Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 222-233.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-02-0222
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Characteristics and differences of rainstorm in the southern Xinjiang during warm season under different climatic backgrounds
YANG Xia1( ), XU Tingting1, ZHANG Linmei1, HUA Ye1, ZHOU Hongkui2
), XU Tingting1, ZHANG Linmei1, HUA Ye1, ZHOU Hongkui2
- 1. Xinjiang Meteorological Observatory, Urumqi 830002, China
2. Xinjiang Meteorological Information Center, Urumqi 830002, China
-
Received:2021-01-22Revised:2021-03-19Online:2022-04-30Published:2022-05-10
不同气候背景下南疆暖季暴雨特征和差异
- 1.新疆维吾尔自治区气象台,新疆 乌鲁木齐 830002
2.新疆维吾尔自治区气象信息中心,新疆 乌鲁木齐 830002
-
作者简介:杨霞(1980— ),女,甘肃武威人,硕士,正研级高级工程师,主要从事灾害性天气机理和预报技术研究. E-mail: Yangxia921@163.com。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金地区基金项目(42065001);国家自然科学基金重点项目(42030612);第二次青藏高原综合科学考察研究项目(2019QZKK0102)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
YANG Xia, XU Tingting, ZHANG Linmei, HUA Ye, ZHOU Hongkui. Characteristics and differences of rainstorm in the southern Xinjiang during warm season under different climatic backgrounds[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(2): 222-233.
杨霞, 许婷婷, 张林梅, 华烨, 周鸿奎. 不同气候背景下南疆暖季暴雨特征和差异[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(2): 222-233.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-02-0222

Fig.1 The terrain (the shadow, Unit: m, the same as below) and distribution of meteorological stations (the red dots are the capital sites, the green dots are the mountain sites, the blue dots are plain sites) in the southern Xinjiang
| 时段 | 暴雨日数/ d | 暴雨站次 | 暴雨雨量/ mm | 暴雨强度/ (mm·d-1) | 暴雨雨量占 总降水比例/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 暖干期 | 47.3 | 64 | 2051.8 | 31.1 | 10.0 |
| 暖湿期 | 62.3 | 89 | 2932.7 | 32.7 | 10.6 |
