Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (6): 867-877.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-06-0867
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Precipitation characteristics associated with the Qinghai Plateau vortex and environmental field analysis of different quadrants
SHEN Xiaoyan1,2( ), MA Yuancang1,2(
), MA Yuancang1,2( ), SHEN Yanling1,2, QUAN Chen1,2, GUAN Qin1,2, AN Lin1,2, WANG Huiping1,2
), SHEN Yanling1,2, QUAN Chen1,2, GUAN Qin1,2, AN Lin1,2, WANG Huiping1,2
1. Qinghai Institute of Meteorological Science Xining 810001, China 2. Qinghai Provincial Key Laboratory of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Xining 810001, China
-
Received:2025-02-22Revised:2025-04-22Online:2025-12-31Published:2026-01-19
青海高原低涡关联降水特征及不同象限环境场分析
沈晓燕1,2( ), 马元仓1,2(
), 马元仓1,2( ), 申燕玲1,2, 权晨1,2, 管琴1,2, 安琳1,2, 王惠平1,2
), 申燕玲1,2, 权晨1,2, 管琴1,2, 安琳1,2, 王惠平1,2
1.青海省气象科学研究所 青海 西宁 810001 2.青海省防灾减灾重点实验室 青海 西宁 810001
-
通讯作者:马元仓 -
作者简介:沈晓燕(1992—),女,青海乐都人,高级工程师,主要从事数值模式及检验研究。E-mail:sxygwm@163.com。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(62162053);青海省科技计划项目(2023-SF-111);青海省气象局科技项目(QXGS2023-06)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
SHEN Xiaoyan, MA Yuancang, SHEN Yanling, QUAN Chen, GUAN Qin, AN Lin, WANG Huiping. Precipitation characteristics associated with the Qinghai Plateau vortex and environmental field analysis of different quadrants[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(6): 867-877.
沈晓燕, 马元仓, 申燕玲, 权晨, 管琴, 安琳, 王惠平. 青海高原低涡关联降水特征及不同象限环境场分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(6): 867-877.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-06-0867

Fig.2 Comparison scatterplot of daily precipitation between ERA5 reanalysis data and station observations over the Qinghai Plateau from 2016 to 2021 (N represents total number of samples)
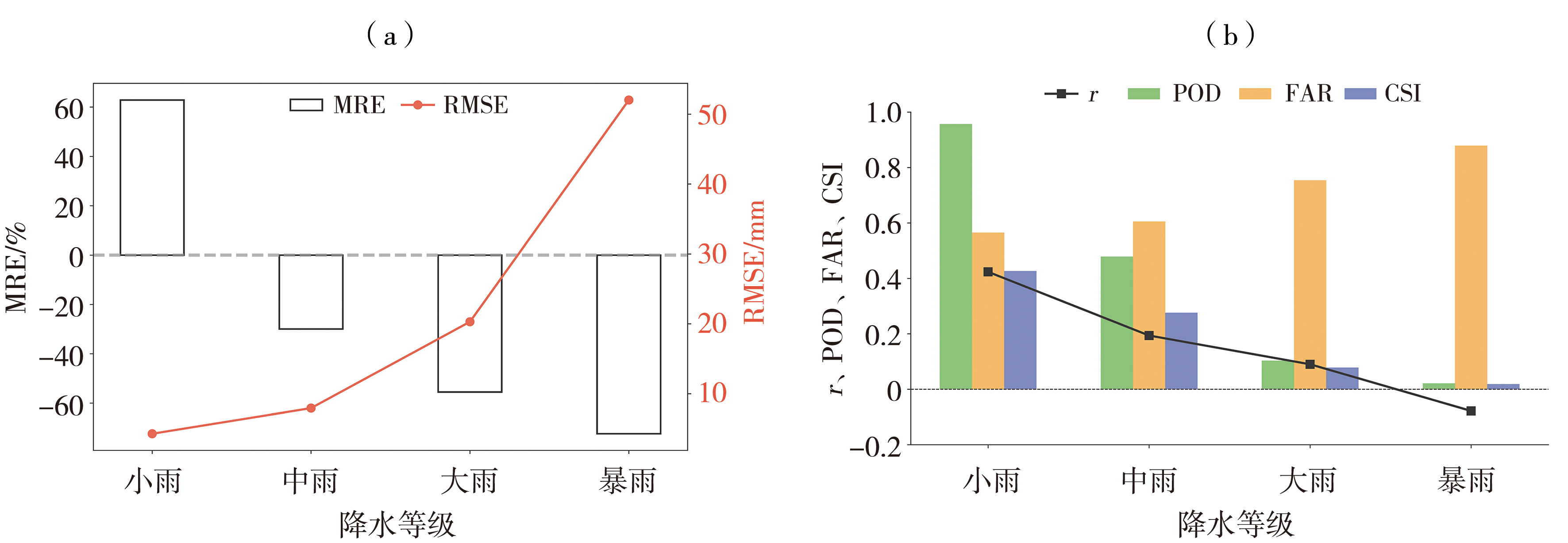
Fig.3 The MRE and RMSE (a), and r, POD, FAR, and CSI (b) of ERA5 precipitation data over the Qinghai Plateau during 2016-2021 under different precipitation levels

Fig.4 The inter-annual variation of the number of plateau vortices (a), and the moving paths of plateau vortices passing through the Qinghai Plateau (b) from 1950 to 2021 (The blue and red dots denote the generation and dissipation locations of plateau vortices, respectively, the area enclosed by the solid black line denotes Qinghai Province)

Fig.5 The spatial distribution of the proportion of plateau vortex days(fTPV)for the whole year (a), warm season (b), and cold season (c) from 1979 to 2021 (Unit: %)
| 时段 | 普通降水日平均降水量 | 高原低涡降水日平均降水量 |
|---|---|---|
| 全年 | 2.29 | 4.41 |
| 暖季 | 3.29 | 4.80 |
