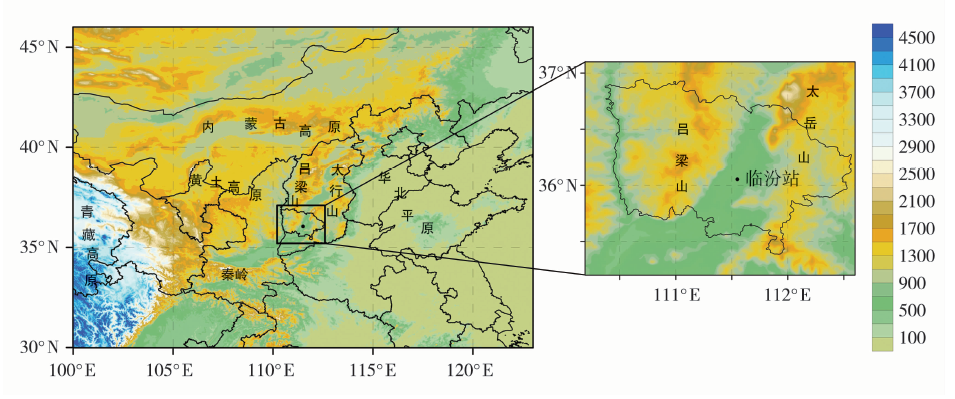
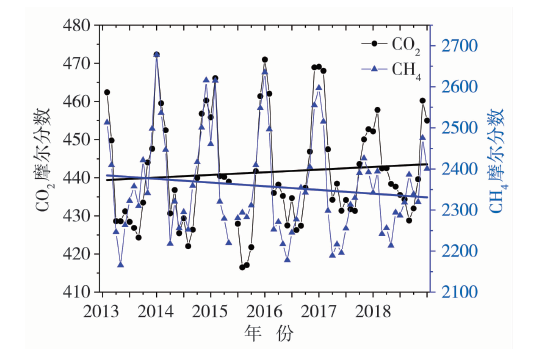
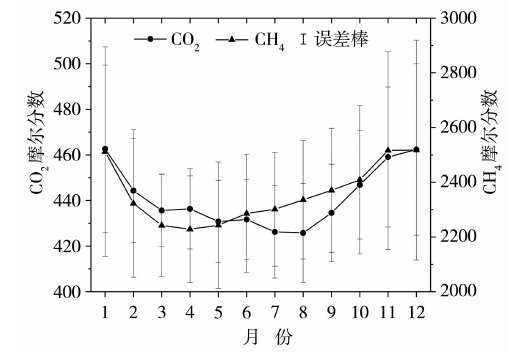
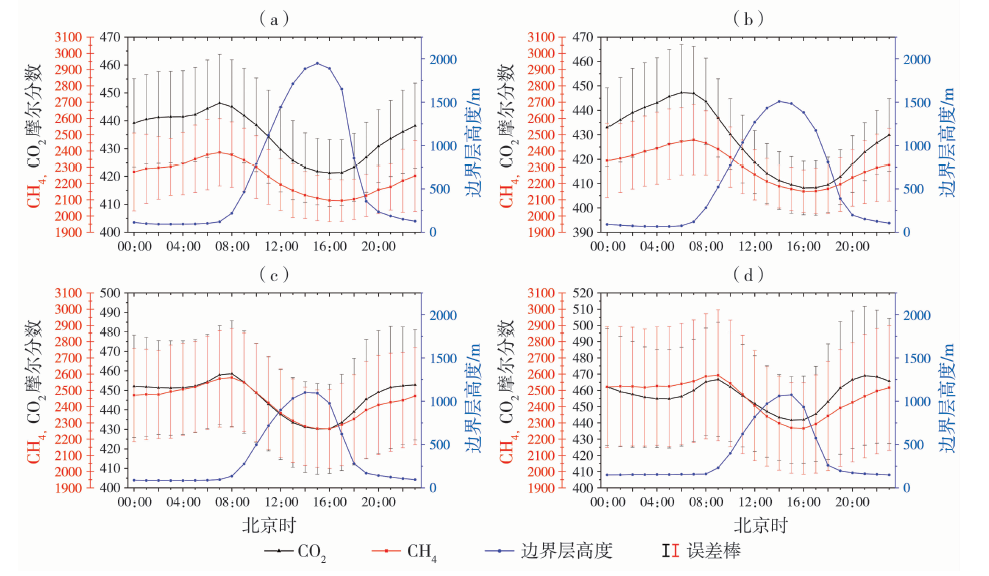
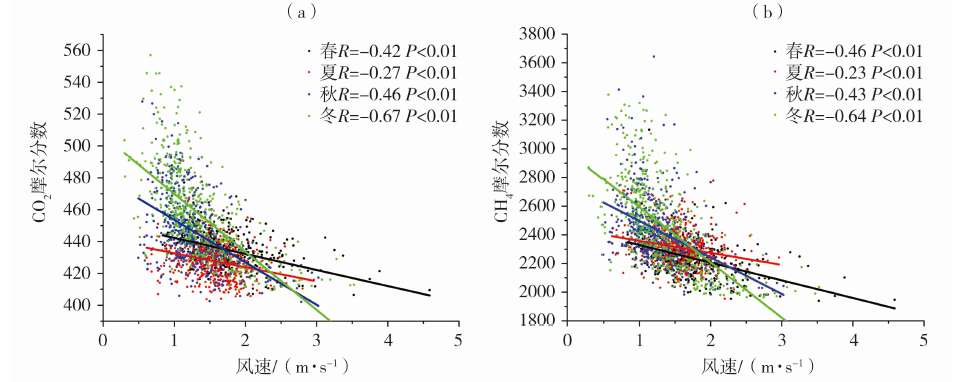
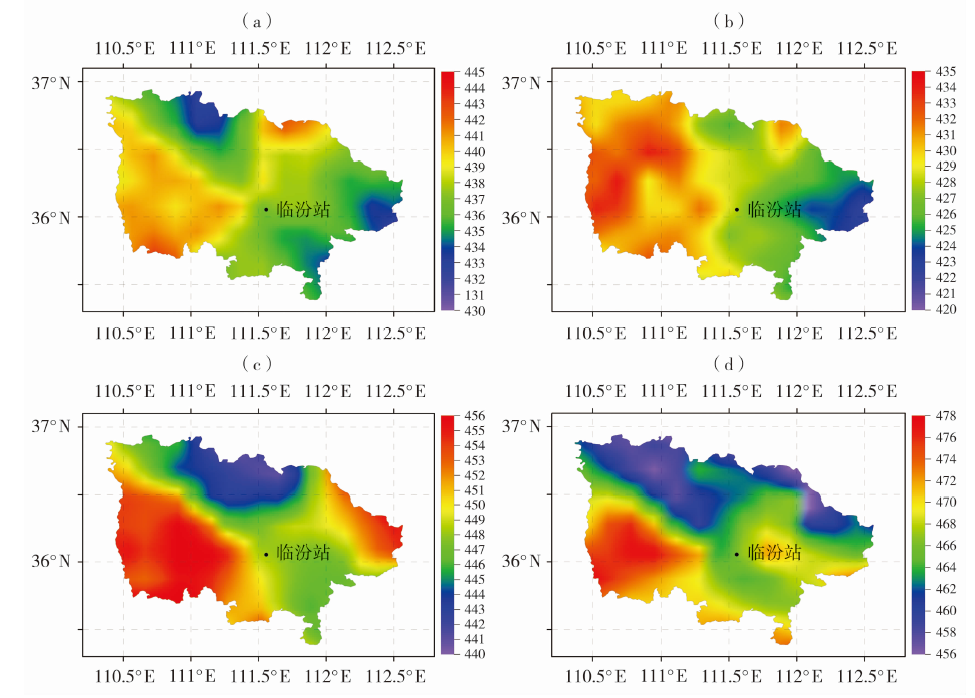
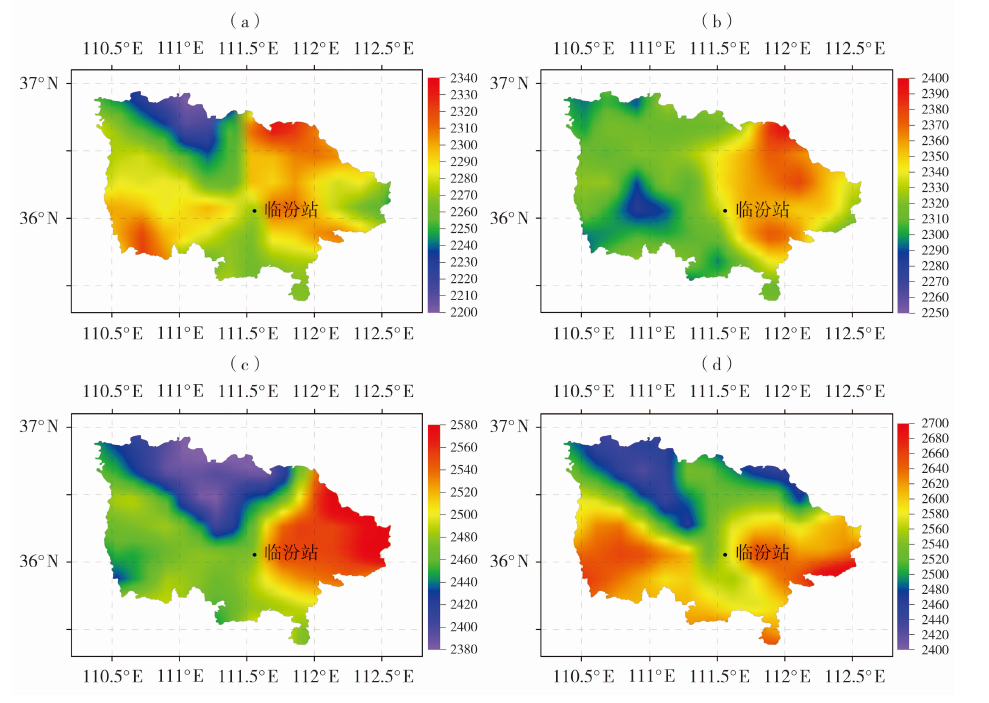
| [1] |
VINOGRADOVA A A, FEDOROVA E I, BELIKOV I B, et al. Temporal variations in carbon dioxide and methane concentrations under urban conditions[J]. Izvestiya Atmospheric and Oceanic Physics, 2007, 43(5):599-611.
DOI
URL
|
| [2] |
KEPPLER F, HAMILTON J T G, BRAßM, et al. Methane emissions from terrestrial plants under aerobic conditions[J]. Nature, 2006, 439:187-191.
DOI
URL
|
| [3] |
VAGHJIANI G L, RAVISHANKARA A R. New measurement of the rate coefficient for the reaction of OH with methane[J]. Nature, 1991, 350(6317):406-409.
DOI
URL
|
| [4] |
