Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (4): 549-566.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-04-0549
• Overview • Previous Articles Next Articles
New progress and prospect of drought research since the 21st century
WANG Ying1( ), ZHANG Qiang1,2(
), ZHANG Qiang1,2( ), WANG Jinsong1, HAN Lanying1,3, WANG Suping1, ZHANG Liang1, YAO Yubi1,4, HAO Xiaocui1, WANG Sheng1
), WANG Jinsong1, HAN Lanying1,3, WANG Suping1, ZHANG Liang1, YAO Yubi1,4, HAO Xiaocui1, WANG Sheng1
- 1. Institute of Arid Meteorology, China Meteorological Administration, Key Laboratory of Arid Climatic Change and Reducing Disaster of Gansu Province, Key Open Laboratory of Arid Climate Change and Disaster Reduction of CMA, Lanzhou 730020, China
2. Gansu Provincial Meteorological Bureau, Lanzhou 730020, China
3. Lanzhou Regional Climate Center, Lanzhou 730020, China
4. Lanzhou Resources & Environment Voc-Tech University, Lanzhou 730021, China
-
Received:2022-04-03Revised:2022-06-01Online:2022-08-31Published:2022-09-21 -
Contact:ZHANG Qiang
21世纪以来干旱研究的若干新进展与展望
王莺1( ), 张强1,2(
), 张强1,2( ), 王劲松1, 韩兰英1,3, 王素萍1, 张良1, 姚玉璧1,4, 郝小翠1, 王胜1
), 王劲松1, 韩兰英1,3, 王素萍1, 张良1, 姚玉璧1,4, 郝小翠1, 王胜1
- 1. 中国气象局兰州干旱气象研究所,甘肃省干旱气候变化与减灾重点实验室/中国气象局干旱气候变化与减灾重点开放实验室,甘肃 兰州 730020
2. 甘肃省气象局,甘肃 兰州 730020
3. 兰州区域气候中心,甘肃 兰州 730020
4. 兰州资源环境职业技术大学,甘肃 兰州 730021
-
通讯作者:张强 -
作者简介:王莺(1984—),女,研究员,博士,从事干旱灾害风险评估研究. E-mail: wangyn924@163.com。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金重点项目(42230611);国家自然科学基金(41630426);甘肃省基础研究创新群体(20JR5RA121);甘肃省自然科学基金(21JR7RA696);中国气象局兰州干旱气象研究所创新团队(GHSCXTD-2020-2)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
WANG Ying, ZHANG Qiang, WANG Jinsong, HAN Lanying, WANG Suping, ZHANG Liang, YAO Yubi, HAO Xiaocui, WANG Sheng. New progress and prospect of drought research since the 21st century[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(4): 549-566.
王莺, 张强, 王劲松, 韩兰英, 王素萍, 张良, 姚玉璧, 郝小翠, 王胜. 21世纪以来干旱研究的若干新进展与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(4): 549-566.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-04-0549
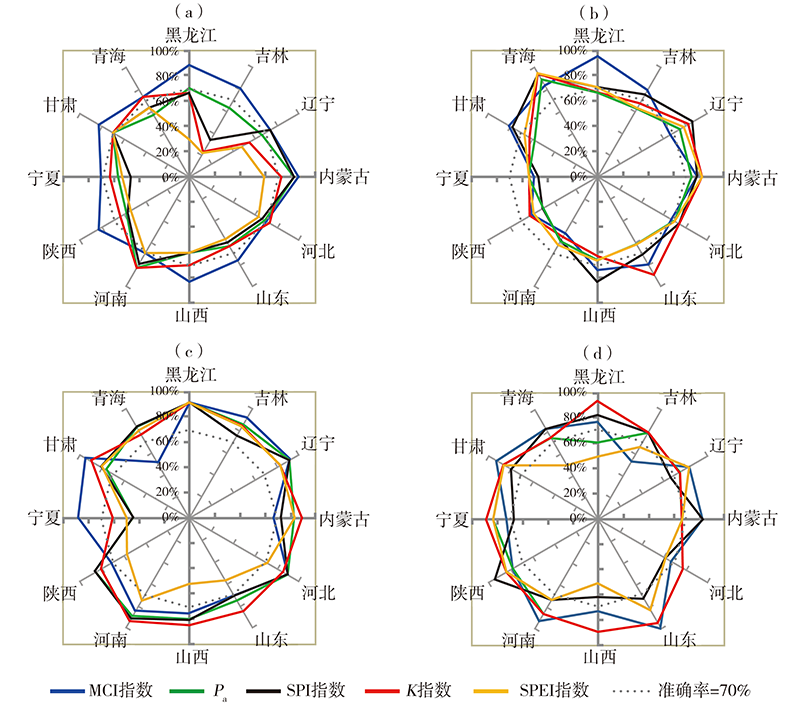
Fig.1 The monitoring accuracy of each drought index for different regions and different seasons (cited from literature [31]) (a) spring, (b) summer, (c) autumn, (d) winter
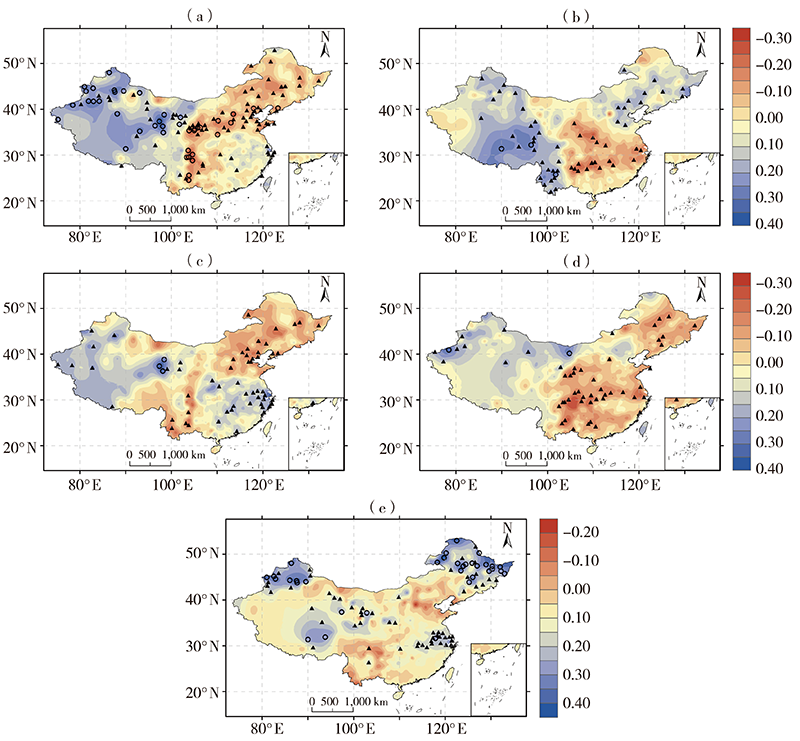
Fig.2 Spatial distributions of the trend of SPI from 1960 to 2011 (cited from literature [35])(○ and ▲ represent passing the confidence level of 99.9% and 95%, respectively) (a) the whole year, (b) spring, (c) summer, (d) autumn, (e) winter