| 冷季 | 1.07 | 2.56 |
Tab.1 The average precipitation on general and plateau vortex precipitation days over the Qinghai Plateau in different periods from 1979 to 2021
| 时段 | 普通降水日平均降水量 | 高原低涡降水日平均降水量 |
|---|---|---|
| 全年 | 2.29 | 4.41 |
| 暖季 | 3.29 | 4.80 |
| 冷季 | 1.07 | 2.56 |

Fig.6 The spatial distribution of the proportion of extreme precipitation days associated with plateau vortex to the total extreme precipitation days (${f}_{\mathrm{E}\mathrm{X}}^{\mathrm{T}\mathrm{P}\mathrm{V}}$) (a, b, c) and the proportion of extreme precipitation days associated with plateau vortex to the plateau vortex days (${f}_{\mathrm{T}\mathrm{P}\mathrm{V}}^{\mathrm{E}\mathrm{X}}$) (d, e, f) for the whole year (a, d), warm season (b, e), and cold season (c, f) from 1979 to 2021 (Unit: %)

Fig.7 Monthly variation of the proportion of plateau vortex days (fTPV), the proportion of extreme precipitation days associated with plateau vortex to the total extreme precipitation days (${f}_{\mathrm{E}\mathrm{X}}^{\mathrm{T}\mathrm{P}\mathrm{V}}$), and the proportion of extreme precipitation days associated with plateau vortex to the plateau vortex days (${f}_{\mathrm{T}\mathrm{P}\mathrm{V}}^{\mathrm{E}\mathrm{X}}$) in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau region (a) and the Qinghai Plateau region (b) from 1979 to 2021
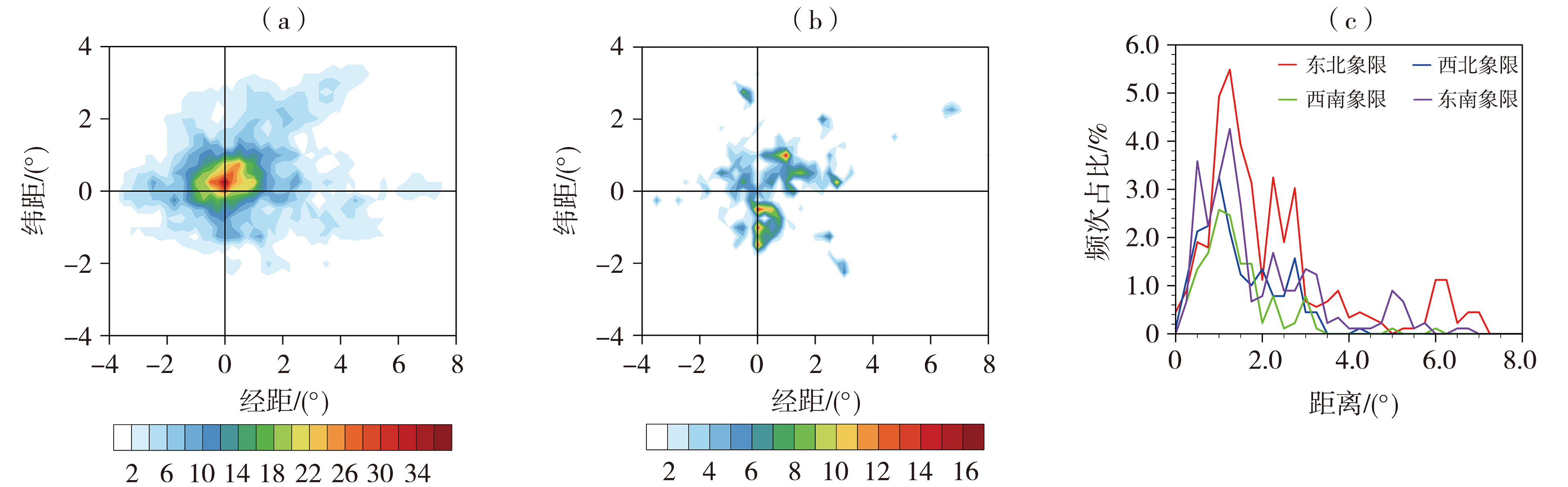
Fig.8 The composite distribution of heavy rain frequency centered on the plateau vortex core based on ERA5 grids (a) and meteorological station data (b) (Unit: times), and the proportion of heavy rain frequency at different distances from the plateau vortex core in different quadrants (c)

Fig.9 Box plots of CAPE (a), K index (b), 500 hPa pseudo equivalent potential temperature (c), 500 hPa specific humidity (d), 600 hPa specific humidity (e), whole layer water vapor flux divergence (f), 500 hPa vorticity (g), 200 hPa divergence (h), and 500 hPa vertical velocity (i) in different quadrants of plateau vortices associated with heavy rainfall from 2016 to 2021

Fig.10 The spatial distribution of convective available potential energy (Unit: J·kg-1) (a), K index (b, Unit: K), 500 hPa pseudo-equivalent potential temperature (c, Unit: K), integrated water vapor flux (arrows, Unit: kg·m-1·s-1) and its divergence (the color shaded, Unit: 10-5 kg·m-2·s-1) (d), the 500 hPa vorticity (the color shaded, Unit: 10-5 s-1) and 200 hPa divergence (contours, Unit: 10-5 s-1) (e), 500 hPa vertical velocity (f, Unit: Pa·s-1), dynamically composited relative to the center of the plateau vortex associated with heavy rainfall from 2016 to 2021
| [1] | 曹艳察, 郑永光, 孙继松, 等, 2024. 东北冷涡背景下三类区域性强对流天气过程时空分布和环境特征对比分析[J]. 气象学报, 82(1): 22-36. |
