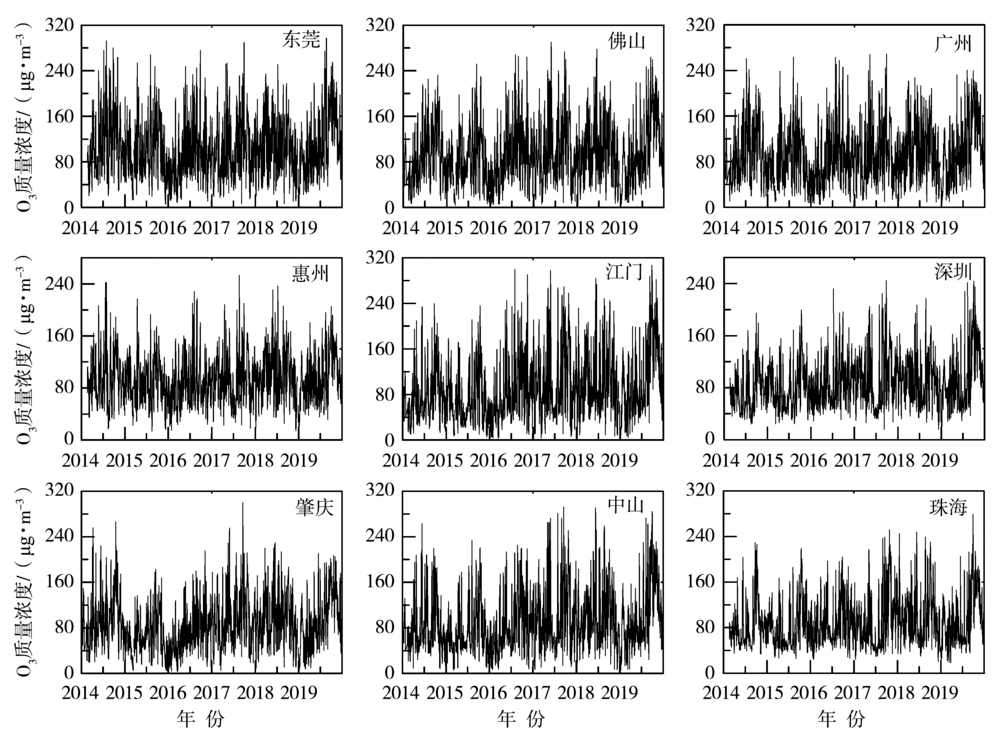
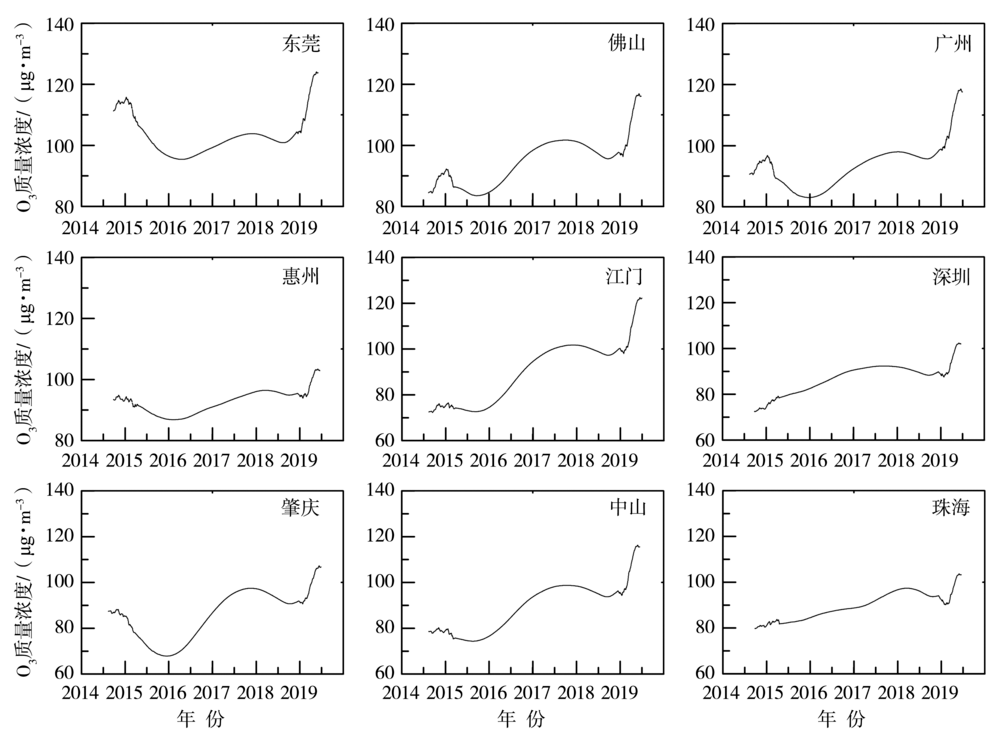
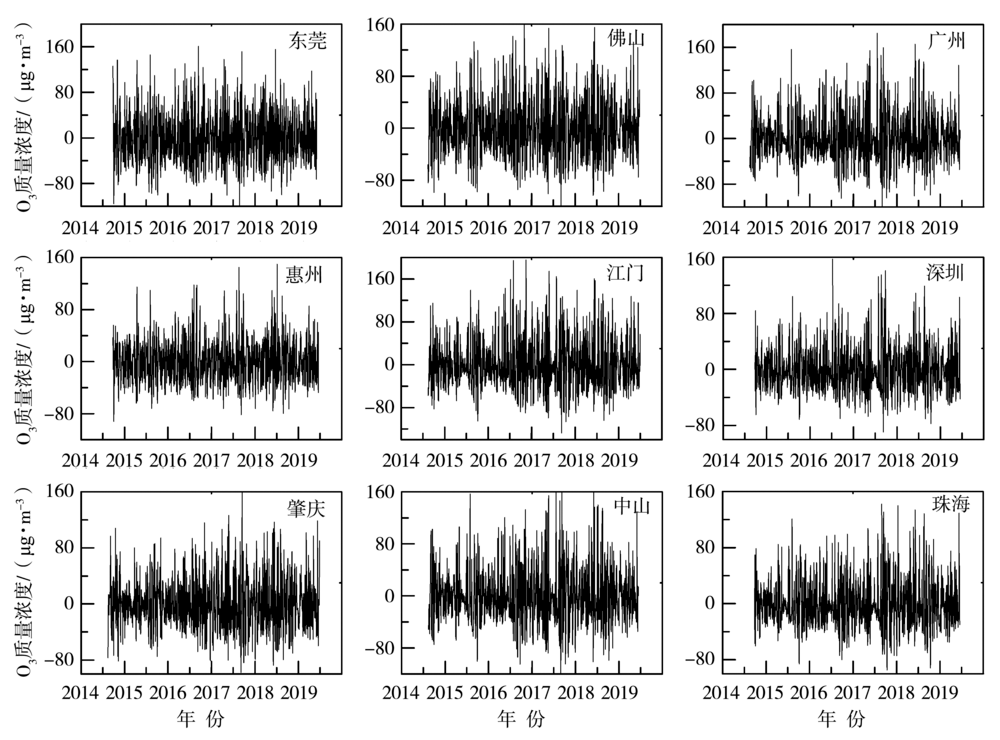
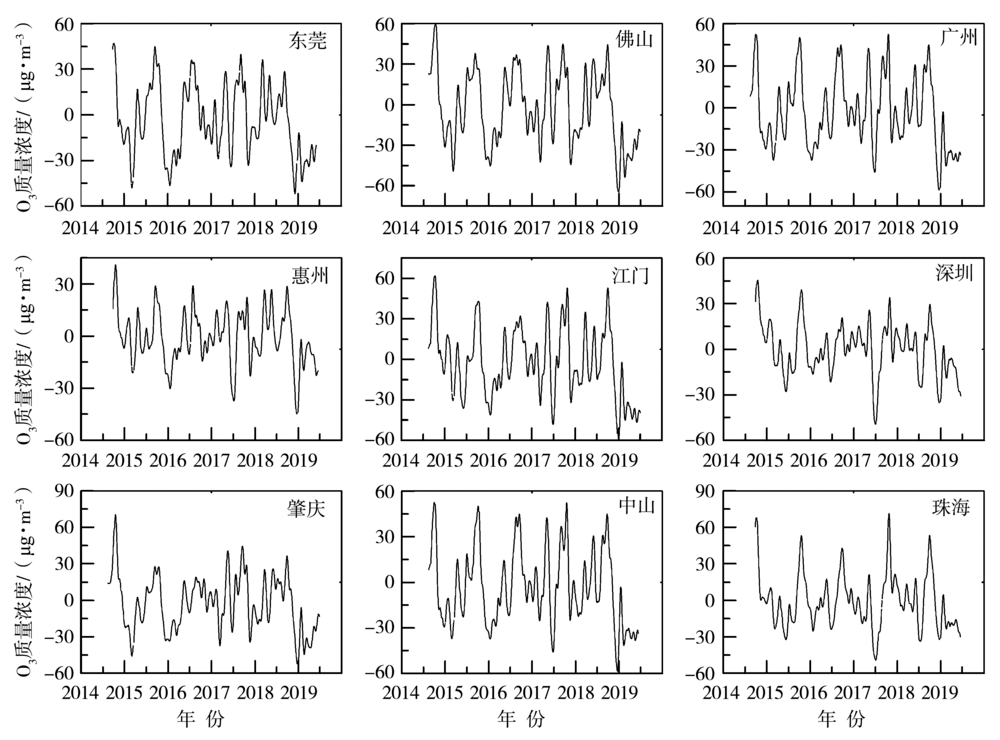
Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 266-274.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-02-0266
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Quantitative assessment of influence of meteorological conditions on ozone pollution in Guangzhou during 2014-2019
BU Qiaoli( ), YU Lefu, CHEN Chen
), YU Lefu, CHEN Chen
- Foshan Meteorological Bureau of Guangdong Province, Foshan 528000, Guangdong, China
-
Received:2021-04-19Revised:2022-03-18Online:2022-04-30Published:2022-05-10
广州2014—2019年气象条件对O3污染影响的定量评估
- 广东省佛山市气象局,广东 佛山 528000
-
作者简介:步巧利(1987— ),女,硕士,工程师,研究方向为环境气象. E-mail: buqiaoli@126.com。 -
基金资助:“龙卷等致灾雷暴大风精细化探测机理研究”院士专家工作站(2021002);“2DVD雨滴谱特征分析及对双偏振雷达定量降水估测的改进”(GRMC2020M28)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
BU Qiaoli, YU Lefu, CHEN Chen. Quantitative assessment of influence of meteorological conditions on ozone pollution in Guangzhou during 2014-2019[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(2): 266-274.
