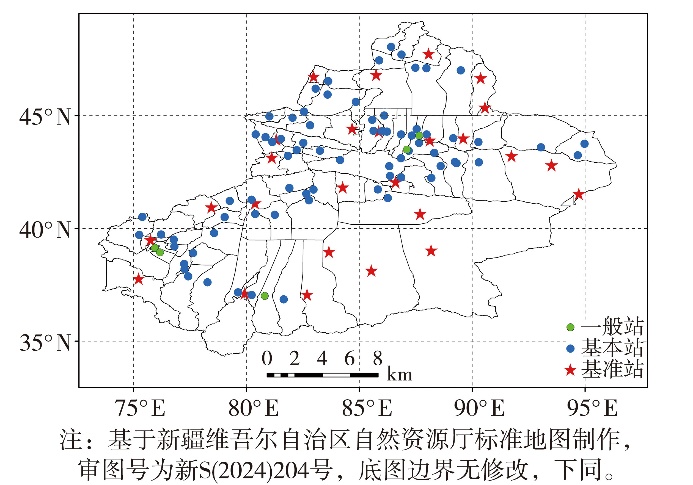
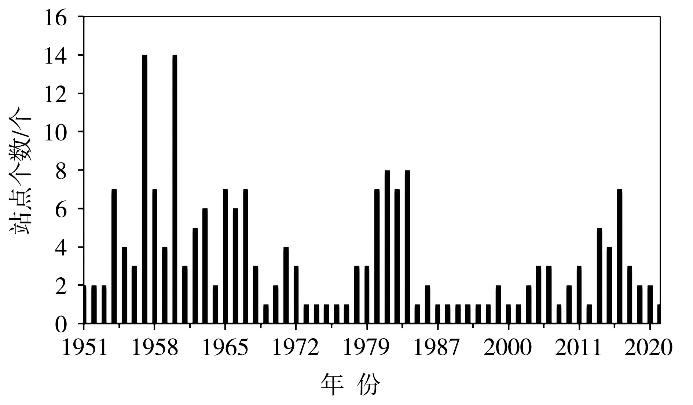
Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (3): 394-402.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-03-0394
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Homogeneity test of extreme temperature in Xinjiang and analysis of its temporal and spatial characteristics
LIU Weiping1,2( ), CAO Lijuan2(
), CAO Lijuan2( ), ZHANG Pu1, LI Zhen3, YUAN Fang2, FEI Ye2, WANG Qiwen1, LI Qinglei2
), ZHANG Pu1, LI Zhen3, YUAN Fang2, FEI Ye2, WANG Qiwen1, LI Qinglei2
- 1. Xinjiang Meteorological Information Center, Urumqi 830002, China
2. National Meteorological Information Center, Beijing 100081, China
3. Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100029, China
-
Received:2024-06-01Revised:2024-08-22Online:2025-06-30Published:2025-07-12
新疆极端气温均一性检验及变化趋势时空特征
刘卫平1,2( ), 曹丽娟2(
), 曹丽娟2( ), 张璞1, 李珍3, 远芳2, 费烨2, 王琪雯1, 李庆雷2
), 张璞1, 李珍3, 远芳2, 费烨2, 王琪雯1, 李庆雷2
- 1.新疆气象信息中心,新疆 乌鲁木齐 830002
2.国家气象信息中心,北京 100081
3.中国科学院大气物理研究所,北京 100029
-
通讯作者:曹丽娟 -
作者简介:刘卫平(1981—),女,高级工程师,主要从事气候资料处理与分析研究。E-mail:liuweiping121@126.com。 -
基金资助:中国气象局创新发展专项“新疆地区气温极值均一化气候数据产品和极端低温事件专题产品研制(CXFZ2024J040)”;新疆气象科技发展基金重点项目“中亚基础气象数据产品研发及其应用(ZD202304)”和国家自然科学基金项目(42475182)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LIU Weiping, CAO Lijuan, ZHANG Pu, LI Zhen, YUAN Fang, FEI Ye, WANG Qiwen, LI Qinglei. Homogeneity test of extreme temperature in Xinjiang and analysis of its temporal and spatial characteristics[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(3): 394-402.
