Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (6): 922-932.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-06-0922
• Study on rainstorm in arid region • Previous Articles Next Articles
Analysis on precipitation extremity of a torrential rain event in semi-arid region of eastern Gansu
ZHANG Junxia1,2( ), HUANG Wubin2(
), HUANG Wubin2( ), YANG Xiumei2, LIU Weicheng2, ZHOU Zihan2, SHA Honge2
), YANG Xiumei2, LIU Weicheng2, ZHOU Zihan2, SHA Honge2
- 1. Key Laboratory of Arid Climate and Reducing Disaster of Gansu Province, Lanzhou 730020, China
2. Lanzhou Central Meteorological Observatory, Lanzhou 730020, China
-
Received:2022-08-24Revised:2022-09-28Online:2022-12-31Published:2023-01-10 -
Contact:HUANG Wubin
陇东半干旱区一次特大暴雨事件的降水极端性分析
张君霞1,2( ), 黄武斌2(
), 黄武斌2( ), 杨秀梅2, 刘维成2, 周子涵2, 沙宏娥2
), 杨秀梅2, 刘维成2, 周子涵2, 沙宏娥2
- 1.甘肃省干旱气候变化与减灾重点实验室,甘肃 兰州 730020
2.兰州中心气象台,甘肃 兰州 730020
-
通讯作者:黄武斌 -
