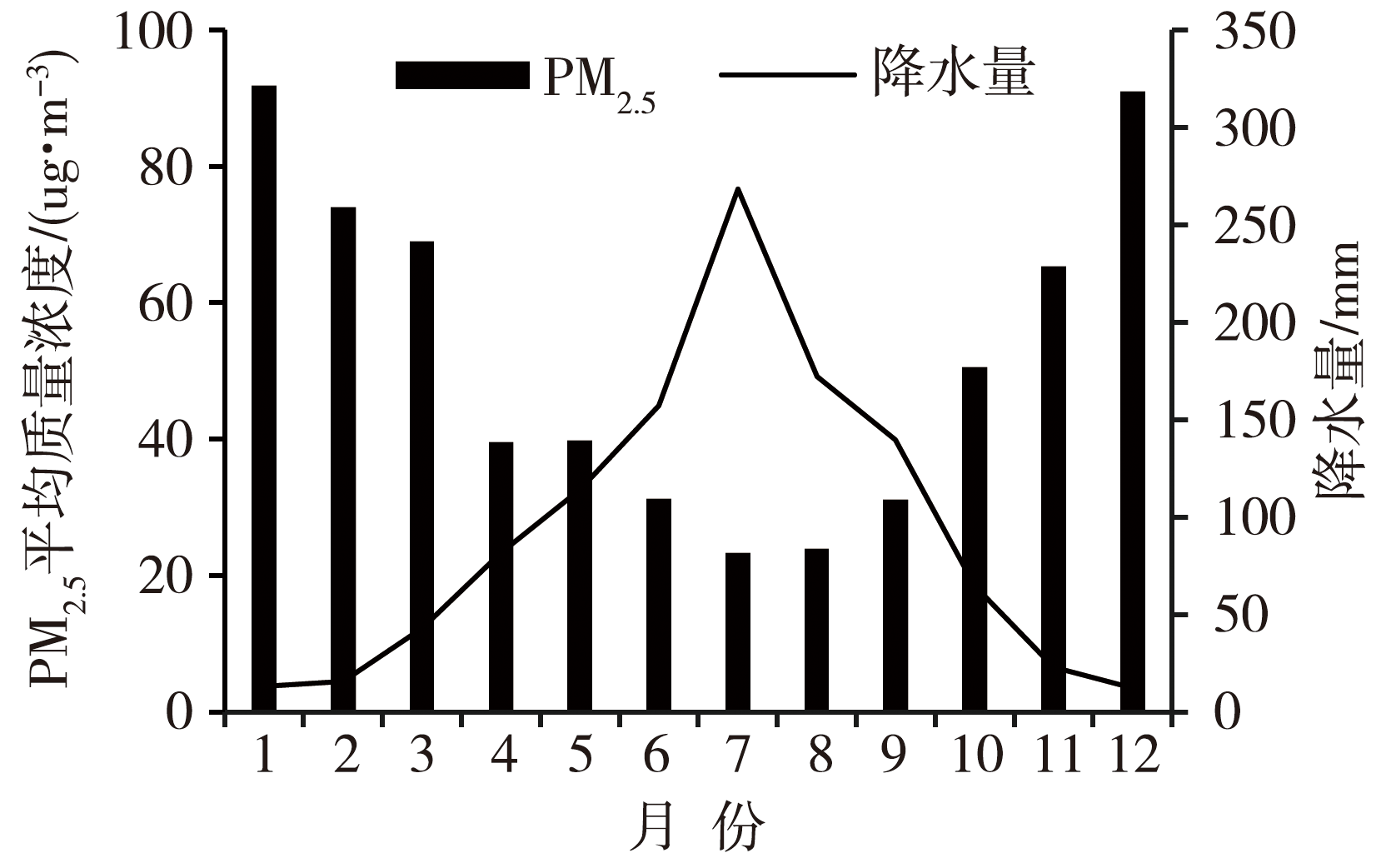
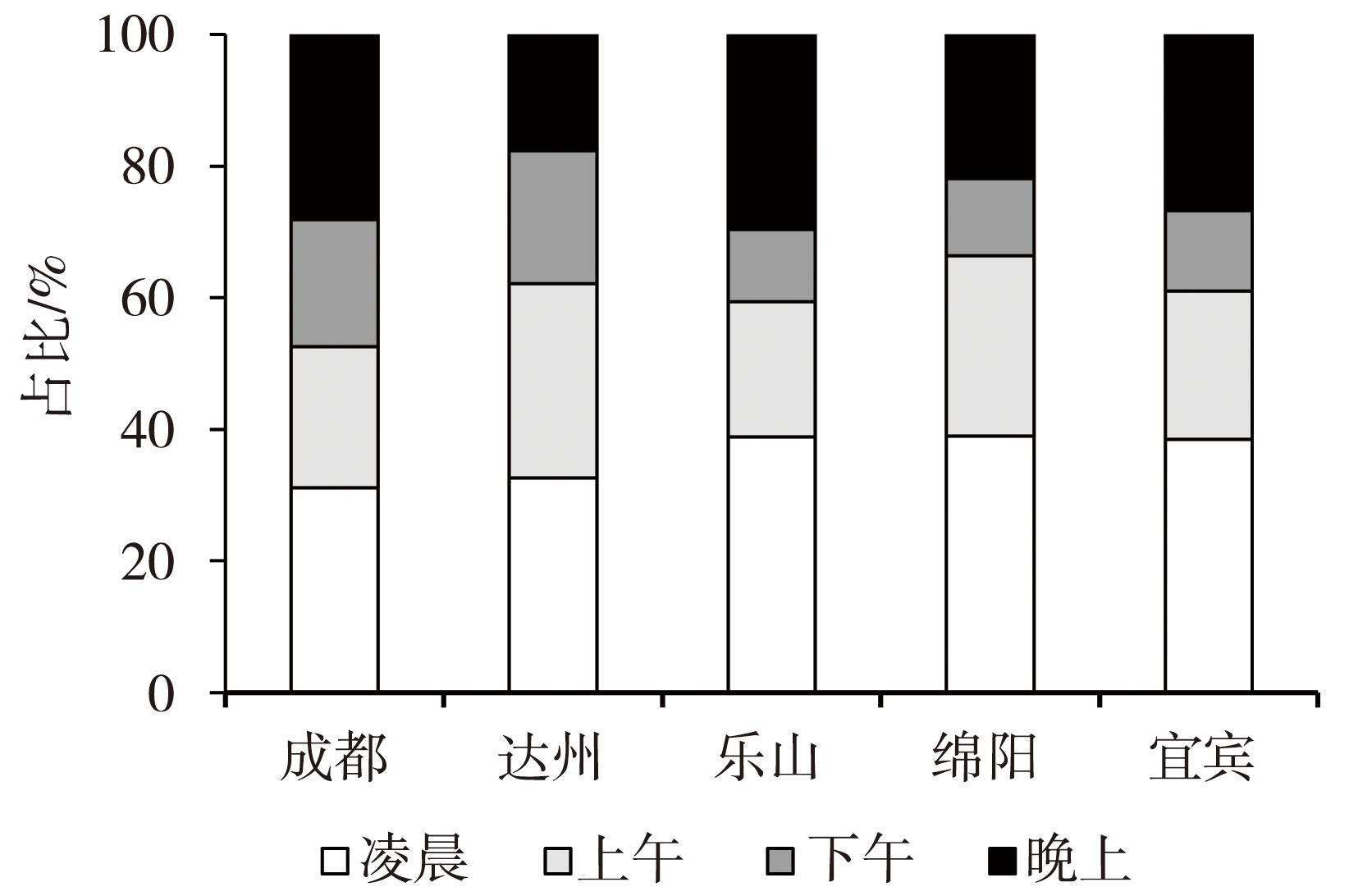
Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (4): 620-628.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-04-0620
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Analysis on scavenging effect of precipitation processes on PM2.5 in different cities of Sichuan Basin
LIN Dan1,2,3( ), GUO Xiaomei1, WANG Weijia1,2
), GUO Xiaomei1, WANG Weijia1,2
- 1. Weather Modification Office of Sichuan Province, Chengdu 610072, China
2. CMA Cloud-Precipitation Physics and Weather Modification Key Laboratory, Beijing 100081, China
3. Heavy Rain and Drought-Flood Disasters in Plateau and Basin Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province,Chengdu 610072, China
-
Received:2022-04-21Revised:2022-09-17Online:2023-08-31Published:2023-08-29
四川盆地不同区域城市降水过程对PM2.5清除作用分析
- 1.四川省人工影响天气办公室,四川 成都 610072
2.中国气象局云降水物理与人工影响天气重点开放实验室,北京 100081
3.高原与盆地暴雨旱涝灾害四川省重点实验室,四川 成都 610072
-
作者简介:林丹(1987—),女,四川成都人,硕士,高级工程师,主要从事大气物理与大气环境研究。E-mail:ld8768@hotmail.com。 -
基金资助:四川省科技计划项目(2022YFS0545);四川省应用基础研究计划项目(2019YJ0621);中国气象局大气探测重点开放实验室开放课题(2021KLAS04M);高原与盆地暴雨旱涝灾害四川省重点实验室科技发展基金项目(SCQXKJYJXZD202207)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LIN Dan, GUO Xiaomei, WANG Weijia. Analysis on scavenging effect of precipitation processes on PM2.5 in different cities of Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(4): 620-628.
