Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (3): 524-535.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-03-0524
• Technical Reports • Previous Articles Next Articles
Verification and assessment of precipitation forecast based on global and regional numerical models in Gansu in flood season of 2020
CHEN Xiaoyan1( ), KONG Xiangwei1(
), KONG Xiangwei1( ), PENG Xiao1, LIU Xinwei1, WU Jing1, REN Shuyuan2
), PENG Xiao1, LIU Xinwei1, WU Jing1, REN Shuyuan2
- 1. Lanzhou Center Meteorological Observatory, Lanzhou 730020, China
2. Lanzhou Meteorological Bureau of Gansu Province, Lanzhou 730020, China
-
Received:2021-05-17Revised:2022-03-01Online:2022-06-30Published:2022-06-28 -
Contact:KONG Xiangwei
全球和区域数值模式在甘肃2020年汛期降水预报中的检验评估
陈晓燕1( ), 孔祥伟1(
), 孔祥伟1( ), 彭筱1, 刘新伟1, 吴晶1, 任淑媛2
), 彭筱1, 刘新伟1, 吴晶1, 任淑媛2
- 1.兰州中心气象台,甘肃 兰州 730020
2.甘肃省兰州市气象局,甘肃 兰州 730020
-
通讯作者:孔祥伟 -
作者简介:陈晓燕(1985—),女,高级工程师,主要从事数值天气预报研究.E-mail: hutcxy@163.com。 -
基金资助:甘肃省气象局气象科研项目(Zd2021-01);GRAPES数值预报系统发展专项“甘肃不同类型强降水的GRAPES预报产品检验评估”和甘肃省气象局创新团队(GSQXCXTD-2020-01)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
CHEN Xiaoyan, KONG Xiangwei, PENG Xiao, LIU Xinwei, WU Jing, REN Shuyuan. Verification and assessment of precipitation forecast based on global and regional numerical models in Gansu in flood season of 2020[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(3): 524-535.
陈晓燕, 孔祥伟, 彭筱, 刘新伟, 吴晶, 任淑媛. 全球和区域数值模式在甘肃2020年汛期降水预报中的检验评估[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(3): 524-535.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-03-0524
| 模式 | 水平分辨率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 全球模式 | ECMWF高分辨率模式 | 0.125°×0.125° |
| GRAPES_GFS模式 | 0.25°×0.25° | |
| NCEP_GFS模式 | 0.5°×0.5° | |
| 区域模式 | 华东区域数值预报系统(SMS-WARMS) | 9 km |