作者简介:张君霞(1990—),女,甘肃白银人,助理工程师,主要从事模式客观订正方法研究.E-mail:18419611389@163.com。 -
基金资助:甘肃省气象局气象科研项目重点项目(Zd2023-03);干旱气象科学研究基金(IAM202206);甘肃省青年科技基金计划(2021-0406-JCC-0030);甘肃省科技计划项目(20YF3FA012);甘肃省科技计划项目(21JR7RA702);甘肃省气象局人才专项(2122rczx-青年优秀科技人才-05);甘肃省气象局人才专项(2122rczx-十人计划-01);甘肃省气象局创新团队项目(GSQXCXTD-2020-01)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHANG Junxia, HUANG Wubin, YANG Xiumei, LIU Weicheng, ZHOU Zihan, SHA Honge. Analysis on precipitation extremity of a torrential rain event in semi-arid region of eastern Gansu[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 922-932.
张君霞, 黄武斌, 杨秀梅, 刘维成, 周子涵, 沙宏娥. 陇东半干旱区一次特大暴雨事件的降水极端性分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(6): 922-932.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-06-0922

Fig.1 Spatial distribution of accumulated precipitation from 20:00 BST 14 to 20:00 BST 15 July 2022 (a, Unit: mm) and terrain elevation (the color shaded, Unit: m) and meteorological stations (b) in Qingyang (the rectangular regions for position of strong rainfall center)
