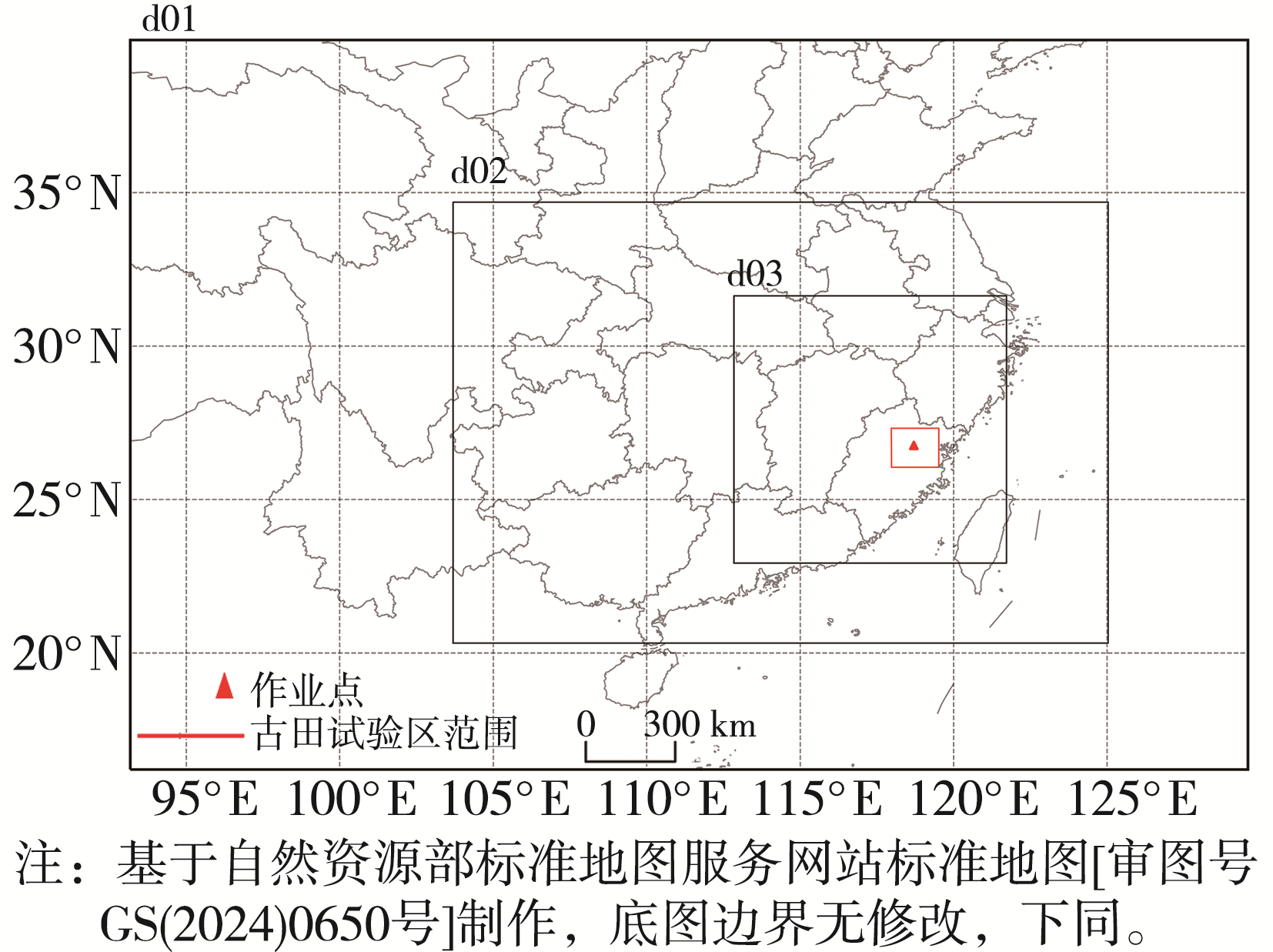
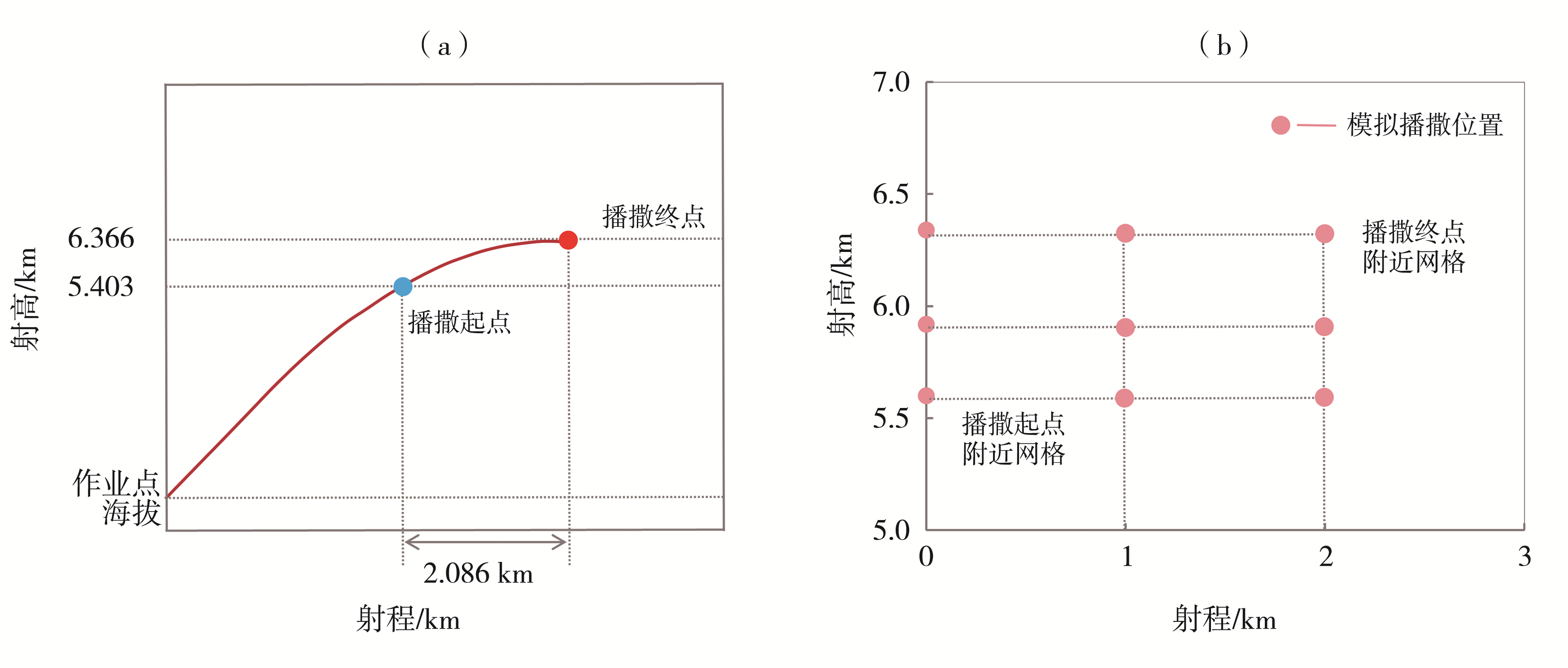
Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (5): 770-781.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-05-0770
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
A numerical simulation study on a convective cloud artificial rain enhancement seeding experiment in Gutian, Fujian Province
XIE Zuxin1,2,3( ), LIN Wen1,2,3, LI Dan1,2,3, HUA Shaofeng4(
), LIN Wen1,2,3, LI Dan1,2,3, HUA Shaofeng4( )
)
- 1. Fujian Meteorological Science Institute, Fuzhou 350008, China
2. Fujian Key Laboratory of Severe Weather, Fuzhou 350008, China
3. Key Open Laboratory for Strait Disaster Weather of CMA, Fuzhou 350008, China
4. China Meteorological Administration Weather Modification Centre, Beijing 100081, China