| GRAPES区域数值预报业务系统(GRAPES_3 km) | 0.03°×0.03° | |
| 西北区域区域模式(GRAPES_LZ10 km) | 0.1°×0.1° | |
| 西北区域快速更新循环预报系统(GRAPES_LZ3 km) | 0.03°×0.03° |
Tab.1 Introduction of seven operational models
| 模式 | 水平分辨率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 全球模式 | ECMWF高分辨率模式 | 0.125°×0.125° |
| GRAPES_GFS模式 | 0.25°×0.25° | |
| NCEP_GFS模式 | 0.5°×0.5° | |
| 区域模式 | 华东区域数值预报系统(SMS-WARMS) | 9 km |
| GRAPES区域数值预报业务系统(GRAPES_3 km) | 0.03°×0.03° | |
| 西北区域区域模式(GRAPES_LZ10 km) | 0.1°×0.1° | |
| 西北区域快速更新循环预报系统(GRAPES_LZ3 km) | 0.03°×0.03° |
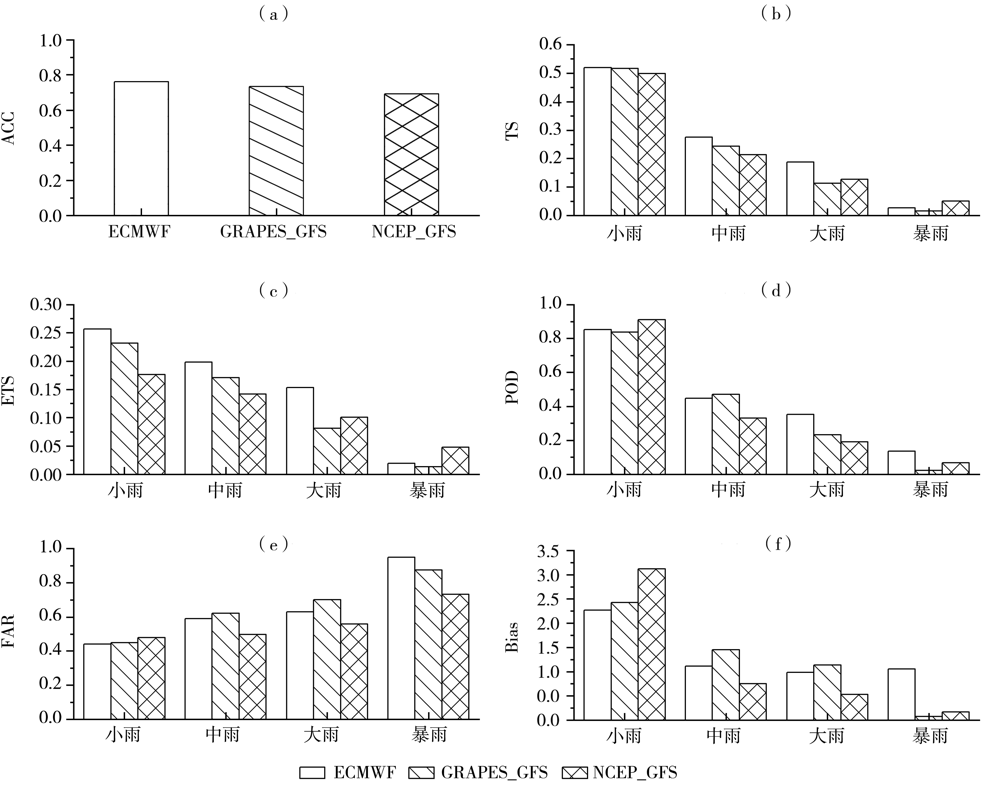
Fig.2 The accuracy of rain probability forecast and forecast scores of 24 h accumulated rainfall of global models from June to August 2020(a) ACC, (b) TS, (c) ETS, (d) POD, (e) FAR, (f) Bias
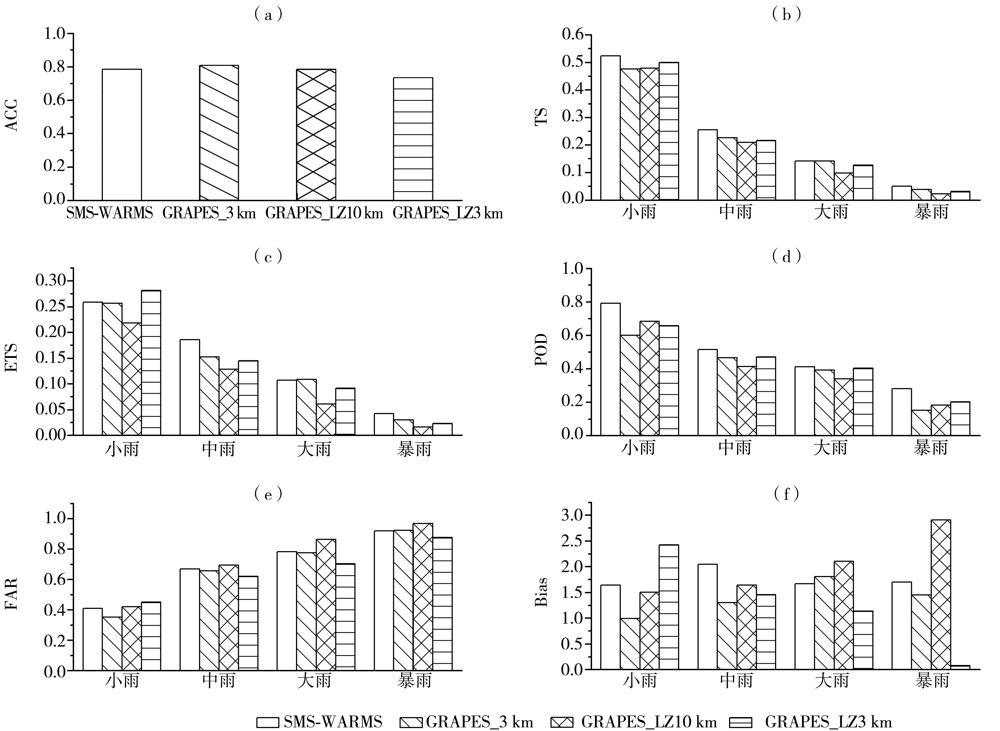
Fig.3 The accuracy of rain probability forecast and forecast scores of 24 h accumulated rainfall of regional models from June to August 2020(a) ACC, (b) TS, (c) ETS, (d) POD, (e) FAR, (f) Bias

Fig.4 The accuracy of rain probability forecast and forecast scores of 24 h accumulated rainfall of global models and regional models for 4 sub-high marginal precipitation processes in flood season of 2020(a,b) ACC,(c,d) TS,(e,f) ETS,(g,h) POD,(i,j) FAR,(k,l) Bias
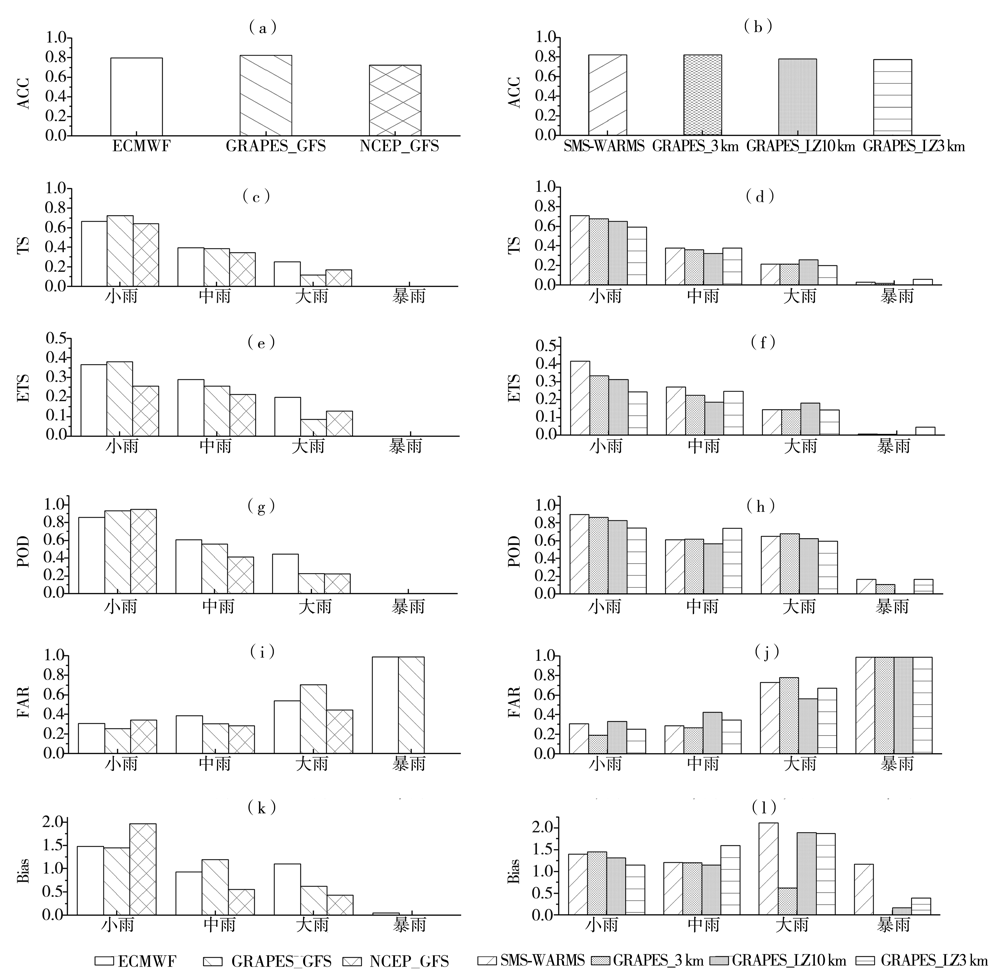
Fig.5 The accuracy of rain probability forecast and forecast scores of 24h accumulated rainfall of global models andregional models for 3 low-trough precipitation processes in flood season of 2020(a,b) ACC,(c,d) TS,(e,f) ETS,(g,h) POD,(i,j) FAR,(k,l) Bias
| 不同等级 降水 | 模式 | 面积比 | 质心距离/ km | 轴角差/ (°) | 50%分位强度 比率 | 90%分位强度 比率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中雨 | ECMWF | 1.46 | 22.84 | 8.87 | 0.90 | 1.05* |
| GRAPES_GFS | 1.67 | 29.40 | 6.99* | 0.93 | 0.74 | |