林丹, 郭晓梅, 王维佳. 四川盆地不同区域城市降水过程对PM2.5清除作用分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(4): 620-628.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-04-0620
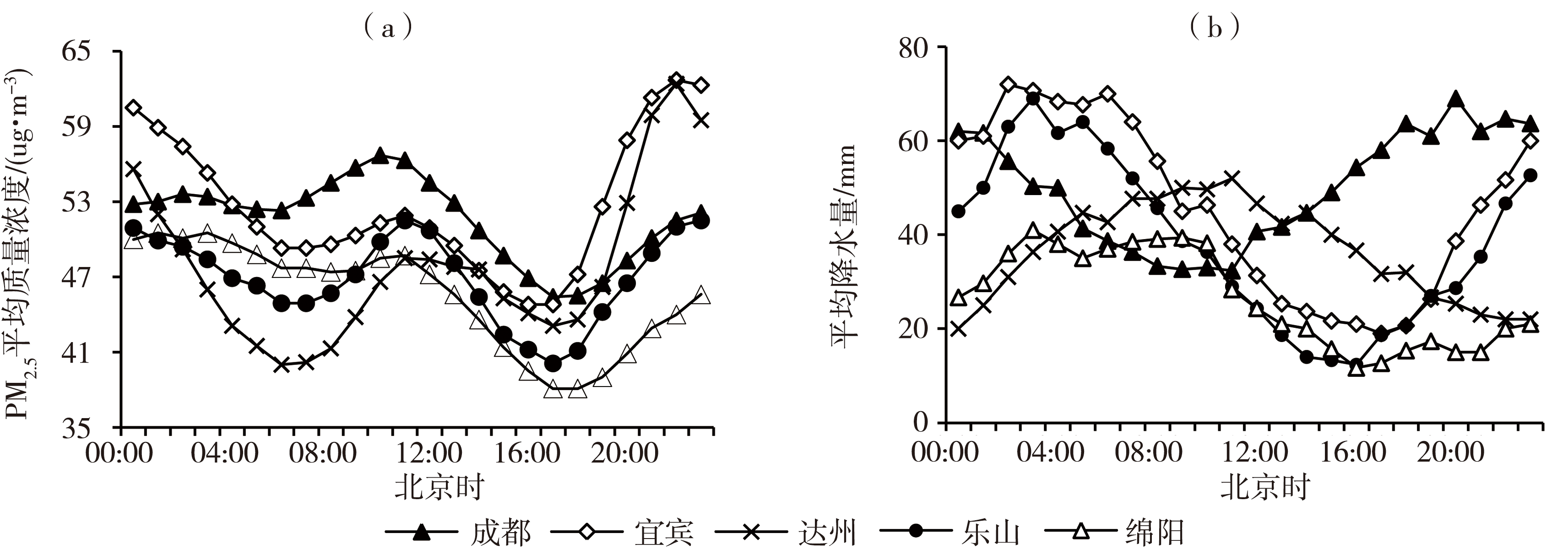
Fig.2 The diurnal variation of mean mass concentration of PM2.5 (a) and mean precipitation (b) in representative cities of different regions of Sichuan Basin during 2016-2021
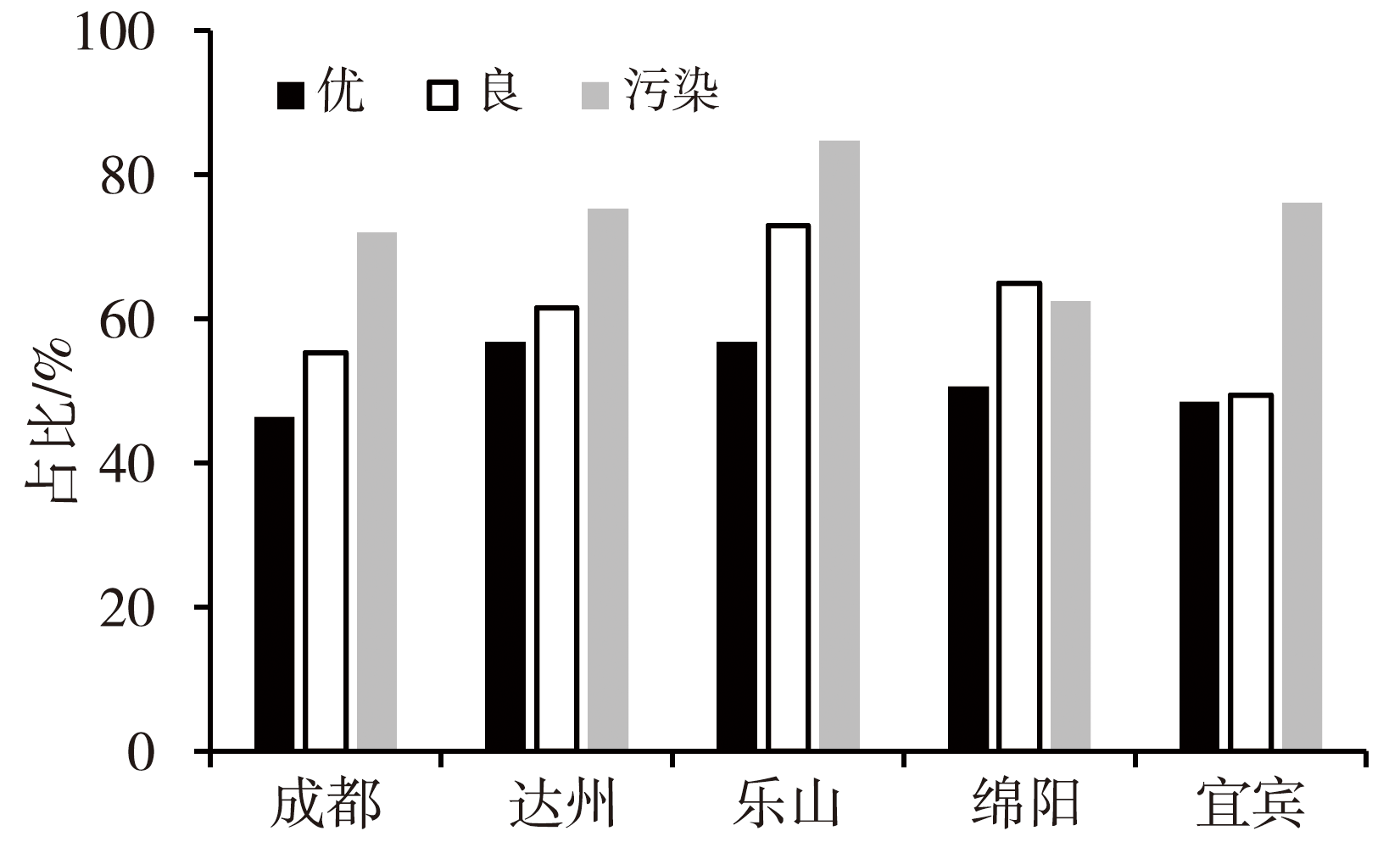
Fig.3 The proportion of positive scavenging processes under different air qualities in representative cities of different regions of Sichuan Basin during 2016-2021
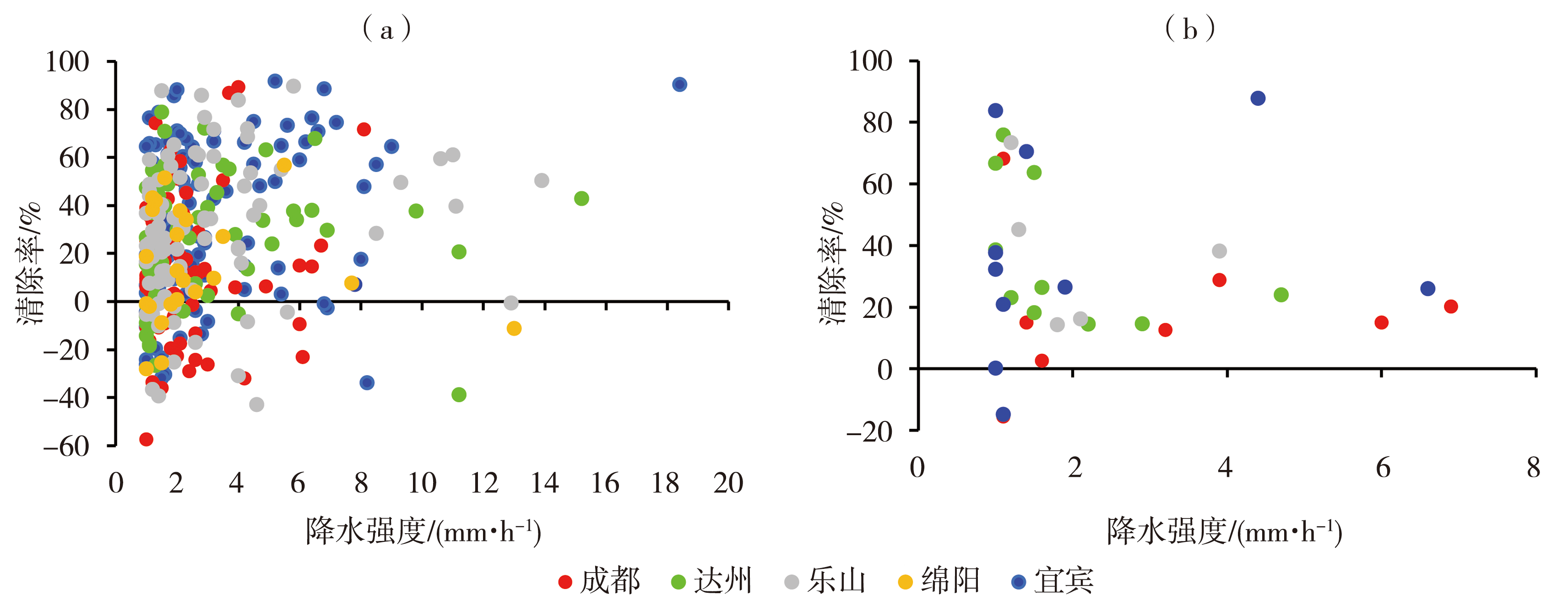
Fig.4 The relation of scavenging rate of rainfall processes with different precipitation intensities under different initial mass concentrations of PM2.5 in representative cities of different regions of Sichuan Basin during 2016-2021 (a) initial mass concentration of PM2.5 between 35 and 75 μg·m-3, (b) initial mass concentration of PM2.5 higher than 75 μg·m-3
| 降水强度/(mm·h-1) | 成都 | 达州 | 乐山 | 绵阳 | 宜宾 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <1 | 49.5 | 55.8 | 57.6 | 52.7 | 54.7 |
| 1~4 | 58.9 | 69.6 | 70.8 | 56.5 | 71.4 |
| >4 | 58.1 | 72.6 | 81.5 | 63.5 | 88.6 |
Tab.1
| 降水强度/(mm·h-1) | 成都 | 达州 | 乐山 | 绵阳 | 宜宾 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <1 | 49.5 | 55.8 | 57.6 | 52.7 | 54.7 |
| 1~4 | 58.9 | 69.6 | 70.8 | 56.5 | 71.4 |
| >4 | 58.1 | 72.6 | 81.5 | 63.5 | 88.6 |
| 降水强度/(mm·h-1) | 正清除 个例 | 正清除率 | 负清除 个例 | 负清除率 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~<10 | 10~<30 | 30~<50 | ≥50 | >-10~0 | >-30~-10 | >-50~-30 | ≤-50 | |||
