Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (1): 95-106.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2024)-01-0095
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Characteristic analysis of early spring hail in Chengdu based on S-band polarization radar
ZHOU Cong1( ), ZHANG Tao1, XIA Xin2(
), ZHANG Tao1, XIA Xin2( ), ZHANG Kui1
), ZHANG Kui1
- 1. Chengdu Meteorological Observatory,Chengdu 610072,China
2. Tianfu New District Branch of Chengdu Meteorological Bureau,Chengdu 610072,China
-
Received:2023-04-23Revised:2023-07-28Online:2024-02-29Published:2024-03-06
基于S波段双偏振雷达的成都初春冰雹特征分析
- 1.成都市气象台,四川 成都 610072
2.成都市气象局天府新区分局,四川 成都 610072
-
通讯作者:夏昕(1972—),男,四川岳池人,高级工程师,主要从事气象数据分析及应用平台研发。E-mail: 10509987@qq.com。 -
作者简介:周聪(1993—),男,江苏扬州人,硕士,工程师,主要从事雷达数据应用与气象数据深度学习研究。E-mail: 2420997398@qq.com。 -
基金资助:四川省科技计划重点研发项目“成渝超大城市极端天气监测预警关键技术与应用”(2023YFS0430);高原与盆地暴雨旱涝灾害四川省重点实验室科技发展基金项目(SCQXKJYJXZD202308);高原与盆地暴雨旱涝灾害四川省重点实验室科技发展基金项目(SCQXKJZD202103)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHOU Cong, ZHANG Tao, XIA Xin, ZHANG Kui. Characteristic analysis of early spring hail in Chengdu based on S-band polarization radar[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(1): 95-106.
周聪, 张涛, 夏昕, 张葵. 基于S波段双偏振雷达的成都初春冰雹特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(1): 95-106.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2024)-01-0095
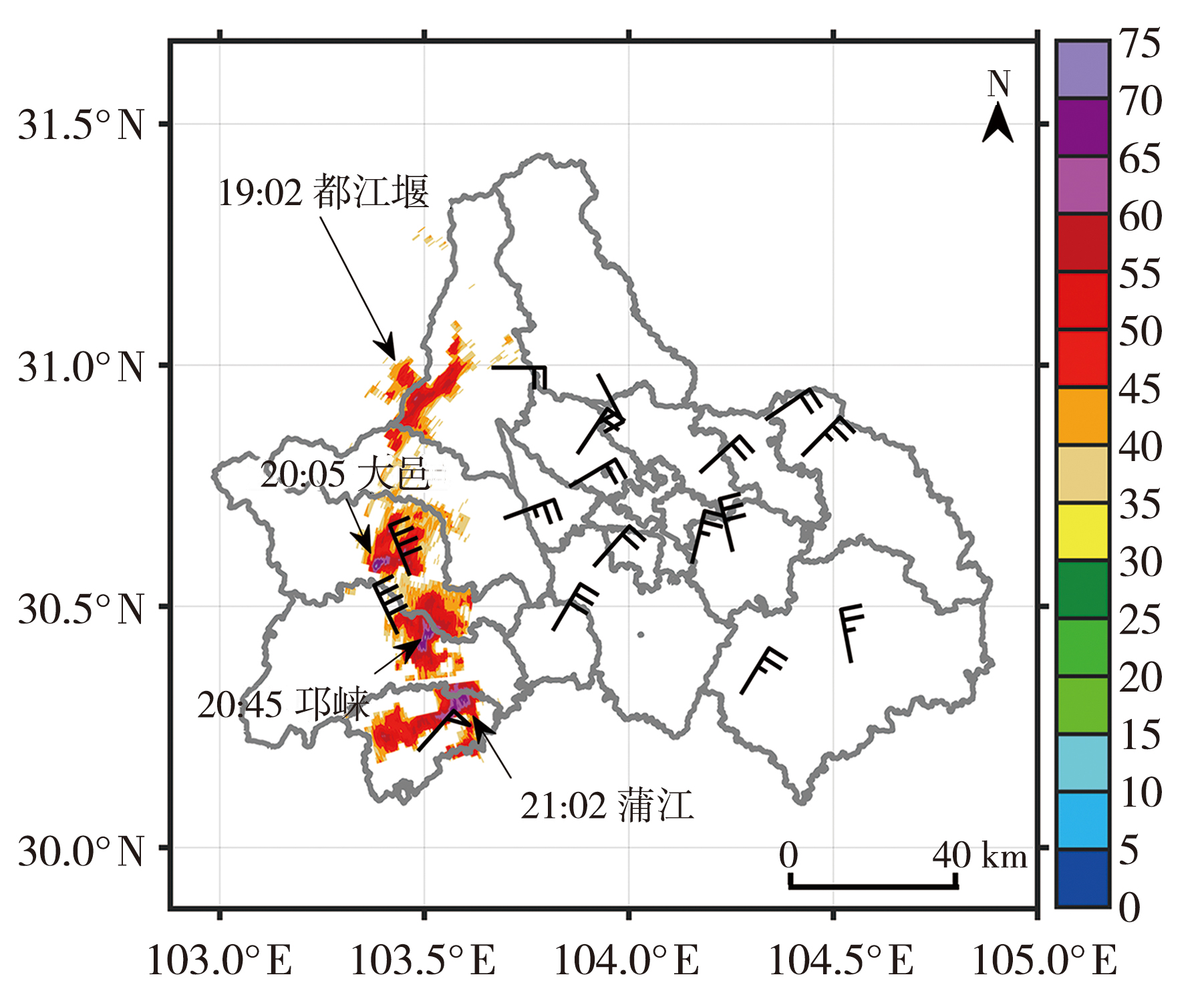
Fig.1 The hail cloud reflectivity factor ZH(color shaded, Unit: dBZ) at 1.5°elevation from Chengdu radar at different times from 19:02 to 21:02, and