Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 318-327.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-02-0318
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Application evaluation of multi-source remote sensing data in spring dust weather monitoring in Beijing
XU Luyang1( ), ZHAI liang1(
), ZHAI liang1( ), WANG Yuanyuan1, LEI Lei1, YU Bo1, HAO Cui1, QIN Qingchang2,3
), WANG Yuanyuan1, LEI Lei1, YU Bo1, HAO Cui1, QIN Qingchang2,3
- 1. Beijing Weather Forecast Center, Beijing 100089, China
2. CMA Earth System Modeling and Prediction Center, Beijing 100081, China
3. State Key Laboratory of Severe Weather, Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences, Beijing 100081, China
-
Received:2022-02-10Revised:2022-04-20Online:2023-04-30Published:2023-05-09
多源遥感数据在北京春季沙尘天气监测中的应用评估
徐路扬1( ), 翟亮1(
), 翟亮1( ), 王媛媛1, 雷蕾1, 于波1, 郝翠1, 秦庆昌2,3
), 王媛媛1, 雷蕾1, 于波1, 郝翠1, 秦庆昌2,3
- 1.北京市气象台,北京 100089
2.中国气象局地球系统数值预报中心,北京 100081
3.中国气象科学研究院灾害天气国家重点实验室,北京 100081
-
通讯作者:翟亮(1980—),男,内蒙古赤峰人,正高级工程师,主要从事天气分析和预报工作。E-mail: liang6302@163.com。 -
作者简介:徐路扬(1990—),男,浙江衢州人,工程师,主要从事灾害性天气预报预警研究。E-mail: xuluyang1990@163.com。 -
基金资助:中国气象局创新发展专项项目(CXFZ2022J013)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
XU Luyang, ZHAI liang, WANG Yuanyuan, LEI Lei, YU Bo, HAO Cui, QIN Qingchang. Application evaluation of multi-source remote sensing data in spring dust weather monitoring in Beijing[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(2): 318-327.
徐路扬, 翟亮, 王媛媛, 雷蕾, 于波, 郝翠, 秦庆昌. 多源遥感数据在北京春季沙尘天气监测中的应用评估[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(2): 318-327.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-02-0318

Fig.1 Hourly variation of visibility and PM10 mass concentration at Daxing (a), Haidian (b), Huairou (c) and Yanqing (d) station in Beijing on 15 March 2021

Fig.2 Hourly variation of visibility and PM10 mass concentration at Daxing (a), Haidian (b), Huairou (c) and Yanqing (d) station in Beijing on 28 March 2021