| NCEP_GFS | 1.43 | 21.45 | 8.88 | 0.81 | 0.80 | |
| SMS-WARMS | 1.40 | 26.47 | 10.62 | 1.13 | 1.57 | |
| GRAPES_3 km | 1.23 | 30.35 | 11.47 | 1.06 | 1.17 | |
| GRAPES_LZ10 km | 1.31 | 10.97* | 8.53 | 1.14 | 1.17 | |
| GRAPES_LZ3 km | 1.18* | 25.85 | 11.14 | 1.01* | 1.08 | |
| 大雨 | ECMWF | 1.30 | 16.16 | 5.92 | 1.11 | 1.34 |
| GRAPES_GFS | 1.39 | 24.77 | 29.19 | 0.86 | 0.67 | |
| NCEP_GFS | 1.07* | 26.00 | 11.56 | 0.96 | 0.90 | |
| SMS-WARMS | 1.83 | 12.02* | 5.11* | 1.26 | 1.60 | |
| GRAPES_3 km | 1.48 | 23.10 | 11.25 | 1.08 | 1.13 | |
| GRAPES_LZ10 km | 1.69 | 14.92 | 6.20 | 1.09 | 1.07 | |
| GRAPES_LZ3 km | 1.29 | 28.34 | 21.87 | 1.03* | 1.03* | |
| 暴雨 | ECMWF | 1.75 | 21.91 | 31.30 | 1.06 | 1.18 |
| GRAPES_GFS | 3.80 | 14.40* | 51.70 | 0.96 | 0.84 | |
| NCEP_GFS | 0.79* | 16.78 | 36.50 | 1.04 | 0.93 | |
| SMS-WARMS | 4.16 | 29.63 | 22.59* | 1.17 | 1.42 | |
| GRAPES_3 km | 4.45 | 33.35 | 52.60 | 1.03* | 1.06* | |
| GRAPES_LZ10 km | 5.54 | 36.03 | 33.00 | 1.10 | 1.12 | |
| GRAPES_LZ3 km | 48.00 | 36.47 | 52.00 | 1.11 | 1.15 | |
| 大暴雨 | ECMWF | 2.31 | 16.32 | 32.58* | 1.04* | 1.15 |
| GRAPES_GFS | — | — | — | — | — | |
| NCEP_GFS | 1.51* | 4.72* | 58.12 | 0.84 | 0.68 | |
| SMS-WARMS | 6.85 | 24.56 | 46.52 | 1.07 | 1.08* | |
| GRAPES_3 km | 2.44 | 16.35 | 40.73 | 0.93 | 0.93 | |
| GRAPES_LZ10 km | — | — | — | — | — | |
| GRAPES_LZ3 km | 0.07 | 7.05 | 56.03 | 0.89 | 0.68 |
Tab.2 The attribute values of matching objects of 24 h accumulated rainfall prediction based on global and regional models and observations for 4 sub-high marginal precipitation processes in flood season of 2020
| 不同等级 降水 | 模式 | 面积比 | 质心距离/ km | 轴角差/ (°) | 50%分位强度 比率 | 90%分位强度 比率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中雨 | ECMWF | 1.46 | 22.84 | 8.87 | 0.90 | 1.05* |
| GRAPES_GFS | 1.67 | 29.40 | 6.99* | 0.93 | 0.74 | |