| [2] | 陈功, 李国平, 李跃清, 2012. 近20年来青藏高原低涡的研究进展[J]. 气象科技进展, 2(2): 6-12. |
| [3] | 陈乾, 1964. 青藏高原地区500 hPa低涡的天气气候分析[Z]. 兰州天动会议技术资料. 兰州, 27-29. |
| [4] | 陈小婷, 赵强, 刘慧, 等, 2022. 黄土高原两次不同类型暴雨水汽特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 40(6): 968-980. |
| [5] | 邓中仁, 葛旭阳, 姚秀萍, 等, 2022. 辐射对高原涡形成和发展影响的模拟研究[J]. 大气科学, 46(3): 541-556. |
| [6] | 丁禹钦, 胡文东, 邵建, 等, 2021. 青藏高原低涡客观识别与图像学分析[J]. 成都信息工程大学学报, 36(6): 674-679. |
| [7] | 董元昌, 李国平, 2014. 凝结潜热在高原涡东移发展不同阶段作用的初步研究[J]. 成都信息工程学院学报, 29(4): 400-407. |
| [8] | 何光碧, 2019. 高原天气研究若干进展:基于中国气象局成都高原气象研究所相关研究[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 39(1): 1-5. |
| [9] | 华维, 邓浩, 夏昌基, 等, 2024. 青藏高原水循环中高原低涡及多季风交汇的研究进展[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 18(2): 1-11. |
| [10] | 黄晓龙, 吴薇, 许剑辉, 等, 2023. ERA5-Land降水再分析资料在中国西南地区的适用性评估[J]. 高原气象, 42(6): 1 562-1 575. |
| [11] | 李博, 李跃清, 陈永仁, 2023. 近十年高原低涡与中亚低涡研究进展[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 43(1): 17-25. |
| [12] | 李国平, 2021. 青藏高原天气动力学研究的新进展[J]. 气象科技进展, 11(3): 58-65. |
| [13] | 李国平, 李山山, 黄楚惠, 2017. 高原切变线与高原低涡相互作用的研究现状与展望[J]. 地球科学进展, 32(9): 919-925. |
| [14] | 李国平, 张万诚, 2019. 高原低涡、切变线暴雨研究新进展[J]. 暴雨灾害, 38(5): 464-471. |
| [15] | 李生辰, 张青梅, 沈晓燕, 等, 2022. 青海高原暴雨的形成条件与基本特征分析[J]. 高原气象, 41(2): 526-540. |
| [16] | 李跃清, 2022. 青藏高原热源与天气系统影响灾害性天气的研究进展[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 42(3): 1-12. |
| [17] | 林志强, 2021. 青藏高原低涡年际年代际变化特征、机理及其未来预估[D]. 南京: 南京大学. |
| [18] | 林志强, 郭维栋, 姚秀萍, 等, 2023. 基于多源资料的高原低涡源地研究[J]. 大气科学, 47(3): 837-852. |
| [19] | 林志强, 周振波, 假拉, 2013. 高原低涡客观识别方法及其初步应用[J]. 高原气象, 32(6): 1 580-1 588. |
| [20] | 林志强, 2015. 1979—2013年ERA-Interim资料的青藏高原低涡活动特征分析[J]. 气象学报, 73(5): 925-939. |
| [21] | 马婷, 刘屹岷, 吴国雄, 等, 2020. 青藏高原低涡形成、发展和东移影响下游暴雨天气个例的位涡分析[J]. 大气科学, 44(3): 472-486. |
| [22] | 佘王康, 杨勤丽, 阳坤, 等, 2024. 青藏高原雪水比例时空变化特征[J]. 水科学进展, 35(2): 348-356. |
| [23] | 沈新勇, 张弛, 高焕妍, 等, 2020. 三类高空冷涡的划分及其动态合成分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 39(1): 1-9. |
| [24] | 汤欢, 傅慎明, 孙建华, 等, 2023. 基于高分辨率再分析风场的高原涡三维识别技术及应用[J]. 大气科学, 47(3): 698-712. |
| [25] | 唐信英, 周长艳, 王鸽, 2014. 青藏高原低涡活动特征统计分析[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 34(3): 41-44. |
| [26] | 王雅君, 罗菊英, 程烈海, 等, 2024. 基于机器学习的湖北省夏季干旱预测模型构建与检验[J]. 干旱气象, 42(5): 661-670. |
| [27] | 魏栋, 刘丽伟, 田文寿, 等, 2021. 基于卫星资料的西北地区高原涡强降水分析[J]. 高原气象, 40(4): 829-839. |
| [28] | 杨磊, 郑永光, 2023. 东北地区雷暴大风观测特征及其与东北冷涡的关系研究[J]. 气象学报, 81(3):416-429. |
| [29] | 姚秀萍, 马嘉理, 刘俏华, 等, 2021. 青藏高原夏季降水研究进展[J]. 气象科技进展, 11(3): 66-74. |
| [30] | 郁淑华, 高文良, 2019. 移出与未移出青藏高原的高原低涡涡源区域的地面加热特征分析[J]. 高原气象, 38(2): 299-313. |
| [31] | 郁淑华, 高文良, 彭骏, 2012. 青藏高原低涡活动对降水影响的统计分析[J]. 高原气象, 31(3): 592-604. |
