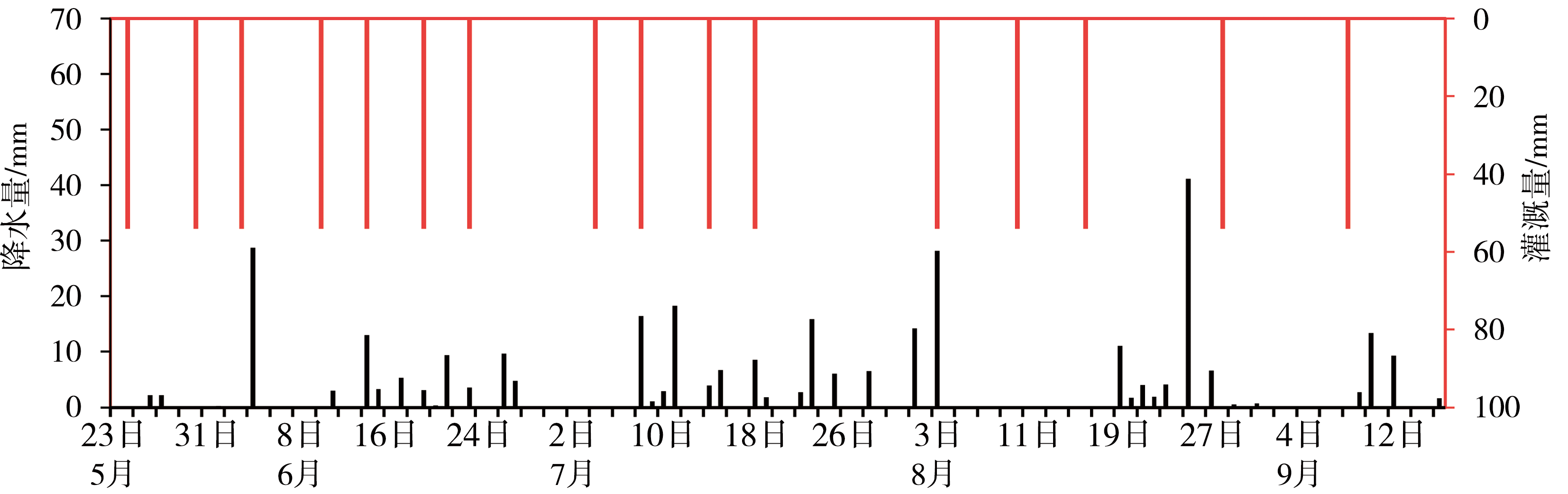
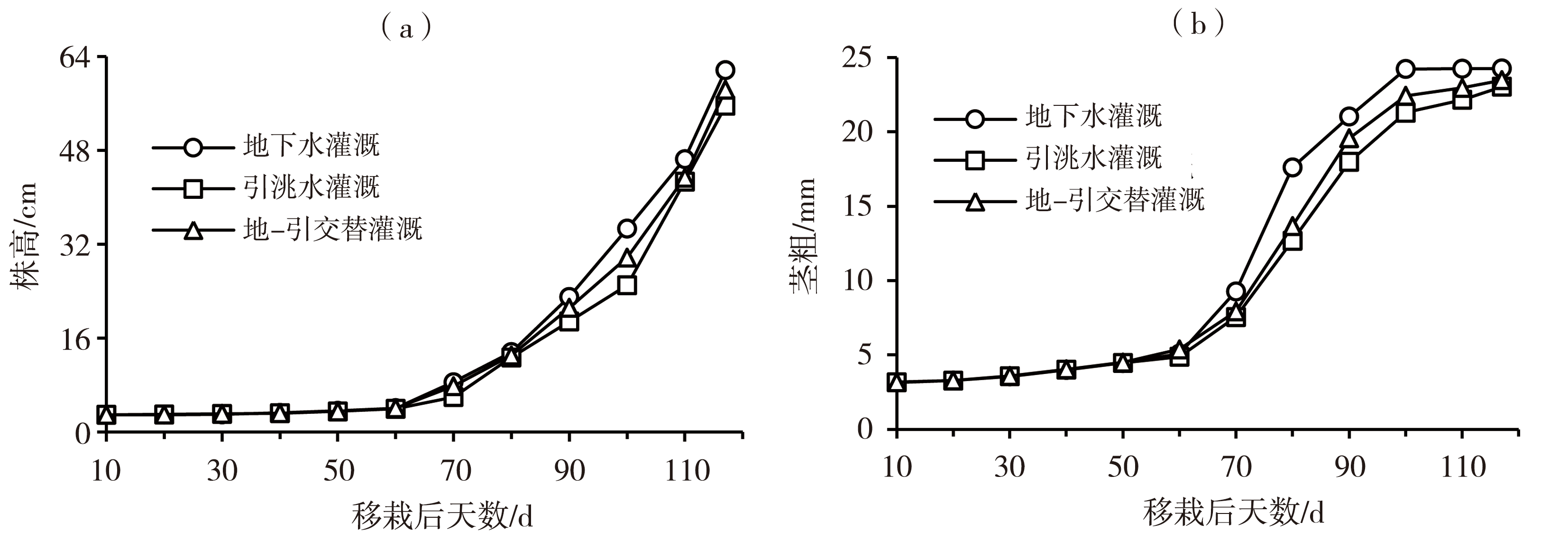
Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (3): 359-367.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-03-0359
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of different irtigation sources on growth characteristics and yields of celery in semi-arid region
- 1. Dingxi Hydraulic Science Research Institute of Gansu Province, Dingxi 743000, Gansu, China
2. College of Grassland Science, Gansu Agricultural University, Lanzhou 730070, China
-
Received:2023-01-14Revised:2023-03-13Online:2023-06-30Published:2023-07-02
半干旱区不同灌溉水源对芹菜生长特性和产量的影响
- 1.甘肃省定西市水利科学研究所,甘肃 定西 743000
2.甘肃农业大学草业学院,甘肃 兰州 730070
-
作者简介:李拥军(1968—),男,甘肃定西人,高级工程师,主要从事灌溉试验及水利科研工作。E-mail: 461585428@qq.com。 -
基金资助:2020年市级科技计划项目(DX2020N07)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LI Yongjun, ZHAO Xiaole. Effects of different irtigation sources on growth characteristics and yields of celery in semi-arid region[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(3): 359-367.
李拥军, 赵晓乐. 半干旱区不同灌溉水源对芹菜生长特性和产量的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(3): 359-367.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-03-0359
