Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (4): 576-587.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2024)-04-0576
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Spatial-temporal distribution and meteorological conditions of thunderstorm gales in Shaanxi
JING Yu1( ), CHEN Chuang2, ZHAO Qiang1, LIU Juju1
), CHEN Chuang2, ZHAO Qiang1, LIU Juju1
- 1. Shaanxi Meteorological Observatory, Xi’an 710014, China
2. Shaanxi Institute of Meteorological Sciences, Xi’an 710016, China
-
Received:2023-05-10Revised:2023-07-17Online:2024-08-31Published:2024-09-13
陕西雷暴大风时空分布和气象条件分析
- 1.陕西省气象台,陕西 西安 710014
2.陕西省气象科学研究所,陕西 西安 710016
-
作者简介:井宇(1985—),女,陕西米脂人,高级工程师,主要从事短临天气预报技术研究。E-mail: jingyu.1128@163.com。 -
基金资助:陕西省自然科学基础研究计划项目(2023-JC-QN-0367)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
JING Yu, CHEN Chuang, ZHAO Qiang, LIU Juju. Spatial-temporal distribution and meteorological conditions of thunderstorm gales in Shaanxi[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(4): 576-587.
井宇, 陈闯, 赵强, 刘菊菊. 陕西雷暴大风时空分布和气象条件分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(4): 576-587.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2024)-04-0576
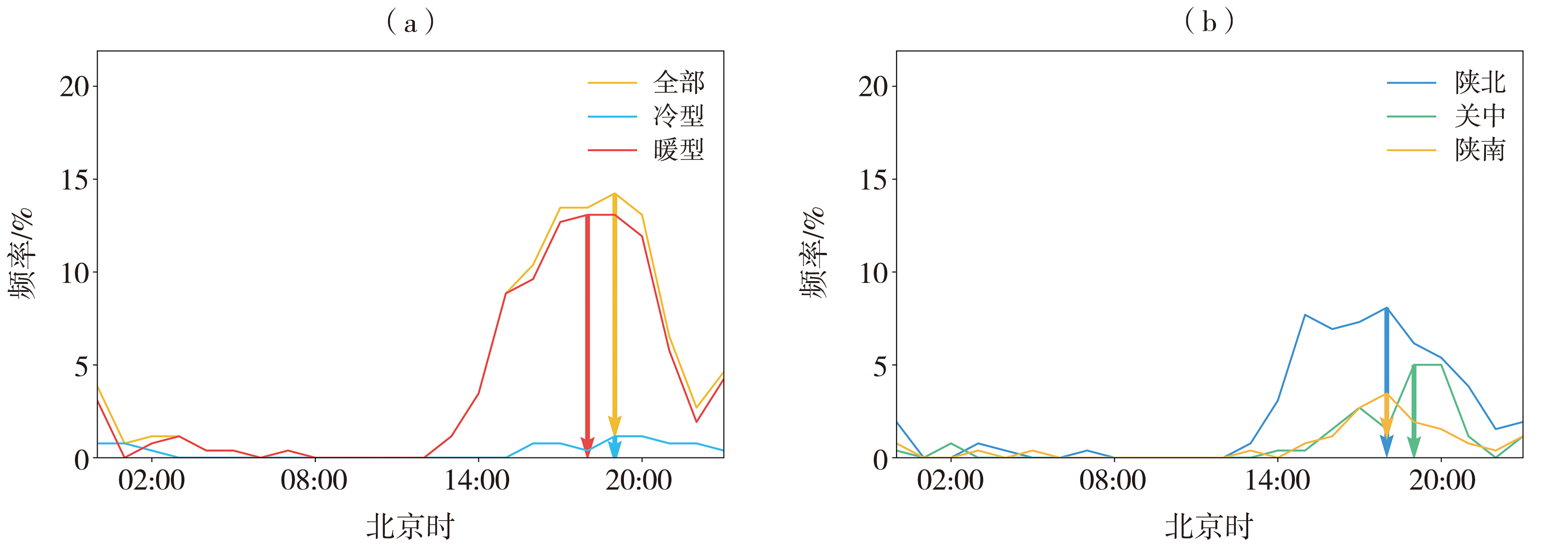
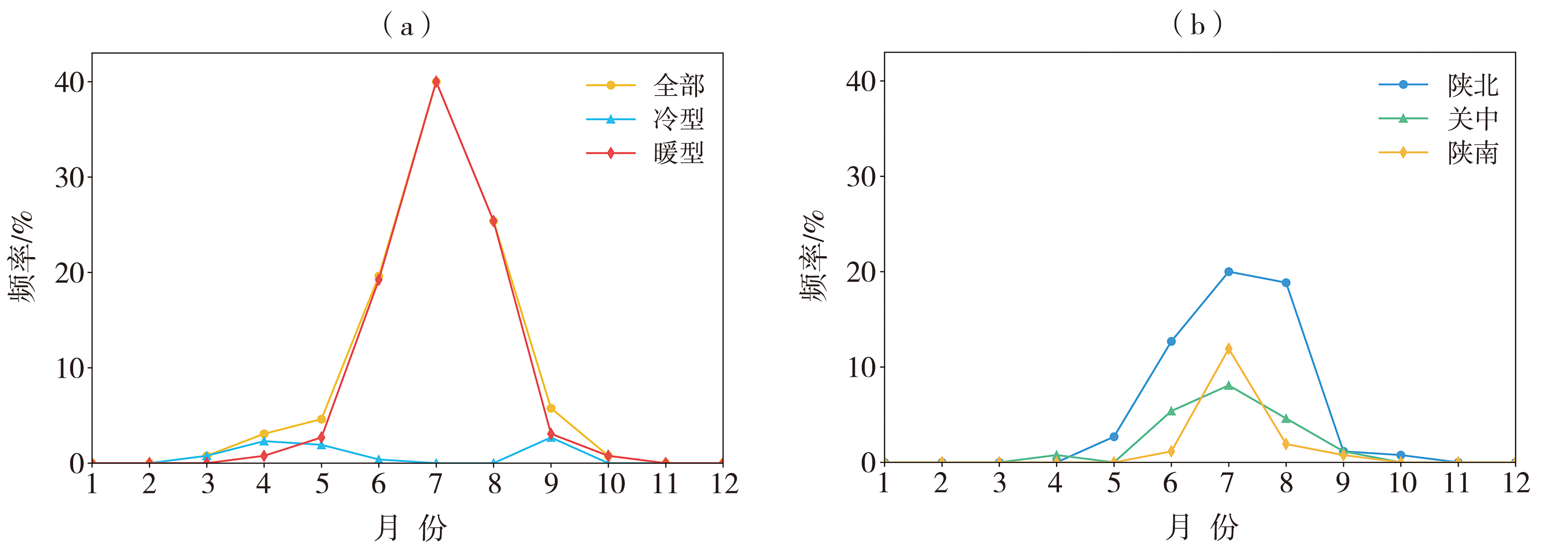
Fig.5 Diurnal variation of frequency of thunderstorm gales in Shaanxi Province during 2017-2022 (a) all, cold and warm type, (b) warm type in different regions

Fig.6 Boxplots of MLCAPE (a), MLLCL (b) and DCAPE (c) from 6 hours before the occurrence of warm type thunderstorm gales to the occurrence time in each region of Shaanxi Province (The broken line is the median of each parameter changing with time. the same as bellow)
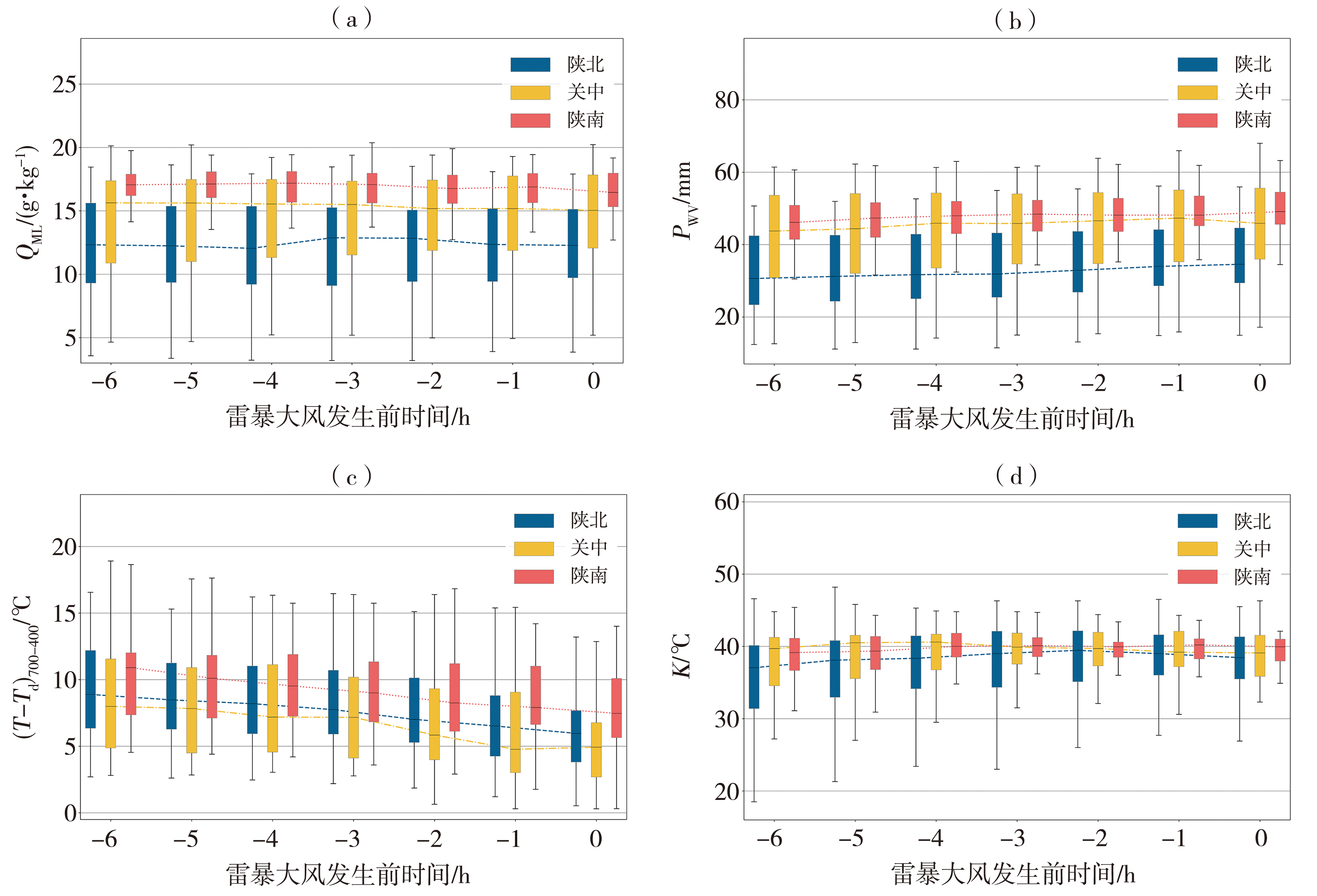
Fig.7 Boxplots of QML (a), PWV (b), (T-Td)700-400 (c), and K index (d) from 6 hours before the occurrence of warm type thunderstorm gales to the occurrence time in each region of Shaanxi Province
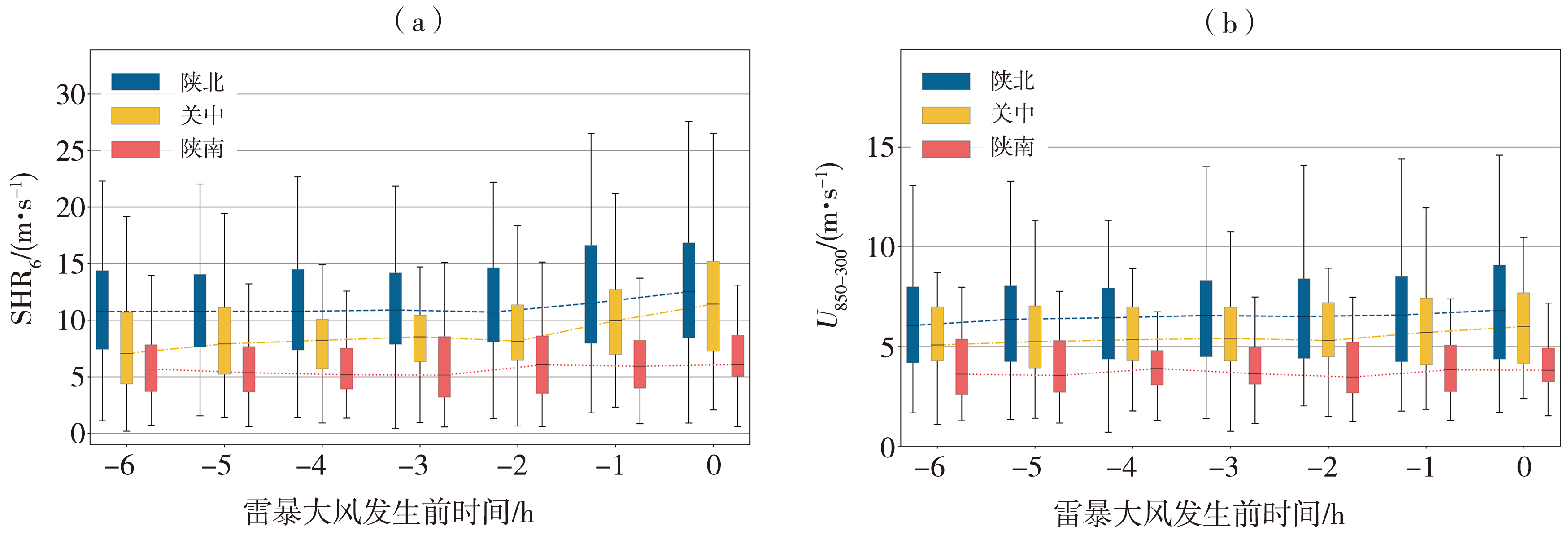