刘卫平, 曹丽娟, 张璞, 李珍, 远芳, 费烨, 王琪雯, 李庆雷. 新疆极端气温均一性检验及变化趋势时空特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(3): 394-402.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-03-0394
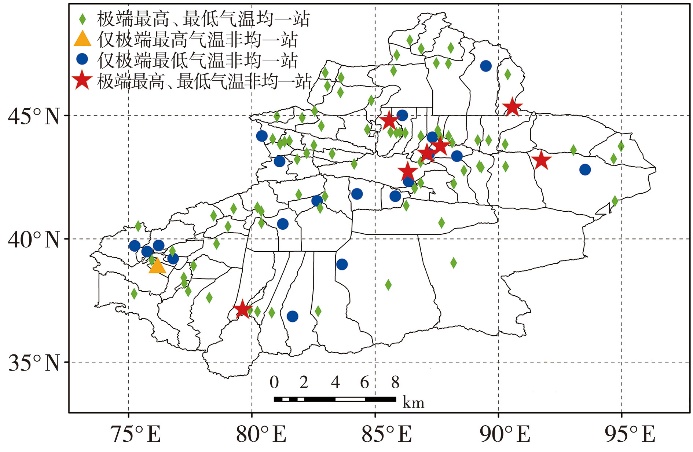
Fig.3 Spatial distribution of homogeneous and inhomogeneous stations for monthly extreme maximum and minimum temperature series in Xinjiang from 1951 to 2022
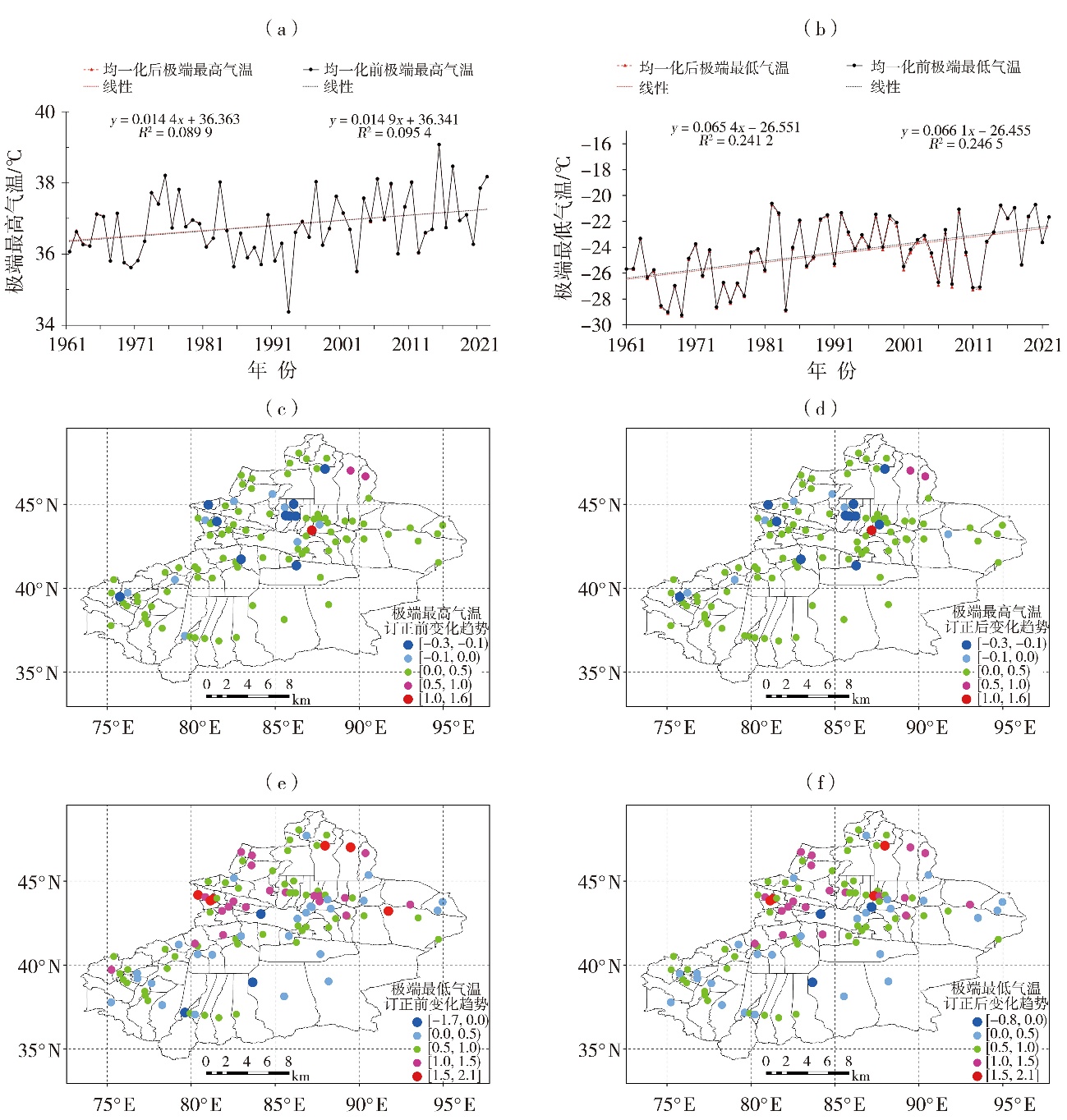
Fig.4 The annual extreme maximum (a) and minimum (b) temperature series before and after correction of 105 stations in Xinjiang from 1961 to 2022, as well as the spatial distribution of the trends (Unit: ℃·(10 a)-1) of annual extreme maximum (c, d) and minimum (e, f) temperatures before (c, e) and after (d, f) correction

Fig.5 The annual mean extreme maximum (a, c) and extreme minimum (b, d) temperature series at Moyu (a), Fuyun (b), Shisanjianfang (c), and Tazhong (d) stations
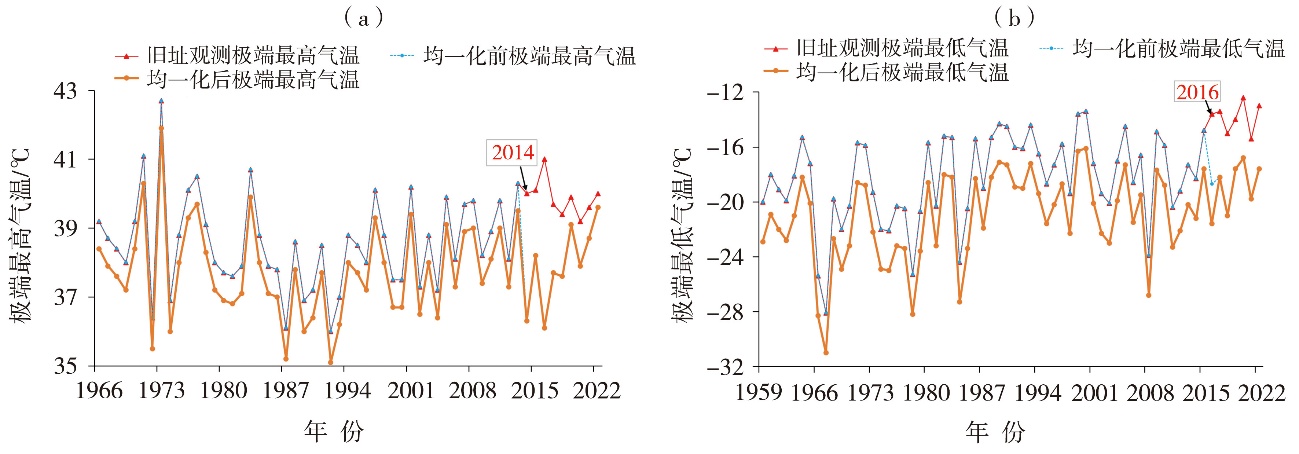