-
Received:2025-03-21Revised:2025-07-17Online:2025-10-31Published:2025-11-09
福建古田一次对流云人工增雨催化试验的数值模拟研究
谢祖欣1,2,3( ), 林文1,2,3, 李丹1,2,3, 花少烽4(
), 林文1,2,3, 李丹1,2,3, 花少烽4( )
)
- 1.福建省气象科学研究所,福建 福州 350008
2.福建省灾害天气重点实验室,福建 福州 350008
3.中国气象局海峡灾害天气重点开放实验室,福建 福州 350008
4.中国气象局人工影响天气中心,北京 100081
-
通讯作者:花少烽 -
作者简介:谢祖欣(1987—),女,高级工程师,主要从事人工影响天气和云降水物理研究。E-mail: xie_zuxin@163.com。 -
基金资助:福建省自然科学基金项目(2021J01452);福建省自然科学基金项目(2023N0029);国家重点研发计划项目(2023YFC3007603-04);国家重点研发计划项目(2019YFC1510303);华东区域气象科技协同创新基金合作项目(QYHZ202312)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
XIE Zuxin, LIN Wen, LI Dan, HUA Shaofeng. A numerical simulation study on a convective cloud artificial rain enhancement seeding experiment in Gutian, Fujian Province[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(5): 770-781.