Tab.1 The rainstorm days, rainstorm stations, rainstorm rainfall, rainstorm intensity and proportion of rainstorm rainfall in total precipitation in southern Xinjiang in the warm-dry periods and the warm-wet periods from May to September during 1961-2020
| 时段 | 暴雨日数/ d | 暴雨站次 | 暴雨雨量/ mm | 暴雨强度/ (mm·d-1) | 暴雨雨量占 总降水比例/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 暖干期 | 47.3 | 64 | 2051.8 | 31.1 | 10.0 |
| 暖湿期 | 62.3 | 89 | 2932.7 | 32.7 | 10.6 |
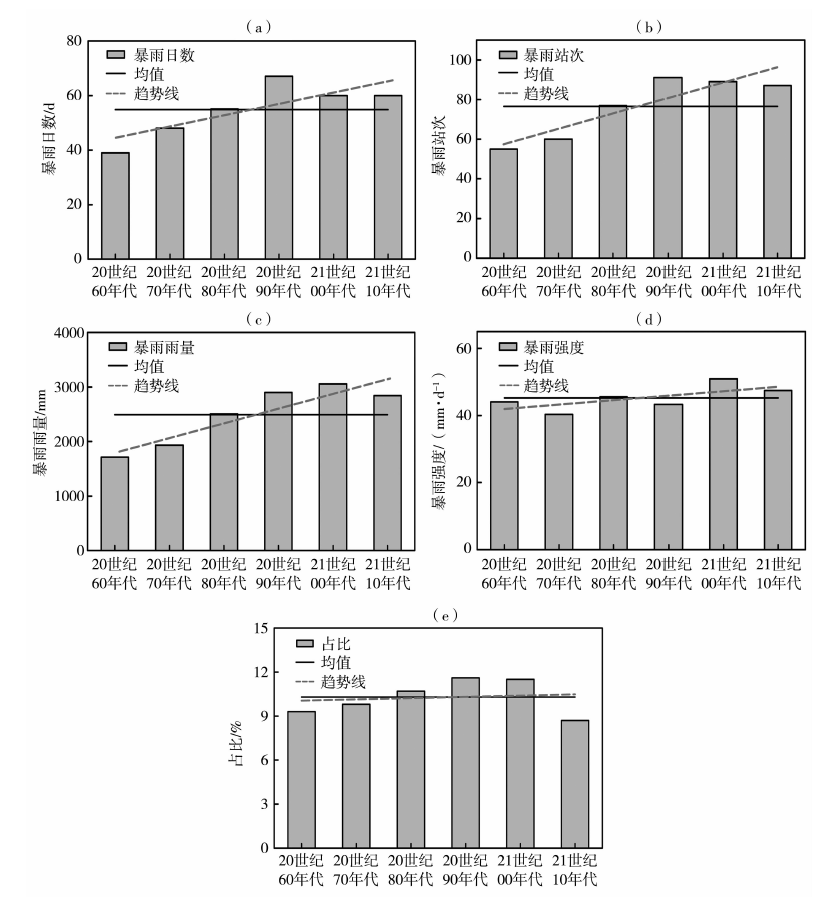
Fig.2 The interdecadal variation of rainstorm days (a), rainstorm stations (b), rainstorm rainfall (c), daily rainstorm intensity (d) and proportion of rainstorm rainfall in total precipitation (e) in the southern Xinjiang from May to September during 1961-2020

Fig.3 The spatial distribution of accumulated rainstorm days (the clolor dots) in the southern Xinjiang during the warm season (Unit: d) (a) the 1960s, (b) the 1970s, (c) the 1980s, (d) the 1990s, (e) the 2000s, (f) the 2010s, (g) the warm-dry periods, (h) the warm-wet periods

Fig.4 The spatial distribution of accumulated rainstorm rainfall (the clolor dots) in the southern Xinjiang during the warm season (Unit: mm) (a) the 1960s, (b) the 1970s, (c) the 1980s, (d) the 1990s, (e) the 2000s, (f) the 2010s, (g) the warm-dry periods, (h) the warm-wet periods

Fig.5 The spatial distribution of rainstorm intensity (the clolor dots) in the southern Xinjiang during the warm season (Unit: mm·d-1) (a) the 1960s, (b) the 1970s, (c) the 1980s, (d) the 1990s, (e) the 2000s, (f) the 2010s, (g) the warm-dry periods, (h) the warm-wet periods

Fig.6 The spatial distribution of percentage of rainstorm rainfall in total precipitation (the clolor dots) in the southern Xinjiang during the warm season (Unit: %) (a) the 1960s, (b) the 1970s, (c) the 1980s, (d) the 1990s, (e) the 2000s, (f) the 2010s, (g) the warm-dry periods, (h) the warm-wet periods
| 时期 | 低槽型暴雨 | 低涡型暴雨 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 发生次数/次 | 占比/% | 发生次数/次 | 占比/% | ||