| 土层深度/cm | 全氮/ (g·kg-1) | 全磷/ (g·kg-1) | 全钾/ (g·kg-1) | 有机质/ (g·kg-1) | 水解氮/ (mg·kg-1) | 速效磷/ (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾/ (mg·kg-1) | pH值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~20 | 0.59 | 0.68 | 25.93 | 10.12 | 72.12 | 8.34 | 125.12 | 7.78 |
| >20~40 | 0.49 | 0.59 | 23.87 | 8.25 | 35.41 | 4.35 | 86.23 | 7.73 |
Tab.1 The chemical properties of soil at different depths of the topsoil
| 土层深度/cm | 全氮/ (g·kg-1) | 全磷/ (g·kg-1) | 全钾/ (g·kg-1) | 有机质/ (g·kg-1) | 水解氮/ (mg·kg-1) | 速效磷/ (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾/ (mg·kg-1) | pH值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~20 | 0.59 | 0.68 | 25.93 | 10.12 | 72.12 | 8.34 | 125.12 | 7.78 |
| >20~40 | 0.49 | 0.59 | 23.87 | 8.25 | 35.41 | 4.35 | 86.23 | 7.73 |
| 类 型 | 总氮/(mg·L-1) | 总磷/(mg·L-1) | 氨氮/ (mg·L-1) | 钙/ (mg·L-1) | 镁/ (mg·L-1) | 铁/ (mg·L-1) | 钾/ (mg·L-1) | 矿化度/ (mg·L-1) | pH值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地下水 | 10.60 | 0.11 | 1.12 | 98.40 | 229.21 | <0.025 | 17.54 | 2 140 | 7.49 |
| 引洮水 | 0.75 | 0.01 | <0.025 | 16.67 | 38.04 | <0.025 | 1.66 | 298 | 7.30 |
Tab.2 Water quality of irrigation water