Fig.3 Hourly variation of visibility and PM10 mass concentration at Daxing (a), Haidian (b), Huairou (c) and Yanqing (d) station in Beijing on 15 April 2021

Fig.4 The mie scattering extinction coefficient (a, c)(Unit: km-1) and depolarization ratio (b, d)(Unit: %) detected by the lidar at Huairou station in Beijing from 12:01 on 14 to 11:59 on 19 March (a, b) and from 00:00 to 23:59 on 15 April (c, d) 2021
| 过程时间 | 沙尘发生前 | 沙尘过程中 | 沙尘过程后 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3月15日 | 0.10~0.60 | 0.90~1.60 | 0.10~0.60 |
| 4月15日 | 0.10~0.50 | 0.80~1.60 | 0.10~0.50 |
Tab.1 The maximum extinction coefficient of the lidar near the ground layer (less than100 m) at Huairou station in Beijing before, during and after the dust weather processes on March 15 and April 15, 2021
| 过程时间 | 沙尘发生前 | 沙尘过程中 | 沙尘过程后 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3月15日 | 0.10~0.60 | 0.90~1.60 | 0.10~0.60 |
| 4月15日 | 0.10~0.50 | 0.80~1.60 | 0.10~0.50 |

Fig.5 The hourly variation of backscatter coefficient (the color shaded, Unit: 10-9m-1·srad-1) and cloud-base height (the black solid line) from the laser cloud altimeter at Haidian station in Beijing on 15 (a), 28 (b) March, and 15 April (c) 2021
| 过程时间 | 沙尘发生前 | 沙尘过程中 | 沙尘过程后 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3月15日 | 16 432~50 581 | 1 048 575 | 1 048 575 |
| 3月28日 | 9 125~26 012 | 1 048 575 | 1 048 575 |
| 4月15日 | 688~3 234 | 1 048 575 | 1 048 575 |
Tab.2 Maximum backscatter coefficient of the laser cloud altimeter at Haidian station in Beijing before, during and after the three dust weather processes on March 15, March 28 and April 15, 2021
| 过程时间 | 沙尘发生前 | 沙尘过程中 | 沙尘过程后 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3月15日 | 16 432~50 581 | 1 048 575 | 1 048 575 |
| 3月28日 | 9 125~26 012 | 1 048 575 | 1 048 575 |
