Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (5): 857-867.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-05-0857
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Atmospheric circulation characteristics and mechanism of a heavy rain and snow process in Zhejiang region
XU Jinping1( ), LIU Kun2(
), LIU Kun2( ), LI Yun1
), LI Yun1
- 1. Anji County Meteorological Bureau of Zhejiang Province, Anji 313300, Zhejiang,China
2. Shenzhen Municipality Meteorological Bureau of Guangdong Province, Shenzhen 518040, Guangdong,China
-
Received:2021-08-08Revised:2022-05-31Online:2022-10-31Published:2022-11-10 -
Contact:LIU Kun
浙江一次强雨雪过程大气环流特征及成因分析
- 1.浙江省安吉县气象局,浙江 安吉 313300
2.广东省深圳市气象局,广东 深圳 518040
-
通讯作者:刘琨 -
作者简介:许金萍(1991—),女,硕士,工程师,主要从事应用气象与服务研究.E-mail:xujinpingxjp@126.com。 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划资助项目(2019YFB2102003);浙江省气象局2021年度科技计划项目(2021YB22);湖州市科技局2018公益性技术研究项目(2018GZ32)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
XU Jinping, LIU Kun, LI Yun. Atmospheric circulation characteristics and mechanism of a heavy rain and snow process in Zhejiang region[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(5): 857-867.
许金萍, 刘琨, 李云. 浙江一次强雨雪过程大气环流特征及成因分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(5): 857-867.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-05-0857
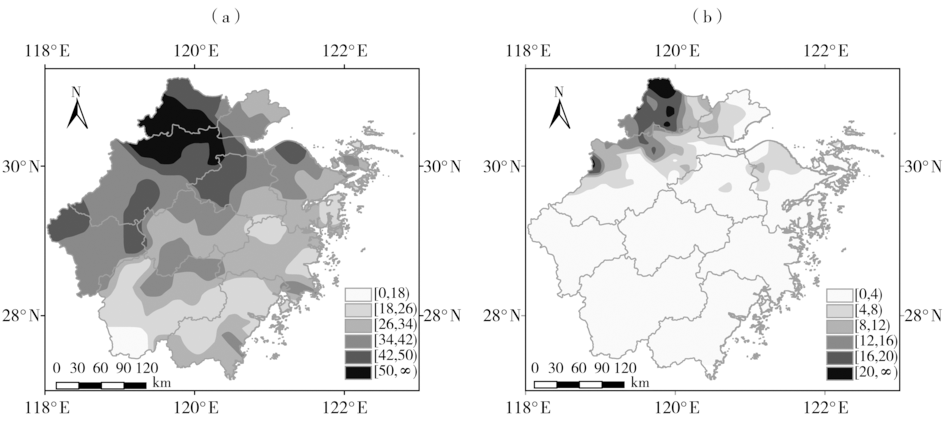
Fig.1 The spatial distribution of accumulated precipitation (a, Unit: mm) and the maximum snow cover depth (b, Unit: cm) in Zhejiang from 20:00 BST 23 to 20:00 BST 28 January2018
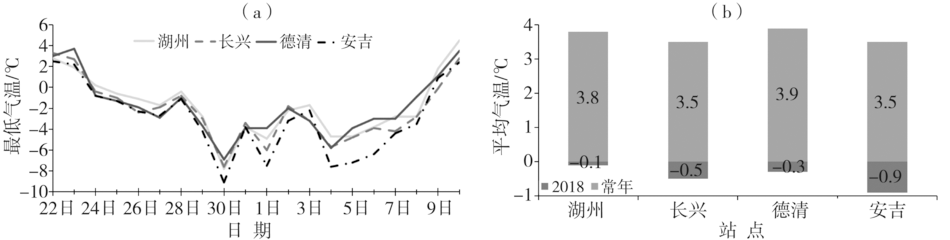
Fig.2 The daily minimum temperature from January 22 to February 10, 2018 (a) and average temperature from January 24 to February 8, 2018 and during historical corresponding period (b) in Huzhou