谢祖欣, 林文, 李丹, 花少烽. 福建古田一次对流云人工增雨催化试验的数值模拟研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(5): 770-781.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-05-0770
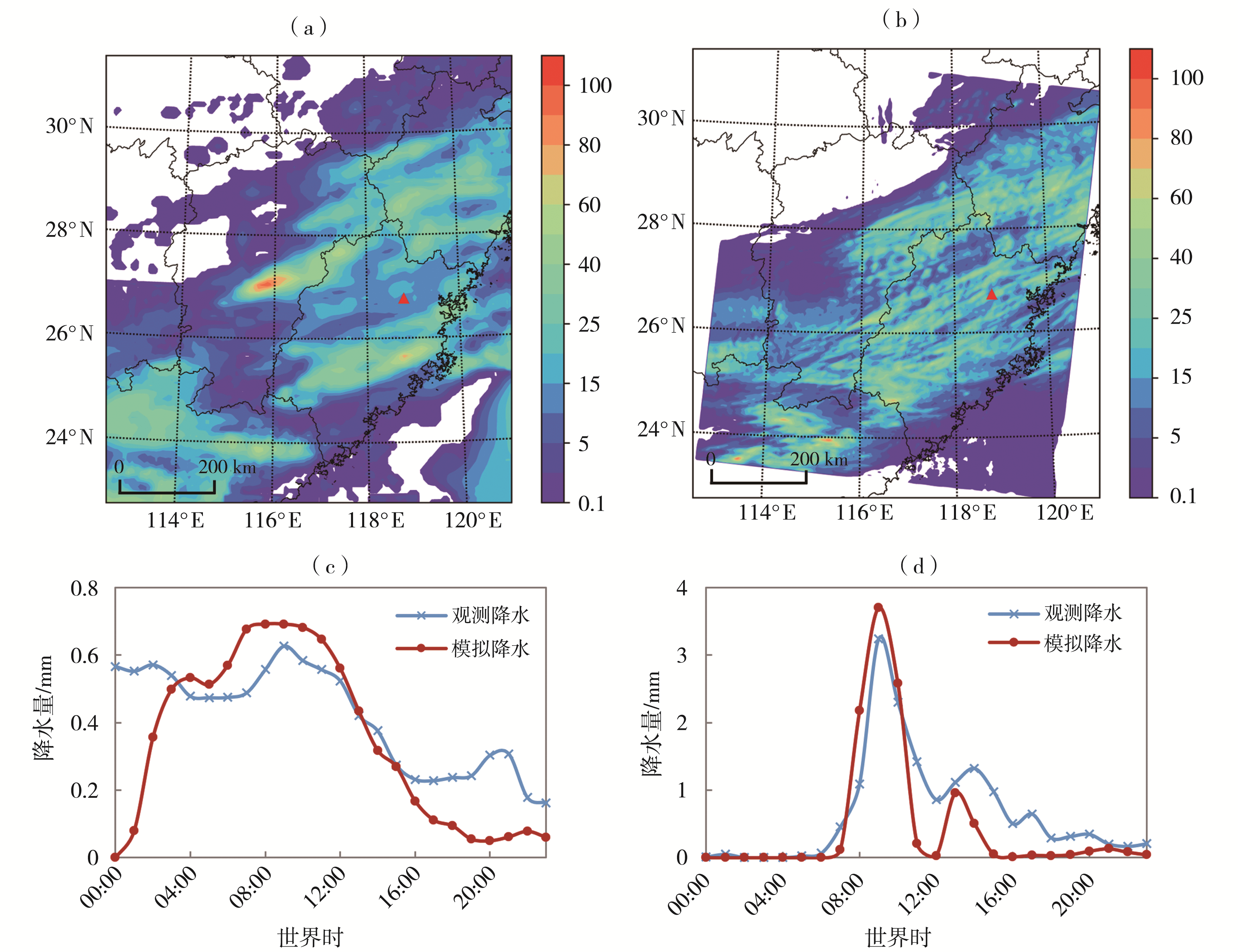
Fig.3 The distribution of observed (a) and simulated (b) precipitation from 00:00 May 4 to 00:00 May 5 in 2021 in the d03 area, and the hourly evolution of precipitation in the d03 area (c) and the testing area of Gutian (d) (The red triangle indicates the location of the operation point)

Fig.4 The evolution of radar composite reflectivity observed (a, b, c) and simulated (e, f, g) from 08:00 to 10:00 on May 4, 2021, and the observed (d) and simulated (h) reflectivity profiles along the purple line segment in figure 4(b) (Unit: dBZ) (The purple line segment in figure 4(b) indicates the direction of AgI seeding and diffusion)
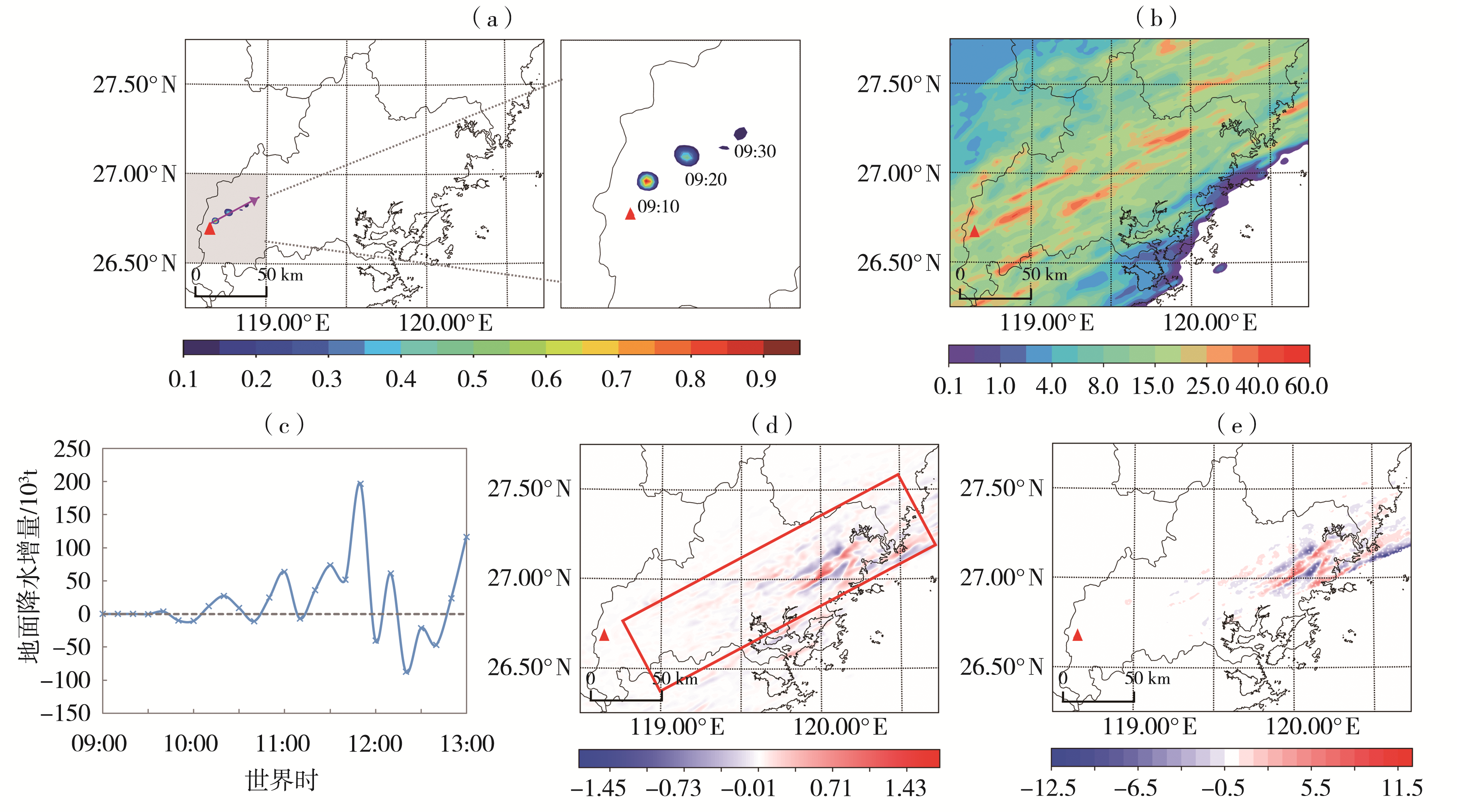
Fig.6 The mass concentration (the color shaded, Unit: 10-3 μg?kg-1) and movement path (the arrow direction) of AgI after its dissemination from 09:10 to 09:30 on May 4, 2021 (a), and the natural cloud precipitation (b, Unit: mm), ground precipitation increment (c), precipitation increment (d, Unit: mm), and rain enhancement rate (e, Unit: %) after catalysis from 09:00 to 13:00 May 4, 2021 (The red triangles denote approximate locations of the artificial rain enhancement operation site, the same as below; The rectangular box indicates the seeding influence area)

Fig.7 The distribution of water condensate in the cloud (the color shaded, Unit: kg?m-2), the vertical accumulation of supercooled water (blue isolines, Unit: kg?m-2), and the mass concentration of AgI (the red shaded, Unit: 10-3 μg?kg-1) during the AgI seeding nucleation period on May 4, 2021 (a) 09:00, (b) 09:10, (c) 09:20, (d) 09:30

Fig.8 Vertical profiles of mass concentration (the gray shaded, Unit: 10-3 μg?kg-1) of AgI, ice crystal number concentration (pink isolines, Unit: particles·L-1), vertical velocity (blue isolines, positive values indicate updrafts and negative values indicate downdrafts, Unit: m·s-1), air temperature (red isolines, Unit: ℃), and ice surface supersaturation water vapor mixing ratio (the color shaded, Unit: g?kg-1) during AgI deposition, nuclearization period on May 4, 2021 (a) 09:00, (b) 09:10, (c) 09:20, (d) 09:30

Fig.10 Time-height evolution of number or mass concentration of the hydrometeor contents in natural cloulds (blue isolines) and their increments (the color shaded) after seeding (a, b, c, d, e), and vertical velocity (isolines) and its changes after seeding (f) from 09:00 to 13:00 on May 4, 2021
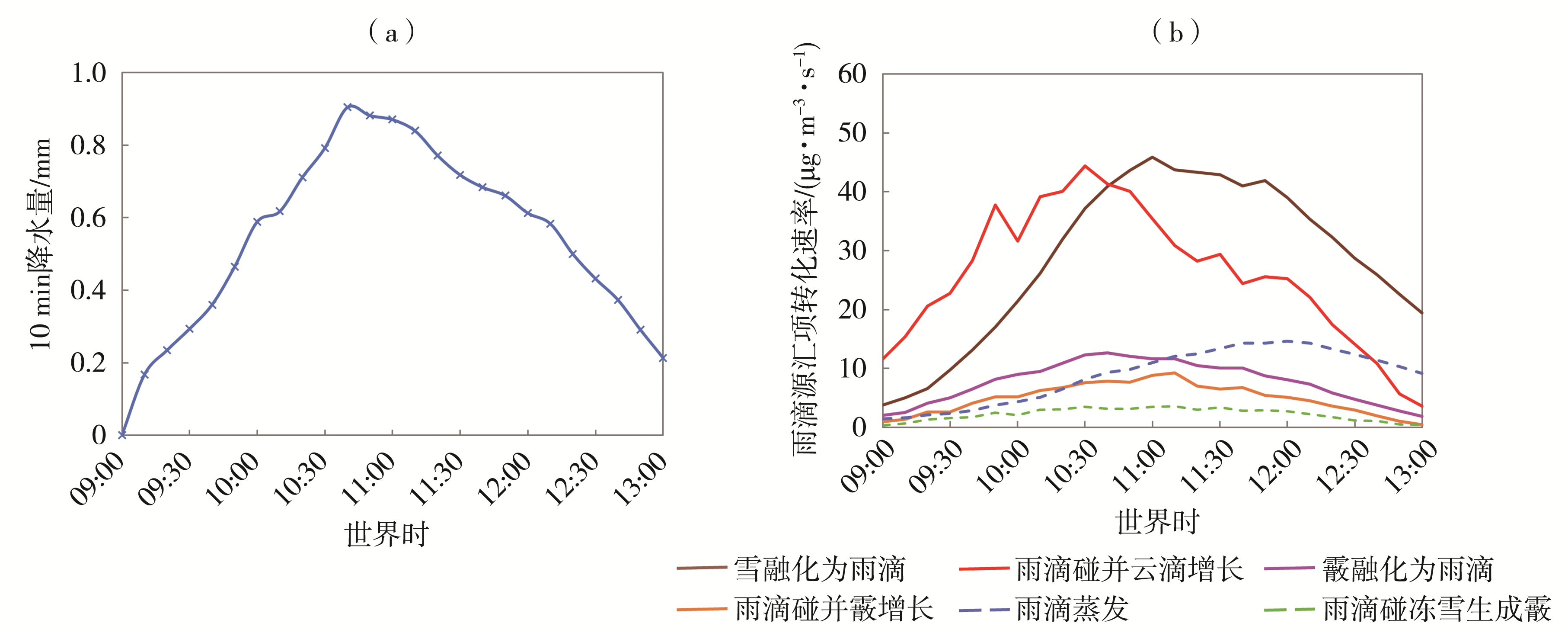
Fig.11 Variations of 10 min natural precipitation (a) and microphysical process transformation rates of raindrop source and sink terms (b) in the seeding influence area from 09:00 to 13:00 on May 4, 2021
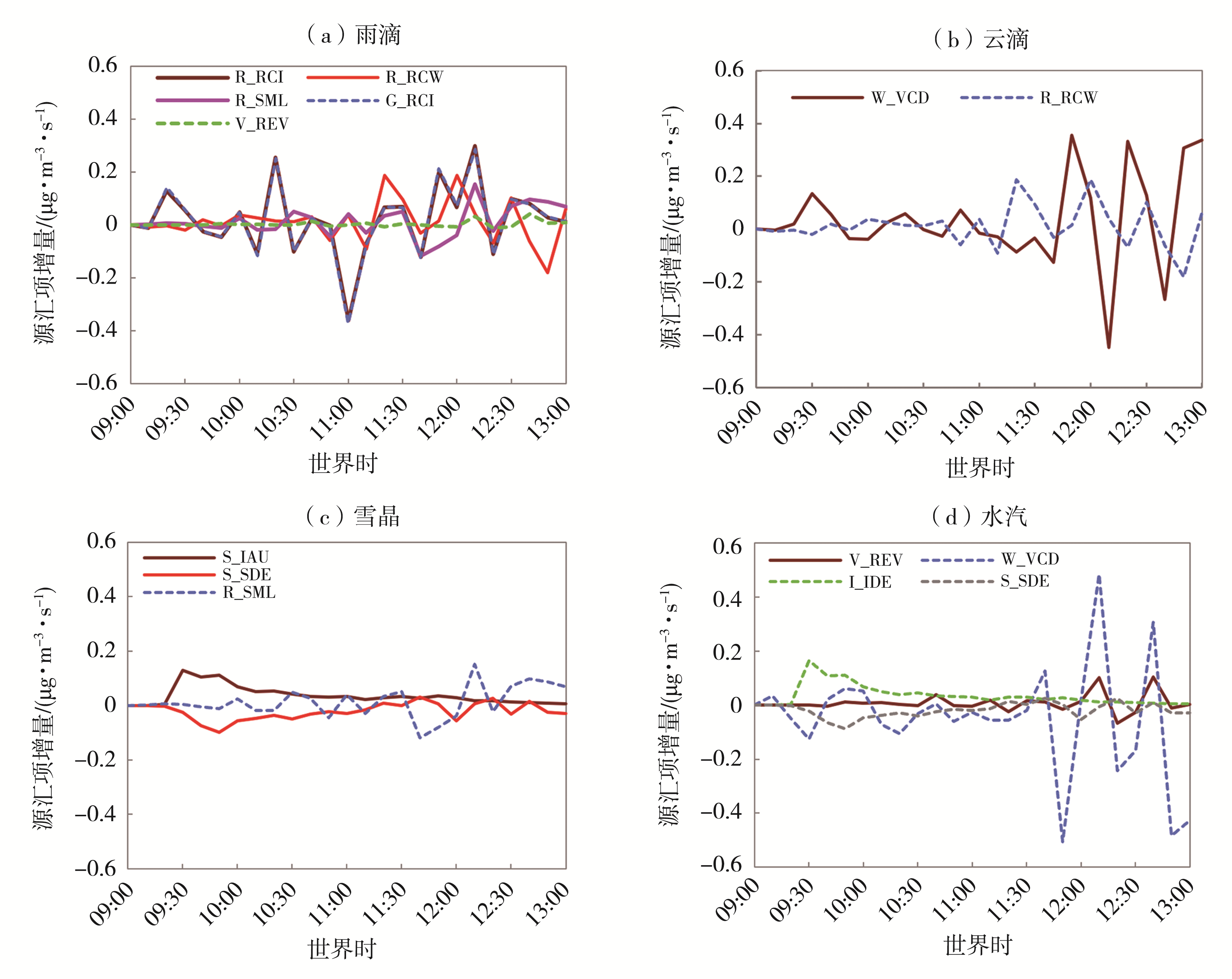
Fig.12 The changes of micro-physical processes source and sink terms in clouds after seeding from 09:00 to 13:00 on May 4, 2021 (a) raindrops, (b) cloud droplets, (c) snow crystal, (d) water vapor
| [1] | 段婧, 楼小凤, 汪会, 等, 2020. 人工影响天气用碘化银催化剂对区域环境影响的研究进展[J]. 气象, 46(2): 257-268. |
| [2] | 酆大雄, 陈汝珍, 蒋耿旺, 等, 1995. 高效碘化银焰火剂及其成冰性能的研究[J]. 气象学报, 53(1): 82-90. |
| [3] | 冯宏芳, 林文, 曾光平, 2019. 福建省古田水库人工增雨随机回归试验回顾及展望[J]. 海峡科学(5):21-29. |
| [4] | 付远, 杨洁帆, 刘汉华, 等, 2024. 基于集合预报的浙江省积层混合云人工增雨数值模拟研究[J]. 大气科学, 48(4): 1 405-1 419. |
| [5] | 郭学良, 方春刚, 卢广献, 等, 2019. 2008—2018年我国人工影响天气技术及应用进展[J]. 应用气象学报, 30(6): 641-650. |
| [6] | 洪延超, 1998. 三维冰雹云催化数值模式[J]. 气象学报, 56(6):641-653. |