Fig.6 The parallel observation series of annual extreme maximum temperature at the old site of Moyu Station (a) and annual extreme minimum temperature at Korla Station (b), as well as the observation series of them before and after homogenization at the new sites
| [1] | 曹丽娟, 严中伟, 2011. 地面气候资料均一性研究进展[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 7(2):129-135. |
| [2] | 陈颖, 贾孜拉·拜山, 邵伟玲, 等, 2022. 增暖背景下北极涛动对新疆冬季平均气温的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 10(2):195-201. |
| [3] |
丁一汇, 柳艳菊, 徐影, 等, 2023. 全球气候变化的区域响应:中国西北地区气候“暖湿化”趋势、成因及预估研究进展与展望[J]. 地球科学进展, 38(6):551-562.
DOI |
| [4] | 郝增超, 陈阳, 2024. 地球系统视角下的多圈层复合极端事件研究进展与展望[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 54(2):360-393. |
| [5] | 孔婷, 胡义成, 刘卫平, 等, 2021. 北疆气象站迁址气温均一性检验与订正[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 15(5):116-122 |
| [6] | 李景林, 张山清, 普宗朝, 等, 2013. 近50 a新疆气温精细化时空变化分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 36(2):228-237. |
| [7] | 李庆祥, 2016. 我国气候资料均一性研究现状与展望[J]. 气象科技进展, 6(3):67-74. |
| [8] | 李庆祥, MENNE M J, WILLIAMS Jr C N, 等, 2005. 利用多模式对中国气温序列中不连续点的检测[J]. 气候与环境研究, 10(4):736-742. |