extreme wind(wind vectors, Unit: m·s-1) at Chengdu national weather stations from 18:00 to 21:00 on 16 March 2022

Fig.2 The ZH (a, Unit: dBZ) at 1.5° elevation, and vertical cross-section of ZH (b, Unit: dBZ) and V (c, Unit: m·s-1) along the AB line segment from Chengdu radar at 19:59 on 16 March 2022
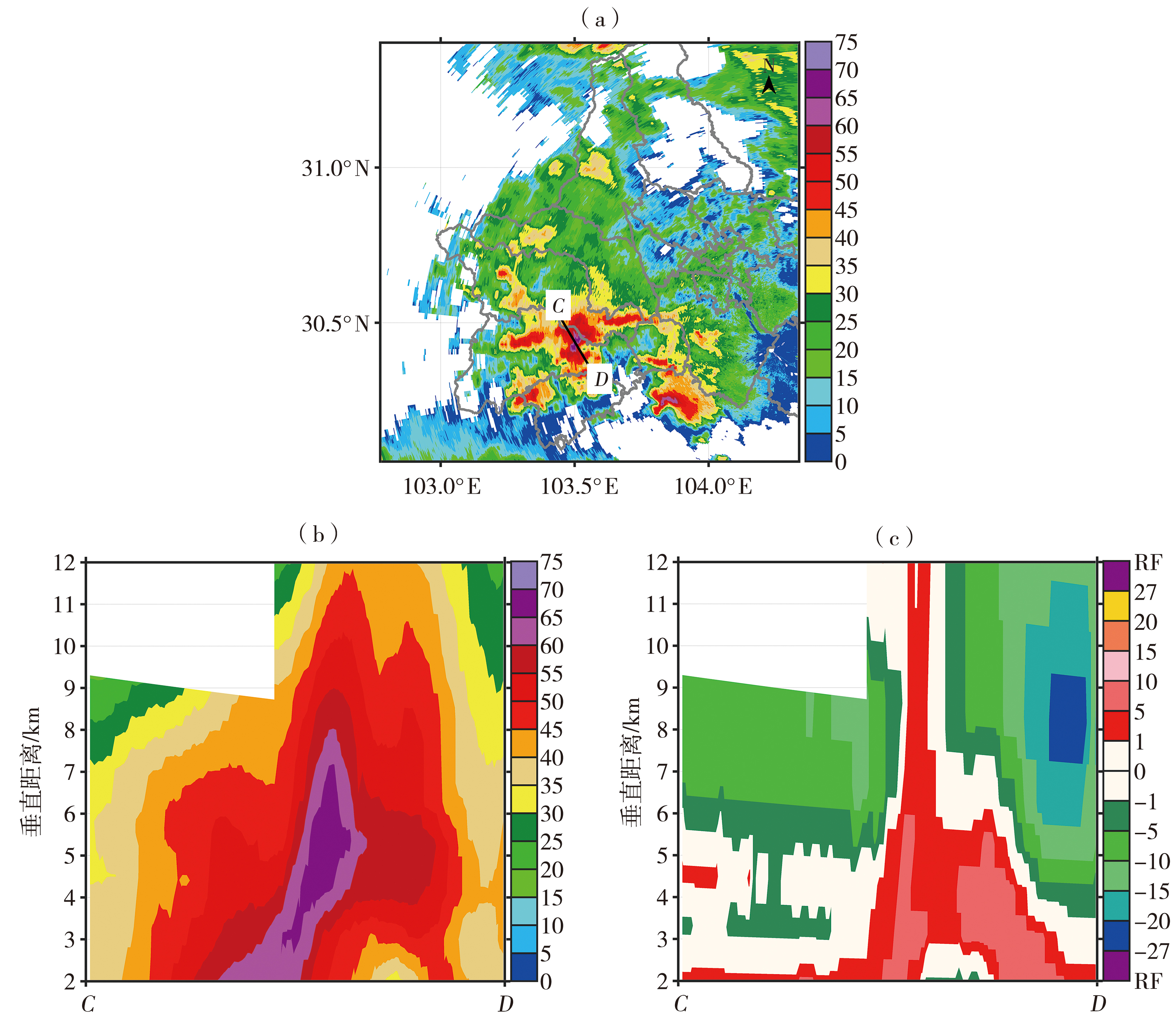
Fig.3 The ZH (a, Unit: dBZ) at 1.5° elevation, vertical cross-section of ZH (b, Unit: dBZ) and V (c, Unit: m·s-1) along the CD line segment from Chengdu radar at 20:45 on 16 March 2022

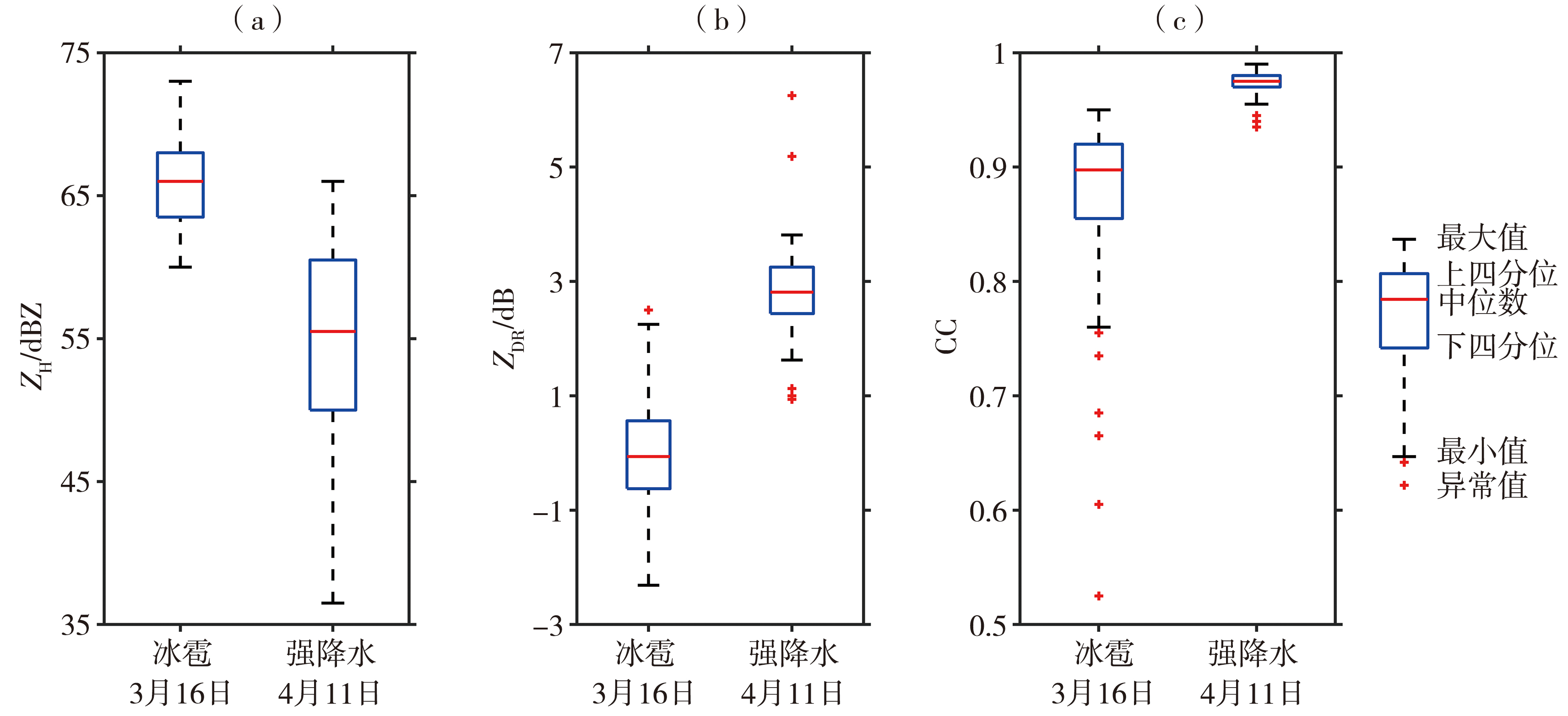
Fig.4 The ZH (a, b) (Unit: dBZ), ZDR (c, d) (Unit: dB), KDP (e, f) (Unit: (°)·km-1) and CC (g, h) at 1.5° elevation from Chengdu radar at 20:22 (a, c, e, g) and 20:45 (b, d, f, h) on 16 March 2022