| 暖干期 | 12 | 41.4 | 17 | 58.6 | |
| 暖湿期 | 37 | 82.2 | 8 | 17.8 | |
Tab.2 The statistics of rainstorm processes of different types in the southern Xinjiang in the warm-dry periods and the warm-wet periods from May to September during 1961-2020
| 时期 | 低槽型暴雨 | 低涡型暴雨 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 发生次数/次 | 占比/% | 发生次数/次 | 占比/% | ||
| 暖干期 | 12 | 41.4 | 17 | 58.6 | |
| 暖湿期 | 37 | 82.2 | 8 | 17.8 | |
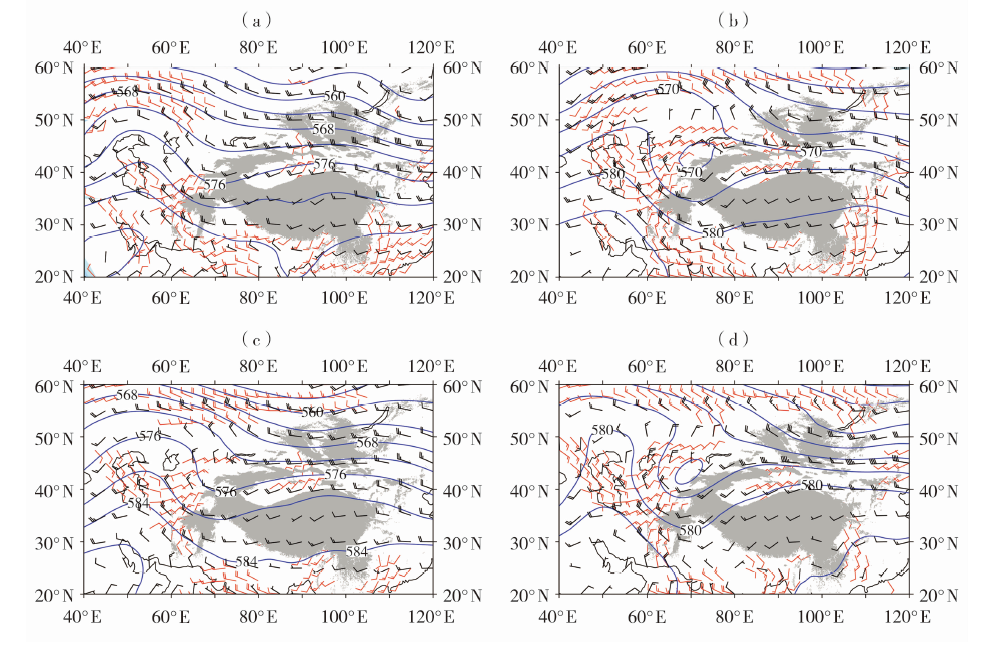
Fig.7 The composition of geopotential height field (blue lines, Unit: dagpm), wind field (black wind barbs, Unit: m·s-1) at 500 hPa and wind field at 850 hPa (red wind barbs, only plotting wind speed greater than or equal to 4 m·s-1) of low trough rainstorm (a, c) and low vortex rainstorm (b, d) in the warm-dry periods (a, b) and the warm-wet periods (c, d) in the southern Xinjiang (the gray shaded area for terrain greater than or equal to 1500 m, the same as below)
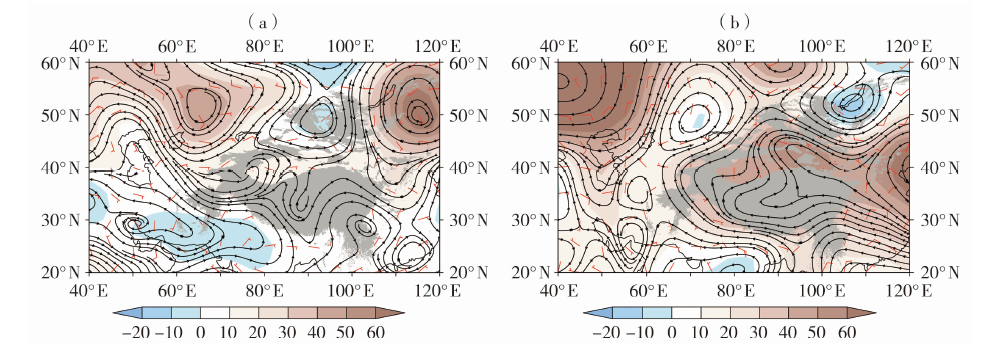
Fig.8 The difference of geopotential height field (color shaded area, Unit: gpm), flow field (black line) at 500 hPa and wind field at 850 hPa (red wind barbs) of low trough rainstorm (a) and low vortex rainstorm (b) in the warm-wet periods and the warm-dry periods in the southern Xinjiang
| [1] | TAO S, DING Y. Observational evidence of the influence of the Qinghai Xizang (Tibet) Plateau on the occurrence of heavy rain and severe convective storms in China[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Societ, 1981, 62(1):23-30. |
| [2] | 陶诗言. 中国之暴雨[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1980:255. |
| [3] | 郑小华, 娄盼星, 马永永, 等. 2018年陕西省暴雨灾害气象服务效益评估[J]. 气象与环境科学, 2022, 45(1):90-95. |
| [4] | 司福意, 张一平, 赵海青, 等. 豫北“7·9”特大暴雨的形成与极端性探析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 2021, 44(1):65-73. |
| [5] | 宋清芝, 吕林宜. 黄河中游一次致洪暴雨过程的形成机理[J]. 气象与环境科学, 2018, 41(2):54-61. |