| <1 | 3 386 | 33.9 | 42.5 | 16.6 | 6.9 | 2 882 | 40.2 | 39.5 | 11.2 | 9.1 |
| 1~4 | 702 | 16.5 | 39.6 | 25.2 | 18.7 | 365 | 31.9 | 40.2 | 14.8 | 13.1 |
| >4 | 226 | 12.4 | 30.2 | 23.1 | 34.2 | 78 | 39.2 | 43.1 | 13.7 | 3.9 |
Tab.2
| 降水强度/(mm·h-1) | 正清除 个例 | 正清除率 | 负清除 个例 | 负清除率 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~<10 | 10~<30 | 30~<50 | ≥50 | >-10~0 | >-30~-10 | >-50~-30 | ≤-50 | |||
| <1 | 3 386 | 33.9 | 42.5 | 16.6 | 6.9 | 2 882 | 40.2 | 39.5 | 11.2 | 9.1 |
| 1~4 | 702 | 16.5 | 39.6 | 25.2 | 18.7 | 365 | 31.9 | 40.2 | 14.8 | 13.1 |
| >4 | 226 | 12.4 | 30.2 | 23.1 | 34.2 | 78 | 39.2 | 43.1 | 13.7 | 3.9 |
| 城市 | 负清除过程 | 正清除过程 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 优 | 良 | 污染 | 优 | 良 | 污染 | |||||||
| ≤3 h | >3 h | ≤3 h | >3 h | ≤3 h | >3 h | ≤3 h | >3 h | ≤3 h | >3 h | ≤3 h | >3 h | |
| 成都 | -21.4 | -30.5 | -13.4 | -16.0 | -7.2 | -9.0 | 21.5 | 25.3 | 16.3 | 24.7 | 11.5 | 26.1 |
| 达州 | -23.5 | -23.5 | -16.3 | -14.3 | -9.8 | -18.6 | 18.1 | 25.4 | 16.7 | 31.6 | 12.6 | 29.6 |
| 乐山 | -25.1 | -31.3 | -13.4 | -12.5 | -4.8 | — | 19.9 | 33.2 | 19.2 | 33.6 | 17.5 | 39.7 |
| 绵阳 | -22.8 | -32.5 | -12.1 | -13.0 | -6.2 | -7.8 | 17.6 | 25.9 | 13.4 | 25.0 | 12.6 | 24.3 |
| 宜宾 | -24.8 | -24.5 | -12.6 | -11.6 | -9.2 | -6.5 | 20.1 | 31.6 | 18.0 | 35.8 | 14.6 | 36.5 |
| 盆地 | -23.5 | -28.5 | -13.6 | -13.5 | -7.4 | -10.5 | 19.4 | 28.3 | 16.7 | 30.1 | 13.7 | 31.2 |
Tab.3
| 城市 | 负清除过程 | 正清除过程 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 优 | 良 | 污染 | 优 | 良 | 污染 | |||||||
| ≤3 h | >3 h | ≤3 h | >3 h | ≤3 h | >3 h | ≤3 h | >3 h | ≤3 h | >3 h | ≤3 h | >3 h | |