Fig.5 The ZH (a, Unit: dBZ) at 1.5° elevation, vertical cross-section of ZH (b, c, gray solid lines) (Unit: dBZ), ZDR (b, color filled) (Unit: dB) and CC (c, color filled) along the EF line segment, respectively, from Chengdu radar at 20:22 on 16 March 2022
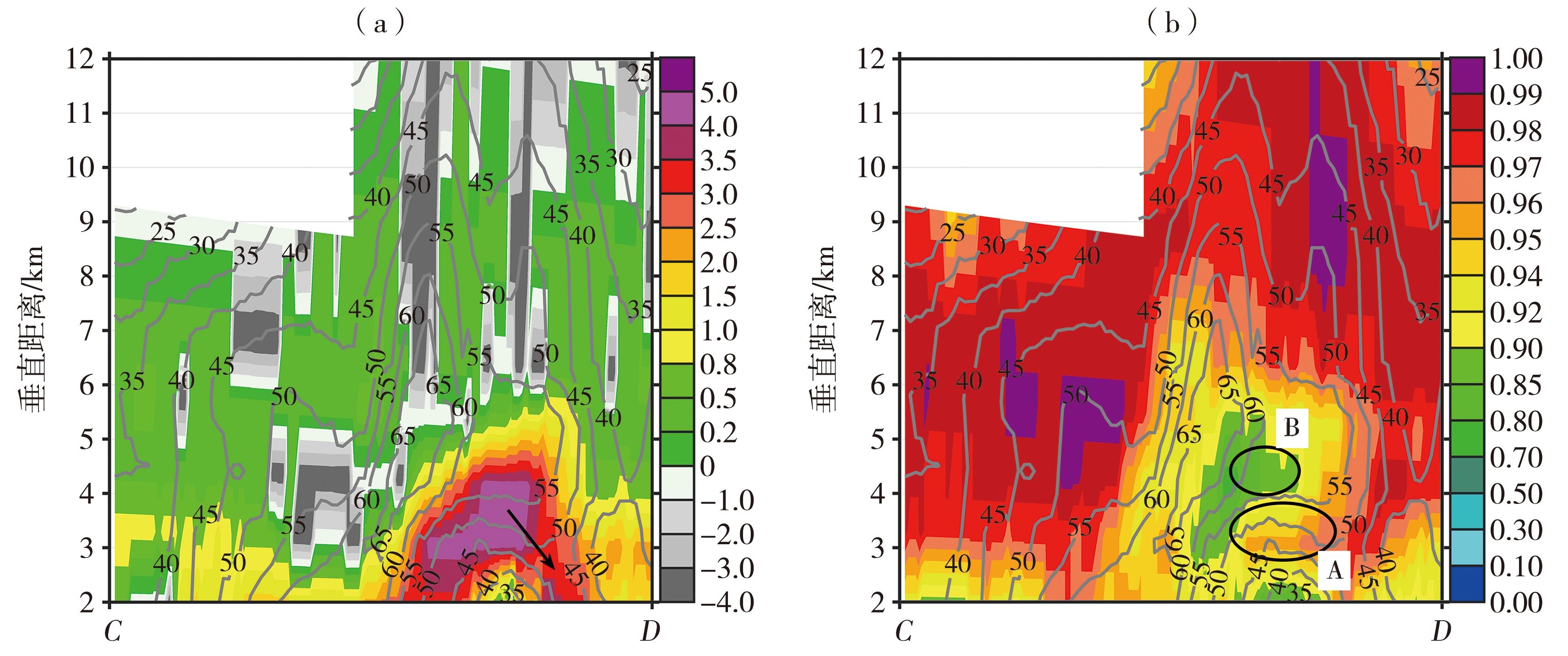
Fig.6 The vertical cross-section of ZH(a, b, gray solid lines)(Unit: dBZ), ZDR(a, color filled)(Unit: dB) and CC(b, color filled) along the CD line segment in fig.3(a), respectively, from Chengdu radar at 20:45 on 16 March 2022

Fig.7 The ZH (a, Unit: dBZ) at 1.5° elevation, and vertical cross-section of ZH (b, c, gray solid lines) (Unit: dBZ), ZDR (b, color filled) (Unit: dB) and CC (c, color filled) along the GH line segment, respectively, from Chengdu radar at 20:47 on 11 April 2022