| [7] | 洪延超, 1999. 冰雹形成机制和催化防雹机制研究[J]. 气象学报, 57(1):30-44. |
| [8] | 胡淑萍, 林文, 段卿, 等, 2019. 福建古田人工增雨试验区大气冰核观测研究[J]. 干旱气象, 37(5): 844-849. |
| [9] | 胡淑萍, 林文, 林长城, 等, 2023. 2014—2022年古田人工增雨随机试验物理检验[J]. 应用气象学报, 34(6): 706-716. |
| [10] | 花少烽, 查思佳, 陈宝君, 2024. 环境湿度影响人工催化消减雨效果的数值模拟研究[J]. 大气科学, 48(2):572-584. |
| [11] | 雷恒池, 洪延超, 赵震, 等, 2008. 近年来云降水物理和人工影响天气研究进展[J]. 气候与环境研究, 32(4): 967-974. |
| [12] | 李丹, 林文, 刘群, 等, 2024. 机器学习在人工增雨效果统计检验中的应用[J]. 应用气象学报, 35(1): 118-128. |
| [13] | 李宏宇, 嵇磊, 周嵬, 等, 2014. 北京地区人工增雨效果和防雹经济效益评估[J]. 高原气象, 33(4): 1 119-1 130. |
| [14] | 李兴宇, 洪延超, 2005. 三维冰雹云数值催化模式改进与个例模拟研究[J]. 气象学报, 63(6): 874-888. |
| [15] | 刘诗军, 胡志晋, 游来光, 2005. 碘化银核化过程的数值模拟研究[J]. 气象学报, 63(1): 30-40. |
| [16] | 刘卫国, 陶玥, 周毓荃, 等, 2021. 基于飞机真实轨迹的一次层状云催化的增雨效果及其作用机制的模拟研究[J]. 气象学报, 79(2): 340-358. |
| [17] | 刘卫国, 陶玥, 党娟, 等, 2016. 2014年春季华北两次降水过程的人工增雨催化数值模拟研究[J]. 大气科学, 40 (4): 669-688. |
| [18] | 刘玉宝, 丁秋冀, 史月琴, 等, 2021. 云解析人工影响天气数值模式的改进、初步试验和展望[J]. 气象科技进展, 11(5): 77-85. |
| [19] |
楼小凤, 何观芳, 胡志晋, 等, 2013. 三维对流云盐粉催化模式的发展和催化模拟试验[J]. 高原气象, 32(2): 491-500.
DOI |
| [20] | 楼小凤, 师宇, 李集明, 2016. 云降水和人工影响天气催化数值模式的发展及应用[J]. 气象科技进展, 6(3): 75-82. |