| 成都 | -21.4 | -30.5 | -13.4 | -16.0 | -7.2 | -9.0 | 21.5 | 25.3 | 16.3 | 24.7 | 11.5 | 26.1 |
| 达州 | -23.5 | -23.5 | -16.3 | -14.3 | -9.8 | -18.6 | 18.1 | 25.4 | 16.7 | 31.6 | 12.6 | 29.6 |
| 乐山 | -25.1 | -31.3 | -13.4 | -12.5 | -4.8 | — | 19.9 | 33.2 | 19.2 | 33.6 | 17.5 | 39.7 |
| 绵阳 | -22.8 | -32.5 | -12.1 | -13.0 | -6.2 | -7.8 | 17.6 | 25.9 | 13.4 | 25.0 | 12.6 | 24.3 |
| 宜宾 | -24.8 | -24.5 | -12.6 | -11.6 | -9.2 | -6.5 | 20.1 | 31.6 | 18.0 | 35.8 | 14.6 | 36.5 |
| 盆地 | -23.5 | -28.5 | -13.6 | -13.5 | -7.4 | -10.5 | 19.4 | 28.3 | 16.7 | 30.1 | 13.7 | 31.2 |

Fig.6 The proportion of the positive and negative scavenging processes in each interval in representative cities of different regions of Sichuan Basin during 2016-2021
| [1] | 曹杨, 刘炜桦, 王晨曦, 等, 2020a. 成都市降水对大气污染物的清除效果分析[J]. 环境科学研究, 33(2): 305-311. |
| [2] | 曹杨, 王晨曦, 赵晓莉, 等, 2020b. 成都市PM2.5污染特征及其与地面气象要素的关系分析[J]. 中低纬山地气象, 44(4): 59-64. |
| [3] | 陈慧忠, 吴兑, 袁志扬, 2021. 东莞地区PM2.5湿清除的观测研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 41(5): 1 741-1 752. |
| [4] | 陈仁杰, 陈秉衡, 阙海东, 2010. 我国113个城市大气颗粒物污染的健康经济学评价[J]. 中国环境科学, 30(3): 410-415. |
| [5] | 陈婷, 敖天其, 2020. 2015年以来成都市PM2.5演变特征及与气象要素相关性分析[J]. 四川环境, 39(5): 96-100. |
| [6] | 缑晓辉, 严晓瑜, 刘玉兰, 等, 2016. 银川地区大气颗粒物浓度变化特征及其与气象条件的关系[J]. 气象与环境学报, 32(6): 58-68. |
| [7] | 韩力慧, 张海亮, 张鹏, 等, 2017. 北京市春夏季降水及其对大气环境的影响研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 37(6): 2 047-2 054. |
| [8] | 何涛, 彭燕, 雷正翠, 2021. 常州市颗粒物湿清除和雨后PM2.5浓度增长研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 43(9): 1 114-1 117. |
| [9] | 黄秋霞, 赵克明, 艾克代·沙拉木, 等, 2023. 乌鲁木齐一次重污染过程及其边界层特征量分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 17(3): 93-98. |