Fig.3 The 500 hPa (a, c, e, g) and 850 hPa (b, d, f, h) wind field (wind vectors, Unit: m·s-1), geopotential height (contour, Unit: dagpm) and its anomaly (color shaded areas, Unit: dagpm) in January 24(a, b) , 26(c, d) ,27(e, f) and 28 (g, h) ,2018

Fig.4 The 600 hPa wind field (arrow vectors, Unit: m·s-1) and vertical velocity (color shaded area, Unit: m·s-1) from January 19 to 23, 2018 (a) , from January 24 to 28, 2018 (b) , from January 29 to February 7, 2018 (c) ,and meridional vertical circulation anomaly averaged over 119°E-123°E (arrow vectors,Unit: m·s-1, vertical velocity is magnified 100 times) and mean zonal wind anomaly (color shaded areas, Unit: m·s-1) from January 24 to 28, 2018 (d)

Fig.5 The whole troposphere water vapor flux (a, b) and 850 hPa water vapor flux anomaly (c, d) (Unit: kg·m-1·s-1),850 hPa water vapor flux divergence (color shaded area) and its anomaly (isoline) (Unit: 10-9 kg·hPa-1·cm-2·s-1) (e, f) from January 24 to 28(a, c, e) and from January 29 to February 7 (b, d, f) in 2018 [The grey rectangular boxes in Fig.5 (a, b, c, d) are range of Fig.5 (e, f)]

Fig.6 The MJO phase from December 23, 2017 to February 5, 2018 (a) and time-longitude cross section of 850 hPa zonal wind anomaly (color shaded areas) and RMM index (isoline) averaged from 15°S to 15°N(b, Unit: m·s-1) [RMM index from October 31, 2017 to February 27, 2018 were monitoring value, while RMM index from February 28 to April 18, 2018 was forecast value, the arrow denotes zonal wind anomaly and RMM index propagation direction in fig.6 (b)]

Fig.7 The time-longitude cross section of OLR anomaly field from January 1 to February 28, 2018 averaged over 10°S-10°N (a) and OLR anomaly field (b, Unit: W·m-2) in the 5th (b), the 6th (c) pentad of January and in the 1st pentad of February(d) 2018

Fig.8 The 200 hPa (a), 500 hPa (b),850 hPa (c) wave activity flux (arrow vector, Unit: m2·s-2) and height anomaly field (color shaded areas, Unit: gpm) during the snowfall period (January 24-28, 2018) in Zhejiang and zonal vertical wave activity flux averaged from 25°N to 35°N (arrow vector, Unit: m2·s-2, the vertical component is magnified by 10000 times) and the height anomaly field (color shaded areas, Unit: gpm)(d)

