凤, 吕爱锋, 等, 2015. IPCC AR5全球气候模式对1996—2005年中国气温模拟精度评价[J]. 地理科学进展, 34(10): 1 229-1 240.
|
| [11] |
王澄海, 吴永萍, 崔洋, 2009. CMIP研究计划的进展及其在中国地区的检验和应用前景[J]. 地球科学进展, 24(5): 461-468.
DOI
|
| [12] |
王连喜, 李凤霞, 黄峰, 等, 2008. 宁夏农业气候资源及其分析[M]. 银川: 宁夏人民出版社.
|
| [13] |
王胜杰, 赵国强, 王旻燕, 等, 2021. 1961—2020年黄河流域气候变化特征研究[J]. 气象与环境科学, 44(6): 1-8.
|
| [14] |
王晓峰, 勒斯木初, 张明明, 2019. “两屏三带”生态系统格局变化及其影响因素[J]. 生态学杂志, 38(7): 2 138-2 148.
|
| [15] |
王有恒, 谭丹, 韩兰英, 等, 2021. 黄河流域气候变化研究综述[J]. 中国沙漠, 41(4): 235-246.
|
| [16] |
魏凤英, 2007. 现代气候统计诊断与预测技术[M]. 北京: 气象出版社.
|
| [17] |
伍清, 蒋兴文, 谢洁, 等, 2018. 基于CMIP5资料的西南地区2020—2050年气温多模式集合预估[J]. 干旱气象, 36(6): 971-978.
|
| [18] |
吴绍洪, 赵东升, 2020. 中国气候变化影响、风险与适应研究新进展[J]. 中国人口资源与环境, 30(6): 1-9.
|
| [19] |
武新英, 郝增超, 张璇, 等, 2021. 中国夏季复合高温干旱分布及变异趋势[J]. 水利水电技术(中英文), 52(12): 90-98.
|
| [20] |
肖国举, 张强, 李裕, 等, 2010. 气候变暖对宁夏引黄灌区土壤盐分及其灌水量的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 26(6): 7-13.
|
| [21] |
杨肖丽, 郑巍斐, 林长清, 等, 2017. 基于统计降尺度和SPI的黄河流域干旱预测[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版), 45(5): 377-383.
|
| [22] |
杨兴国, 孙银川, 王素艳, 等, 2021. 宁夏气候与生态环境[M]. 北京: 气象出版社.
|
| [23] |
杨绚, 李栋梁, 汤绪, 2014. 基于CMIP5多模式集合资料的中国气温和降水预估及概率分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 34(3): 795-804.
|
| [24] |
翟盘茂, 周佰铨, 陈阳, 等, 气候变化科学方面的几个最新认知[J]. 2021. 气候变化研究进展, 17(6): 629-635.
|
| [25] |
张镭, 黄建平, 梁捷宁, 等, 2020. 气候变化对黄河流域的影响及应对措施[J]. 科技导报, 38(17): 42-51.
|
| [26] |
张丽霞, 陈晓龙, 辛晓歌, 2019. CMIP6情景模式比较计划(ScenarioMIP)概况与评述[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 15(5): 519-525.
|
| [27] |
张强, 陈丽华, 王润元, 等, 2012. 气候变化与西北地区粮食和食品安全[J]. 干旱气象, 30(4): 509-513.
|
| [28] |
赵东升, 吴绍洪, 2013. 气候变化情景下中国自然生态系统脆弱性研究[J]. 地理学报, 68(5): 602-610.
|
| [29] |
赵鸿, 王润元, 尚艳, 等, 2016. 粮食作物对高温干旱胁迫的响应及其阈值研究进展与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 34(1): 1-12.
DOI
|
| [30] |
周国逸, 李琳, 吴安驰, 2020. 气候变暖下干旱对森林生态系统的影响[J]. 南京信息工程大学学报(自然科学版), 12(1): 81-88.
|
| [31] |
周天军, 邹立维, 陈晓龙, 2019. 第六次国际耦合模式比较计划(CMIP6)评述[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 15(5): 445-456.
|
| [32] |
周天军, 陈梓明, 邹立维, 等, 2020. 中国地球气候系统模式的发展及其模拟和预估[J]. 气象学报, 78(3): 332-350.
|
| [33] |
周天军, 陈梓明, 陈晓龙, 等, 2021. IPCC AR6报告解读:未来的全球气候——基于情景的预估和近期信息[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 17(6): 652-663.
|
| [34] |
周文翀, 韩振宇, 2018. CMIP5全球气候模式对中国黄河流域气候模拟能力的评估[J]. 气象与环境学报, 34(6): 42-55.
|
| [35] |
ALLEN R G, PEREIRA L S, RAES D, et al, 1998. Crop evapotranspiration: guidelines for computing crop water requirements-FAO irrigation and drainage paper 56[EB/OL]. [2022-12-08]. https://www.fao.org/3/X0490E/X0490E00.htm.
|
| [36] |
CAI W J, ZHANG C, SUEN H P, et al, 2020. The 2020 China report of the lancet countdown on health and climate change[J]. The Lancet Public Health, 6(1): 64-81.
|
| [37] |
IPCC, 2021. Climate change 2021: the physical science basis[R/OL]. [2021-08-06]. https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1/#FullReport.
|
| [38] |
O’NEILL B C, TEBALDI C, VAN VUUREN D P, et al, 2016. The scenario model intercomparison project (ScenarioMIP) for CMIP6[J]. Geoscientific Model Development, 9(9): 3 461-3 482.
DOI
URL
|
| [39] |
WU X Y, HAO Z C, TANG Q H, et al, 2021. Projected increase in compound dry and hot events over global land areas[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 41(1): 393-403.
DOI
URL
|
| [40] |
XIE X D, HUANG X X, WANG T J, et al, 2018. Simulation of non-homogeneous CO2 and its impact on regional temperature in East Asia[J]. Journal of Meteorological Research, 32(3): 456-468.
DOI
URL
|
 ), 崔洋1,2(
), 崔洋1,2( ), 张雯1,2, 李欣1,2
), 张雯1,2, 李欣1,2
 ), CUI Yang1,2(
), CUI Yang1,2( ), ZHANG Wen1,2, LI Xin1,2
), ZHANG Wen1,2, LI Xin1,2