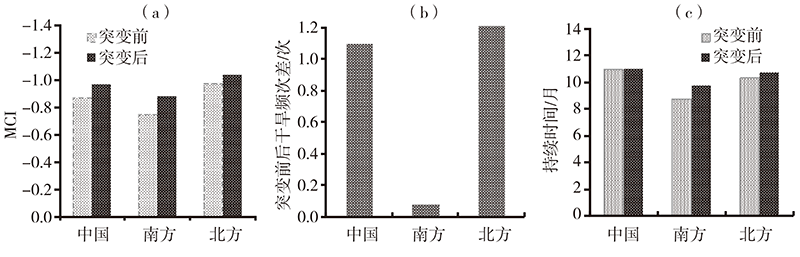
Fig.3 Variation of drought severity (a), frequency (b) and duration (c) before and after temperature abrupt change in China (cited from literature [37])
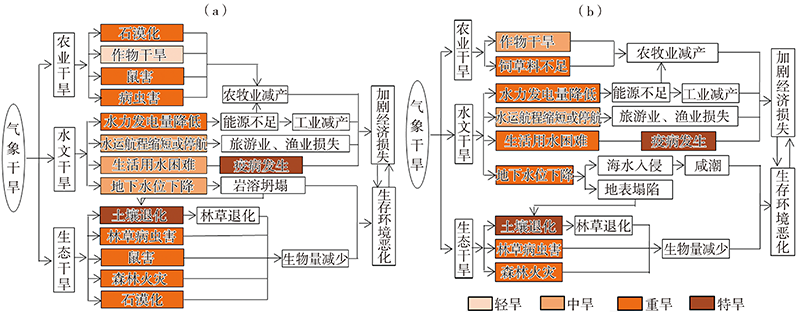
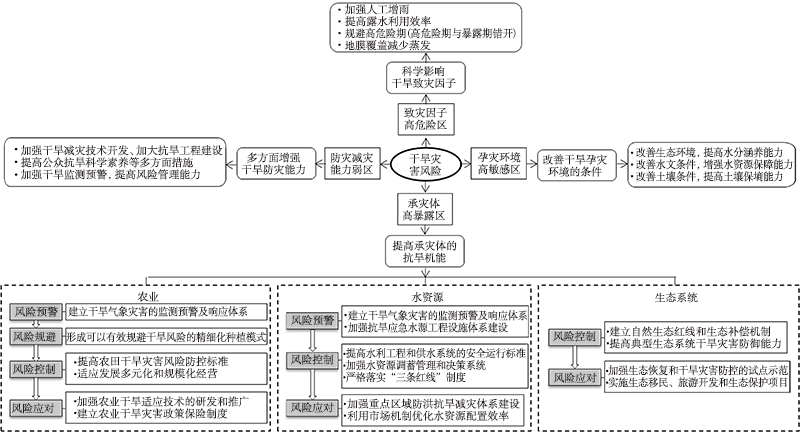
Fig.5 Drought disaster chain in southwestern China (a) and South China (b) (modified from literature [47]) (The color labels represent the corresponding disaster-affected body by drought disaster with different levels)
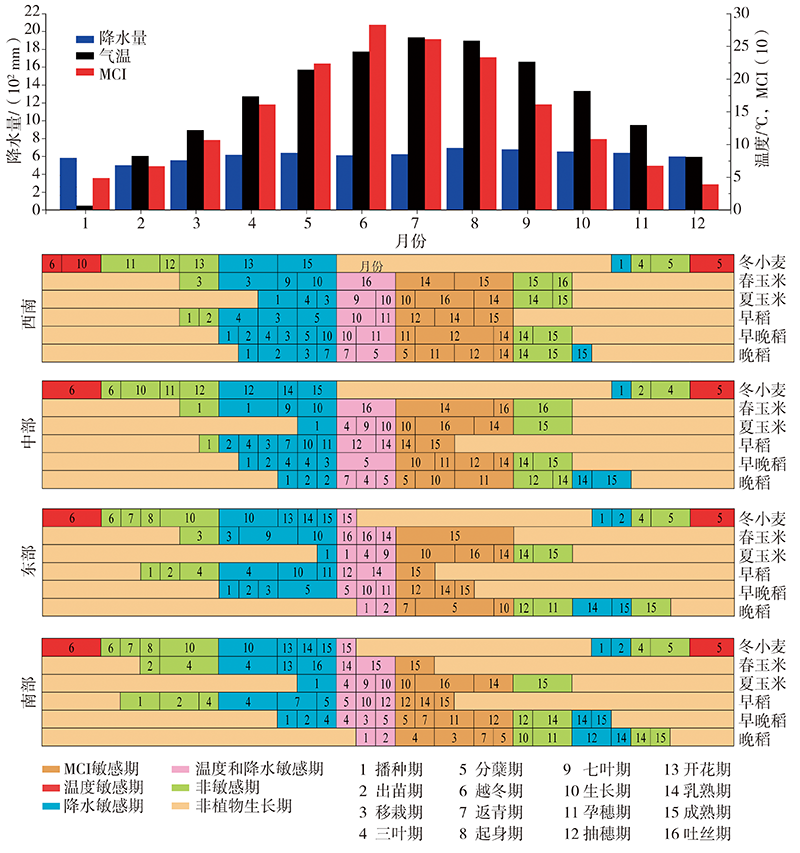
Fig.6 The trends for the three key climate factors (monthly total precipitation, mean temperature and MCI) and their relationships to crop growth and development periods (cited from literature [48])
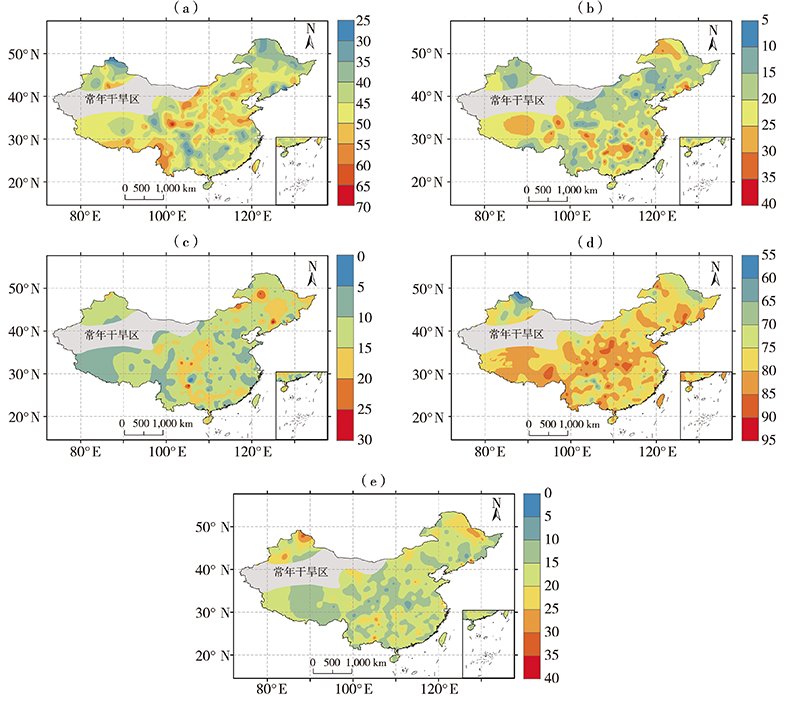
Fig.7 Probability of drought disaster under precipitation deficit at different cumulative time scales (Unit: %) (a) 1 month, (b) 2 months, (c) 3 months, (d) 1-3 months, (e) 4-6 months
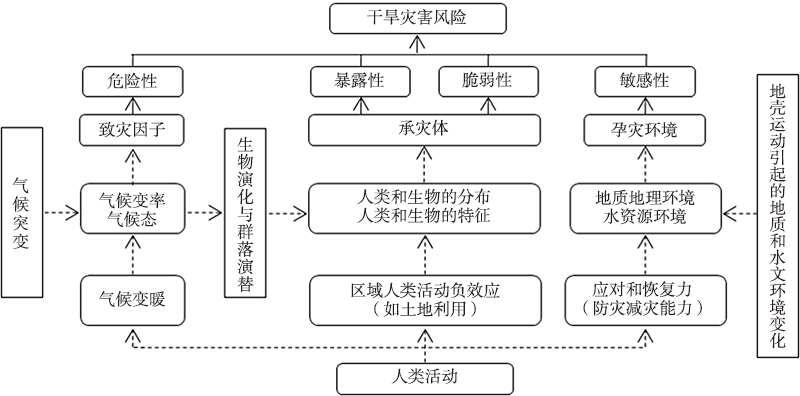
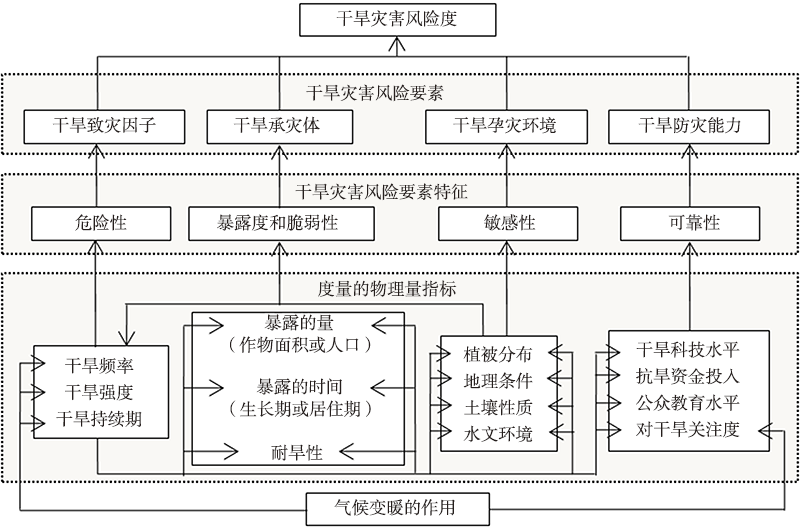
Fig.8 Conceptual model of drought disaster risk formation mechanism (cited from literature [46]) (solid lines for direct impact, and dotted lines for indirect impact)
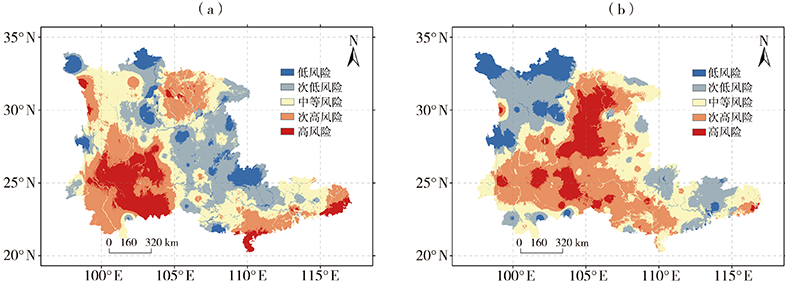
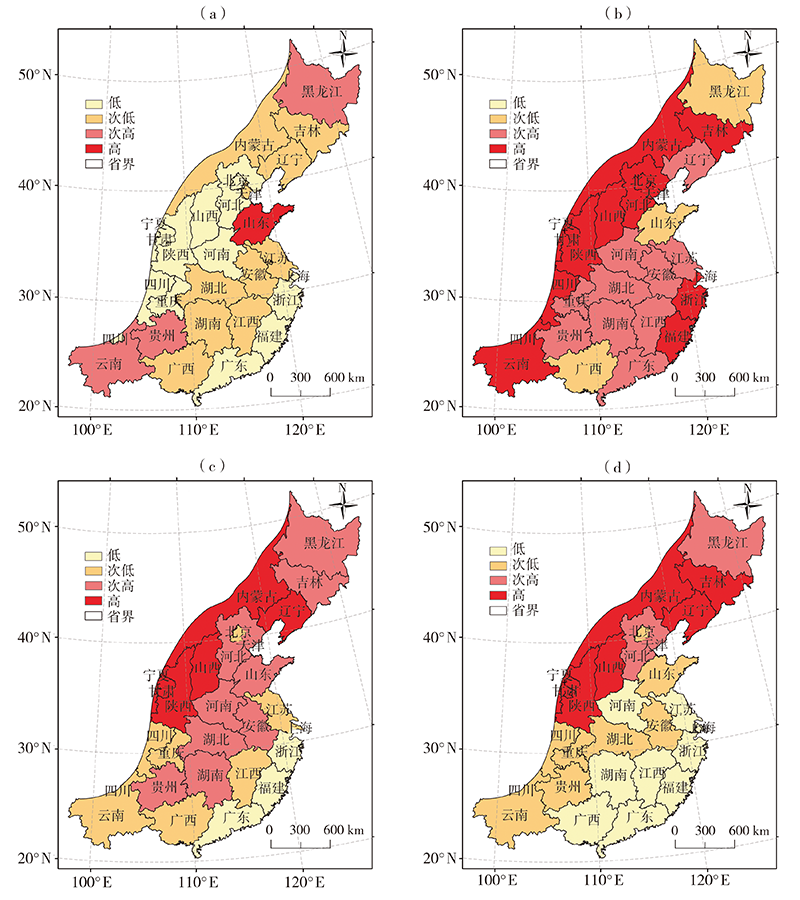
Fig.11 Characteristics of drought disaster risk in South China and southwestern China before (a) and after (b) temperature abrupt change (cited from literature [46])
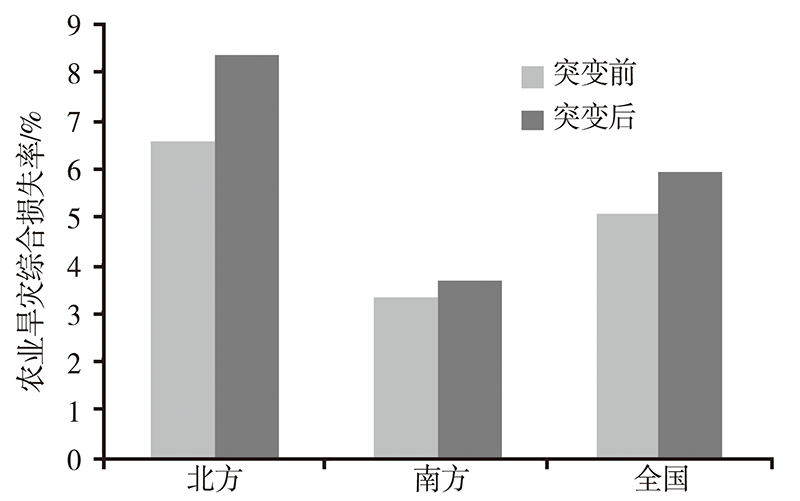
Fig.12 Changes of the average comprehensive loss rate of agriculture drought before and after the increases of annual average temperature in northern, southern China and the whole China (cited from literature [18])
| [1] | CHIANG F, MAZDIYASNI O, AGHAKOUCHAK A. Evidence of anthropogenic impacts on global drought frequency, duration, and intensity[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12, 2754. DOI:10.1038/s41467-021-22314-w. |
| [2] | WITZE A. Native ecosystems blitzed by drought[J]. Nature, 2014, 512:121-122. |
| [3] | ZHANG Y, KEENAN T F, ZHOU S. Exacerbated drought impacts on global ecosystems due to structural overshoot[J]. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 2021, 5: 1490-1498. |
| [4] | 竺可桢. 华北之干旱及其前因后果[J]. 李良骐,译. 地理学报, 1934(2):1-9. |
| [5] | 张强, 张良, 崔显成, 等. 干旱监测与评价技术的发展及其科学挑战[J]. 地球科学进展, 2011, 26(7):763-778. |
| [6] | 周广胜. 气候变化对中国农业生产影响研究展望[J]. 气象与环境科学, 2015, 38(1):80-94. |