| 类 型 | 总氮/(mg·L-1) | 总磷/(mg·L-1) | 氨氮/ (mg·L-1) | 钙/ (mg·L-1) | 镁/ (mg·L-1) | 铁/ (mg·L-1) | 钾/ (mg·L-1) | 矿化度/ (mg·L-1) | pH值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地下水 | 10.60 | 0.11 | 1.12 | 98.40 | 229.21 | <0.025 | 17.54 | 2 140 | 7.49 |
| 引洮水 | 0.75 | 0.01 | <0.025 | 16.67 | 38.04 | <0.025 | 1.66 | 298 | 7.30 |
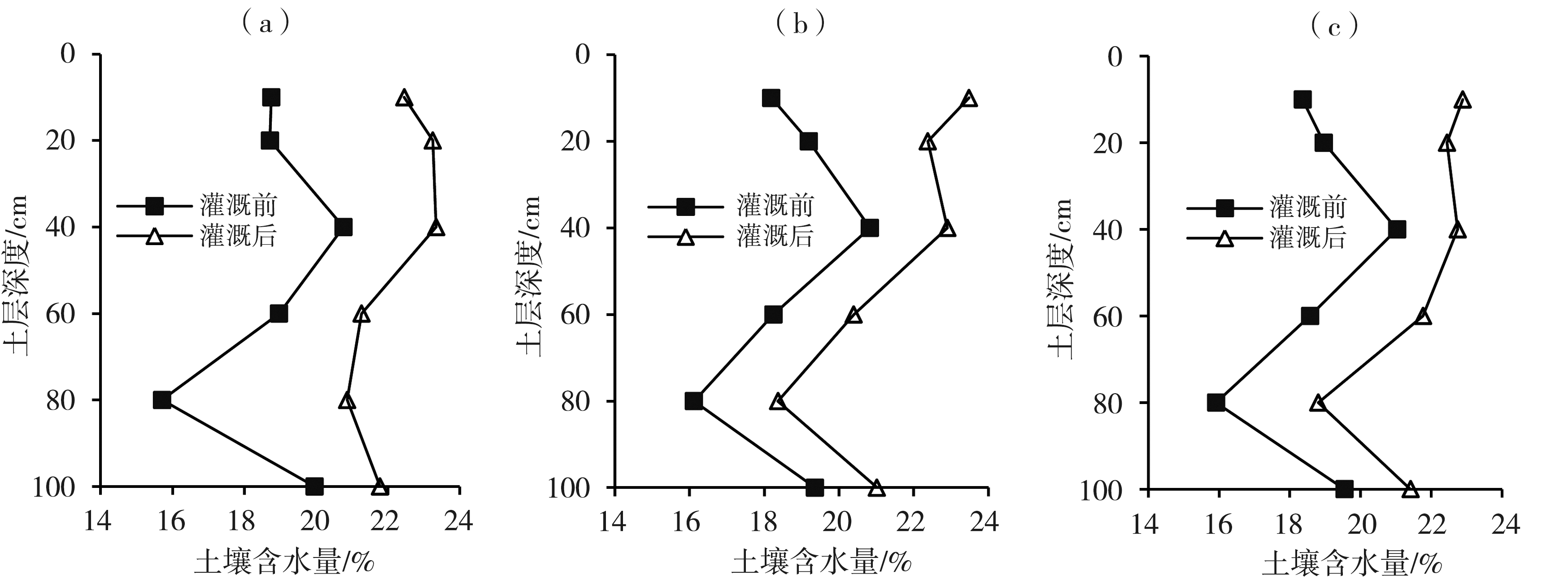
Fig.3 Change of soil water content before and after the first irrigation (on 24 May) of different water sources (a) underground water irrigation, (b) Tao river irrigation, (c) alternative irrigation both underground water and Tao river
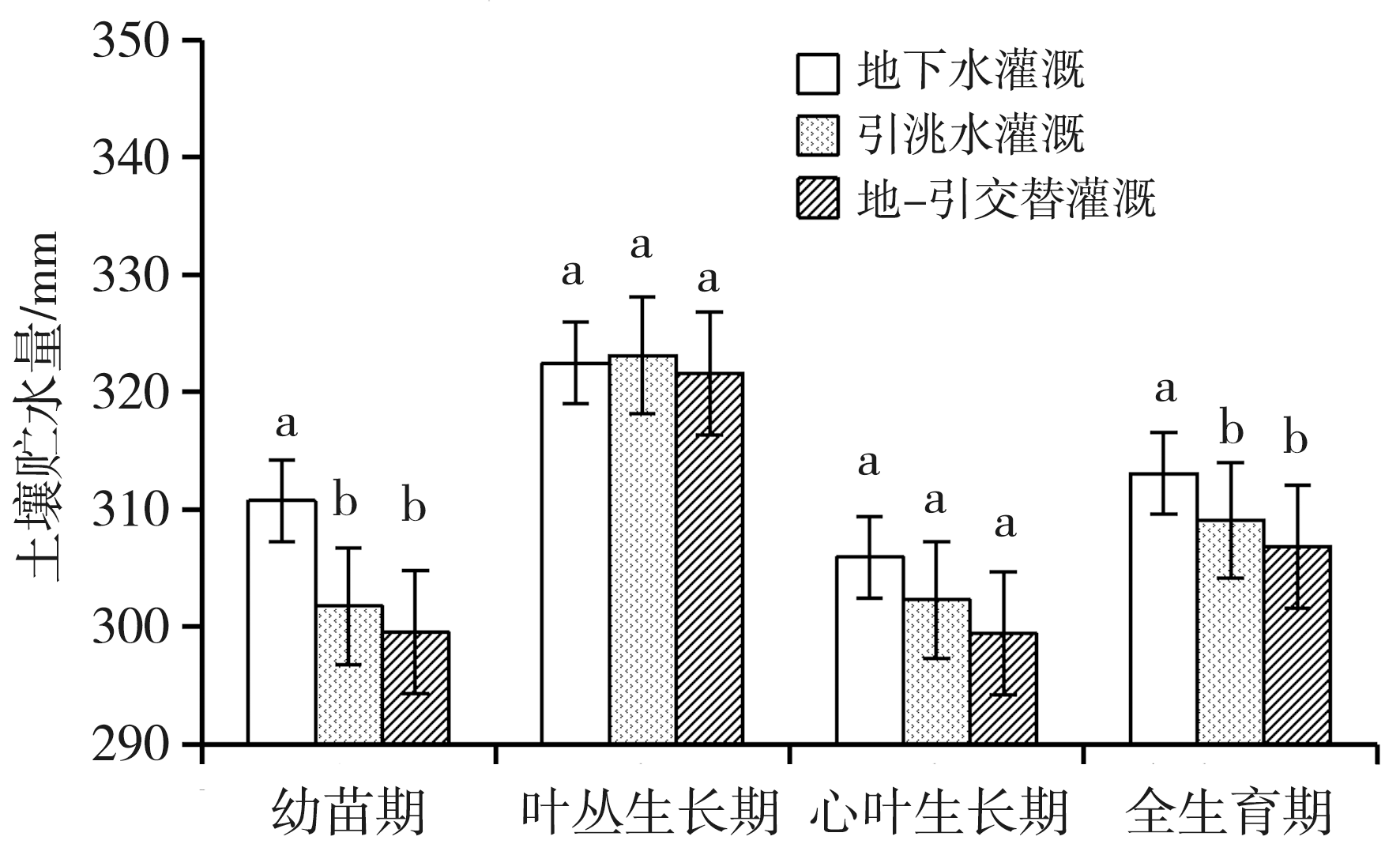
Fig.4 Soil water storage at 0-100 cm depth under different irrigation water sources at different growth periods (The different letters indicate that the difference is significant under different treatments at P<0.05 level, while the same letters indicate that the difference isn’t significant. the same as below)

Fig.5 Water consumption (a) and intensity of daily water consumption (b) of celery under different irrigation water sources at different growth periods
| 不同处理 | 初始土壤贮水量/mm | 季末土壤贮水量/mm | 产量/ (kg·hm-2) | 水分利用效率/(kg·hm-2·mm-1) | 灌溉水利用效率/(kg·hm-2·mm-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地下水灌溉 | 273.0a | 306.0a | 67 635a | 118.0a | 157.3a |
| 引洮水灌溉 | 270.4a | 302.3a | 57 433b | 99.6b | 132.9b |