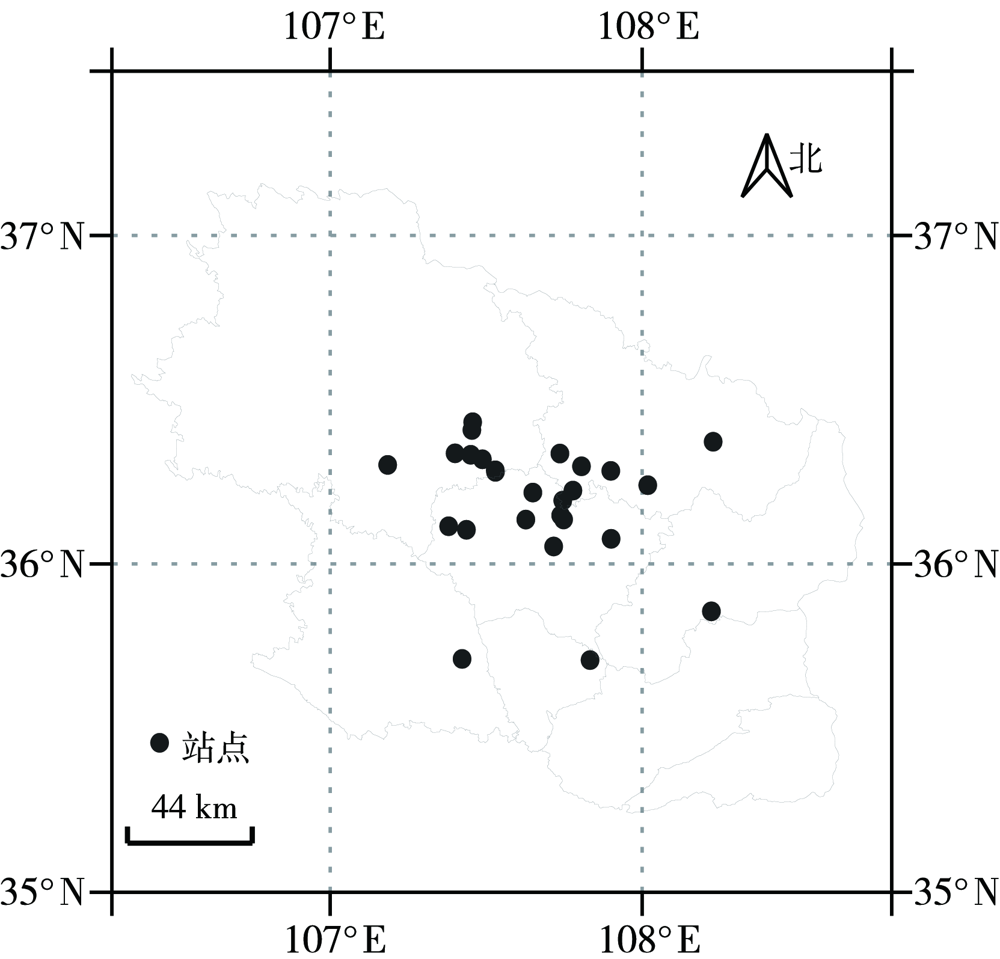
Fig.2 The distribution of stations with maximum cumulative precipitation from 20:00 BST 14 to 20:00 BST 15 July 2022 in Qingyang since the establishment of each station

Fig.3 The accumulative precipitation on 14 to 15 July 2022 and historical mean precipitation in flood season and July at the top 10 stations in terms of the cumulative precipitation during the severe torrential rain process in Qingyang
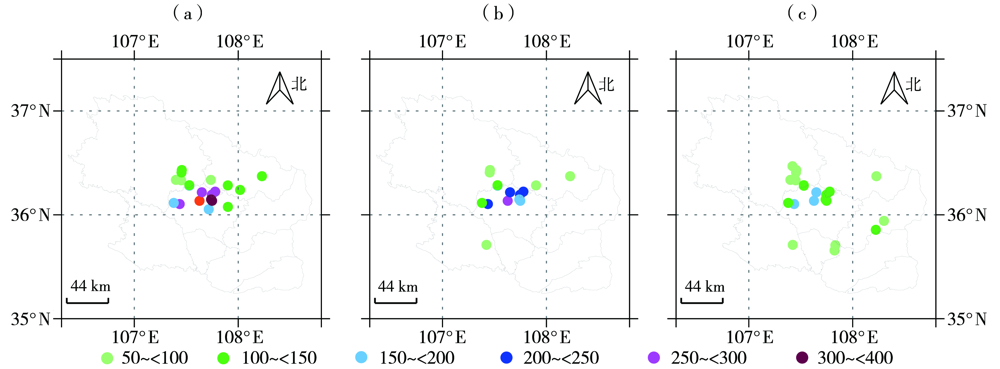
Fig.4 The distribution of accumulative precipitation in 12 (a), 6 (b) and 3 (c) hours from 20:00 BST 14 to 20:00 BST 15 July 2022 at stations with maximum cumulative precipitation during historical same period since the establishment in Qingyang (Unit: mm)
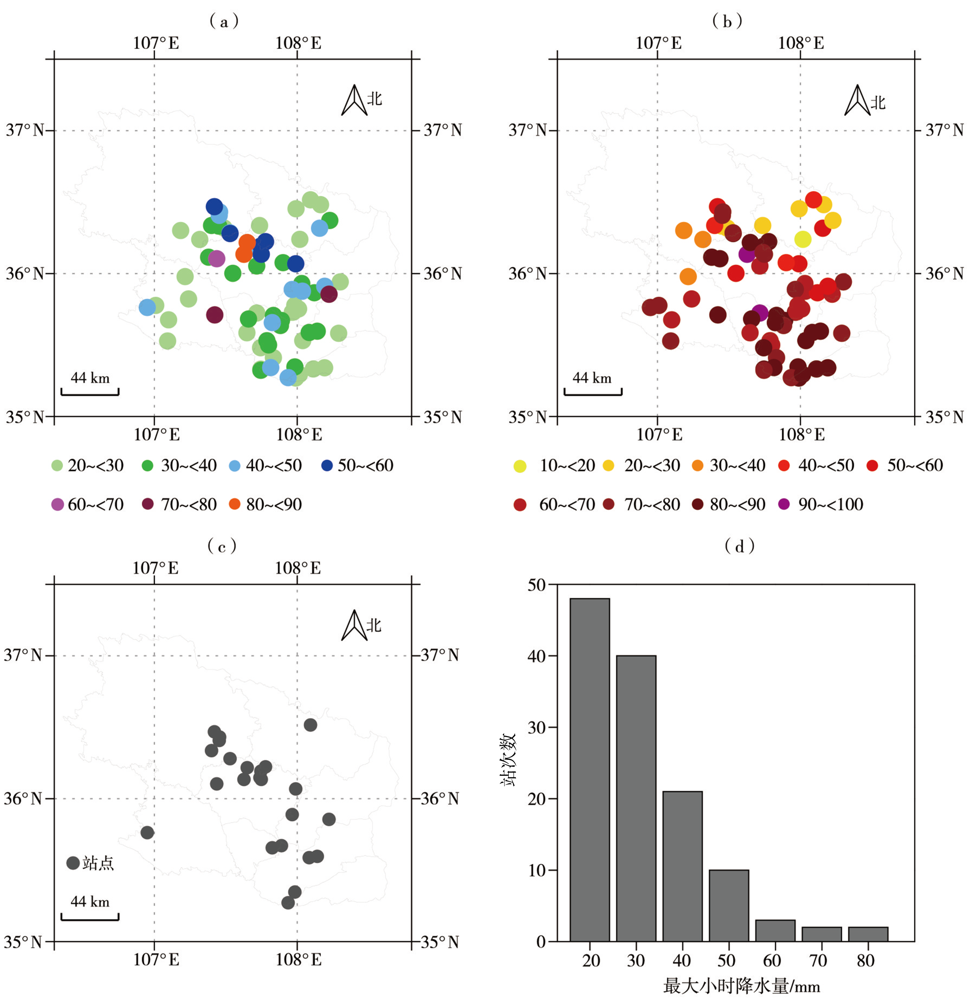