| [7] | WANG Q, LIU Y Y, ZHANG Y Z, et al. Assessment of spatial agglomeration of agricultural drought disaster in China from 1978 to 2016[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9, 14393. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-51042-x. |
| [8] | SU B, HUANG J, FISCHER T, et al. Drought losses in China might double between the 1.5 ℃ and 2.0 ℃ warming[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(42): 10 600-10 605. |
| [9] | DOUVILLE H, RAGHAVAN K, RENWICK J, et al. Water cycle changes[M]// IPCC. Climate change 2021: the physical science basis. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2021. |
| [10] | QIU J. China drought highlights future climate threats[J]. Nature, 2010, 465: 142-143. |
| [11] | 张更喜, 粟晓玲, 刘文斐. 考虑CO2浓度影响的中国未来干旱趋势变化[J]. 农业工程学报, 2021, 37(1):84-91. |
| [12] | WANG Y, YUAN X. Anthropogenic speeding up of South China flash droughts as exemplified by the 2019 summer-autumn transition season[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2021, 48(9), e2020GL091901. DOI:10.1029/2020GL091901. |
| [13] | 中国气象局. 2020年中国气候公报[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. 2020. |
| [14] | 袁星, 王钰淼, 张苗, 等. 关于骤旱研究的一些思考[J]. 大气科学学报, 2020, 43(6):1086-1095. |
| [15] | WANG Y, ZHANG Q, WANG S P, et al. Characteristics of agro-meteorological disasters and their risk in Gansu Province against the background of climate change[J]. Natural Hazards, 2017, 89(2):899-921. |
| [16] | BALTING D F, AGHAKOUCHAK A, LOHMANN G, et al. Northern Hemisphere drought risk in a warming climate[J]. Climate and Atmospheric Science, 2021, 4, 61. DOI:10.1038/s41612-021-00218-2. |
| [17] | GETIRANA A, LIBONATI R, CATALDI M. Brazil is in water crisis—it needs a drought plan[J]. Nature, 2021, 600: 218-220. |
| [18] | 张强, 韩兰英, 郝小翠, 等. 气候变化对中国农业旱灾损失率的影响及其南北区域差异性[J]. 气象学报, 2015, 73(6):1092-1103. |
| [19] | 张卓群, 冯冬发, 侯宇恒. 基于Copula函数的黄河流域干旱特征研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2022, 36(1):66-72. |
| [20] | 张强, 姚玉璧, 李耀辉, 等. 中国干旱事件成因和变化规律的研究进展与展望[J]. 气象学报, 2020, 78(3):500-521. |
| [21] | PADMA T V. African nations push UN to improve drought research[J]. Nature, 2019, 573, 319. DOI:10.1038/d41586-019-02760-9. |
| [22] | 王劲松, 郭江勇, 倾继祖. 一种K干旱指数在西北地区春旱分析中的应用[J]. 自然资源学报, 2007, 22(5):709-717. |
| [23] | 王劲松, 任余龙, 宋秀玲. K干旱指数在甘肃省干旱监测业务中的应用[J]. 干旱气象, 2008, 26(4):75-79. |
| [24] | 吴哲红, 詹沛刚, 陈贞宏, 等. 基于CI指数和K指数的近40 a贵州安顺区域干旱演变特征[J]. 冰川冻土, 2013, 35(4): 1044-1055. |
| [25] | WANG J S, WANG S P, LI Y P, et al. A study of the K drought monitoring model[J]. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 2018, 27(1): 335-343. |