| [6] | 丁一汇. 暴雨和中尺度气象学问题[J]. 气象学报, 1994, 52(3):274-284. |
| [7] | 高守亭, 赵思雄, 周晓平, 等. 次天气尺度及中尺度暴雨系统研究进展[J]. 大气科学, 2003, 27(4):618-627. |
| [8] | 鲍名, 黄荣辉. 近40年中我国暴雨的年代际变化特征[J]. 大气科学, 2006, 30(6):1057-1067. |
| [9] | 王军, 席乐, 王超杰, 等. “温比亚”引发河南特大暴雨的中尺度系统特征分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 2021, 44(4):16-23. |
| [10] | 林建, 杨贵名. 近30年中国暴雨时空特征分析[J]. 气象, 2014, 40(7):816-826. |
| [11] | 黄荣辉, 陈际龙, 刘永. 我国东部夏季降水异常主模态的年代际变化及其与东亚水汽输送的关系[J]. 大气科学, 2011, 35(4):589-606. |
| [12] | 陈栋, 陈际龙, 黄荣辉, 等. 中国东部夏季暴雨的年代际跃变及其大尺度环流背景[J]. 大气科学, 2016, 40(3):581-590. |
| [13] | 罗连升, 徐敏, 何冬燕. 2000年以来淮河流域夏季降水年代际特征及大气环流异常[J]. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(4):540-549. |
| [14] | 张庆云, 陶诗言, 张顺利. 夏季长江流域暴雨洪涝灾害的天气气候条件[J]. 大气科学, 2003, 27(6):1018-1030. |
| [15] |
NING L, QIAN Y F. Interdecadal change in extreme precipitation over south China and its mechanism[J]. Advances in atmospheric sciences, 2009, 26(1):109-118.
DOI URL |
| [16] | 刘小宁. 我国暴雨极端事件的气候变化特征[J]. 灾害学, 1999, 14(1):54-59. |
| [17] |
史培军, 孔峰, 方佳毅. 中国年代际暴雨时空变化格局[J]. 地理科学, 2014, 34(11):1281-1290.
DOI |
| [18] | 李柔珂, 李耀辉, 徐影. 未来中国地区的暴雨洪涝灾害风险预估[J]. 干旱气象, 2018, 36(3):341-352. |
| [19] | 张家宝, 苏起元, 孙沈清, 等. 新疆短期天气预报指导手册[M]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆人民出版社, 1986. |
| [20] | 马淑红, 席元伟. 新疆暴雨的若干规律性[J]. 气象学报, 1997, 55(2):239-248. |
| [21] | 程善俊, 梁苏洁. 基于3种指数的全球干湿变化年代际特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2018, 36(2):176-184. |
| [22] | 施雅风, 沈永平, 李栋梁, 等. 中国西北气候由暖干向暖湿转型的特征和趋势探讨[J]. 第四纪研究, 2003, 23(2):152-164. |
| [23] | 韩萍, 薛燕, 苏宏超. 新疆降水在气候转型中的信号反映[J]. 冰川冻土, 2003, 25(2):179-182. |
| [24] | 蓝永超, 沈永平, 苏宏超, 等. 全球变暖情景下新疆降水的变化[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2008, 22(10):66-71. |
| [25] | 杨莲梅. 新疆极端降水的气候变化[J]. 地理学报, 2003, 58(4):577-583. |
| [26] | 张家宝, 邓子风. 新疆降水概论[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 1987. |
| [27] |
杨霞, 李云, 赵逸舟, 等. 新疆一次深秋局地短时大暴雨的成因分析[J]. 高原气象, 2014, 33(1):162-170.