| NCEP_GFS | 1.43 | 21.45 | 8.88 | 0.81 | 0.80 | |
| SMS-WARMS | 1.40 | 26.47 | 10.62 | 1.13 | 1.57 | |
| GRAPES_3 km | 1.23 | 30.35 | 11.47 | 1.06 | 1.17 | |
| GRAPES_LZ10 km | 1.31 | 10.97* | 8.53 | 1.14 | 1.17 | |
| GRAPES_LZ3 km | 1.18* | 25.85 | 11.14 | 1.01* | 1.08 | |
| 大雨 | ECMWF | 1.30 | 16.16 | 5.92 | 1.11 | 1.34 |
| GRAPES_GFS | 1.39 | 24.77 | 29.19 | 0.86 | 0.67 | |
| NCEP_GFS | 1.07* | 26.00 | 11.56 | 0.96 | 0.90 | |
| SMS-WARMS | 1.83 | 12.02* | 5.11* | 1.26 | 1.60 | |
| GRAPES_3 km | 1.48 | 23.10 | 11.25 | 1.08 | 1.13 | |
| GRAPES_LZ10 km | 1.69 | 14.92 | 6.20 | 1.09 | 1.07 | |
| GRAPES_LZ3 km | 1.29 | 28.34 | 21.87 | 1.03* | 1.03* | |
| 暴雨 | ECMWF | 1.75 | 21.91 | 31.30 | 1.06 | 1.18 |
| GRAPES_GFS | 3.80 | 14.40* | 51.70 | 0.96 | 0.84 | |
| NCEP_GFS | 0.79* | 16.78 | 36.50 | 1.04 | 0.93 | |
| SMS-WARMS | 4.16 | 29.63 | 22.59* | 1.17 | 1.42 | |
| GRAPES_3 km | 4.45 | 33.35 | 52.60 | 1.03* | 1.06* | |
| GRAPES_LZ10 km | 5.54 | 36.03 | 33.00 | 1.10 | 1.12 | |
| GRAPES_LZ3 km | 48.00 | 36.47 | 52.00 | 1.11 | 1.15 | |
| 大暴雨 | ECMWF | 2.31 | 16.32 | 32.58* | 1.04* | 1.15 |
| GRAPES_GFS | — | — | — | — | — | |
| NCEP_GFS | 1.51* | 4.72* | 58.12 | 0.84 | 0.68 | |
| SMS-WARMS | 6.85 | 24.56 | 46.52 | 1.07 | 1.08* | |
| GRAPES_3 km | 2.44 | 16.35 | 40.73 | 0.93 | 0.93 | |
| GRAPES_LZ10 km | — | — | — | — | — | |
| GRAPES_LZ3 km | 0.07 | 7.05 | 56.03 | 0.89 | 0.68 |
| 不同等级 降水 | 模式 | 面积比 | 质心距离/ km | 轴角差/ (°) | 50%分位强度 比率 | 90%分位强度 比率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中雨 | ECMWF | 1.35 | 36.79 | 9.62 | 0.91 | 0.98* |
| GRAPES_GFS | 1.68 | 70.00 | 16.17 | 0.96 | 1.06 | |
| NCEP_GFS | 1.07* | 38.61 | 24.78 | 0.87 | 0.88 | |
| SMS-WARMS | 1.32 | 19.10* | 10.52 | 1.15 | 1.52 | |
| GRAPES_3 km | 1.83 | 49.10 | 16.39 | 1.17 | 1.39 | |