| [10] | 姜江, 郭文利, 王春玲, 2021. 春节期间北京地区交通出行对热岛和大气污染的影响[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 15(2): 89-97. |
| [11] | 蒋婷梅, 胡勇, 茆平, 等, 2015. 南京市秋冬季大气颗粒物污染状况及其与气象因素的关系[J]. 中国粉体技术, 21(6): 61-67. |
| [12] | 蒋婉婷, 2019. 成都市西南部冬季大气颗粒物污染特征及典型个例分析[D]. 成都: 成都信息工程大学. |
| [13] | 李培荣, 向卫国, 2018. 四川盆地逆温层特征对空气污染的影响[J]. 成都信息工程大学学报, 33(2): 220-226. |
| [14] | 刘超, 周雅蔓, 魏娟娟, 等, 2022. 乌鲁木齐重污染日PM2.5不同增长型的污染特征及气象条件分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 16(5): 127-134. |
| [15] | 刘孟琴, 汤家法, 刘小青, 等, 2017. 四川省近15年以来PM2.5的时空分布特征及原因分析[J]. 四川环境, 36(3): 74-81. |
| [16] | 刘培川, 罗彬, 张巍, 等, 2019. 四川盆地城市细颗粒物污染特征分类分析研究[J]. 四川环境, 38(2): 53-57. |
| [17] | 栾天, 郭学良, 张天航, 等, 2019. 不同降水强度对PM2.5的清除作用及影响因素[J]. 应用气象学报, 30(3): 279-291. |
| [18] | 罗小靖, 2020. 四川省典型城市大气PM2.5组分特征及来源解析[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学. |
| [19] | 钱骏, 冯小琼, 陈军辉, 等, 2021. 四川盆地典型城市PM2.5污染过程组分特征和来源解析[J]. 环境科学学报, 41(11): 4 366-4 376. |
| [20] | 屈丽玮, 赵强, 马晓华, 等, 2022. 西安市一次持续重污染过程的清除特征分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 16(2): 8-15. |
| [21] | 王振, 杨卫芬, 叶香, 等, 2020. 气象因素对常州市区PM2.5浓度影响[J]. 气象与环境学报, 36(3): 26-32. |
| [22] | 危诗敏, 冯鑫媛, 王式功, 等, 2021. 四川盆地多层逆温特征及其对大气污染的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 41(3): 1 005-1 013 |
| [23] | 武高峰, 王丽丽, 董洁, 等, 2021. 北京城区降水对PM2.5和PM10清除作用分析[J]. 中国环境监测, 37(3): 83-92. |
| [24] | 熊险平, 张唯, 朱锐, 等, 2021. 降水对河北沧州大气污染物质量浓度的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 39(2): 296-301. |
| [25] | 杨柳, 2018. 四川盆地典型城市空气污染特征及降水对其影响的研究[D]. 成都: 成都信息工程大学. |