DOI |
| [28] | 杨霞, 张云惠, 张超, 等. 南疆西部“5·21”极端大暴雨成因分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 2020, 4(1):1-30. |
| [29] | 努尔比亚·吐尼牙孜, 张超, 李泽巍, 等. 南疆西部2016年8月4次暴雨过程特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(2):301-311. |
| [30] | 张云惠, 李海燕, 蔺喜禄, 等. 南疆西部持续性暴雨环流背景及天气尺度的动力过程分析[J]. 气象, 2015, 41(7):816-824. |
| [31] | 杨霞, 周鸿奎, 许婷婷, 等. 南疆夏季不同类型暴雨的精细化特征对比分析[J]. 干旱区研究, 2021, 38(3):747-756. |
| [1] | JIAO Yang, ZHANG Yongjing, YIN Chengmei, CHU Yingjia, . Response of summer rainstorm in Shandong Province to change of spring atmospheric heat sources in southeastern Tibet Plateau and its adjacent areas [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(3): 406-414. |
| [2] | MA Simin, MU Jianhua, SHU Zhiliang, SUN Yanqiao, DENG Peiyun, ZHOU Nan, . Topography sensitivity simulation test of a typical rainstorm process in Liupan Mountain region [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(3): 457-468. |
| [3] | SHEN Xiaoling, PAN Lingjie, ZUO Jun, SANG Minghui, ZHANG Lina. Comparative analysis on two similar falling area rainstorms during Meiyu period in western Zhejiang Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(2): 244-255. |
| [4] | GOU Aning, WU Cuihong, WANG Yujuan, DU Muyun, LIU Wenting, LENG Liang, DENG Hong. Meso and small-scale characteristics of heavy rain during Meiyu period in Hubei based on wind profile radar [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(1): 84-94. |
| [5] | HE Fen, LAI Shaojun, CHI Yanzhen, PAN Hang, CAO Rong, BAO Ruijuan. Variation characteristics of drought circulation in Fujian Province from March to June 2018 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(1): 22-29. |
| [6] | ZHUANG Xiaocui, LI Boyuan, ZHAO Jiangwei, LI Jiangang, ZHANG Linmei. Water vapor source and transport characteristics of rainstorm processes in warm season on southern slope of the Tianshan Mountains [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(1): 30-40. |
| [7] | LIU Xinwei,WANG Chenghai,GUO Runxia,YANG Xiaojun,DI Xiaohong. Climate and Circulation Characteristics of Extreme Rainstorm Processes in Gansu from 1981 to 2018 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(5): 750-758. |
| [8] | YANG Wei,FENG Wen,ZENG Li,CHEN Youlong. Temporal and Spatial Distribution and Anomalous Circulation Characteristics of Winter Rainstorms in Hainan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(5): 759-765. |
| [9] | SHI Rui, HE Guangbi, ZHOU Chunhua. Condition of Water Vapor and Multi-scale System During a Continuous Heavy Rainfall Process in Sichuan [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(3): 415-425. |
| [10] | FENG Yao, Ayixianmu·niyazi, Reyila·yunusi. Cause Analysis of an Extreme Heavy Rainstorm Process on July 31 of 2018 in Hami of Xinjiang [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(3): 426-435. |
| [11] | ZHAO Zhinan, WANG Lirong, WANG Congmei, HAN Xiaoqing. Risk Distribution Characteristics of Rainstorm and Flood Disaster Based on Flood Area Model in the Xiaoma River Basin of Xingtai [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(3): 486-493. |
| [12] |
WANG Jiajin, ZHANG Qi, ZHANG Tao, LONG Keji, SHI Rui, .
Low-level Wind Field Characteristic Observed by Wind Profile Radar During Two Rainstorm Processes in Chengdu#br#
#br#
[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(1): 87-95.
|
| [13] | QIU Yixuan, REN Xiaofeng, YANG Xueyan, JIANG Zhongbao, LI Yufan. Rainstorm Intensity Formula and Design Rainstorm Pattern for Jilin City [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(1): 151-158. |
| [14] | WANG Xiaoci, LI Shuangjun, MENG Yingjie. Characteristics and difference analysis of main rainstorm processes in Yangtze River Basin from June to July during 2016-2020 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(06): 921-929. |
| [15] | WEI Yanying, GONG Meiling, LI Haihua. Spatial-temporal distribution and influence of disastrous rainstorm in southern Xinjiang during 2010-2019 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(06): 930-938. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||