Fig.8 The correlation between ZH and ZDR(a), KDP(b), CC(c) of severe convective echo at 1.5° elevation from Chengdu radar on 11 April 2022, respectively
| [1] | 曹俊武, 刘黎平, 葛润生, 等, 2005. 模糊逻辑法在双偏振雷达识别降水粒子相态中的研究[J]. 大气科学, 29(5): 827-836. |
| [2] |
陈关清, 杨群, 李伟栋, 等, 2016. 贵州铜仁连续两次冰雹天气过程的对比分析[J]. 干旱气象, 34(1): 163-172.
DOI |
| [3] |
褚颖佳, 郭飞燕, 高帆, 等, 2023. 冷涡影响下两次不同类型强对流过程对比分析[J]. 干旱气象, 41(2): 279-289.
DOI |
| [4] | 范思睿, 陶丽, 张恒, 等, 2017. 四川一次超级单体风暴的多普勒雷达观测分析[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 37(1): 73-79. |
| [5] | 冯晋勤, 张深寿, 吴陈锋, 等, 2018. 双偏振雷达产品在福建强对流天气过程中的应用分析[J]. 气象, 44(12): 1 565-1 574. |
| [6] |
姬雪帅, 王丽婧, 郭宏, 2022. 基于多源观测资料对张家口一次雨雪天气降水相态特征的分析[J]. 干旱气象, 40(3): 507-515.
DOI |
| [7] |
雷瑜, 黄武斌, 黎倩, 等, 2022. 不同天气分型下甘肃河东地区强冰雹天气多普勒雷达产品特征[J]. 干旱气象, 40(2): 234-243.