STOCKER T F, QIN D, PLATTNER G K, et al. Technical Summary, in: Climate Change 2013:The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013:13-16.
|
| [5] |
HUANG J P, YU H P, GUAN X D, et al. Accelerated dryland expansion under climate change[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2016, 6:166-171.
DOI
URL
|
| [6] |
中国气象局气候变化中心. 中国温室气体公报[R]. 北京: 中国气象局, 2019.
|
| [7] |
MAKAROVA M V, POBEROVSKII A V, YAGOVKINA S V, et al. Study of the formation of the methane field in the atmosphere over northwestern Russia[J]. Izvestiya Atmospheric and Oceanic Physics, 2006, 42(2):215-227.
DOI
URL
|
| [8] |
高娜, 孙健, 高睿娜, 等. 气候变化背景下宁夏冬季气温月尺度变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(1):38-45.
|
| [9] |
马浩, 刘昌杰, 钱奇峰, 等. 2018年5月浙江省极端高温气候特征及环流背景[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(6):909-919.
|
| [10] |
World Meteorological Organization. WMO global atmosphere watch (GAW) strategic plan: 2008-2015[R]. Geneva: WMO, 2007.
|
| [11] |
周凌晞, 汤洁, 张晓春, 等. 气相色谱法观测本底大气中的甲烷和二氧化碳[J]. 环境科学学报, 1998, 18(4):356-361.
|
| [12] |
周秀骥. 中国大气本底基准观象台进展总结报告(1994-2004)[M]. 北京: 气象科学出版社, 2005:18-19.
|
| [13] |
温玉璞, 汤洁, 邵志清, 等. 瓦里关山大气二氧化碳浓度变化及地表排放影响的研究[J]. 应用气象学报, 1997, 8(2):129-136.
|
| [14] |
方双喜, 周凌晞, 许林, 等. 我国4个WMO/GAW本底站大气CH4浓度及变化特征[J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(9):2917-2923.
|
| [15] |
HELFTER C, TREMPER A, ZAZZERI G, et al. Sources of greenhouse gases and carbon monoxide in central London (UK)[C]// EGU General Assembly, Vienna, Austria, 2015.
|
| [16] |
麦博儒, 邓雪娇, 安兴琴, 等. 基于卫星遥感的广东地区对流层二氧化碳时空变化特征[J]. 中国环境科学, 2014, 34(5):1098-1106.
|
| [17] |
赵引弟. 中国主要温室气体卫星柱浓度与人为排放估计值比较研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2014.
|
| [18] |
SHAN Y, GUAN D, ZHENG H. et al. China CO2 emission accounts 1997-2015[J]. Scientific Data, 2018, 5:170201.