Fig.8 Boxplots of SHR6 (a) and U850-300 (b) from 6 hours before the occurrence of warm type thunderstorm gales to the occurrence time in each region of Shaanxi Province

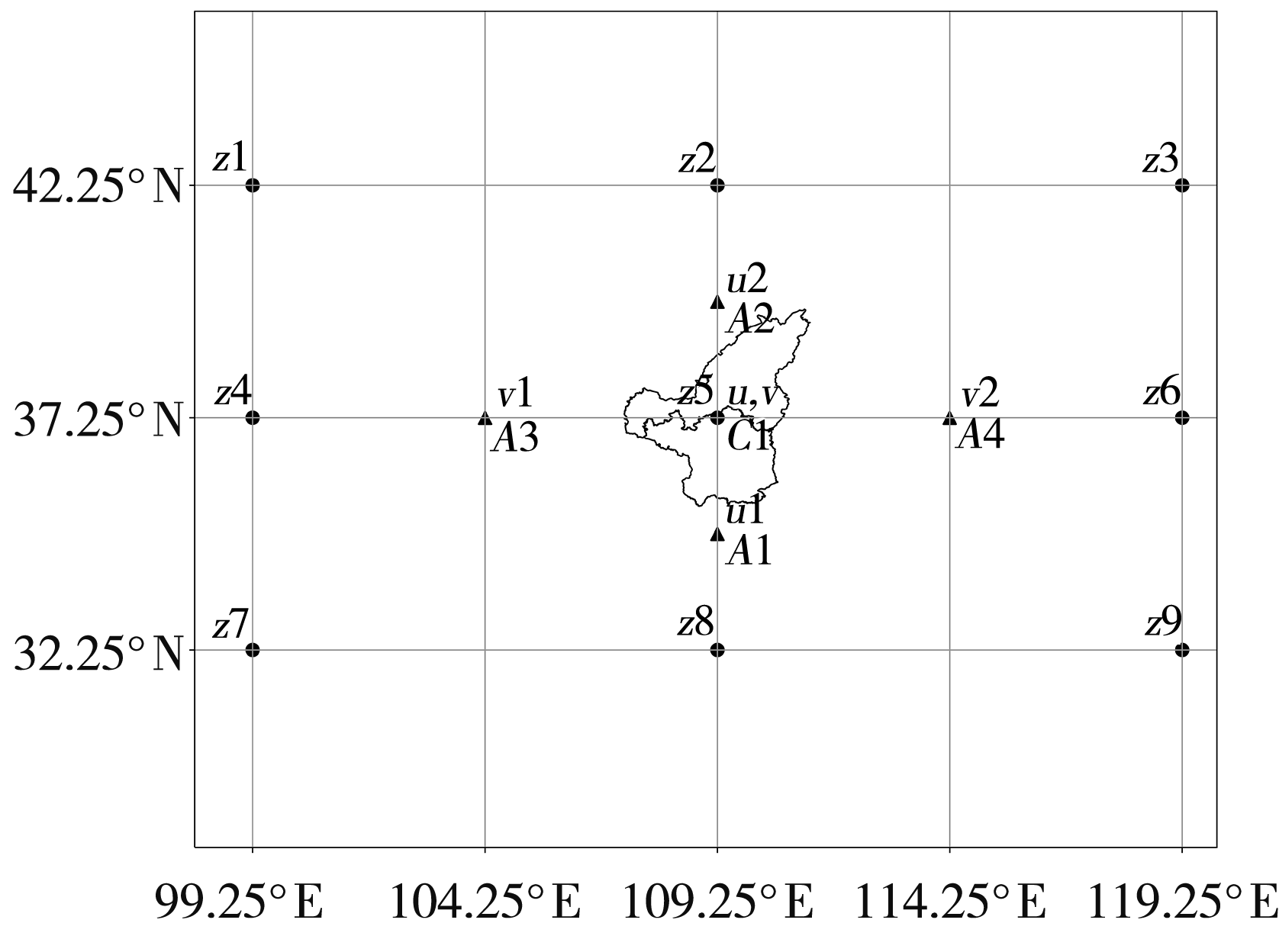
Fig.9 Synthetic analysis of 500 hPa height field (contours, Unit: dagpm) and wind field (wind vectors, Unit: m·s-1) for warm type thunderstorm gales with circulation type frequency greater than 15% in each region of Shaanxi Province (The solid circles and triangles are the occurrence and average location of warm type thunderstorm gale, respectively, the hollow circles indicate the wind speed is less than 2 m·s-1)

Fig.10 The vertical profiles of the composite fields of wind field (wind vectors, Unit: m·s-1), vertical velocity (the color shaded, Unit: Pa·s-1) and relative humidity (isolines, Unit: %) along the average location of warm type thunderstorm gales with 500 hPa circulation type frequency greater than 15% in each region of Shaanxi Province Grey shaded