| [9] | 刘卫平, 古丽格娜, 王秋香, 等, 2020. 库尔勒城市化对气象要素的影响分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 14(1):89-94. |
| [10] |
吕婷, 武胜利, 葛欢欢, 等, 2020. 1962—2013年新疆阿勒泰极端气温时空变化特征[J]. 冰川冻土, 42(3):745-755.
DOI |
| [11] | 毛炜峄, 南庆红, 史红政, 2008. 新疆气候变化特征及气候分区方法研究[J]. 气象, 34(10):67-73. |
| [12] | 普宗朝, 张山清, 李景林, 等, 2014. 1961—2010年新疆不同保证率极端最低气温变化分析[J]. 中国农业气象, 35(1):10-16. |
| [13] | 曲姝霖, 仝纪龙, 唐睿, 等, 2017. 西北地区极端高温变化及其对气候变暖停滞的响应[J]. 气象与环境学报, 33(4):78-85. |
| [14] | 施雅风, 沈永平, 李栋梁, 等, 2003. 中国西北气候由暖干向暖湿转型的特征和趋势探讨[J]. 第四纪研究, 23(2):152-164. |
| [15] | 唐国利, 2020. 气候序列均一化研究与应用[M]. 北京: 气象出版社:10-50. |
| [16] | 王姣妍, 2023. 新疆气候暖湿化背景下干旱分布与演变特征[J]. 干旱环境监测, 37(1): 15-21. |
| [17] | 王秋香, 古丽格娜, 刘叶, 等, 2018. 阿克苏长序列气候资料分析及其均一性研究[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 12(1):7-14. |
| [18] | 吴莹莹, 刘旭阳, 王振亭, 2022. 巴丹吉林沙漠腹地沙尘事件对近地表气温和太阳总辐射的影响[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 16(2):82-90. |
| [19] |
许婷婷, 杨霞, 周鸿奎, 2022. 1981—2019年新疆区域性高温天气过程时空特征及其环流分型[J]. 干旱气象, 40(2):212-221.