| [26] | 郝小翠, 张强, 杨泽粟, 等. 一种基于地表能量平衡的遥感干旱监测新方法及其在甘肃河东地区干旱监测中的应用初探[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016, 59(9): 3188-3201. |
| [27] | ZHANG L, ZHANG H Q, ZHANG Q, et al. On the potential application of land surface models for drought monitoring in China[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 2017, 128(3/4):649-665. |
| [28] | 张良, ZHANG Huqiang, 张强, 等. 应用陆面模式进行干旱监测的过程和实现[J]. 干旱区研究, 2016, 33(3):584-592. |
| [29] | HEIM R R. A review of twentieth-century drought indices used in the United States[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2002, 83(8):1149-1166. |
| [30] | 王作亮, 文军, 李振朝, 等. 典型干旱指数在黄河源区的适宜性评估[J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(21):186-195. |
| [31] | 王素萍, 王劲松, 张强, 等. 多种干旱指数在中国北方的适用性及其差异原因初探[J]. 高原气象, 2020, 39(3):628-640. |
| [32] | 王劲松, 李忆平, 任余龙, 等. 多种干旱监测指标在黄河流域应用的比较[J]. 自然资源学报, 2013, 28(8):1337-1349. |
| [33] | 王素萍, 王劲松, 张强, 等. 几种干旱指标对西南和华南区域月尺度干旱监测的适用性评价[J]. 高原气象, 2015, 34(6): 1616-1624. |
| [34] | 宋琳琳, 张强, 任余龙, 等. PDSI及sc_PDSI干旱指数在中国西南地区适用性分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(2):242-251. |
| [35] | 王素萍, 张存杰, 李耀辉, 等. 基于标准化降水指数的1960—2011年中国不同时间尺度干旱特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2014, 34(3): 827-834. |
| [36] | 张红丽, 张强, 刘骞, 等. 中国干旱状况的时空分布特征及影响因素[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 52(4):484-491. |
| [37] | 韩兰英, 张强, 贾建英, 等. 气候变暖背景下中国干旱强度、频次和持续时间及其南北差异性[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(5):1-10. |
| [38] | WANG J S, WANG S P, ZHANG Q, et al. Characteristics of drought disaster-causing factor anomalies in southwestern and southern China against the background of global warming[J]. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 2015, 24(5):2241-2251. |
| [39] | 杨金虎, 张强, 王劲松, 等. 近60年来西南地区旱涝变化及极端和持续性特征认识[J]. 地理科学, 2015, 35(10):1333-1340. |
| [40] | 姚玉璧, 张强, 王劲松, 等. 中国西南干旱对气候变暖的响应特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2014, 23(9):1409-1417. |
| [41] | 姚玉璧, 张强, 王劲松, 等. 气候变暖背景下中国西南干旱时空分异特征[J]. 资源科学, 2015, 37(9):1774-1784. |
| [42] | 王莺, 王劲松, 姚玉璧, 等. 中国华南地区持续干期日数时空变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2014, 23(1):86-94. |
| [43] | 韩兰英, 张强, 姚玉璧, 等. 近60年中国西南地区干旱灾害规律与成因[J]. 地理学报, 2014, 69(5):632-639. |
| [44] | 史培军. 灾害研究的理论与实践[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 1991(11):37-42. |
| [45] | 张强, 韩兰英, 张立阳, 等. 论气候变暖背景下干旱和干旱灾害风险特征与管理策略[J]. 地球科学进展, 2014, 29(1):80-91. |
| [46] | 张强, 王劲松, 姚玉璧, 等. 干旱灾害风险及其管理[M]. 2版. 北京: 气象出版社, 2018. |
| [47] | 王劲松, 张强, 王素萍, 等. 西南和华南干旱灾害链特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2015, 33(2):187-194. |