Fig.5 Spatial distribution of maximum hourly precipitation (a, Unit: mm) and its contribution rate to the total precipitation(b, Unit: %) and stations with maximum hourly precipitation since the establishment of station (c), and station numbers occurring maximum hourly precipitation (d) from 20:00 BST 14 to 20:00 BST 15 July 2022
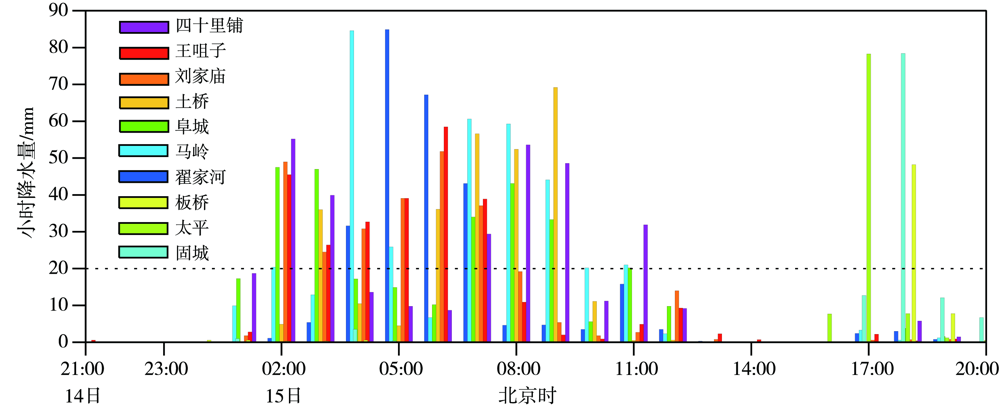
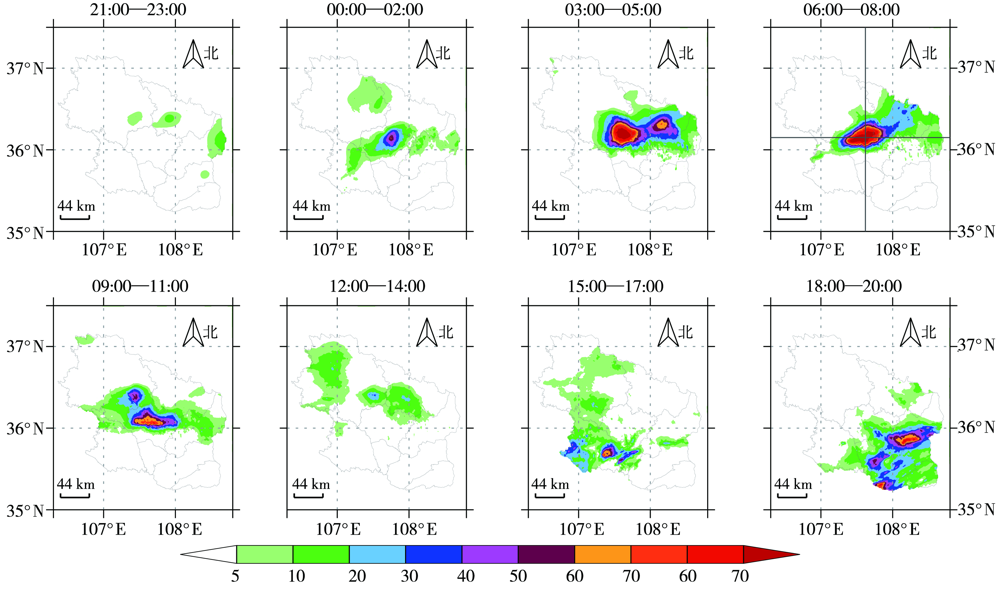
Fig.6 The variation of hourly precipitation of short-term heavy rain at the typical representative stations from 21:00 BST 14 to 20:00 BST 15 July 2022 in Qingyang
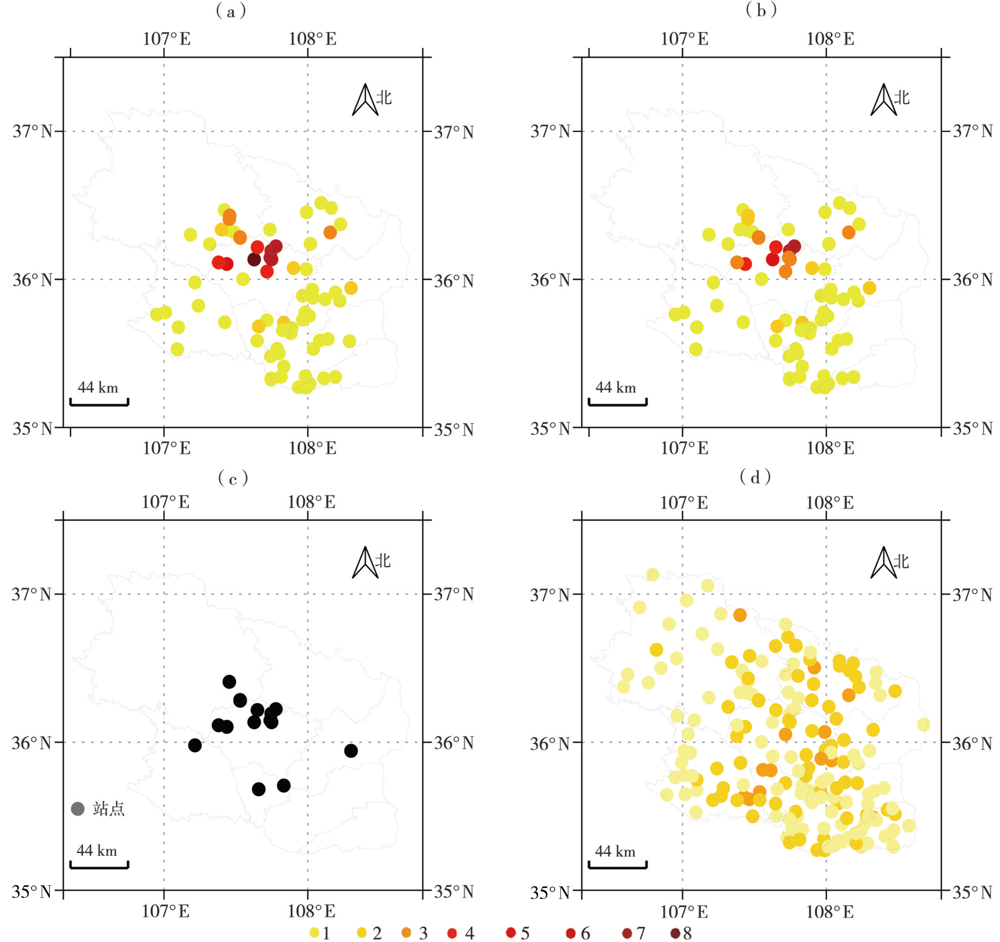
Fig.7 The distribution of occurring times (a, Unit: times) and duration (b, Unit: h) of short-term heavy rain and stations with extreme rainfall intensity of short-term heavy rain (c) from 20:00 BST 14 to 20:00 BST 15 July 2022, and the distribution of longest duration of short-term heavy rain before this process (d, Unit: h) in Qingyang