DOI |
| [20] | 严中伟, 丁一汇, 翟盘茂, 2020. 近百年中国气候变暖趋势之再评估[J]. 气象学报, 78(3): 370-378. |
| [21] | 杨霞, 赵逸舟, 李圆圆, 等, 2009. 乌鲁木齐极端天气事件及其与区域气候变化的联系[J]. 干旱区地理, 32(6):867-873. |
| [22] | 余君, 赵美艳, 刘霄, 等, 2014. 重庆地区降水序列的均一性检验及其对气候变化的影响[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 34(2):68-71. |
| [23] | 张林梅, 黄阿丽, 谢秀琴, 等, 2013. 新疆阿勒泰地区冬季极端低温事件特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 31(1):89-94. |
| [24] |
张强, 杨金虎, 马鹏里, 等, 2023. 西北地区气候暖湿化增强东扩特征及其形成机制与重要环境影响[J]. 干旱气象, 41(3):351-358.
DOI |
| [25] |
张延伟, 葛全胜, 姜逢清, 等, 2016. 北疆地区1961—2010年极端气温事件变化特征[J]. 地理科学, 36(2):296-302.
DOI |
| [26] | 张志高, 苗运玲, 邱双娟, 等, 2019. 1951—2016年新疆哈密极端气温变化研究[J]. 新疆大学学报:自然科学版, 36(1):89-97. |
| [27] | 周波涛, 钱进, 2021. IPCC AR6报告解读:极端天气气候事件变化[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 17(6):713-718. |
| [28] | 周昊楠, 王秋香, 华烨, 2012. 乌鲁木齐逐月气温资料均一性检验和订正[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 6(1):27-30. |
| [29] | ALEXANDERSSON H, 1986. A homogeneity test applied to precipitation data[J]. Journal of Climatology, 6(6): 661-675. |
| [30] | CAO L J, ZHU Y N, TANG G L, et al, 2016. Climatic warming in China according to a homogenized data set from 2419 stations[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 36(13): 4 384-4 392. |
| [31] | LI Z, YAN Z W, CAO L J, et al, 2018. Further-adjusted long-term temperature series in China based on MASH[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 35(8): 909-917. |
| [32] | MENNE M J, WILLIAMS C N, 2009. Homogenization of temperature series via pairwise comparisons[J]. Journal of Climate, 22(7):1700-1 717. |
| [33] | SZENTIMREY T, 1999. Multiple analysis of series for homogenization (MASH)[C]// Proceeding Second Seminar for Homogenization of surface climatological data, Budapest: WMO, WCDMP-No. 41, 27-46. |
| [34] | TORETI A, KUGLITSCH F G, XOPLAKI E, et al, 2010. A novel method for the homogenization of daily temperature series and its relevance for climate change analysis[J]. Journal of Climate, 23(19): 5 325-5 331. |
| [35] | VINCENT L A, WANG X L, MILEWSKA E J, et al, 2012. A second generation of homogenized Canadian monthly surface air temperature for climate trend analysis[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 117(D18): 2012 JD017859. DOI:10.1029/2012D017859. |
| [36] | WANG X L, 2008a. Accounting for autocorrelation in detecting mean shifts in climate data series using the penalized maximal t or F test[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 47(9): 2 423-2 444. |
| [37] | WANG X L, 2008b. Penalized maximal F test for detecting undocumented mean shift without trend change[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 25(3): 368-384. |
| [38] | WANG X L, WEN Q H, WU Y H, 2007. Penalized maximal t test for detecting undocumented mean change in climate data series[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 46(6): 916-931. |
| [39] | WANG X L, CHEN H F, WU Y H, et al, 2010. New techniques for the detection and adjustment of shifts in daily precipitation data series[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 49(12): 2 416-2 436. |
| [40] | XU W H, LI Q X, WANG X L, et al, 2013. Homogenization of Chinese daily surface air temperatures and analysis of trends in the extreme temperature indices[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 118(17): 9 708-9 720. |