| [21] | 师宇, 楼小凤, 单云鹏, 等, 2017. 北京地区一次降雪过程的人工催化数值模拟研究[J]. 高原气象, 36(5): 1 276-1 289. |
| [22] | 史月琴, 赵俊杰, 孙晶, 等, 2022. 华北地区一次低槽冷锋云系结构和增雨条件研究[J]. 干旱气象, 40(6): 1 003-1 013. |
| [23] | 孙晶, 杨文霞, 周毓荃, 2015. 河北一次降水层状云系结构和增雨条件的模拟研究[J]. 高原气象, 34(6): 1 699-1 710. |
| [24] | 唐林, 李琼, 黎祖贤, 等, 2020. 一次积层混合云云系微物理结构数值模拟与增雨条件分析[J]. 干旱气象, 38(1): 100-108. |
| [25] | 王飞, 李集明, 姚展予, 等, 2022. 我国人工增雨作业效果定量评估研究综述[J]. 气象, 48(8): 945-962. |
| [26] | 肖明静, 郭学良, 肖稳安, 2006. 碘化银、液态CO2播撒对流云防雹增雨的数值模拟[J]. 南京气象学院学报, 29(1): 48-55. |
| [27] |
邢峰华, 黄菲婷, 李光伟, 等, 2023. 海南岛中部山区暖云人工增雨催化试验物理效果分析[J]. 干旱气象, 41(1): 114-122.
DOI |
| [28] | 许焕斌, 2009. 关于在人工影响天气中更新学术观念的探讨[J]. 干旱气象, 27(4): 305-307. |
| [29] |
许志丽, 徐亮亮, 毕力格, 等, 2025. 内蒙古中部地区层状云微物理特征及可播度分析[J]. 干旱气象, 43(1): 126-132.
DOI |
| [30] | 查思佳, 张慧娇, 李逍潇, 等, 2020. 2014年南京青奥会开幕式日降水过程数值模拟研究[J]. 大气科学, 44(6): 1 258-1 274. |
| [31] |
DEE D P, UPPALA S M, SIMMONS A J, et al, 2011. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 137(656): 553-597.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
DUDHIA J, 1989. Numerical study of convection observed during the winter monsoon experiment using a mesoscale two dimensional model[J]. Journal of the Atmosphere Science, 46(20): 3 077-3 107.
