Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (6): 1033-1041.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-06-1033
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
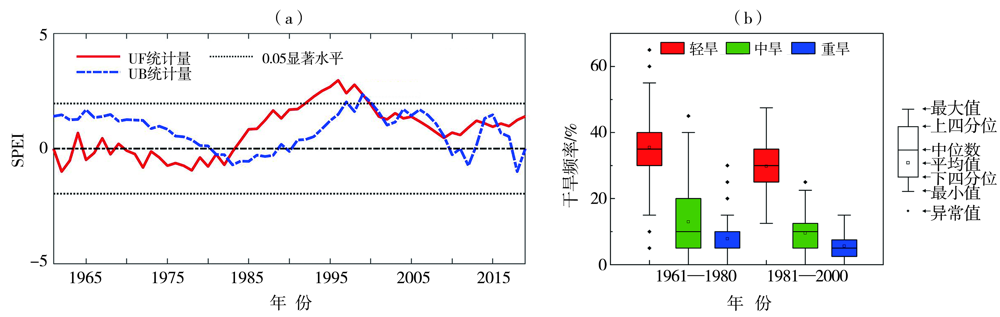
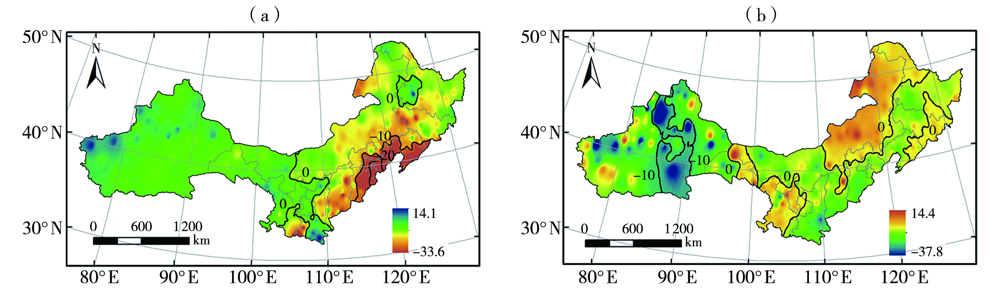
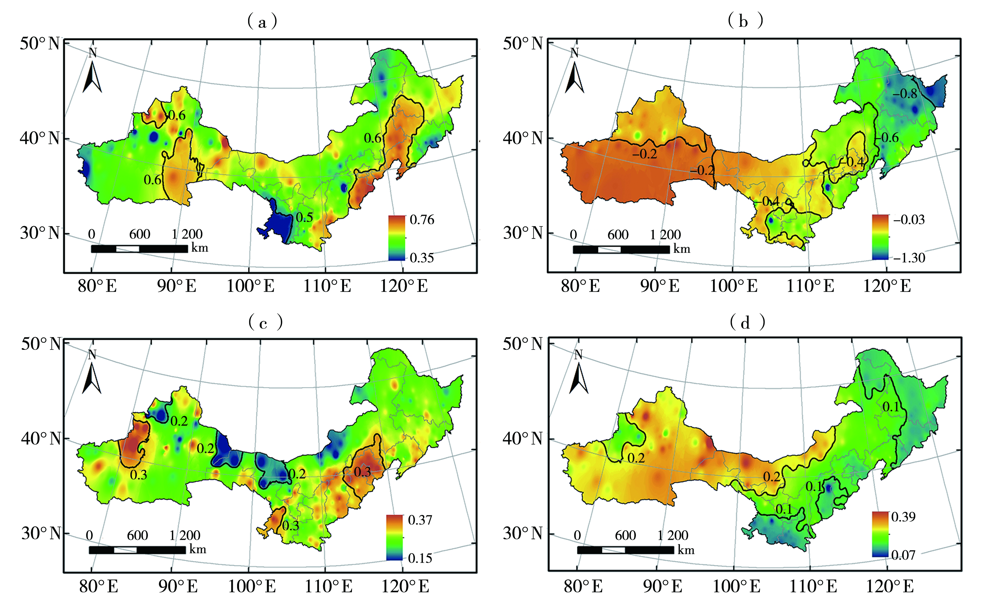
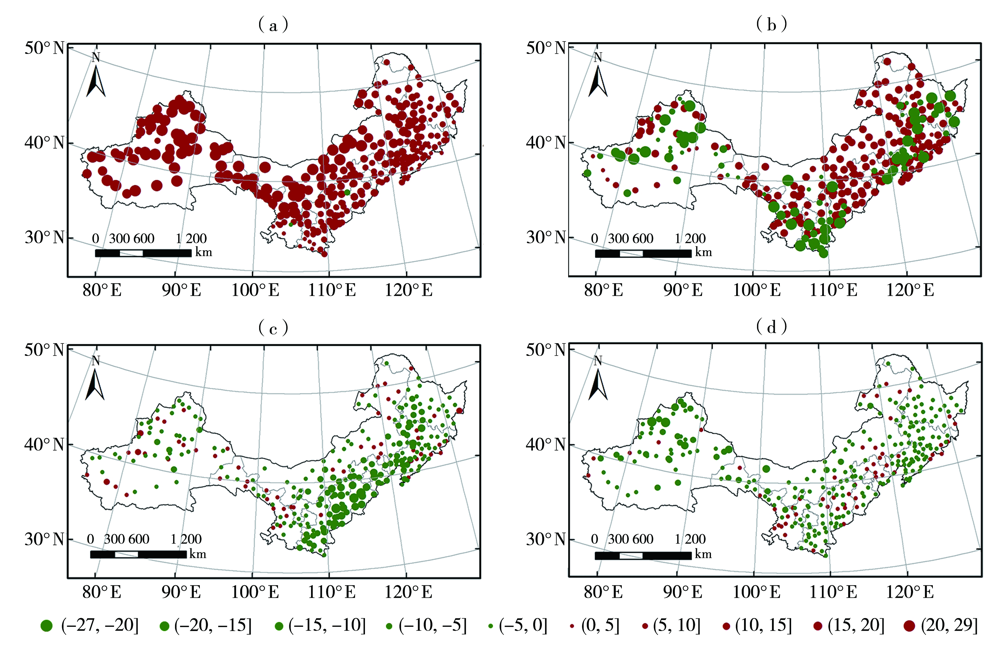
Characteristics of dry and wet changes in sunflower growing areas in northern China and their causes from 1961 to 2020
WANG Xiaochen1,2( ), MA Xueqing1,2, HE Huayun1,2, REN Siqi1,2, TANG Shuyue1,2, ZHAO Jinyuan1,2, PAN Zhihua1,2, WANG Jing1,2, PAN Xuebiao1,2, HU Qi1,2(
), MA Xueqing1,2, HE Huayun1,2, REN Siqi1,2, TANG Shuyue1,2, ZHAO Jinyuan1,2, PAN Zhihua1,2, WANG Jing1,2, PAN Xuebiao1,2, HU Qi1,2( )
)
- 1. College of Resources and Environmental Sciences, China Agricultural University, Beijing 100193, China
2. China Meteorological Administration-China Agricultural University Joint Laboratory for Addressing Climate Change in Agriculture, Beijing 100193, China
1961—2020年中国北方向日葵种植区干湿变化特征及其成因分析
王晓晨1,2( ), 马雪晴1,2, 和骅芸1,2, 任思琪1,2, 唐书玥1,2, 赵金媛1,2, 潘志华1,2, 王靖1,2, 潘学标1,2, 胡琦1,2(
), 马雪晴1,2, 和骅芸1,2, 任思琪1,2, 唐书玥1,2, 赵金媛1,2, 潘志华1,2, 王靖1,2, 潘学标1,2, 胡琦1,2( )
)
- 1.中国农业大学资源与环境学院,北京 100193
2.中国气象局-中国农业大学农业应对气候变化联合实验室,北京 100193