| [32] | 张敬萍, 靳双龙, 冯双磊, 等, 2023. 中尺度涡旋客观识别与三维追踪的新方法及其效果评估[J]. 大气科学, 47(5): 1 434-1 450. |
| [33] | 张恬月, 李国平, 2018. 青藏高原夏季地面感热通量与高原低涡生成的可能联系[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 12(2): 1-6. |
| [34] | LI L, ZHANG R H, WEN M, et al, 2018. Effect of the atmospheric quasi-biweekly oscillation on the vortices moving off the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Climate Dynamics, 50(3/4):1 193-1 207. |
| [35] | LI L, ZHANG R H, WEN M, et al, 2022. Effects of the atmospheric dynamic and thermodynamic fields on the eastward propagation of Tibetan Plateau vortices[J]. Tellus A: Dynamic Meteorology and Oceanography, 71(1): 1647088. DOI:10.1080/16000870.2019.1647088. |
| [36] | LIN Z Q, GUO W D, JIA L, et al, 2020. Climatology of Tibetan Plateau vortices derived from multiple reanalysis datasets[J]. Climate Dynamics, 55(7): 2 237-2 252. |
| [37] | LIN Z Q, YAO X P, GUO W D, et al, 2022. Extreme precipitation events over the Tibetan Plateau and its vicinity associated with Tibetan Plateau vortices[J]. Atmospheric Research, 280(1): 106433. DOI:10.1016/j.atmosres.2022.106433. |
| [38] | WU D, ZHANG F M, WANG C H, 2018. Impacts of diabatic heating on the genesis and development of an inner Tibetan Plateau vortex[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 123(20): 11 691-11 704. |
| [39] | YANG L, ZHENG Y G, 2024. The short-duration heavy rainfall in different quadrants of Northeast China cold vortices[J]. Journal of Meteorological Research, 38(2): 321-338. |
| [40] | ZHANG F M, WANG C H, PU Z X, 2019. Genesis of Tibetan Plateau vortex: Roles of surface diabatic and atmospheric condensational latent heating[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 58(12): 2 633-2 651. |
| [41] | ZHANG P F, LI G P, FU X, et al, 2014. Clustering of Tibetan Plateau vortices by 10-30-day intraseasonal oscillation[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 142(1):290-300. |
| [1] | AI Runbing, WANG Lulu. Characteristics and forecasting approaches of tropical cyclone remote precipitations in Zhumadian [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(6): 891-900. |
| [2] | HU Jiaying, ZHAO Guixiang, YAN Hui, XU Yiwen, CAO Junwei. Organization and causation of a squall line under the complex terrain [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(2): 289-299. |
| [3] | ZHANG Qi, LI Yueqing, QING Quan. Stratosphere-troposphere exchange processes caused by deep southwest vortex and plateau vortex [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(1): 32-40. |