Fig.9 The longitude-time section along 36.15°N (a) and latitude-time section along 107.6°E (b) of hourly precipitation from 21:00 BST 14 to 20:00 BST 15 July 2022 in Qingyang (Unit: mm)
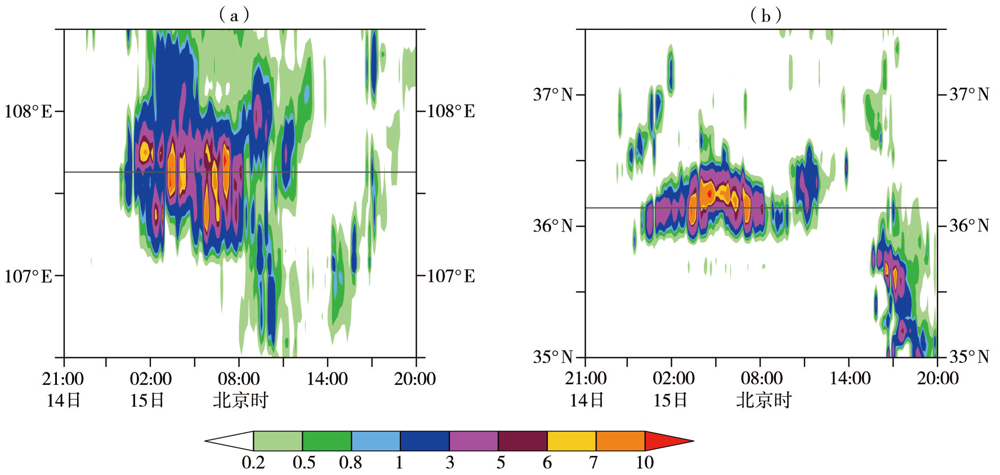
Fig.10 The longitude-time section along 36.15°N (a) and latitude-time section along 107.6°E (b) of 10-minitue precipitation from 21:00 BST 14 to 20:00 BST 15 July 2022 in Qingyang (Unit: mm)
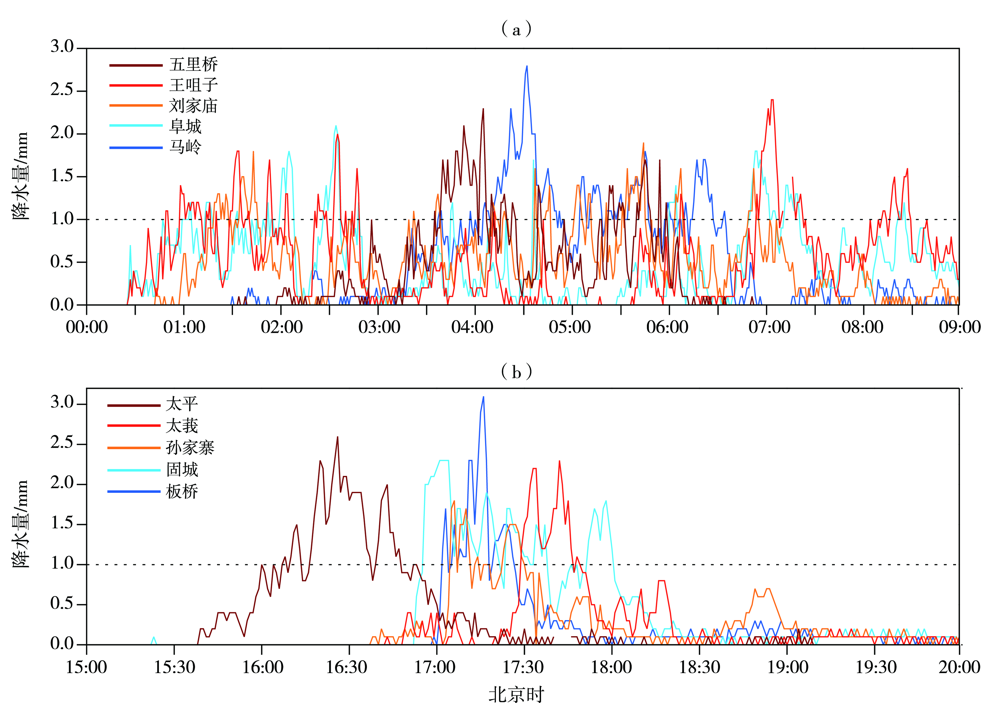
Fig.11 Minutely precipitation evolution at typical representative stations from 00:00 BST to 09:00 BST (a) and from 15:00 BST to 20:00 BST (b) on 15 July 2022
| [1] | 郑国光, 矫梅燕, 丁一汇, 等. 中国气候[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2019. |
| [2] | 丁一汇, 蔡则怡, 李吉顺. 1975年8月上旬河南特大暴雨的研究[J]. 大气科学, 1978, 2(4): 276-289. |
| [3] | 丁一汇. 论河南“75·8”特大暴雨的研究: 回顾与评述[J]. 气象学报, 2015, 73(3): 411-424. |