| [48] | ZHANG Q, HAN L Y, ZENG J, et al. Climate factors during key periods affect the comprehensive crop losses due to drought in southern China[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2020, 55:2313-2325. |
| [49] | 张强, 韩兰英, 王胜, 等. 影响南方农业干旱灾损率的气候要素关键期特征[J]. 科学通报, 2018, 63(23):2378-2392. |
| [50] | WANG S P, WANG J S, ZHANG Q, et al. Cumulative effect of precipitation deficit preceding severe droughts in southwestern and southern China[J]. Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society, 2016 (3):1-10. DOI:10.1155/2016/2890852. |
| [51] | LI H W, LI Z, CHEN Y N, et al. Drylands face potential threat of robust drought in the CMIP6 SSPs scenarios[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2021, 16, 114004. DOI:10.1088/1748-9326/ac2bce. |
| [52] | 郑大玮, 李茂松, 霍治国. 农业灾害与减灾对策[M]. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社, 2013. |
| [53] | ZHANG Q, WANG Y. Distribution of hazard and risk caused by agricultural drought and flood and their correlations in summer monsoon-affected areas of China[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 2022. DOI:10.1007/s00704-022-04093-6. |
| [54] | 王莺, 赵文, 张强. 中国北方地区农业干旱脆弱性评价[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(4):149-158. |
| [55] | 韩兰英, 张强, 马鹏里, 等. 气候变暖背景下黄河流域干旱灾害风险空间特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(4):225-234. |
| [56] | 王莺, 李耀辉, 赵福年, 等. 基于信息扩散理论的甘肃省农业旱灾风险分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2013, 31(1):43-48. |
| [57] | 王莺, 王劲松, 姚玉璧. 甘肃省河东地区气象干旱灾害风险评估与区划[J]. 中国沙漠, 2014, 34(4):1115-1124. |
| [58] | 姚玉璧, 李耀辉, 石界, 等. 基于GIS的石羊河流域干旱灾害风险评估与区划[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2014, 32(2):21-28. |
| [59] | 王莺, 王静, 姚玉璧, 等. 基于主成分分析的中国南方干旱脆弱性评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2014, 23(12):1897-1904. |
| [60] | 王莺, 张强, 韩兰英. 基于信息扩散理论的中国南方水旱灾害风险特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2016, 34(6):919-926. |
| [61] | 王莺, 沙莎, 王素萍, 等. 中国南方干旱灾害风险评估[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(5):12-24. |
| [62] | 刘晓云, 王劲松, 李耀辉, 等. 基于Copula函数的中国南方干旱风险特征研究[J]. 气象学报, 2015, 73(6):1080-1091. |
| [63] | 姚小英, 张强, 王劲松, 等. 甘肃冬小麦主产区40年干旱变化特征及影响风险评估[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2014, 32(2):1-6. |
| [64] | WANG Y, ZHANG Q, YAO Y B. Drought vulnerability assessment for maize in the semiarid region of northwestern China[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 2020, 140: 1207-1220. |