is for topography, the five-pointed star is the average occurrence position of the processes, the hollow circle indicates the wind speed is less than 2 m·s-1

Fig.11 Composite T-ln P diagram of warm type thunderstorm gales with 500 hPa circulation type frequency greater than 15% in each region of Shaanxi Provinse (The red curve is environmental temperature, the green curve is environmental dew point temperature, the black curve is parcel temperature, the black dot is lifting condensation level)
| [1] | 柴东红, 杨晓亮, 吴紫煜, 等, 2017. 京津冀地区雷暴大风天气的统计分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 36(3): 193-199. |
| [2] | 陈涛, 代刊, 张芳华, 2013. 一次华北飑线天气过程中环境条件与对流发展机制研究[J]. 气象, 39(8): 945-954. |
| [3] | 陈晓欣, 俞小鼎, 王秀明, 2022. 中国大范围雷暴大风事件(Derechos)研究:时空分布, 环境背景和对流系统形态特征[J]. 气象学报, 80(1): 67-81. |
| [4] | 陈云辉, 许爱华, 许彬, 等, 2019. 江西一次极端雷暴大风过程的中尺度特征与成因分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 38(2): 126-134. |
| [5] | 董春卿, 武永利, 郭媛媛, 等, 2021. 山西强对流天气分类指标与判据的应用[J]. 干旱气象, 39(2): 345-355. |