| [4] | 李泽椿谌芸, 张芳华, 等. 由河南“75·8”特大暴雨引发的思考[J]. 气象与环境科学, 2015, 38(3): 1-12. |
| [5] | 杨浩, 周文, 汪小康, 等. “21·7”河南特大暴雨降水特征及极端性分析[J]. 气象, 2022, 48(5): 571-579. |
| [6] | 梁旭东, 夏茹娣, 宝兴华, 等. 2021年7月河南极端暴雨过程概况及多尺度特征初探[J]. 科学通报, 2022, 67(10): 997-1011. |
| [7] | 张哲, 戚友存, 李东欢, 等. 2021年郑州“7·20”极端暴雨雨滴谱特征及其对雷达定量降水估测的影响[J]. 大气科学, 2022, 46(4): 1002-1016. |
| [8] | 齐道日娜, 何立富, 王秀明, 等. “7·20”河南极端暴雨精细观测及热动力成因[J]. 应用气象学报, 2022, 33(1):1-15. |
| [9] | 苏爱芳, 席乐, 吕晓娜, 等. 豫北“21·7”极端暴雨过程特征及成因分析[J]. 气象, 2022, 48(5): 556-570. |
| [10] | 景丞, 陶辉, 王艳君, 等. 基于区域气候模式CCLM的中国极端降水事件预估[J]. 自然资源学报, 2017, 32(2): 266-277. |
| [11] | 江志红, 陈威霖, 宋洁, 等. 7个IPCC AR4模式对中国地区极端降水指数模拟能力的评估及其未来情景预估[J]. 大气科学, 2009, 33(1): 109-120. |
| [12] | 陈海山, 范苏丹, 张新华. 中国近50 a极端降水事件变化特征的季节性差异[J]. 大气科学学报, 2009, 32(6): 744-751. |
| [13] | 高荣, 宋连春, 钟海玲. 2016年汛期中国降水极端特征及与1998年对比[J]. 气象, 2018, 44(5): 699-703. |
| [14] |
卢珊, 胡泽勇, 王百朋, 等. 近56年中国极端降水事件的时空变化格局[J]. 高原气象, 2020, 39(4): 683-693.