| 4月15日 | 688~3 234 | 1 048 575 | 1 048 575 |
| 站点 | 发生前 | 沙尘过程中 | 过程后 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 海淀 | -41~-27 | -10~5 | -41~-10 |
| 延庆 | -41~-25 | -13~4 | -41~-8 |
| 观象台 | -41~-26 | -8~7 | -41~-9 |
| 霞云岭 | -41~-27 | 0~11 | -41~-9 |
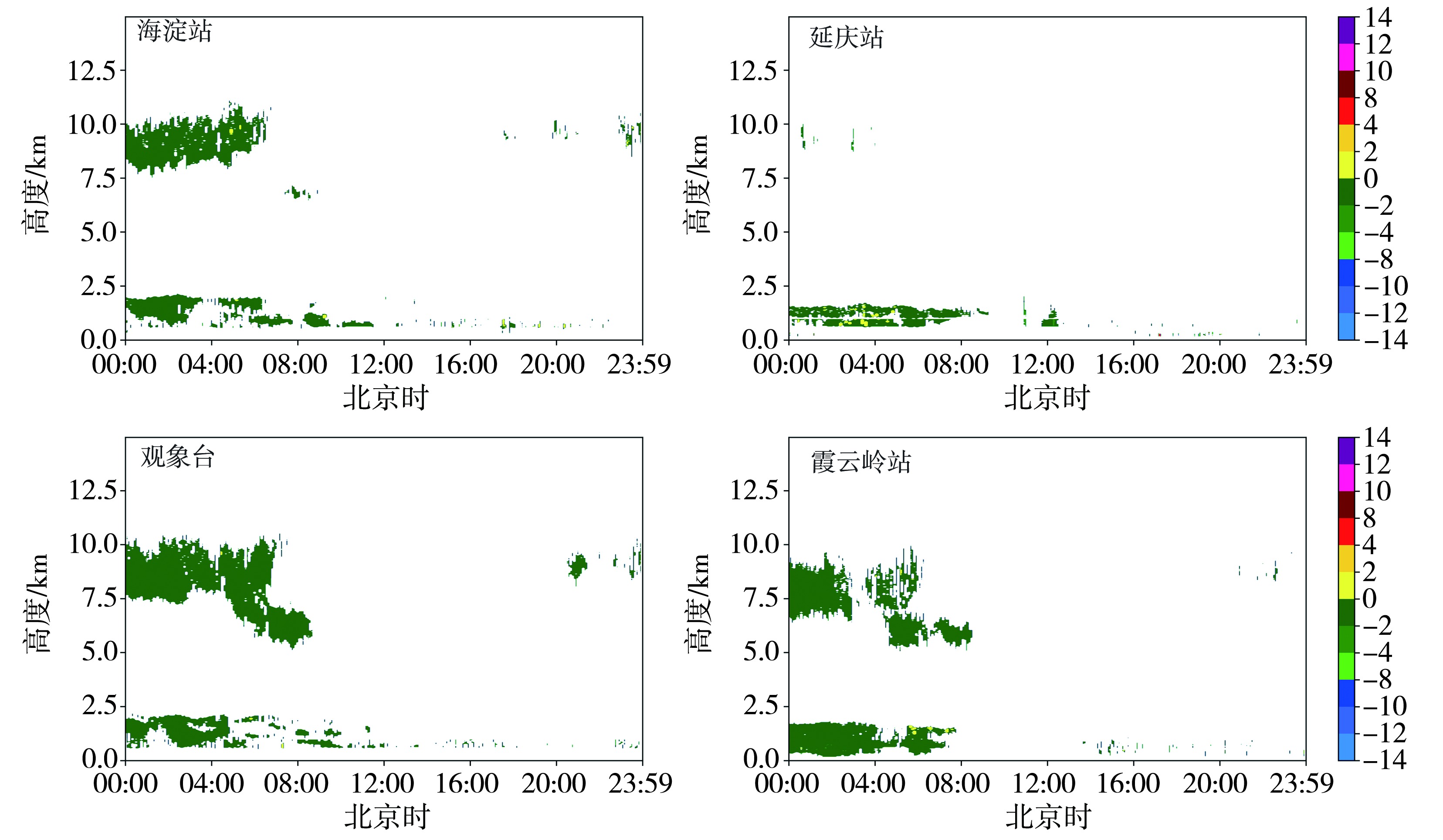
Tab.3 The reflectivity factor from the cloud radar at four meteorological stations in Beijing before, during and after dust weather process on 15 March 2021
| 站点 | 发生前 | 沙尘过程中 | 过程后 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 海淀 | -41~-27 | -10~5 | -41~-10 |
| 延庆 | -41~-25 | -13~4 | -41~-8 |
| 观象台 | -41~-26 | -8~7 | -41~-9 |
| 霞云岭 | -41~-27 | 0~11 | -41~-9 |
| [1] | 蔡嘉仪, 苗世光, 李炬, 等, 2020. 基于激光云高仪反演全天边界层高度的两步曲线拟合法[J]. 气象学报, 78(5): 864-876. |
| [2] | 曹贤洁, 张镭, 周碧, 等, 2009. 利用激光雷达观测兰州沙尘气溶胶辐射特性[J]. 高原气象, 28(5): 1 115-1 120. |
| [3] | 陈广庭, 2001. 近50年北京的沙尘天气及治理对策[J]. 中国沙漠, 21(4): 402-407. |
| [4] | 陈羿辰, 金永利, 丁德平, 等, 2018. 毫米波测云雷达在降雪观测中的应用初步分析[J]. 大气科学, 42(1): 134-149. |
| [5] | 董旭辉, 祁辉, 任立军, 等, 2007. 偏振激光雷达在沙尘暴观测中的数据解析[J]. 环境科学研究, 20(2): 106-111. |
| [6] | 董旭辉, 杉本伸夫, 白雪椿, 等, 2006. 激光雷达在沙尘观测中的应用——2004年春季北京和呼和浩特沙尘天气的解析[J]. 中国沙漠, 26(6): 942-947. |
| [7] | 段伯隆, 刘新伟, 郭润霞, 等, 2021. “3·15”北方强沙尘暴天气成因分析[J]. 干旱气象, 39(4): 541-553. |
| [8] | 高庆先, 苏福庆, 任阵海, 等, 2002. 北京地区沙尘天气及其影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 22(5): 468-471. |
| [9] | 郭伟, 卜令兵, 贾小芳, 等, 2016. 基于激光云高仪的北京沙尘气溶胶特征分析[J]. 气象, 42(12): 1 540-1 546. |
| [10] | 黄浩杰, 王鹤婷, 许敏, 2021. 京津冀一次沙尘天气的多源资料分析[J]. 农业灾害研究, 11(6): 32-36+151. |
| [11] | 刘慧, 井宇, 黄少妮, 等, 2021. 陕西关中地区一次霾转沙尘过程的气象条件分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 44(3): 8-15. |
| [12] | 刘黎平, 2021. 毫米波云雷达观测和反演云降水微物理及动力参数方法研究进展[J]. 暴雨灾害, 40(3): 231-242. |
| [13] | 邱金桓, 郑斯平, 黄其荣, 等, 2003. 北京地区对流层中上部云和气溶胶的激光雷达探测[J]. 大气科学, 27(1): 1-7. |
| [14] |
宋嘉尧, 张文煜, 张宇, 等, 2013. 基于微脉冲激光雷达观测资料的半干旱区沙尘天气消光效应分析[J]. 干旱气象, 31(4): 672-676.