| [65] | WANG Y, ZHAO W, ZHANG Q, et al. Characteristics of drought vulnerability for maize in the eastern part of Northwest China[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9, 964. DOI:10.1038/s41598-018-37362-4 |
| [66] | 贾建英, 贺楠, 韩兰英, 等. 基于自然灾害风险理论和ArcGIS的西南地区玉米干旱风险分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(4): 152-159. |
| [67] | 王莺, 王健顺, 张强. 中国草原干旱灾害风险特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8):1-12. |
| [68] | 姚玉璧, 杨金虎, 肖国举, 等. 气候变暖对西北雨养农业及农业生态影响研究进展[J]. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(7): 2170-2179. |
| [69] | WANG Y, WANG C, ZHANG Q. Synergistic effects of climatic factors and drought on maize yield in the east of Northwest China against the background of climate change[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 2021, 143(1): 1017-1033. |
| [70] | 姚玉璧, 王莺, 王劲松. 气候变暖背景下中国南方干旱灾害风险特征及对策[J]. 生态环境学报, 2016, 25(3):432-439. |
| [71] | 姚小英, 姚玉璧, 袁佰顺, 等. 玉米干旱气象保险指数研究——以陇东南为例[J]. 中国农学通报, 2018, 34(3):140-144. |
| [72] | 张强, 孙昭萱, 陈丽华, 等. 祁连山空中云水资源开发利用研究综述[J]. 干旱区地理, 2009, 32(3):381-390. |
| [73] | 张强, 王胜. 关于干旱和半干旱区陆面水分过程的研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2007, 25(4):1-4. |
| [74] | AGAM N, BERLINER P R. Dew formation and water vapor adsorption in semi-arid environments—A review[J]. Journal of Arid Environments, 2006, 65(4): 572-590. |
| [75] | 张强, 王胜, 王闪闪, 等. 半干旱区土壤水汽吸附的影响因素及变化特征[J]. 中国科学:D辑地球科学, 2016, 46(11):1515-1527. |
| [76] | 张强, 王胜, 曾剑. 论干旱区非降水性陆面液态水分分量及其与土壤水分的关系[J]. 干旱区研究, 2010, 27(3):392-400. |
| [77] | 张强, 陈丽华, 问晓梅, 等. 陆面露水资源开发利用技术初探[J]. 干旱气象, 2008, 26(4):1-4. |
| [78] | 王胜, 张强. 黄土高原半干旱区露水形成的大气物理特征研究[J]. 物理学报, 2011, 60(5):059203. |
| [79] | ZHANG Q, WANG S, YANG F L, et al. Characteristics of dew formation and distribution, and its contribution to the surface water budget in a semi-arid region in China[J]. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 2015, 154:317-331. |
| [80] | LI Y H, YUAN X, ZHANG H S, et al. Mechanisms and early warning of drought disasters: an experimental drought meteorology research over China[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2019, 100(4): 673-687. |
| [81] | 叶培龙, 张强, 王莺, 等. 1980—2018年黄河上游气候变化及其对生态植被和径流量的影响[J]. 大气科学学报, 2020, 43(6): 967-979. |
| [82] | WANG L Y, YUAN X. Two types of flash drought and their connections with seasonal drought[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2018, 35(12): 1478-1490. |
| [83] | OTKIN J, SVOBODA M, HUNT E D, et al. Flash droughts: a review and assessment of the challenges imposed by rapid-onset droughts in the United States[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2018, 99(5): 911-919. |