Fig.9 Sea surface temperature anomaly (a, c, e) in the 5th pentad (a, b), 6th pentad (c, d) of January, 1st pentad of February (e, f) and SST difference between it and its previous pentad(d, e, f) (Unit: ℃)
| [1] | 宗海锋, 布和朝鲁, 彭京备, 等. 中国南方大范围持续性低温、雨雪和冰冻组合性灾害事件:客观识别方法及关键特征[J]. 大气科学, 2022, 46(5): 1055-1070. |
| [2] | 蓝俊倩, 余健, 王健疆. 浙江2011-01-20强降雪过程降雪带南压成因的诊断分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 2011, 34(4):52-58. |
| [3] | 汪天颖, 廖玉芳, 李晶. 2018年末湖南雨雪冰冻过程对农业的影响及大棚积雪致灾指标构建[J]. 气象与环境科学, 2019, 42(4):1-9. |
| [4] | 王记芳, 顾万龙, 潘攀, 等. 2008年初河南低温雨雪冰冻天气的气候特征及环流特点[J]. 气象与环境科学, 2009, 32(1):51-54. |
| [5] | 李崇银, 杨辉, 顾薇. 中国南方雨雪冰冻异常天气原因的分析[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2008, 13(2): 113-122. |
| [6] | 廖治杰. 持续性暴雪事件中热带低频振荡和高空急流协同变化特征分析[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2014. |
| [7] | 王东海, 柳崇健, 刘英, 等. 2008年1月中国南方低温雨雪冰冻天气特征及其天气动力学成因的初步分析[J]. 气象学报, 2008, 66(3): 405-422. |
| [8] | 邵勰, 张祖强, 陶丽. 2007/2008年冬季中国南方低温雨雪天气期间大气准双周振荡作用分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 2011, 34(3):1-6. |
| [9] | 杨贵名, 孔期, 毛冬艳, 等. 2008年初“低温雨雪冰冻”灾害天气的持续性原因分析[J]. 气象学报, 2009, 66(5): 836-849. |
| [10] |
BAO Q, JING Y, LIU Y M, et al. Roles of anomalous Tibetan Plateau warming on the severe 2008 winter storm in central-southern China[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 2010, 138(6): 2375-2384.
DOI URL |
| [11] | 彭京备, 孙淑清. 2018年1月南方雨雪天气的形成及其与冬季风异常的关系[J]. 大气科学, 2019, 43(6):1233-1244. |
| [12] | 白旭旭, 李崇银, 李琳. MJO对中国春季降水影响的数值模拟研究[J]. 气象学报, 2012, 70(5): 986-1003. |
| [13] | 朱玉祥, 俞小鼎, 赵亮, 等. 10—30天延伸期预报及其策略思考[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 2013, 7(4):38-44. |
| [14] | 冯俊阳, 肖子牛. 热带低频振荡的强度和相位对中国南方冬季降水的影响[J]. 气象, 2012(11): 45-56. |
| [15] | 琚建华, 赵尔旭. 东亚夏季风区的低频振荡对长江中下游旱涝的影响[J]. 热带气象学报, 2005, 21(2): 163-171. |
| [16] | 贾小龙, 梁潇云. 热带MJO对2009年11月我国东部大范围雨雪天气的可能影响[J]. 热带气象学报, 2011, 27(5): 639-648. |
| [17] |
JEONG J H, KIM B M, HO C H, et al. Systematic variation in wintertime precipitation in East Asia by MJO-induced extratropical vertical motion[J]. Journal of Climate, 2008, 21(4):788-801.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
ZHANG C, DONG M. Seasonality in the Madden Julian Oscillation.[J]. Journal of Climate, 2015, 17(17): 3169-3180.
DOI URL |
| [19] | 朱红蕊, 刘赫男, 张洪玲, 等. 热带大气季节内振荡与2008年初中国南方雪灾的关系[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2013, 29(4): 77-83. |
| [20] | 吴捷, 任宏利, 许小峰, 等. MJO对我国降水影响的季节调制和动力-统计降尺度预测[J]. 气象, 2018, 44(6):737-751. |
| [21] | 米瑞芝, 牛法宝, 向影, 等. MJO影响下2016年云南首场强降水过程的成因[J]. 干旱气象, 2017, 35(2):232-238. |
| [22] | 马锋敏, 章毅之, 黄彩婷, 等. 2015年6月江西强降水的环流背景及与MJO的可能联系[J]. 干旱气象, 2017, 35(2):208-213. |
| [23] | 周弘媛, 钱卓蕾, 周晓燕, 等. 2018年浙江低温雨雪天气的特征和成因分析[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2019, 60(11):2142-2144+2147. |
| [24] | 吴捷, 任宏利, 赵崇博, 等. 国家气候中心MJO监测预测业务产品研发及应用[J]. 应用气象学报, 2016, 27(6): 641-653. |
| [25] |
WHEELER M C, HENDON H H. An all-season real-time multivariate MJO index: development of an index for monitoring and prediction[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 2004, 132(8):1917-1932.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
TAKAYA K, NAKAMURA H. A formulation of a wave-activity flux of stationary Rossby waves on a zonally varying basic flow[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1997, 24(23): 2985-2988.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
王文, 许金萍, 蔡晓军, 等. 2013年夏季长江中下游地区高温干旱的大气环流特征及成因分析[J]. 高原气象, 2017, 36(6):1595-1607.
DOI |
| [28] | 梅笑冬. 北大西洋海温对NAO型大气环流异常的影响研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2015. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||