DOI
URL
|
| [19] |
焦凡凡. 低碳经济下临汾市产业结构调整优化研究[D]. 临汾: 山西师范大学, 2018.
|
| [20] |
栾天. 黑龙江龙凤山区域大气本底站温室气体浓度特征及源汇研究[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2015.
|
| [21] |
LIU G, LIU J, TARASICK D W, et al. A global tropospheric ozone climatology from trajectory-mapped ozone soundings[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2013, 13(21):10 659-10 675.
|
| [22] |
DRAXLER R R, HESS G D. Description of the HYSPLIT 4 modelling system[R]. Maryland: NOAA, Air Resources Laboratory, 1997.
|
| [23] |
FANG S X, TANS P P, STEINBACHER M, et al. Comparison of the regional CO2 mole fraction filtering approaches at a WMO/GAW regional station in China[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2015, 8:5301-5313.
DOI
URL
|
| [24] |
NECKI J, SCHMIDT M, ROZANSKI K, et al. Six-year record of atmospheric carbon dioxide and methane at a high-altitude mountain site in Poland[J]. Tellus B: Chemical and Physical Meteorology, 2003, 55(2):94-104.
DOI
URL
|
| [25] |
WEI C, WANG M, FU Q, et al. Temporal characteristics of greenhouse gases (CO2 and CH4) in the megacity Shanghai, China: association with air pollutants and meteorological conditions[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2020, 235:104759.
DOI
URL
|
| [26] |
韦芬芬, 林惠娟, 曹舒娅, 等. 苏南地区CO2本底浓度及源汇特征[J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(3):975-982.
|
| [27] |
陈昆, 沈竞, 陈鲍发. 景德镇地区大气CO2浓度变化特征[J]. 气象与减灾研究, 2019, 42(2):113-118.
|
| [28] |
夏玲君, 刘立新. 北京上甸子站大气CH4数据筛分及变化特征[J]. 中国环境科学, 2017, 37(11):4044-4051.
|
| [29] |
刘彬, 李丹, 刘振宇, 等. 天津市区温室气体浓度变化特征分析[J]. 环境保护与循环经济, 2018, 38(2):53-56.
|
| [30] |
陈超, 杨乐, 徐鸿, 等. 杭州市主要温室气体浓度变化特征[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2014, 36(1):69-72.
|
| [31] |
徐宏辉, 浦静姣, 顾骏强, 等. 临安区域本底站大气甲烷浓度变化特征[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2012, 21(2):204-208.
|
| [32] |
SREENIVAS G, MAHESH P, SUBIN J, et al. Influence of Meteorology and interrelationship with greenhouse gases (CO2 and CH4) at a suburban site of India[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2016, 16(6):3953-3967.
|
| [33] |
王长科, 王跃思, 刘广仁. 北京城市大气CO2浓度变化特征及影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 2003, 24(4):13-17.
|
| [34] |
李邹, 方双喜, 和春荣, 等. 香格里拉本底站大气CO2浓度及变化特征初步研究[J]. 环境化学, 2012, 31(12):1996-2001.
|
| [35] |
STULL R B. An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology[M]. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1988:347-404.
|
| [36] |
MAHESH P, SHARMA N, DADHWAL V K, et al. Impact of land-sea breeze and rainfall on CO2 variations at a coastal station[J]. Journal of Earth Science and Climatic Change, 2014, 5(6):1000201.
|
| [37] |
NISHANTH T, PRASEED K M, SATHEESH, K M K, et al. Observational study of surface O3, NOx, CH4 and total NMHCs at Kannur, India[J]. Aerosol and Air Quality Research, 2014, 14(3):1074-1088.
DOI
URL
|
| [38] |
RAMACHANDRAN S, RAJESH T. A. Black carbon aerosol mass concentrations over Ahmedabad, an urban location in western India: comparison with urban sites in Asia, Europe, Canada, and the United States[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2007, 112:D06211.
|
| [39] |
韩燕, 刘保双, 张裕芬, 等. 临汾市地形气象特征及大气自净能力分析[J]. 南开大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 52(6):92-98.
|
 ), ZHU Lingyun(
), ZHU Lingyun( ), YAN Shiming, PEI Kunning, ZHANG Fengsheng, WANG Shumin, CHENG Pengwei
), YAN Shiming, PEI Kunning, ZHANG Fengsheng, WANG Shumin, CHENG Pengwei
 ), 朱凌云(
), 朱凌云( ), 闫世明, 裴坤宁, 张逢生, 王淑敏, 成鹏伟
), 闫世明, 裴坤宁, 张逢生, 王淑敏, 成鹏伟