| GRAPES_LZ10 km | 1.42 | 34.71 | 9.42* | 1.14 | 1.21 | |
| GRAPES_LZ3 km | 1.20 | 58.00 | 14.83 | 0.99* | 1.07 | |
| 大雨 | ECMWF | 1.00* | 23.77* | 11.93* | 0.91 | 0.75 |
| GRAPES_GFS | 1.36 | 84.56 | 26.49 | 0.98 | 0.78 | |
| NCEP_GFS | 0.51 | 57.69 | 14.11 | 0.90 | 0.65 | |
| SMS-WARMS | 2.76 | 27.23 | 12.35 | 1.12 | 1.25 | |
| GRAPES_3 km | 3.78 | 49.34 | 12.33 | 1.04 | 1.07 | |
| GRAPES_LZ10 km | 2.22 | 32.79 | 12.69 | 1.02 | 1.00* | |
| GRAPES_LZ3 km | 1.60 | 52.65 | 6.28 | 0.99* | 0.93 | |
| 暴雨 | ECMWF | 0.15 | 8.84* | 44.98 | 1.04 | 0.98* |
| GRAPES_GFS | — | — | — | — | — | |
| NCEP_GFS | — | — | — | — | — | |
| SMS-WARMS | 7.34 | 27.82 | 17.3 | 1.02* | 1.15 | |
| GRAPES_3 km | 4.73 | 26.91 | 6.03 | 0.98 | 1.07 | |
| GRAPES_LZ10 km | 3.29 | 55.93 | 5.43* | 0.97 | 0.88 | |
| GRAPES_LZ3 km | 0.90* | 45.26 | 29.34 | 0.85 | 0.84 |
Tab.3 The attribute values of matching objects of 24 h accumulated rainfall forecast based on global and regional models and observations for 3 low-trough precipitation processes in flood season of 2020
| 不同等级 降水 | 模式 | 面积比 | 质心距离/ km | 轴角差/ (°) | 50%分位强度 比率 | 90%分位强度 比率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中雨 | ECMWF | 1.35 | 36.79 | 9.62 | 0.91 | 0.98* |
| GRAPES_GFS | 1.68 | 70.00 | 16.17 | 0.96 | 1.06 | |
| NCEP_GFS | 1.07* | 38.61 | 24.78 | 0.87 | 0.88 | |
| SMS-WARMS | 1.32 | 19.10* | 10.52 | 1.15 | 1.52 | |
| GRAPES_3 km | 1.83 | 49.10 | 16.39 | 1.17 | 1.39 | |
| GRAPES_LZ10 km | 1.42 | 34.71 | 9.42* | 1.14 | 1.21 | |
| GRAPES_LZ3 km | 1.20 | 58.00 | 14.83 | 0.99* | 1.07 | |
| 大雨 | ECMWF | 1.00* | 23.77* | 11.93* | 0.91 | 0.75 |
| GRAPES_GFS | 1.36 | 84.56 | 26.49 | 0.98 | 0.78 | |
| NCEP_GFS | 0.51 | 57.69 | 14.11 | 0.90 | 0.65 | |
| SMS-WARMS | 2.76 | 27.23 | 12.35 | 1.12 | 1.25 | |