步巧利, 余乐福, 陈辰. 广州2014—2019年气象条件对O3污染影响的定量评估[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(2): 266-274.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-02-0266
| 站点 | O3质量浓度日均值序列各分量方差 | 方差贡献率 合计 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 长期 | 短期 | 季节 | ||
| 东莞 | 6 | 42 | 23 | 71 |
| 惠州 | 4 | 31 | 15 | 50 |
| 江门 | 13 | 45 | 25 | 83 |
| 佛山 | 8 | 42 | 27 | 77 |
| 广州 | 7 | 41 | 25 | 73 |
| 肇庆 | 11 | 34 | 22 | 67 |
| 珠海 | 6 | 34 | 22 | 62 |
| 深圳 | 6 | 30 | 17 | 53 |
| 中山 | 10 | 41 | 25 | 76 |
Tab.1
| 站点 | O3质量浓度日均值序列各分量方差 | 方差贡献率 合计 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 长期 | 短期 | 季节 | ||
| 东莞 | 6 | 42 | 23 | 71 |
| 惠州 | 4 | 31 | 15 | 50 |
| 江门 | 13 | 45 | 25 | 83 |
| 佛山 | 8 | 42 | 27 | 77 |
| 广州 | 7 | 41 | 25 | 73 |
| 肇庆 | 11 | 34 | 22 | 67 |
| 珠海 | 6 | 34 | 22 | 62 |
| 深圳 | 6 | 30 | 17 | 53 |
| 中山 | 10 | 41 | 25 | 76 |
| 站名 | 逐步回归方程 | 解释方差/% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 长期分量 | 佛山 | | 72 |
| 广州 | | 55 | |
| 短期分量 | 佛山 | | 45 |
| 广州 | | 19 | |
| 季节分量 | 佛山 | | 69 |
| 广州 | | 53 |
Tab.2 The stepwise regression equations for each component of daily mean mass concentration of O3 and their explained variance in Foshan and Guangzhou
| 站名 | 逐步回归方程 | 解释方差/% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 长期分量 | 佛山 | | 72 |
| 广州 | | 55 | |
| 短期分量 | 佛山 | | 45 |
| 广州 | | 19 | |
| 季节分量 | 佛山 | | 69 |
| 广州 | | 53 |
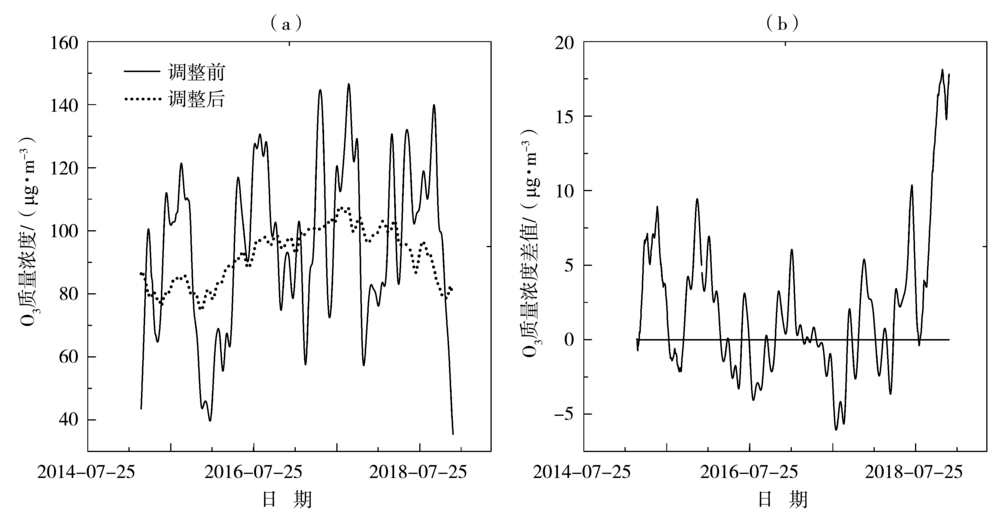
Fig.6 Variations of long-term components of O3 daily mean mass concentration before and after meteorological adjustment (a) and their difference change (b) in Guangzhou
| [1] | 张洁琼, 王雅倩, 高爽, 等. 不同时间尺度气象要素与空气污染关系的KZ滤波研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(10):64-74. |
| [2] |
SARAH C K, JENNIFER G M. Understanding ozone-meteorology correlation: a role for dry deposition[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2017, 44(6):2922-2931.