DOI |
| [15] | 谭金华, 2018. 沙尘环境下交通流跟驰模型及仿真[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 18(3): 63-67. |
| [16] |
王金玉, 李盛, 王式功, 等, 2013. 沙尘污染对暴露人群呼吸系统健康的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 33(3): 826-831.
DOI |
| [17] | 王孟, 黄伟宁, 2020. 沙尘暴对Ka频段信号影响的研究[J]. 中国无线电, (7): 44-46. |
| [18] | 王小兰, 闫世明, 王雁, 等, 2021. 太原市冬季一次霾和沙尘“混合型污染”过程天气成因分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 44(4):43-52. |
| [19] | 魏凤英, 1999. 现代气候统计诊断与预测技术[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [20] | 熊亚军, 唐宜西, 寇星霞, 等, 2017. 北京春季一次霾和沙尘混合污染天气过程分析[J]. 干旱气象, 35(1): 100-107. |
| [21] | 于杰, 车慧正, 陈权亮, 等, 2016. 2010—2012年我国西北地区沙尘个例气溶胶特征分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 39(2): 33-40. |
| [22] | 袁静, 潘哲, 李伶俐, 等, 2019. 基于激光云高仪的雾和霾监测研究[J]. 气象水文海洋仪器, 36(2): 8-14. |
| [23] | 尹青, 何金海, 张华, 2009. 激光雷达在气象和大气环境监测中的应用[J]. 气象与环境学报, 25(5): 48-56. |
| [24] | 张怀清, 胡红玲, 鞠洪波, 等, 2009. 激光雷达沙尘参数提取技术研究[J]. 林业科学研究, 22(2): 161-165. |
| [25] |
张晋茹, 陈玉宝, 卜令兵, 2018. 基于气溶胶和大气风场激光雷达对北京一次沙尘过程分析[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 55(8), DOI: 10.3788/LOP55.080102.
DOI |
| [26] | 张墅, 2021. 激光云高仪和毫米波云雷达协同测量云底高技术的融合算法研究[J]. 高技术通讯, 31(2): 163-169. |
| [27] | 张迎新, 李林, 曹晓冲, 等, 2021. 京津冀地区一次持续时间较长浮尘天气的分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 15(4): 123-129. |
| [28] | 赵静, 曹晓钟, 代桃高, 等, 2017. 毫米波云雷达与探空测云数据对比分析[J]. 气象, 43(1): 101-107. |
| [29] | 朱君, 曹晓钟, 李晓兰, 2017. 激光云高仪与可见光测云仪观测试验对比[J]. 气象科技, 45(4): 611-615. |
| [30] | 祝廷成, 梁存柱, 陈敏, 等, 2004. 沙尘暴的生态效益[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 18(增刊1): 33-37. |
| [31] |
CHEN S, ZHAO C, QIAN Y, et al, 2014. Regional modeling of dust mass balance and radiative forcing over East Asia using WRF-Chem[J]. Aeolian Research, 15: 15-30.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
HUANG J, MINNIS P, LIN B, et al, 2006. Possible influences of Asian dust aerosols on cloud properties and radiative forcing observed from MODIS and CERES[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 33, DOI: 10.1029/2005GL024724.
DOI |
| [33] |
LUE Y L, LIU L Y, HU X, et al, 2010. Characteristics and provenance of dustfall during an unusual floating dust event[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 44(29):3477-3 484.