| [4] | YAN Ruotong, DENG Fengdong, XU Dongbei, MAI Zhening. Analysis of the occurrence rules of the moving-out vortex over the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau and the differences in the development mechanism of typical cases in warm seasons [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(6): 910-921. |
| [5] | XING Fenghua, HUANG Yanbin, LI Chunluan, HUANG Feiting, LI Guangwei, AO Jie. Characteristics of tropical isolated convective clouds in Hainan Island [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(3): 442-449. |
| [6] | FENG Xiaoli, DUO Jiezhuome, LI Wanzhi, SHEN Hongyan, CHEN Jiqing. Spatiotemporal Variations of Extreme Temperature Indices over Qinghai Plateau During 1961-2018 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(1): 28-37. |
| [7] | WANG Xiwen, ZHANG Feimin, WANG Zhilan, YANG Kai, WANG Chenghai. Numerical Simulation Study of a Tibetan Plateau Vortex over the Western Tibetan Plateau [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(1): 54-64. |
| [8] | ZHU Ping, YU Xiaoding, WANG Zhenhui, XIAO Jianshe. Temporal and Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Disastrous Convective Weather over the Qinghai Plateau [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(3): 377-. |
| [9] | YAN Zhenning1, MA Xueqian2. Comparison and Analysis of Precipitable Water Vapor in Different Regions of the Qinghai Plateau [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(3): 365-. |
| [10] | MU Dan1, LI Yueqing2. Statistical Characteristics Summary of the Southwest China Vortex [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(2): 175-181. |
| [11] | ZHAO Guixiang1, WANG Xiaoli1, WU Hong2. Statistical Characteristics of Mesoscale Convective Systems over the Middle Reaches Area of the Yellow River During 2005-2014 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2016, 34(6): 1016-1026. |
| [12] | SHI Rui, HE Guangbi, LONG Keji. Analysis on a Heavy Vortex Rainstorm in Sichuan Basin from 29 June to 2 July 2013 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(5): 845-855. |
| [13] | ZHANG Lei,ZHANG Jidong,Rasul Abla. Analysis on Identifying Indexes of Hail Weather Process in Akesu of the Southern Xinjiang [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2014, 32(4): 629-635. |
| [14] | WANG Xiuqin,DUAN Wei. Statistical Characteristics of High Temperature Days in Mosuowan of Xinjiang [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2014, 32(2): 220-225. |
| [15] | MIAO Aimei,DONG Wenxiao,JIA Lidong,LI Miao,WANG Hongxia. The Statistical Characteristics and Conceptual Model of Different Phase Precipitation in Recent 30 a in Shanxi Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2014, 32(1): 23-31. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