| [6] | 方翀, 王西贵, 盛杰, 等, 2017. 华北地区雷暴大风的时空分布及物理量统计特征分析[J]. 高原气象, 36(5): 1 368-1 385. |
| [7] | 费海燕, 王秀明, 周小刚, 等, 2016. 中国强雷暴大风的气候特征和环境参数分析[J]. 气象, 42(12): 1 513-1 521. |
| [8] | 付炜, 叶成志, 王东海, 等, 2018. 一次南岭山脉前汛期强对流天气过程诊断分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 37(6): 511-521. |
| [9] | 高晓梅, 俞小鼎, 王令军, 等, 2018. 鲁中地区分类强对流天气环境参量特征分析[J]. 气象学报, 76(2): 196-212. |
| [10] | 贾丽伟, 李维京, 陈德亮, 等, 2006. 东北地区月平均大气环流型与哈尔滨气候关系的初步研究[J]. 气象学报, 64(2): 236-245. |
| [11] | 李强, 王秀明, 张亚萍, 等, 2019. 一次副高影响下的局地强风暴触发及维持机制探析[J]. 气象, 45(2): 203-215. |
| [12] | 刘彬, 邹灵宇, 李晓鹏, 等, 2022. 云南雷暴大风天气的环境条件特征分析[J]. 气象, 48(11): 1 402-1 417. |
| [13] | 刘娜, 熊安元, 张强, 等, 2021. 强对流天气人工智能应用训练基础数据集构建[J]. 应用气象学报, 32(5): 530-541. |
| [14] | 马鸿青, 张江涛, 李彦, 等, 2019. 河北保定“7.9”致灾雷暴大风环境场与风暴特征[J]. 干旱气象, 37(4): 613-621. |
| [15] | 马淑萍, 王秀明, 俞小鼎, 2019. 极端雷暴大风的环境参量特征[J]. 应用气象学报, 30(3): 292-301. |
| [16] | 蒙伟光, 张艳霞, 吴亚丽, 等, 2019. 季风槽环境中暴雨中尺度对流系统的分析与数值预报试验[J]. 气象学报, 77(6): 980-998. |