| GRAPES_3 km | 3.78 | 49.34 | 12.33 | 1.04 | 1.07 | |
| GRAPES_LZ10 km | 2.22 | 32.79 | 12.69 | 1.02 | 1.00* | |
| GRAPES_LZ3 km | 1.60 | 52.65 | 6.28 | 0.99* | 0.93 | |
| 暴雨 | ECMWF | 0.15 | 8.84* | 44.98 | 1.04 | 0.98* |
| GRAPES_GFS | — | — | — | — | — | |
| NCEP_GFS | — | — | — | — | — | |
| SMS-WARMS | 7.34 | 27.82 | 17.3 | 1.02* | 1.15 | |
| GRAPES_3 km | 4.73 | 26.91 | 6.03 | 0.98 | 1.07 | |
| GRAPES_LZ10 km | 3.29 | 55.93 | 5.43* | 0.97 | 0.88 | |
| GRAPES_LZ3 km | 0.90* | 45.26 | 29.34 | 0.85 | 0.84 |
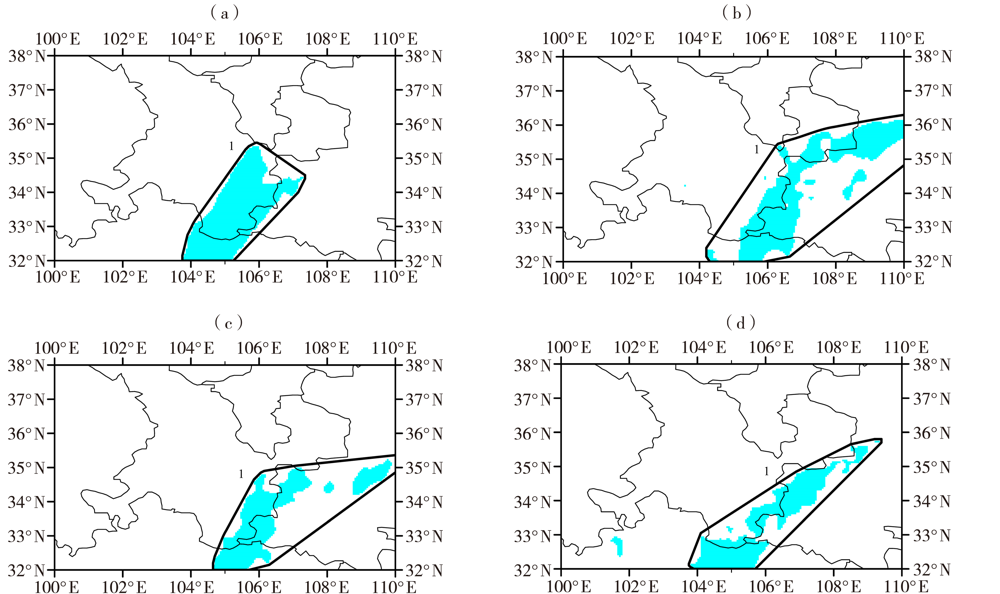
Fig.6 The matching objects of rainstorm identified by MODE method during the rainfall process on 15-17 August 2020 (The number “1” represents a successful target pair of observation and model forecast, the blue area is rainstorm area. the same as below) (a)ECMWF,(b)SMS-WARMS,(c)GRAPES_3 km,(d)observation
| 日期 | 模式 | 面积比 | 质心距离/ km | 轴角差/ (°) | 50%分位强度 比率 | 90%分位强度 比率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8月15—17日 | ECMWF | 1.18 | 16.10 | 12.46 | 1.22 | 1.93 |
| SMS-WARMS | 1.53 | 15.53 | 2.17 | 1.29 | 1.38 | |
| GRAPES_3 km | 1.02 | 11.19 | 7.83 | 1.13 | 1.06 | |
| 6月25—26日 | ECWMF | 0.16 | 8.84 | 44.98 | 1.04 | 0.98 |
| SMS-WARMS | 7.69 | 21.91 | 10.07 | 1.05 | 1.31 | |
| GRAPES_3 km | 7.26 | 42.24 | 2.64 | 1.00 | 1.13 |
Tab.4 The attribute values of matching objects of rainstorm prediction based on three models and observation for the two rainfall processes
| 日期 | 模式 | 面积比 | 质心距离/ km | 轴角差/ (°) | 50%分位强度 比率 | 90%分位强度 比率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8月15—17日 | ECMWF | 1.18 | 16.10 | 12.46 | 1.22 | 1.93 |
| SMS-WARMS | 1.53 | 15.53 | 2.17 | 1.29 | 1.38 | |
| GRAPES_3 km | 1.02 | 11.19 | 7.83 | 1.13 | 1.06 | |
| 6月25—26日 | ECWMF | 0.16 | 8.84 | 44.98 | 1.04 | 0.98 |