DOI URL |
| [3] | 吴宜航, 白鹤鸣, 师华定, 等. 气象条件对呼和浩特市空气质量变化的影响评估[J]. 干旱区研究, 2016, 33(2):292-298. |
| [4] | 翁佳烽, 梁晓媛, 邓开强, 等. 不同季节肇庆市PM2.5和O3污染特征及潜在源区分析[J]. 环境科学研究, 2021, 34(6):1306-1317. |
| [5] | 卢文, 王红磊, 朱彬. 等. 南京江北2014-2016年PM2.5质量浓度分布特征及气象和传输影响因素分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 2019, 39(4):1039-1048. |
| [6] | RAO S T, ZURBENKO I G. Detecting and tracking changes in ozone air quality[J]. Joural of the Air & Waste Management Association, 1994, 44(9):1089-1092. |
| [7] | BOTLAGUDURU V S V, KOMMALAPATI R R, HUQUE Z. Long-term meteorologically independent trend analysis of ozone air quality at an urban site in the greater Houston area[J]. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 2018, 68(10):1051-1064. |
| [8] |
AGUDELO-CASTANEDA D M, TEIXEIRA E C, PEREIRA F N. Time-series analysis of surface ozone and nitrogen oxides concentrations in an urban area at Brazil[J]. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 2014, 5(3):411-420.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
BOLETI E, HUEGLIN C, TAKAHAMA S. Ozone time scale decomposition and trend assessment from surface observations in Switzerland[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2018, 191:440-451.
DOI URL |
| [10] | SEO J, YOUN D, KIM J Y, et al. Extensive spatiotemporal analysis of surface ozone and related meteorological variables in South Korea for the period 1999-2010[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2014, 14(12):6395-6415. |
| [11] |
WISE E K, COMRIE A C. Meteorologically adjusted urban air quality trends in the Southwestern United States[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2005, 39(16):2969-2980.
DOI URL |
| [12] | 秦人洁, 张洁琼, 王雅倩, 等. 基于KZ滤波法的河北省PM2.5和O3浓度不同时间尺度分析研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2019, 39(3):821-831. |
| [13] | 余益军, 孟晓艳, 王振, 等. 京津冀地区城市臭氧污染趋势及原因探讨[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(1):106-114. |
| [14] | 符传博, 丹利, 佟金鹤. 2017年秋季海口市一次持续污染过程特征及成因分析[J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(4):1048-1058. |
| [15] |
HUANG Y Q, YAO T, FUNG J C H, et al. Application of air parcel residence time analysis for air pollution prevention and control policy in the Pearl River Delta Region[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 658:744-752.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
DENG T, WANG T J, WANG S Q, et al. Impact of typhon periphery on high ozone and high aerosol pollution in the Pearl River Delta Region[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 668:617-630.
DOI URL |
| [17] | 翁佳烽, 梁晓媛, 谭浩波, 等. 基于K-means聚类分析法的肇庆市干季PM2.5污染天气分型研究[J]. 环境科学学报研究, 2020, 40(2):373-387. |
| [18] | 步巧利, 甘泉, 黄先香, 等. 佛山市近地面O3变化特征与气象因素的关系[J]. 广东气象, 2020, 42(3):46-49. |
| [19] | 陈辰, 洪莹莹, 吴蒙, 等. 2019年佛山臭氧污染及污染气象条件变化[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(增2):16-22. |
| [20] | FLAUM J B, RAO S T, ZURBENKO I G. Moderating the influence of meteorological conditions on ambient ozone concentrations[J]. Air Repair, 1996, 46(1):35-46. |
| [21] | PAPANASTASIOU D K, MELAS D, BARTZANAS T, et al. Estimation of ozone trend in central Greece, based on meteorologically adjusted time series[J]. Environmental Modeling & Assessment, 2012, 17(4):353-361. |
| [22] | 环境保护部. 环境空气质量标准[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2012. |
| [23] | 高晋徽, 朱彬, 王东东, 等. 北京O3、NO2和SO2浓度变化及长/近距离输送的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 2012, 32(5):149-1159. |
| [24] |
MONKS P S. A review of the observations and origins of the spring ozone maximum[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2000, 34(21):3545-3561.