| [17] | 慕建利, 李泽椿, 李耀辉, 2009. 高原东侧特大暴雨过程中秦岭山脉的作用[J]. 高原气象, 28(6): 1 282-1 290. |
| [18] | 孙建华, 郑淋淋, 赵思雄, 2014. 水汽含量对飑线组织结构和强度影响的数值试验[J]. 大气科学, 38(4): 742-755. |
| [19] | 谭丹, 黄玉霞, 沙宏娥, 2022. 甘肃省强对流天气特征分析[J]. 自然灾害学报, 31(2): 222-232. |
| [20] | 王东方, 郄秀书, 袁善锋, 等, 2020. 北京地区的闪电时空分布特征及不同强度雷暴的贡献[J]. 大气科学, 44(2): 225-238. |
| [21] | 王黉, 李英, 宋丽莉, 等, 2020. 川藏地区雷暴大风活动特征和环境因子对比[J]. 应用气象学报, 31(4): 435-446. |
| [22] | 王华, 孙继松, 2008. 下垫面物理过程在一次北京地区强冰雹天气中的作用[J]. 气象, 34(3): 16-21. |
| [23] | 王艳春, 陈宏, 尉英华, 等, 2023. 天津雷暴大风天气的环流场及雷达回波特征分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 17(6): 119-126. |
| [24] | 王毅, 张晓美, 盛杰, 等, 2020. 基于Logistic模型的干、湿环境下江淮夏季雷暴大风潜势预报研究[J]. 气象科学, 40(2): 241-248. |
| [25] | 韦惠红, 许冠宇, 刘希文, 等, 2022. 湖北省不同类型雷暴大风的时空分布及环境参数特征[J]. 暴雨灾害, 41(1): 66-75. |
| [26] | 魏东, 孙继松, 雷蕾, 等, 2011. 三种探空资料在各类强对流天气中的应用对比分析[J]. 气象, 37(4): 412-422. |
| [27] | 辛蕊, 段克勤, 2019. 2017年夏季秦岭降水的数值模拟及其空间分布[J]. 地理学报, 74(11): 2 329-2 341. |
| [28] |
许霖, 姚蓉, 王晓雷, 等, 2017. 湖南省雷暴大风的时空分布和变化特征[J]. 高原气象, 36(4): 993-1 000.