| [26] | 于彩霞, 邓学良, 石春娥, 等, 2018. 降水和风对大气PM2.5、PM10的清除作用分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 38(12): 4 620-4 629. |
| [27] | 张新科, 胡长金, 何跃, 等, 2021. 重庆市荣昌区冬季PM2.5污染的气象因素及区域传输特征[J]. 干旱气象, 39(1): 102-111. |
| [28] | 中国环境监测总站, 中国环境科学研究院, 大连市环境监测中心, 等, 2012. 环境空气质量指数(AQI)技术规定: HJ 633—2012[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| [29] | 中国环境科学研究院, 中国环境监测总站, 2012. 环境空气质量标准: GB 3095—2012[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| [30] | 周彬, 刘端阳, 魏建苏, 等, 2015. 降水对气溶胶颗粒物清除作用的初步分析[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 24(增刊1): 160-170. |
| [31] | 周国治, 潘海婷, 2020. 长沙市秋冬季降水对PM2.5的影响分析[J]. 四川环境, 39(6): 53-58. |
| [32] | 周书华, 倪长健, 刘培川, 2015. 成都地区大气边界层逆温特征分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 31(2): 108-111. |
| [33] | 周文利, 向亚飞, 祝海扬, 等, 2020. 格尔木市低空逆温特征及其对空气污染物浓度的影响[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 14(3): 88-94. |
| [34] | 邹长伟, 黄虹, 杨帆, 等, 2017. 大气颗粒物和气态污染物的降雨清除效率及影响因素[J]. 环境科学与技术, 40(1): 133-140. |
| [35] |
CHATE D M, PRANESHA T S, 2004. Field studies of scavenging of aerosols by rain events[J]. Journal of Aerosol Science, 35(6): 695-706.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
CHATE D M, RAO P S P, NAIK M S, et al, 2003. Scavenging of aerosols and their chemical species by rain[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 37(18): 2 477-2 484.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
CHEN Z Y, CAI J, GAO B B, et al, 2017. Detecting the causality influence of individual meteorological factors on local PM2.5 concentration in the Jing-Jin-Ji region[J]. Scientific Reports, 7, 40735. DOI: 10.1038/srep40735.