| [84] | CHRISTIAN J I, BASARA J B, HUNT E D, et al. Global distribution, trends, and drivers of flash drought occurrence[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12, 6330. DOI:10.1038/s41467-021-26692-z. |
| [85] | YUAN X, WANG L Y, WU P L, et al. Anthropogenic shift towards higher risk of flash drought over China[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10, 4661. DOI:10.1038/s41467-019-12692-7. |
| [86] | 段居琦, 张强, 何雨峰, 等. 基于大气—土壤—植被系统干旱发生发展过程的综合干旱指标构建与应用[J]. 气象学报, 2021, 79(2):229-239. |
| [87] | 叶丽梅, 周月华, 周悦, 等. 暴雨洪涝灾害链实例分析及断链减灾框架构建[J]. 灾害学, 2018, 33(1):65-70. |
| [88] | 贾梦姝, 张宇, 潘婷婷, 等. 面向互联网信息抽取的海洋环境灾害链本体构建——以台风灾害为例[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2020, 22(12):2289-2303. |
| [89] | 尹云鹤, 韩项, 邓浩宇, 等. 中国西南地区地震—滑坡—泥石流灾害链风险防范措施框架研究[J]. 灾害学, 2021, 36(3):77-84. |
| [90] | 张翔, 韦燕芳, 李思宇, 等. 从干旱灾害到干旱灾害链:进展与挑战[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(6):873-883. |
| [91] | PARISI A, MONNO V, FIDELIBUS M D. Cascading vulnerability scenarios in the management of groundwater depletion and salinization in semi-arid areas[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 2018, 30: 292-305. |
| [92] | NAUMANN G, CAMMALLERI C, MENTASCHI L, et al. Increased economic drought impacts in Europe with anthropogenic warming[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2021, 11: 485-491. |
| [93] | CHOQUETTE-LEVY N, WILDEMEERSCH M, OPPEN-HEIMER M, et al. Risk transfer policies and climate-induced immobility among smallholder farmers[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2021, 11: 1046-1054. |
| [94] | 张强, 姚玉璧, 王莺, 等. 中国南方干旱灾害风险特征及其防控对策[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(21):7206-7218. |
| [1] | CHEN Ying, JIAZILA Baishan, SHAO Weiling, LIU Jing. Influence of Arctic Oscillation on winter temperature in Xinjiang under climate warming background [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(2): 195-201. |
| [2] | JI Lingling, XI Zhuxiang, LIU Yuxi, DU Guannan, LIU Ziqi. Spatio-temporal Variation Characteristics of Extreme Wind Speed in Jilin Province and Its Relationship with Climate Warming [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(03): 388-395. |
| [3] | HU Die, SHA Sha, WANG Lijuan, WANG Wei. Drought Monitoring Applications of the European Space Agency Climate Change Initiative Soil Moisture Combined Product in Gansu Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(4): 517-528. |