| SMS-WARMS | 7.69 | 21.91 | 10.07 | 1.05 | 1.31 | |
| GRAPES_3 km | 7.26 | 42.24 | 2.64 | 1.00 | 1.13 |
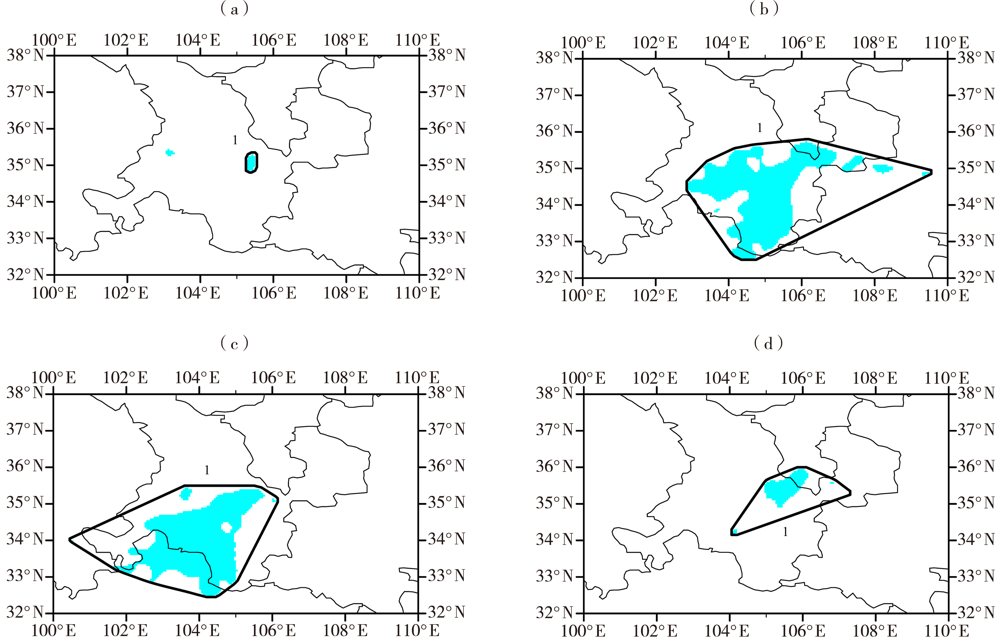
Fig.7 The matching objects of rainstorm identified by MODE method during the rainfall process on 25-26 June 2020 (a)ECMWF,(b)SMS-WARMS,(c)GRAPES_3 km,(d)observation
| [1] | 曾智华, 马雷鸣, 梁旭东,等. MM5数值预报引入GRAPES三维变分同化技术在上海地区的预报和检验[J]. 应用气象学报, 2004, 15(5):534-542. |
| [2] | 张寅, 罗亚丽, 管兆勇. NCEP全球预报系统在ARMSGP站点预报大气温度、湿度和云量的检验[J]. 大气科学, 2012, 36(1):170-184. |
| [3] | 王海燕, 田刚, 徐卫立,等. ECMWF模式在长江上游流域调度关键期的预报检验评估[J]. 干旱气象, 2017, 35(1):142-147. |
| [4] | 贾丽红, 马诺. ECMWF极端天气指数在新疆强降水预报中的检验评估[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 2019, 13(3):25-32. |
| [5] | 李博渊, 赵江伟, 庄晓翠. ECMWF细网格模式探空在阿勒泰地区短时强降水预报中的统计检验[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 2020, 14(3):61-67. |
| [6] | 徐姝, 熊明明, 王颖,等. 改进的ECMWF集合预报融合产品在海河流域的检验与分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 2018, 41(4):43-48. |
| [7] |
潘留杰, 张宏芳, 王建鹏,等. 日本高分辨率模式对中国降水预报能力的客观检验[J]. 高原气象, 2014, 33(2):483-494.
DOI |
| [8] | 张博, 李勇. 2013年6—8月T639、ECMWF及日本模式中期预报性能检验[J]. 气象, 2013, 39(11):1514-1520. |
| [9] | 牟欢. T639和德国模式对新疆地区大降水预报的检验[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 2013, 7(1):12-15. |
| [10] | 姜晓曼. 2014年夏季长江中下游地区降水预报检验[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2016. |
| [11] | 李璠, 王曼, 张瑾文. 华东区域数值预报降水产品在云南区域的检验评估[J]. 云南地理环境研究, 2020, 32(3):34-40. |
| [12] | 徐同, 李佳, 杨玉华,等. SMS-WARMS V2.0模式预报效果检验[J]. 气象, 2016, 42(10):1176-1183. |
| [13] | 陈超君, 李俊, 王明欢. 2013年华中区域中尺度业务数值预报的客观检验[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2014, 33(2):187-192. |
| [14] | 袁晨, 谢清霞, 刘彦华,等. GRAPES_MESO区域区域模式对贵州温度与降水预报的检验评估[J]. 中低纬山地气象, 2020, 44(6):56-59. |
| [15] |
张利红, 何光碧. GRAPES_Meso模式对2011年夏季青藏高原东部及周边区域的预报检验[J]. 高原气象, 2014, 33(1):14-25.