DOI |
| [15] |
WEN X, FANG G, QI H, et al. Changes of temperature and precipitation extremes in China: past and future[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 2015, 126(1/2): 369-383.
DOI URL |
| [16] | HAN J, DU H, WU Z, et al. Changes in extreme precipitation over dry and wet regions of China during 1961-2014[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2019, 124: 5847-5859. |
| [17] | 周璇, 孙继松, 张琳娜, 等. 华北地区持续性极端暴雨过程的分类特征[J]. 气象学报, 2020, 78(5): 761-777. |
| [18] | 刘海文, 丁一汇. 华北夏季降水的年代际变化[J]. 应用气象学报, 2011, 22(2): 129-137. |
| [19] |
ZHAI P, ZHANG X, WAN H, et al. Trends in total precipitation and frequency of daily precipitation extremes over China[J]. Journal of Climate, 2005, 18(7): 1096-1108.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
ZHOU X, BAI Z, YANG Y. Linking trends in urban extreme rainfall to urban flooding in China[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2017, 37(13): 4586-4593.
DOI URL |
| [21] | 谌芸, 孙军, 徐珺, 等. 北京721特大暴雨极端性分析及思考(一)观测分析及思考[J]. 气象, 2012, 38(10): 1255-1266. |
| [22] | 陈涛, 张芳华, 于超, 等. 2020年6—7月长江中下游极端梅雨天气特征分析[J]. 气象, 2020, 46(11):1415-1426. |
| [23] | 张霞, 杨慧, 王新敏, 等. “21·7”河南极端强降水特征及环流异常性分析[J]. 大气科学学报, 2021, 44(5): 672-687. |
| [24] | 孙军, 谌芸, 杨舒楠, 等. 北京721特大暴雨极端性分析及思考(二)极端性降水成因初探及思考[J]. 气象, 2012, 38(10): 1267-1277. |
| [25] | 吕林宜, 王新敏, 栗晗. 华东区域模式对河南“7·19”特大暴雨的数值检验与分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 2019, 42(1): 101-109. |
| [26] | 王宇虹, 徐国强, 贾丽红, 等. 太行山对北京“7.21”特大暴雨的影响及水汽敏感性分析的数值研究[J]. 气象, 2015, 41(4): 389-400. |
| [27] | 赵海英, 薄燕青, 邱贵强, 等. 地形对山西暴雨影响的数值模拟研究[J]. 气象与环境科学, 2017, 40(2): 84-91. |
| [28] | 汪小康, 崔春光, 王婧羽, 等. “21·7”河南特大暴雨水汽和急流特征诊断分析[J]. 气象, 2022, 48(5): 533-544. |
| [29] |
XU H, DUAN Y, XU X. Indirect effects of binary typhoons on an extreme rainfall event in Henan Province, China from 19 to 21 July 2021. Part I: Ensemble-based analysis[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2022, 127, e2021JD036265. DOI:10.1029/2021JD036265.
DOI |
| [30] |
XU H, DUAN Y, LI Y, et al. Indirect effects of binary typhoons on an extreme rainfall event in Henan Province, China from July 19 to 21, 2021. Part II: Numerical study[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2022, e2021JD036083. DOI:10.1029/2021JD036083.