DOI |
| [8] | 李晓霞, 李常德, 马国涛, 等, 2020. 一次冰雹强对流天气过程的潜势条件和中尺度特征分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 14(4): 69-77. |
| [9] | 林文, 张深寿, 罗昌荣, 等, 2020. 不同强度强对流云系S波段双偏振雷达观测分析[J]. 气象, 46(1): 63-72. |
| [10] | 刘黎平, 2002. 双线偏振多普勒天气雷达估测混合区降雨和降雹方法的理论研究[J]. 大气科学, 26(6): 761-772. |
| [11] | 刘黎平, 钱永甫, 王致君, 等, 1996. 用双线偏振雷达研究云内粒子相态及尺度的空间分布[J]. 气象学报, 54(5): 590-599. |
| [12] | 刘黎平, 张鸿发, 王致君, 等, 1993. 利用双线偏振雷达识别冰雹区方法初探[J]. 高原气象, 12(3): 333-337. |
| [13] | 刘晓璐, 刘东升, 张世林, 等, 2012. 近30年四川冰雹气候特征[J]. 气象, 38(10): 1217-1224. |
| [14] | 罗玲, 佘一坤, 王珊, 等, 2018. 四川盆地中部冰雹天气过程成因诊断分析[J]. 农业与技术, 38(17): 135-139. |
| [15] | 潘佳文, 蒋璐璐, 魏鸣, 等, 2020b. 一次强降水超级单体的双偏振雷达观测分析[J]. 气象学报, 78(1): 86-100. |
| [16] | 潘佳文, 魏鸣, 郭丽君, 等, 2020a. 闽南地区大冰雹超级单体演变的双偏振特征分析[J]. 气象, 46(12): 1 608-1 620. |
| [17] | 祁红彦, 刘立兵, 2015. 成都市冰雹的时空变化与地形特征分析[J]. 气象科技, 43(3): 503-505. |
| [18] | 王洪, 吴乃庚, 万齐林, 等, 2018. 一次华南超级单体风暴的S波段偏振雷达观测分析[J]. 气象学报, 76(1): 92-103. |
| [19] | 王建林, 刘黎平, 曹俊武, 等, 2005. 双线偏振多普勒雷达估算降水方法的比较研究[J]. 气象, 31(8): 25-41. |
| [20] | 王小明, 谢静芳, 王侠飞, 等, 1992. 强对流天气的分析及短时预报[M]. 北京: 气象出版社: 28-29. |
| [21] |
许敏, 沈芳, 刘璇, 等, 2022. 京津冀“7·5”强对流天气形成的环境条件及中尺度特征[J]. 干旱气象, 40(6): 993-1 002.
DOI |
| [22] | 杨淑群, 邱予声, 2012. 四川省冰雹的时空变化特征[J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 34(11): 63-68. |
| [23] | 叶东, 2020. 一次强风雹天气的干侵入作用及雷达回波特征分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 14(5): 44-52. |
| [24] | 俞小鼎, 2011. 强对流天气的多普勒天气雷达探测和预警[J]. 气象科技进展, 1(3): 31-41. |
| [25] | 俞小鼎, 2014. 关于冰雹的融化层高度[J]. 气象, 40(6): 649-654. |
| [26] | 俞小鼎, 郑媛媛, 张爱民, 等, 2006. 安徽一次强烈龙卷的多普勒天气雷达分析[J]. 高原气象, 25(5): 914-924. |
| [27] | 张晓茹, 贾宏元, 谭志强, 等, 2008. 宁夏南部山区两次冰雹过程对比分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 15(3): 29-37. |
| [28] | 赵坤, 周仲岛, 潘玉洁, 等, 2008. 台湾海峡中气旋结构特征的单多普勒雷达分析[J]. 气象学报, 66(4): 437-651. |
| [29] | 郑媛媛, 俞小鼎, 方翀, 等, 2004. 一次典型超级单体风暴的多普勒天气雷达观测分析[J]. 气象学报, 62(3): 317-328. |
| [30] | 朱官忠, 1991. 山东盛夏的一次强风暴过程的中尺度分析[J]. 气象, 17(12): 22-26. |
| [31] | BRANDES E A, VIVEKANANDAN J, TUTTLE J D, et al, 1995. A study of thunderstorm microphysics with multiparameter radar and aircraft observations[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 123(11): 3 129-3 143. |
| [32] | BRINGI V N, KNUPP K, DETWILER A, et al, 1997. Evolution of a Florida thunderstorm during the convection and precipitation/electrification experiment: the case of 9 August 1991[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 125(9): 2 131-2 160. |
| [33] | HALL M P M, GODDARD J W F, CHERRY S M, 1984. Identification of hydro-meteors and other targets by dual-polarization radar[J]. Radio Science, 19(1): 132-140. |
| [34] | HUBBERT J C, BRINGI V N, 2000. The effects of three-body scattering on differential reflectivity signatures[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 17(1): 51-61. |
| [35] | KUMJIAN M R, RYZHKOV A V, 2008. Polarimetric signatures in supercell thunderstorms[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 47(7): 1 940-1 961. |
| [36] | KUMJIAN M R, RYZHKOV A V, 2012. The impact of size sorting on the polarimetric radar variables[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 69(6): 2 042-2 060. |
| [37] | KUMJIAN M, 2013. Principles and applications of dual-polarization weather radar. Part II: Warm-and cold-season applications[J]. Journal of Operational Meteorology, 1(20): 243-264. |
| [38] | LESINS G B, LIST R, 1986. Sponginess and drop shedding of gyrating hailstones in a pressure-controlled icing wind tunnel[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 43(23): 2 813-2 825. |
| [39] | SELIGA T A, BRINGI V N, 1976. Potential use of radar differential reflectivity measurements at orthogonal polarizations for measuring precipitation[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 15(1): 69-76. |