DOI URL |
| [34] | RIPOLL J, NTZIACHRISTOS V, 2005. The characteristics of atmospheric aerosol at Aksu, an Asian dust-source region of North-West China: a summary of observations over the three years from March 2001 to April 2004[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, 83A: 45-72. https://doi.org/10.2151/jmsj.83A.45. |
| [35] | WANG W, SAMAT A, ABUDUWAILI J, et al, 2022. Temporal characterization of sand and dust storm activity and its climatic and terrestrial drivers in the Aral Sea region[J]. Atmospheric Research, 275, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2022.106242. |
| [36] | YASUNORI K, MASAO M, 2005. Regional difference in the characteristic of dust event in East Asia: relationship among dust outbreak, surface wind, and land surface condition[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, 83A: 1-18. https://doi.org/10.2151/jmsj.83A.1. |
| [1] | LI Hui, ZHENG Xucheng, SU Lijuan, XIN Yue, ZHANG Jie. Statistical analysis of cloud macrophysical characteristics in the Inner Mongolia section of the Yellow River Basin based on millimeter-wave cloud radar [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(3): 434-441. |
| [2] | JI Xueshuai, WANG Lijing, GUO Hong, KANG Bosi, HUANG Shanjiang, ZHANG Xidan, GUO Xuhui. Analysis of characteristics of precipitation phase during a rain-snow weather process in Zhangjiakou based on multi-source observation data [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(3): 507-515. |
| [3] | DUAN Bolong, LIU Xinwei, GUO Runxia, SONG Qiang, DI Xiaohong, DUAN Mingkeng. Cause Analysis on Severe Dust Storm in Northern China on 15 March 2021 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(4): 541-553. |
| [4] | ZHANG Kaijun, FU Longyan, LI Lanqian, SHAO Aimei. Comparison of Two Lidarbased Alerting Algorithms for Low-level Wind Shear [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(4): 652-661. |
| [5] | REN Yong, CHEN Sai, YU Anan, FAN Mengqi. Reliability Analysis of Wind Field and Boundary Layer Height in Xiamen Retrieved by Coherent Doppler Wind Lidar [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(3): 514-523. |
| [6] |
CAO Xiaoyun, XIAO Jianshe, QIAO Bin, CHEN Guoqian, QUAN Chen, ZHU Cunxiong, SHI Feifei, .
Temporal and Spatial Variation Characteristics of DustIntensity in Qaidam Basin from 1961 to 2019#br#
#br#
[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(1): 46-53.
|
| [7] | . Characteristics of Atmospheric-boundary-layer Height and Its Relationship with Sand-dust Weather in Jiuquan of Gansu Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(6): 979-986. |
| [8] | QI Donglin1,2, ZHAO Quanning1, ZHAO Huifang1, HAN Tingfang3, SU Wenjiang1. Temporal and Spatial Variation Characteristics and Regional Differences of Dust Fall in Qinghai from 2004 to 2017 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(6): 927-. |
| [9] | JIANG Xuegong, LI Xiazi, WANG Dejun. Characteristics of Tropopause Evolution and Dust Vertical Transportation During a Mongolia Cyclone Dust Storm Process [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(1): 1-10. |
| [10] | BAI Bing, ZHANG Qiang,CHEN Xuhui,HAN Haitao . Moving Paths and Spatial Characteristics of Three Typical Dust Processes in East Asia [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(1): 11-16. |
| [11] | ZHOU Chenglong, YANG Xinghua, YANG Fan, HUO Wen,ZHONG Xinjie, PAN Honglin, HE Qing. Analysis of Calculated Dust Emission Threshold Wind Speed Based on the Field Experiments [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(1): 90-96. |
| [12] | WU Huanbo, CHEN Qiang, GU Xinbo, FENG Zhen, WANG Xudong. Analysis of a Severe Dust Weather and its Effect on Temporaland Spatial Distribution of PM10 Concentration [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(1): 117-123. |
| [13] | LI Haifei, YUE Man, YANG Feiyue, WANG Jian, ZHANG Wenyu. Analysis on Macroscopic Characteristics of Winter Cloud in Huainan Area of Anhui Based on Ground-based Cloud Radar Data [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(6): 1011-1014. |
| [14] | . Variation Characteristic of Main Meteorological Elements During Summer Sand-Dust Storm Processes in East of Hexi Corridor [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(3): 427-. |
| [15] | WANG Yanfeng1, HUANG Wubin2, HE Cuiying3, HUANG Shan1. Analysis of a Haze and Sand-dust Mixed Pollution Weather in Spring of Beijing [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(1): 100-107. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||