DOI |
| [29] | 杨晓霞, 胡顺起, 姜鹏, 等, 2014. 雷暴大风落区的天气学模型和物理量参数研究[J]. 高原气象, 33(4):1057-1 068. |
| [30] | 杨晓霞, 尤莉, 夏凡, 等, 2019. 山东内陆和半岛雷暴大风的环境物理量参数特征[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 13(6): 47-56. |
| [31] | 杨新林, 孙建华, 鲁蓉, 等, 2017. 华南雷暴大风天气的环境条件分布特征[J]. 气象, 43(7): 769-780. |
| [32] | 余蓉, 张小玲, 李国平, 等, 2012. 1971—2000年我国东部地区雷暴、冰雹、雷暴大风发生频率的变化[J]. 气象, 38(10): 1 207-1 216. |
| [33] | 袁慧敏, 2019. 利用探空资料确定呼和浩特地区3类强对流天气预警阈值[J]. 气象科技, 47(3): 476-485. |
| [34] | 郑淋淋, 孙建华, 2016. 风切变对中尺度对流系统强度和组织结构影响的数值试验[J]. 大气科学, 40 (2): 324-340. |
| [35] | 郑永光, 陶祖钰, 俞小鼎, 2017. 强对流天气预报的一些基本问题[J]. 气象, 43(6): 641-652. |
| [36] | 郑永光, 王颖, 寿绍文, 2010. 我国副热带地区夏季深对流活动气候分布特征[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 46(5): 793-804. |
| [37] | 郑媛媛, 姚晨, 郝莹, 等, 2011. 不同类型大尺度环流背景下强对流天气的短时临近预报预警研究[J]. 气象, 37(7): 795-801. |
| [38] | 钟利华, 曾鹏, 李勇, 等, 2011. 广西雷暴大风环流特征和物理量诊断分析[J]. 气象, 37(1): 59-65. |
| [39] | 钟利华, 曾鹏, 史彩霞, 等, 2017. 西江流域面雨量与区域大气环流型关系[J]. 应用气象学报, 28(4): 470-480. |
| [40] | 周康辉, 郑永光, 王婷波, 等, 2017. 基于模糊逻辑的雷暴大风和非雷暴大风区分方法[J]. 气象, 43(7): 781-791. |
| [41] | ALLEN J T, KAROLY D J, MILLS G A, 2011. A severe thunderstorm climatology for Australia and associated thunderstorm environments[J]. Australian Meteorological and Oceanographic Journal, 61(3): 143-158. |
| [42] | BROWN A, DOWDY A, 2021. Severe convection-related winds in Australia and their associated environments[J]. Journal of Southern Hemisphere Earth Systems Science, 71(1): 30-52. |
| [43] | EMANUEL K A, 1994. Atmospheric convection[M]. New York: Oxford University Press: 165-188. |
| [44] | EVANS J S, DOSWELL C A, 2001. Examination of derecho environments using proximity soundings[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 16(3): 329-342. |
| [45] | KUCHERA E L, PARKER M D, 2006. Severe convective wind environments[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 21(4): 595-612. |
| [46] | MIRÓ J R, PEPIN N, PEÑA J C, et al, 2020. Daily atmospheric circulation patterns for Catalonia (northeast Iberian Peninsula) using a modified version of Jenkinson and Collison method[J]. Atmospheric Research, 231: 104674. DOI: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2019.104674. |
| [47] | PACEY G P, SCHULTZ D M, GARCIA-CARRERAS L, 2021. Severe convective windstorms in Europe: Climatology, preconvective environments, and convective mode[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 36(1): 237-252. |
| [48] | PÚČIK T, GROENEMEIJER P, RÝVA D, et al, 2015. Proximity soundings of severe and nonsevere thunderstorms in central Europe[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 143(12): 4 805-4 821. |
| [49] | TASZAREK M, BROOKS H E, CZERNECKI B, 2017. Sounding-derived parameters associated with convective hazards in Europe[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 145(4): 1 511-1 528. |
| [50] | TASZAREK M, ALLEN J T, PÚČIK T, et al, 2020. Severe convective storms across Europe and the United States.Part II: ERA5 environments associated with lightning, large hail, severe wind, and tornadoes[J]. Journal of Climate, 33(23): 10 263-10 286. |
| [51] | YANG X, SUN J, ZHENG Y, 2017. A 5-yr climatology of severe convective wind events over China[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 32(4): 1 289-1 299. |
| [1] | ZHOU Jinhong, WANG Xiuming, TIAN Xiaoting, ZHANG Zexiu, LI Shuwen, CAI Xiaofang. Study on circulation characteristics and water vapor anomaly of extreme rainstorm events in Shanxi Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(3): 426-436. |