DOI |
| [31] | 陈婕, 黄伟, 靳立亚, 等. 东亚夏季风的气候北界指标及其年际变化研究[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2018, 48(1): 93-101. |
| [32] | 刘玉芝, 吴楚樵, 贾瑞, 等. 大气环流对中东亚干旱半干旱区气候影响研究进展[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2018, 48(9): 1141-1152. |
| [33] | 李栋梁, 谢金南, 王文. 中国西北夏季降水特征及其异常研究[J]. 大气科学, 1997, 21(3): 331-340. |
| [34] | 赵庆云, 宋松涛, 杨贵名, 等. 西北地区暴雨时空变化及异常年夏季环流特征[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 50(4): 517-522. |
| [35] | 王晖, 隆霄, 马旭林, 等. 近50 a中国西北地区东部降水特征[J]. 干旱区研究, 2013, 30(4): 712-718. |
| [36] | 黄玉霞, 王宝鉴, 黄武斌, 等. 我国西北暴雨的研究进展[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2019, 38(5): 515-525. |
| [37] |
刘新伟, 王澄海, 郭润霞, 等. 1981—2018年甘肃省极端暴雨天气过程的气候与环流特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(5): 750-758.
DOI |
| [38] | 汤旭, 钱维宏, 梁萍. 东亚夏季风边缘带的气候特征[J]. 高原气象, 2006, 25(3): 375-381. |
| [39] | 李栋梁, 吕兰芝. 中国农牧交错带的气候特征与演变[J]. 中国沙漠, 2002, 22(5): 76-81. |
| [40] | 江志红, 卢尧, 丁裕国. 基于时空结构指标的中国融合降水资料质量评估[J]. 气象学报, 2013, 71(5): 891-900. |
| [41] | 宇婧婧, 沈艳, 潘旸, 等. 中国区域逐日融合降水数据集与国际降水产品的对比评估[J]. 气象学报, 2015, 73(2): 394-410. |
| [42] | 孙帅, 师春香, 潘旸, 等. 中国区域三源融合降水产品的改进效果评估[J]. 水文, 2020, 40(6): 10-15. |
| [43] | 俞小鼎. 短时强降水临近预报的思路与方法[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2013, 32(3): 202-209. |
| [1] | SHA Honge, FU Zhao, LIU Weicheng, XU Lili, LIU Na, LIU Xinyu, MA Yihao. Mechanism of trigger and maintenance during an extremely torrential rain in semi-arid region of eastern Northwest China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 933-944. |
| [2] | YANG Yang, QI Yue, ZHAO Hong, MA Yihao, ZHU Dan. Effects and evaluations of water stress on growth development and yield of maize during critical growth periods in arid and semi-arid regions [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 1059-1067. |
| [3] | LI Yu, WANG Xiaohen, LUO Xinpin, KANG Shuhe, CHEN Chen, ZHANG Qiang. Influence of Climate Change on Bioavailability of Micronutrients in Crops in Semiarid Area [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(6): 895-899. |
| [4] | ZHANG Ning, LIU Kenan, WANG Suichan, WANG Ji, CHEN Ziyan. Spatial and Temporal Distribution Characteristics of Short-term Strong Rainfall and Topography Causes in Lanzhou [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(2): 242-248. |
| [5] | WANG Jun. Analysis of Extremity and Mesoscale Characteristic on Two Torrential Rain Processes in North He’nan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(3): 419-. |
| [6] | WANG Jian, TONG Jilong, XIAO Yiqing, WU Xiaoyan, ZHANG Wenyu. Interdecadal Variation Characteristics of Summer Sensible Heat Flux in Typical Arid and Semi-Arid Areas of East Asia [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(2): 203-211. |
| [7] | ZHANG Kai1, WANG Runyuan1, WANG Heling1, ZHAO Hong1,QI Yue1, ZHAO Funian1, CHEN Fei1, LEI Jun2. Effects of Elevated CO2 Concentration on Growth and Yield of Spring Wheat Based on Observational Experiment in Semi-arid Area [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(2): 306-312. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||