DOI |
| [38] |
FU H Y, ZHANG Y T, LIAO C, et al, 2020. Investigating PM2.5 responses to other air pollutants and meteorological factors across multiple temporal scales[J]. Scientific Reports, 10, 15639. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-72722-z.
DOI |
| [39] |
HAN L J, ZHOU W Q, LI W F, et al, 2014. Impact of urbanization level on urban air quality: a case of fine particles (PM2.5) in Chinese cities[J]. Environmental Pollution, 194: 163-170.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
LI Y, LAU A, WONG A, et al, 2014. Decomposition of the wind and nonwind effects on observed year-to-year air quality variation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 119(10): 6 207-6 220.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
LIU Y S, ZHOU Y, LU J X, 2020. Exploring the relationship between air pollution and meteorological conditions in China under environmental governance[J]. Scientific Reports, 10, 14518. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-71338-7.
DOI |
| [42] |
PRANESHA T S, KAMRA A K, 1997. Scavenging of aerosol particles by large water drops: 3. Washout coefficients, half-lives, and rainfall depths[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 102(D20): 23 947-23 953.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
SAMARA C, TSITOURIDOU R, 2000. Fine and coarse ionic aerosol components in relation to wet and dry deposition[J]. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 120(1/2): 71-88.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
SUN Y, ZHAO C F, SU Y F, et al, 2019. Distinct impacts of light and heavy precipitation on PM2.5 mass concentration in Beijing[J]. Earth and Space Science, 6: 1 915-1 925
DOI URL |
| [45] | XU W Y, ZHAO C S, RAN L, et al, 2011. Characteristics of pollutants and their correlation to meteorological conditions at a suburban site in the North China Plain[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 11(230): 4 353-4 369 |
| [46] |
ZHAO X, SUN Y, ZHAO C F, et al, 2020. Impact of precipitation with different intensity on PM2.5 over typical regions of China[J]. Atmosphere, 11(9), 906. DOI:10.3390/atmos-11090906.
DOI |
| [1] | XU Lina, LI Zhong, HU Yanan, GU Xinbo. Analysis on Meteorological Conditions About Frequent Air Pollution in Hohhot in Winter of 2019 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(1): 112-118. |
| [2] | LIU Linchun, LIU Wei, SUN Xin, LIU Xin, DONG Zhulei, ZHANG Yu. Analysis on Characteristic of Extreme Precipitation in Hetao Area, Inner Mongolia [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(4): 535-542. |
| [3] | SUN Junkui, WANG Jiang, KANG Daojun, YAN Liping, ZHOU Xi. Precipitation Forecast of Wudongde Hydropower Station Based on SVM Model Optimized by Multiple Algorithms [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(4): 670-675. |
| [4] | PENG Shuling1, ZHOU Shudao1,2, WANG Min1,2, REN Shangshu1, SHEN Ao1. Characteristics of a Continuous Fog and Haze Weather in Nanjing and Its Causes [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(2): 282-289. |
| [5] | . Study on the Influencing Factors of Haze Weathers in Shanghai [J]. J4, 2012, 30(3): 367-373. |
| [6] | . Influence of Meteorological Condition on Air Quality over Shijiazhuang of Hebei Province [J]. J4, 2011, 29(1): 42-47. |
| [7] | SUN Yin-Chuan- , JIU Qi-Long- , LI Yan-Chun- , SANG Jian-Ren. Prediction Result Analysis of Air Quality Dynamic Prediction System in Yinchuan City [J]. J4, 2006, 24(2): 89-94. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||