| [2] | LIU Juju, ZHAO Qiang, JING Yu, ZHANG Weiran, DAI Changming. Suitability assessment of CMA multi-source precipitation analysis products for short-term heavy rainfall monitoring in Shaanxi [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(2): 263-273. |
| [3] | ZHANG Hongfang, ZHANG Xi, LIANG Jia, GUO Qi, WANG Jingzhong. Characteristics and influence factors of low visibility along Shaanxi section of the Lian-Huo expressway [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(1): 82-90. |
| [4] | CHEN Xiaoting, ZHAO Qiang, LIU Hui, PENG Li. Analysis of water vapor characteristics of two different types of rainstorms over the Loess Plateau [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 968-980. |
| [5] | XU Min, SHEN Fang, LIU Qiqi, LI Na, WANG Jie. Formation conditions and characteristics of heavy precipitation with quasi-linear MCSs [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(4): 596-604. |
| [6] | WENG Zhimei,ZHOU Xuejun,GAN Jingjing,WANG Kai. Rainfall Characteristics of Warm Sector Weathers with Different Patterns in Spring in Zhejiang [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(5): 766-774. |
| [7] | ZHOU Yaman, SUN Di, ZHAO Yong, LI Anbei, GUO Yulin. Characteristics of Wide-range Extreme Precipitation in Summer and Its Circulation Anomalies in Northern Xinjiang#br# [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(2): 215-224. |
| [8] | ZHANG Hongfang, LU Shan, SHEN Jiaojiao, ZHANG Xi, DANG Chaoqi. Temporal and Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Road Icing in Shaanxi and Its Risk Warning Model [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(5): 878-885. |
| [9] | LI Changde, WANG Lei, LI Xiaoxia, ZHAO Jianhua, ZENG Dingwen. Analysis on Circulation Characteristics of Droughts and Floods in April in Loess Plateau and Their Earlier Forcing Signals [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(1): 14-21. |
| [10] | ZHOU Jinhong, ZHAO Caiping, DONG Chunqing. Circulation Classification and Environmental Parameters Analysis on Short-time Heavy Rainfall in Flood Season in Taiyuan [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(3): 392-. |
| [11] | CAI Xinling, LI Yu, LI Qian, HU Shulan. Climatic Characteristics of Autumn Rain in Shaanxi and Their Relationship with Atmospheric Circulation and SST During 1961-2016 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(2): 226-232. |
| [12] | DING Jiangyu, CHEN Xiaoting, WANG Jianpeng, GE Sen, JI Xiaoling. Characteristics of Thunderstorm and Wind Shear Weather in Changle Airport of Fuzhou [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(2): 270-276. |
| [13] | LI Dengke1, QUAN Wenting1, XIE Feizhou2. Meteorological Forecast Model for Stripe Rust of Wheat in Shaanxi Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(1): 128-133. |
| [14] | WANG Wenyan1, 2,WANG Li1,LI Guoping2,LU Yuanping1,TANG Wenzhe1. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of Extreme Precipitation in Flood Season in Shaanxi Province During 1961-2013 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2016, 34(6): 952-957. |
| [15] | LIU Lu, WANG Jinghong, ZHANG Weimin, LI Yanli. Climatic Change Characteristics and Its Impaction on Phenophase of Jujube in Northern Shaanxi During 1971-2010 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2016, 34(5): 841-846. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||