DOI URL |
| [33] | HONG S Y, LIM J O J, 2006. The WRF single-moment 6-class microphysics scheme (WSM6)[J]. Journal of the Korean Meteorological Society, 42(2): 129-151. |
| [34] | HSIE E Y, FARLEY R D, ORVILLE H D, 1980. Numerical simulation of ice-phase convective cloud seeding[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 19(8): 950-977. |
| [35] | HUA S F, CHEN B J, HE H, 2024. Numerical simulation of the cloud seeding operation of a convective rainfall event occurred in Beijing[J]. Atmospheric Research, 304:107386. DOI:10.1016/j.atmosres.2024.107386. |
| [36] | IACONO M J, DELAMERE J S, MLAWER E J, et al, 2008. Radiative forcing by long-lived greenhouse gases: Calculations with the AER radiative transfer models[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 113(D13): D13103-1-D13103-8. |
| [37] |
KAIN J S, 2004. The Kain-Fritsch convective parameterization: An update[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 43(1): 170-181.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
MEYERS M P, DEMOTT P J, COTTON W R, 2010. A comparison of seeded and nonseeded orographic cloud simulations with an explicit cloud model[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 34(4): 834-846.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
ORVILLE H D, 1996. A review of cloud modeling in weather modification[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 77(7): 1 535-1 556.
DOI URL |
| [40] | ROSENFELD D, KHAIN A, LYNN B, et al, 2007. Simulation of hurricane response to suppression of warm rain by sub-micron aerosols[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 7(13): 3 411-3 424. |
| [41] |
SKAMAROCK W C, KLEMP J B, 2008. A time-split nonhydrostatic atmospheric model for weather research and forecasting applications[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 227(7): 3 465-3 485.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
THOMPSON G, FIELD P R, RASMUSSEN R M, et al, 2008. Explicit forecasts of winter precipitation using an improved bulk microphysics scheme. Part II: Implementation of a new snow parameterization[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 136(12): 5 095-5 115.
DOI URL |
| [43] | THOMPSON G, RASMUSSEN R M, MANNING K, 2004. Explicit forecasts of winter precipitation using an improved bulk microphysics scheme. Part I: Description and sensitivity analysis[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 132(2): 75-95. |
| [44] |
XUE L L, WEEKS C, CHEN S S, et al, 2022. Comparison between observed and simulated AgI seeding impacts in a well-observed case from the SNOWIE field program[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 61(4): 345-367.
DOI URL |
| [1] | SHI Yueqin, ZHAO Junjie, SUN Jing, SUN Yuwen. Study on cloud structure and rainfall enhancement condition of a low-trough cold-front cloud over North China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 1003-1013. |
| [2] | ZHANG Lei, SONG Zhe, XU Cheng, HUANG Xuanxuan. Indexes of Doppler radar echo for rainfall enhancement in summer and autumn in Zhejiang Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(5): 888-896. |
| [3] | GU Tingting, PAN Yaying, ZHANG Jiayi. Correction method of surface solar radiation forecast based on ZJWARMS [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(2): 327-332. |
| [4] | DUAN Jingjing, QIAN Yanzhen, JIANG Jiajun, WANG Yi, WU Zeliang. Causes of Rainstorm Enhancement in Northeastern Zhejiang Related with Typhoon Khanun Landing in Guangdong Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(5): 737-746. |
| [5] | WU Qiong, XU Weimin. Near Ground Wind Speed Prediction Under Complex Topography with Lake, Plain and Mountains [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(3): 384-. |
| [6] |
ZHANG Liang, WANG Shi-Gong, CHANG Ge-Zheng, YANG De-Bao.
Review of Researches on Rainfall Enhancement in China
[J]. J4, 2006, 24(4): 73-81.
|
| [7] | JU Yong-Xin, TENG Shui-Chang-2, CA Yuan-Cheng, WANG Sheng-Yuan. A Case Analysis of Rocket Artificial Influence on Rainfall [J]. J4, 2006, 24(2): 33-38. |
| [8] | CAO Ling- , LI Guo-Chang, GUO Jian-Hua, CHEN He-Beng, DOU Yong-Xiang. Application Analysis of Doppler Radar Products in an Artificial Rain Enhancement Operation in Qilian Mountain Area [J]. J4, 2006, 24(2): 39-44. |
| [9] | LI Zong-Xi, YANG Jian-Cai, LI Rong-Qiang, CHENG Ying. The Climatic Analysis on Weather Modification in Mid - section of Qilian Mountain and Available Weather Patterns [J]. J4, 2006, 24(1): 23-27. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||