DOI |
| [16] | 孙婵, 徐国强. GRAPES_Meso区域模式在新疆沙漠地区的检验与评估[J]. 气象科技, 2017, 45(4):658-668. |
| [17] | 井立红, 高婧, 赵忠,等. 数值预报模式在新疆塔城地区降水预报中的检验[J]. 干旱气象, 2017, 35(1):134-141. |
| [18] | 张成军, 纪晓玲, 马金仁,等. 多种数值预报及其释用产品在宁夏天气预报业务中的检验评估[J]. 干旱气象, 2017, 35(1):148-156. |
| [19] |
GILLELAND E, AHIJEVYCH D, BROWN B G, et al. Intercomparison of spatial forecast verification methods[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 2009, 24(5):1416-1430.
DOI URL |
| [20] | 潘留杰, 薛春芳, 张宏芳,等. 三种高分辨率格点降水预报检验方法的对比[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2017, 22(1):45-58. |
| [21] | 于翡, 黄丽萍, 邓莲堂. GRAPES-MESO模式不同空间分辨率对中国夏季降水预报的影响分析[J]. 大气科学, 2018, 42(5):1146-1159. |
| [22] | 王彬雁, 陈朝平, 丛芳,等. MODE方法在西南区域模式降水预报检验中的应用[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 2020, 40(2):26-30. |
| [23] |
DAVIS C A, BROWN B G, BULLOCK R, et al. The method for object-based diagnostic evaluation(MODE) applied to numerical forecasts from the 2005 NSSL/SPC spring program[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 2009, 24(5): 1252-1267.
DOI URL |
| [24] | 白肇烨, 徐国昌, 孙学筠,等. 中国西北天气[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 1988:215-218. |
| [1] | LI Qiang, MIAO Aimei, WANG Hongxia, ZHANG Limei. Statistical characteristics and conceptual models of thunderstorm gales in Shanxi Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(3): 423-433. |
| [2] | SUN Mingyan, ZHANG Shuwen. Cases study of numerical simulation influences of turbulent vertical mixing intensity on local thermal convection in boundary layer [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(2): 290-300. |
| [3] | MA Yang, CUI Yang, ZHANG Wen, LI Xin. Projection of the future temperature changes of Yellow River Basin Ningxia section based on CMIP6 models [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(1): 43-53. |
| [4] | YIN Ninglu, LI Junlin, HONG Ye, GUO Yong, WANG Shigong. Influence of air temperature on number of respiratory diseases hospitalization in two counties of Liaoning Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(1): 132-142. |
| [5] | YUAN Kai, PANG Jing, LI Wujie, LI Ming. Application evaluation of deep learning models in radar echo nowcasting in Wuhan in flood season of 2021 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(1): 173-185. |
| [6] | YANG Lijie, CAO Yanchao, LIU Weicheng, XU Lili, ZHANG Hongfen, SUN Zizhu. Research on spatio-temporal distribution characteristics of short-term heavy rainfall and terrain influence in the Loess Plateau arid region of eastern Gansu [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 945-953. |
| [7] | MAO Wenqian, XIAO Xia, ZHANG Wenyu, MAO Lixin, WANG Kaiqiang, WANG Qi. Application analysis of wind profile radar detection mode combination [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 1092-1098. |
| [8] | XU Min, SHEN Fang, LIU Qiqi, LI Na, WANG Jie. Formation conditions and characteristics of heavy precipitation with quasi-linear MCSs [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(4): 596-604. |
| [9] | MA Simin, MU Jianhua, SHU Zhiliang, SUN Yanqiao, DENG Peiyun, ZHOU Nan. Topography sensitivity simulation test of a typical rainstorm process in Liupan Mountain region [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(3): 457-468. |
| [10] | XU Weiping, MENG Xiangxin, GU Weizong, BO Zhongkai. Relationship between extremely low temperature in spring in Shandong Province and North Atlantic SST in preceding winter [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(2): 202-211. |
| [11] | LI Tao, CHEN Jie, WANG Fang, HAN Rui. A correction algorithm of summer precipitation prediction based on neural network in China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(2): 308-316. |
| [12] | SHEN Xiaoyan, SHEN Yanling, QUAN Chen, DU Huali, YAN Yuqian. Verification and comparison of different methods to prediction performance of model products during the heavy precipitations in 2020 in Qinghai Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(2): 333-343. |
| [13] | ZOU Qian, CHEN Xiaomin, DENG Chengzhi, LONG Meixi. Characteristics of ground-based microwave radiometer profiles under different weather conditions in Chongqing [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(1): 114-124. |
| [14] | HAN Zifen, YAN Pengcheng, LI Yang, LÜ Qingquan, ZHANG Tiejun, BIAN Hongwei, WANG Yongzheng, ZHANG Li. Study on correction of solar radiation forecast in Hexi region of Gansu Province based on short-term historical data [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(1): 125-134. |
| [15] | ZHUANG Xiaocui, LI Boyuan, ZHAO Jiangwei, LI Jiangang, ZHANG Linmei. Water vapor source and transport characteristics of rainstorm processes in warm season on southern slope of the Tianshan Mountains [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(1): 30-40. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||