| [1] | MAVLAN Kader, LIU Xinhua, LI Yunxiang, GUAN Wenjuan. Analysis of basic characteristics of low-level wind shear in the arid regions of northwest China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(3): 347-356. |
| [2] | LIU Lei, LI Luan, ZHANG Li, SUN Dabing, ZHANG Xiaoyi. Construction of temperature series and its decadal characteristics from 1880 to 2020 in Wuhu of Anhui Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(5): 831-839. |
| [3] | CHEN Ying, JIAZILA Baishan, SHAO Weiling, LIU Jing. Influence of Arctic Oscillation on winter temperature in Xinjiang under climate warming background [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(2): 195-201. |
| [4] | YANG Xia, XU Tingting, ZHANG Linmei, HUA Ye, ZHOU Hongkui. Characteristics and differences of rainstorm in the southern Xinjiang during warm season under different climatic backgrounds [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(2): 222-233. |
| [5] | YANG Tao, YANG Lianmei, ZHANG Yunhui, ZHUANG Xiaocui, HUANG Yan. Circulation Configuration of Synoptic System and Radar Echo Characteristics of Shorttime Heavy Rainfall in Xinjiang [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(4): 631-640. |
| [6] | ZHOU Yaman, SUN Di, ZHAO Yong, LI Anbei, GUO Yulin. Characteristics of Wide-range Extreme Precipitation in Summer and Its Circulation Anomalies in Northern Xinjiang#br# [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(2): 215-224. |
| [7] | WEI Yanying, GONG Meiling, LI Haihua. Spatial-temporal distribution and influence of disastrous rainstorm in southern Xinjiang during 2010-2019 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(06): 930-938. |
| [8] | ZHU Hualiang, HUA Liansheng, WEN Huayang, PANG Wenjing, LIANG Li, KONG Qinqin. Homogeneity Analysis of Artificial Thunderstorm Days and Thunderstorm Days Calculated Using the Data of ADTD System [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(6): 1016-1022. |
| [9] | Nurbiye Tunyaz, ZHANG Chao, LI Zewei, SUN Chengyun, HUANG Yan. Characteristics of Four Rainstorm Processes in the West of Southern Xinjiang in August 2016 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(2): 301-311. |
| [10] | PENG Dongmei, CHEN Pengxiang, ZHANG Xu. Estimation of Surface Solar Total Radiation in Xinjiang Based on Satellite Remote Sensing Data [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(2): 322-330. |
| [11] | NURBIYE Tunyaz1,2, REZVANGUL Zebibulla2, MENG Fanxue3, LI Zewei2. Analysis on Forecasting of a Winter Gale in West of Southern Xinjiang [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(6): 1003-. |
| [12] | ZHANG Liancheng1, HU Liequn2, LI Shuai1, WANG Yan3. Comparison of Two Temperature Interpolation Methods in Xinjiang Based on GIS [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(2): 330-336. |
| [13] | SHA Biti, MAI Maiti, HUAN Lexi, HA Bulahati, MU Lati,GENG Yan, FENG Liye, CHEN Liang. Climate Feature and Dry-wet Area Change in Urumqi Region of Xinjiang During 1961-2014 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2016, 34(3): 448-455. |
| [14] | LI Ruqi, LI Jiangang, TANG Ye, LI Anbei, WANG Jiang. Caused by Central Asian Vortex in the West of South Xinjiang [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2016, 34(2): 297-304. |
| [15] | ZHUANG Xiaocui, QIN Jiaxiu, LI Boyuan. Mesoscale Characteristics of a Snowstorm in Western Xinjiang in 2014 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2016, 34(2): 326-334. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||