| 地-引交替灌溉 | 271.8a | 299.4a | 66 572a | 115.1a | 154.1a |
Tab.3 Yield and water use efficiency of celery under different irrigation water sources
| 不同处理 | 初始土壤贮水量/mm | 季末土壤贮水量/mm | 产量/ (kg·hm-2) | 水分利用效率/(kg·hm-2·mm-1) | 灌溉水利用效率/(kg·hm-2·mm-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地下水灌溉 | 273.0a | 306.0a | 67 635a | 118.0a | 157.3a |
| 引洮水灌溉 | 270.4a | 302.3a | 57 433b | 99.6b | 132.9b |
| 地-引交替灌溉 | 271.8a | 299.4a | 66 572a | 115.1a | 154.1a |
| 不同处理 | 支出 | 收入 | 净收益 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 芹菜苗 | 肥料 | 水费 | 人工 | 其他 | |||
| 地下水灌溉 | 15 000 | 5 400 | 13 824 | 750 | 500 | 54 348 | 18 874 |
| 引洮水灌溉 | 15 000 | 5 400 | 4 838 | 750 | 500 | 45 946 | 19 458 |
| 地-引交替灌溉 | 15 000 | 5 400 | 9 331 | 750 | 500 | 53 258 | 22 276 |
Tab.4 Economic benefits of celery under different irrigation water sources
| 不同处理 | 支出 | 收入 | 净收益 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 芹菜苗 | 肥料 | 水费 | 人工 | 其他 | |||
| 地下水灌溉 | 15 000 | 5 400 | 13 824 | 750 | 500 | 54 348 | 18 874 |
| 引洮水灌溉 | 15 000 | 5 400 | 4 838 | 750 | 500 | 45 946 | 19 458 |
| 地-引交替灌溉 | 15 000 | 5 400 | 9 331 | 750 | 500 | 53 258 | 22 276 |
| [1] | 陈亭亭, 杨培伟, 张树辉, 2019. 芹菜素抗肿瘤机制的研究进展[J]. 中国现代应用药学, 36(4):507-510. |