DOI URL |
| [25] | BU Q L, HONG Y Y, TAN H B, et al. The modulation of meteorological parameters on surface PM2.5 and O3 concentrations in Guangzhou, China[J/OL]. Aerosol and Air Quality Research, 2021, 21(1). https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2020.03.0084 |
| [1] | XIONG Xianping, SHEN Ruishan, SUO Chunnan, LI Erjie, ZHANG Wei. Analysis of relationship between ozone mass concentration and meteorological factors in Cangzhou of Hebei Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(1): 108-113. |
| [2] | WANG Dan, DAI Changming, LOU Panxing, WANG Jianpeng. Comparison Study on Test and Correction of Temperature Forecasts of ECMWF, GRAPES_Meso and SCMOC in Shaanxi [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(4): 697-708. |
| [3] | WU Huiqin, YANG Linhan, ZHAGN Zhongjie. Analysis on Forecast Effect of Daily Maximum Power Load Variation in Shijiazhuang Based on Three Models [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(4): 709-715. |
| [4] | YANG Jing, ZHU Haibin, LIU Jianjun, YAN Xiaoyu, NA Li, LIU Yulan. Study on the Effects of Meteorological Conditions on Ozone Mass Concentration near Surface in Yinchuan [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(2): 302-308. |
| [5] | YAN Xiaoyu, GOU Xiaohui, GONG Xiaoli, LIU Jianjun, NA Li, SU Zhansheng, LIU Yao, LI Xiaohong, WU Baoguo. Analysis of Ozone Pollution and Its Transport Paths in Ningxia [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(1): 119-129. |
| [6] | LIU Chuwei, LIAN Xinbo, HUANG Jianping. Research Review on the Spatio-temporal Distribution of Ozone Pollution and Its Causes in China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(03): 355-361. |
| [7] | YANG Yunling, HAO Jufei, YANG Lina, WANG Shaoming, ZHANG Jianbo. Analysis of Meteorological Conditions of a Continuous Ozone Pollution Process in Xingtai of Hebei Province#br# [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(03): 448-456. |
| [8] | LU Qian, FU Jiao, WANG Pengpeng, TIAN Jing, WANG Guohui. Temporal Distribution of Ozone Mass Concentration Near Surface and Their Relations with Weather Conditions in Shijiazhuang of Hebei Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(5): 836-843. |
| [9] | YANG Zhijie, LIU Yekun, HAN Li. Analysis of O3 Pollution Characteristics and Influencing Factors in Jining District of Ulanqab of Inner Mongolia#br# [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(4): 631-638. |
| [10] | DAI Yi, HE Na, FU Zongyu, KANG Yanyan, HAO Cui. Beijing Intelligent Grid Temperature Objective Prediction Method (BJTM) and Verification of Forecast Result [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(2): 339-344. |
| [11] | TAN Changrong1, GUO Xiaoning, CHEN Qi, LI Jinhai,YOU Sangjie, MA Xuelian, MA Yuancang, QI Caihong. Study on Surface Ozone Characteristics and Its Influencing Factors in Xining [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(1): 31-39. |
| [12] | YAN Xinyang, WANG Xiaoyong, DA Xuanfang,ZHAO Funian, NIU Ximei. Variation Characteristics of Expressway Pavement Temperature and Forecast Model in Mountainous Area of Gansu [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(5): 864-872. |
| [13] | LI Yang, ZHANG Jiankai, TIAN Wenshou, XIE Fei, SUO Chunnan. Impact of Dynamic Transmission and Surface Emission on Ozone Change in Troposphere over Beijing [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(2): 157-166. |
| [14] | . Characteristics of O3 Concentration near Surface Layer in Summer of Shanxi Province and Its Influence Factors [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(3): 398-. |
| [15] | SUO Chunnan1,2, TIAN Hongying1, YAN Chunwang2, LUO Jiali1. Influence of the Arctic Polar Vortex on Ozone Change in Stratosphere of the Arctic [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(2): 190-198. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||