| [1] | XING Fenghua, HUANG Yanbin, LI Chunluan, HUANG Feiting, LI Guangwei, AO Jie. Characteristics of tropical isolated convective clouds in Hainan Island [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(3): 442-449. |
| [2] | GUO Feiyan, DIAO Xiuguang, CHU Yingjia, LI Xin, LU Xue, ZHANG Shaobo. Contrast analysis of dual-polarization signatures for the two extreme rainfall storms [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(1): 103-113. |
| [3] | LUO Xiping, LIAO Bo, ZHANG Xiaojuan, CUI Lei, LUO Xiong. Climatic characteristics of hail in Guizhou from 1961 to 2020 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 1024-1032. |
| [4] | ZHANG Haiyao, HUANG Yuxia, WU Huiyan, LI Xia, MU Lamei, YANG Huining. Comparative analysis of two consecutive hail weathers in complex terrain area of loecs plateau [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(4): 646-655. |
| [5] | LIN Chunying, WANG Qihua, LI Hongmei, GUO Qiang, HOU Yonghui, ZHOU Wanfu, ZHANG Liyan. Characteristics and disaster risk analysis of hail in agricultural area of eastern Qinghai Province in recent 60 years [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(3): 436-443. |
| [6] | LEI Yu, HUANG Wubin, LI Qian, HUANG Yuxia, ZHANG Junxia, LIU Na. Characteristics of Doppler radar products of strong hails under different weather classification in Hedong region of Gansu Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(2): 234-243. |
| [7] |
WANG Jiajin, ZHANG Qi, ZHANG Tao, LONG Keji, SHI Rui, .
Low-level Wind Field Characteristic Observed by Wind Profile Radar During Two Rainstorm Processes in Chengdu#br#
#br#
[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(1): 87-95.
|
| [8] | ZENG Yong, DING Min, LUO Xiong, ZOU Shuping, ZHOU Yunjun, LI Lili, HUANG Yu. Characteristics of Lightning Activity During a Large-scale Hail Weather Process in the Slope Transition Zone of Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(5): 771-781. |
| [9] | YI Nana, SU Lijuan, SHI Jinli, DONG Zhulei, XU Zhili. Impact of Different Cloud Microphysics ParameterizationSchemes on Hail Simulation [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(4): 619-631. |
| [10] | SUI Yuxiu, YANG Jingtai, LI Yuqian, WANG Lei, ZHOU Meie, CAO Bo. Climatic Characteristics of Hails in Dalian Region of Liaoning Province from 1971 to 2018 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(2): 249-255. |
| [11] | MO Lixia, GAO Xianquan, OU Huining, ZHOU Yunxia, LIANG Weiliang. Study of Objective Forecast Method of Guangxi Hail Based on Numerical Model Product [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(03): 480-489. |
| [12] | SONG Qiang, WANG Jixin, FU Zhao, LI Hong, LU Guoyang, WEI Sujuan. Characteristic of Precipitation and Lightning Activity of a Hailstorm Event in Gansu Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(3): 400-. |
| [13] | LIU Junqing, Yangjinzhuoma, LIAO Xiaokun, SHI Yueqin, YANG Gang, QIANG Dehou, LIU Duanyang. Verification of Cloud Precipitation Model Forecast Products During a Hailstorm Process in Tibet Plateau [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(3): 477-. |
| [14] | YANG Shuhua, ZHAO Guixiang, CHENG Haixia, WANG Yijie,,LI Laping, SONG Shihua. Comparative Analysis of Three Hail Weather Processes Caused by Pulse Storms in Northern Shanxi Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(1): 67-75. |
| [15] | EI Yinghua, CHEN Hong, ZHANG Nan, HE Qunying, LIN Xiaomeng. Analysis on Meso-scale Characteristics and Cause of a Severe Convective Hailstorm Weather Under Cold Vortex Background [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(1): 27-33. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||