| [2] | 陈云香, 李芳, 陈浩伟, 等, 2022. 甘肃省引洮供水工程水环境效益综合评价研究[J]. 中国农村水利水电,(7):170-174. |
| [3] | 丁艳宏, 屈忠义, 李昌见, 等, 2018. 不同灌溉水源及方式对玉米生长特性及水肥利用效率的影响[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 37(8):1-7. |
| [4] | 董海霞, 2020. 内官-香泉盆地蔬菜种植区地下水利用及水资源置换调查分析[J]. 甘肃水利水电技术, 56(2):18-20. |
| [5] | 方彦杰, 张绪成, 于显枫, 等, 2020. 旱地立式深旋耕方式下有机肥替代对饲用玉米耗水特性和产量的影响[J]. 作物学报, 46(12):1 958-1 969. |
| [6] | 盖钧镒, 2013. 试验统计方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| [7] | 郭勇, 马娟娟, 郑利剑, 等, 2022. 滴灌水分调控对设施芹菜生长与水分利用的影响[J]. 节水灌溉, (9):9-16. |
| [8] | 郝秀芬, 2016. 绿叶菜类蔬菜施肥技术[J]. 天津农林科技,(1):29-30. |
| [9] | 寇霞, 贾晔, 2018. 定西市安定区引洮供水一期工程受水区水资源高效利用探索[J]. 农业科技与信息,(5):99-101. |
| [10] | 李富春, 王琦, 张登奎, 等, 2018. 坡地打结垄沟集雨对水土流失、紫花苜蓿干草产量和水分利用效率的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 32(1):147-156. |
| [11] | 李明, 葛晨昊, 邓宇莹, 等, 2020. 黄土高原气象干旱和农业干旱特征及其相互关系研究[J]. 地理科学, 40(12):2 105-2 114. |
| [12] | 李小东, 张凤华, 朱煜, 2016. 新疆南疆典型地区农业灌溉水质与土壤盐渍化关系的研究[J]. 新疆农业科学, 53(7):1 260-1 267. |
| [13] | 梁丽霞, 杨富元, 张忠扬, 等, 2022. 引洮一期工程对受水区水资源变化影响研究[J]. 中国农村水利水电,(8):84-89. |
| [14] | 梁媛媛, 孙景生, 郭凤台, 等, 2009. 日光温室芹菜适宜灌溉指标研究[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 28(2):48-50. |
| [15] |
刘娜, 黄武斌, 杨建才, 等, 2022. 基于SCTP-RF算法的甘肃省短期定量降水客观预报方法研究[J]. 干旱气象, 40(1): 146-155.