| [4] | JING Hua, KANG Xiuli, MA Aiping, WANG Yuzhi, CUI Huanhu, ZHANG Jiancheng. Effect of Different Altitudes on Characteristics of Soil Water and Water Use Efficiency in Wheat Fields [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(4): 656-662. |
| [5] | WANG Siqi, ZHANG Xiang, CHEN Nengcheng, ZHOU Jiaxiang, HU Chuli, PENG Xiaoting. Monitoring and Comparison of Drought in Five Provinces of the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River Based on the Multiple Drought Indices [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(2): 209-217. |
| [6] | LIU Kai, SUN Li, SUN Haiyue, XUE Wanqing, ZHAI Guanghui. Drought Monitoring in Winter Wheat Planting Area of China Based on FY-3C Microwave Data [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(6): 918-925. |
| [7] | . Drought Monitoring Based on TRMM Precipitation Data in Gansu Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(3): 374-. |
| [8] | WANG Suyan,ZHENG Guangfen,YANG Jianling,LI Xin,ZHANG Zhi,ZHANG Hongying,ZHOU Cuifang,DONG Guoqing. Response of Winter Heating Peroid to Climate Warming in Ningxia [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2016, 34(2): 335-341. |
| [9] | GUO Wei,YANG Fulin,ZHANG Rong,ZHAO Liping,HAO Zhenrong. Change Trend of Ecological Water Requirement of Potatoes and Its Response to Climate Warming in Northwestern of Shanxi Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2014, 32(4): 516-520. |
| [10] | CAO Zhangchi,SHEN Runping,TIAN Ye,LI Feng. Research on Soil Moisture Monitoring Using MODIS Data During the Drought/Wet Conversion Period in Shandong Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2014, 32(3): 340-345. |
| [11] | BAI Meilan,HAO Runquan,LI Xicang,YANG Jing. Variable Characteristics of Extreme Climate Events During 1961 -2010 in Inner Mongolia [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2014, 32(2): 189-193. |
| [12] | . Spatial - temporal Characteristic and Response of Spring Wheat Yield to Climate Change in Gansu Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2013, 31(2): 298-302. |
| [13] | . Characteristics of Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Severe Convective Weather and Its Response to Climate Warming in Qinghai Province [J]. J4, 2011, 29(4): 439-445. |
| [14] | YIN Xue-Lian, HAO Zhi-Yi, WEI Feng, DAI De-Ban. Influence of Clima teWarm ing on Agr iculture in theM iddle of Hex i Corr idor [J]. J4, 2008, 26(2): 90-94. |
| [15] | SUN Guo-Wu, LI Yao-Hui. Study on Creeping Environmental Problems [J]. J4, 2007, 25(2): 5-11. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||