DOI |
| [16] | 马尚宇, 于振文, 张永丽, 等, 2014. 不同畦宽灌溉对小麦耗水特性和产量及水分利用效率的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 47(8):1 531-1 540. |
| [17] | 马筱建, 孙景生, 刘浩, 等, 2018. 不同方式加气灌溉对温室芹菜生长及产量的影响研究[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 37(4):29-33. |
| [18] | 毛盛林, 上官周平, 2022. 近20年黄土高原土地利用/植被覆盖变化特征及其成因[J]. 水土保持研究, 29(5):213-219. |
| [19] | 闵迪, 王增红, 李援农, 等, 2020. 不同灌水和施氮水平对河西春玉米水氮利用效率和经济效益的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 38(5):153-160. |
| [20] | 农业部环境保护科研监测所, 2006. 农田灌溉水质标准:GB5084—2005[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| [21] | 潘春洋, 杨树青, 娄帅, 等, 2020. 多水源交替灌溉模式对玉米生长特性及产量的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料,(1):165-171. |
| [22] | 孙耀民, 王勇, 王则勋, 等, 2021. 引黄灌溉对土壤质地和小麦产量影响的试验研究[J]. 水利科学与寒区工程, 4(5):21-25. |
| [23] | 王艳芳, 曹玲, 陈宝悦, 等, 2014. 咸淡水交替灌溉对芹菜生长及品质的影响[J]. 北方园艺, (10):5-8. |
| [24] | 吴凯, 殷会娟, 何宏谋, 等, 2020. 基于水文连通特征的黄土高原淤地坝系水资源挖潜调控利用体系[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报, 28(3):717-726. |
| [25] | 杨海兴, 张晶, 李强, 等, 2019. 兰州高原夏菜芹菜标准化栽培技术[J]. 中国蔬菜,(1):92-93. |
| [26] | 杨军, 廉晓娟, 王艳, 等, 2016. 滴灌条件下不同灌溉量对芹菜耗水量和水分利用效率的影响[J]. 江苏农业学报, 32(3):656-661. |
| [27] |
杨丽杰, 曹彦超, 刘维成, 等, 2022. 陇东黄土高原旱区短时强降水的时空分布特征及地形影响研究[J]. 干旱气象, 40(6):945-953.
DOI |
| [28] | 杨阳, 刘良旭, 张萍萍, 等, 2023. 黄土高原土壤水分-有机碳-微生物耦合作用研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 43(4):1 714-1 725. |
| [29] | 张凯, 张玉鑫, 陈年来, 等, 2012. 甘肃省高原夏菜种植气候区划[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 40(5):179-185. |
| [30] | 张晓娟, 李玉莲, 王晓军, 等, 2017. 不同栽培与灌溉方式对设施芹菜生长及产量的影响[J]. 中国农村水利水电,(2):40-42. |
| [31] | 朱静, 杨再强, 柳笛, 等, 2012. 设施芹菜光合特性对寡照胁迫的响应[J]. 干旱气象, 30(1):53-58. |
| [32] | 邹宇锋, 蔡焕杰, 张体彬, 等, 2020. 河套灌区不同灌溉方式春玉米耗水特性与经济效益分析[J]. 农业机械学报, 51(9):237-248. |
| [33] |
BELTRÁN SANAHUJA A, PONCE LANDETE M, et al,DOMINGO MARTÍNEZ M I, 2021. Optimization of volatile compounds extraction from industrial Celery (Apium graveolens) by-products by using response surface methodology and study of their potential as antioxidant sources[J]. Foods, 10(11), 2664. DOI: 10.3390/foods10112664.
DOI URL |
| [34] | CAI L P, FAN D L, WEN X J, et al, 2022. Spatiotemporal tendency of agricultural water use efficiency in the northernmost Yellow River: indicator comparison and interactive driving factors[J]. Journal of Arid Environments, 205: 268-379. |
| [35] | MAHESHWARI B L, GREWALH S, 2009. Magnetic treatment of irrigation water: its effects on vegetable crop yield and water productivity[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 96(8): 1 229-1 236. |
| [36] |
MASSERONI D, GANGI F, GALLI A, et al, 2022. Behind the efficiency of border irrigation: lesson learned in Northern Italy[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 269, 107717. DOI:10.1016/j.agwat.2022.107717.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
SUN H Y, LIU C M, ZHANG X Y, et al, 2006. Effects of irrigation on water balance, yield and WUE of winter wheat in the North China Plain[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 85: 211-218.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
TANG J J, FOLMER H, XUE J H, 2015. Technical and allocative efficiency of irrigation water use in the Guanzhong Plain, China[J]. Food Policy, 50:43-52.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
YANG J Y, HE Z L, YANG X E, et al, 2014. Effect of lead on soil enzyme activities in two red soils[J]. Pedosphere, 24(6):817-826.
DOI URL |
| [40] | ZAVADIL J, 2006. Optimization of irrigation regime for early potatoes, late cauliflower, early cabbage and celery[J]. Soil and Water Research, 13(4):139-152. |
| [41] | ZHENG J H, HUANG G H, WANG J, et al, 2013. Effects of water deficits on growth, yield and water productivity of drip-irrigated onion (Allium cepa L.) in an arid region of Northwest China[J]. Irrigation Science, 31(5):995-1 008. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||