Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (4): 577-588.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-04-0577
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Individual and joint influence of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau summer monsoon and boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation on drought and flood in rainy season of southwestern China
MA Mengmeng( ), ZUO Hongchao(
), ZUO Hongchao( ), LI Licheng, DUAN Jikai
), LI Licheng, DUAN Jikai
- College of Atmosphere Sciences, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, China
-
Received:2021-11-21Revised:2022-04-07Online:2022-08-31Published:2022-09-21 -
Contact:ZUO Hongchao
青藏高原夏季风和北半球夏季季节内振荡对中国西南地区雨季旱涝的影响及协同作用
- 兰州大学大气科学学院,甘肃 兰州 730000
-
通讯作者:左洪超 -
作者简介:马萌萌(1997—),女,硕士生,主要从事气候变化研究. E-mail:mamm2019@lzu.edu.cn; 1539844179@qq.com。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(2019QZKK0103)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
MA Mengmeng, ZUO Hongchao, LI Licheng, DUAN Jikai. Individual and joint influence of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau summer monsoon and boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation on drought and flood in rainy season of southwestern China[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(4): 577-588.
马萌萌, 左洪超, 李立程, 段济开. 青藏高原夏季风和北半球夏季季节内振荡对中国西南地区雨季旱涝的影响及协同作用[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(4): 577-588.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-04-0577
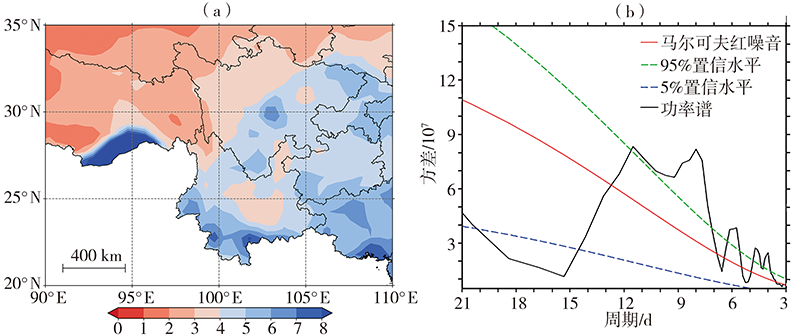
Fig.1 The distribution of mean precipitation (a, Unit: mm·d-1) and mean power spectra of daily precipitation time series (b) in rainy season of southwestern China from 1981 to 2020
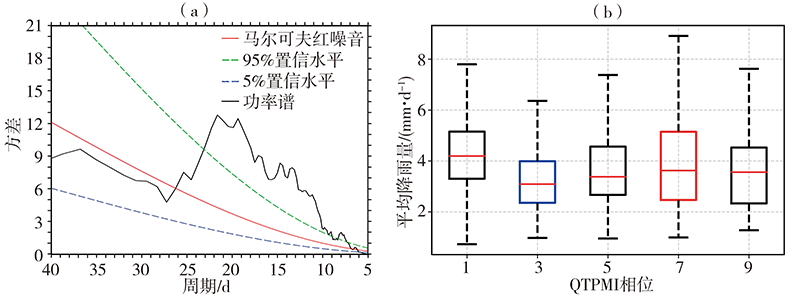
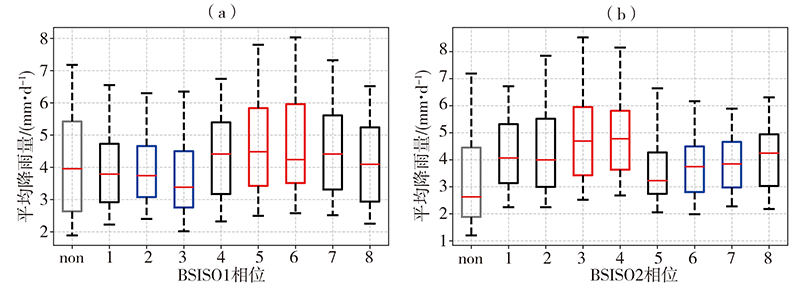
Fig.2 Mean power spectra of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau summer monsoon index (a) and box plot of mean precipitation at different phases of the QTPMI (b) in rainy season of southwestern China from 1981 to 2020 (The value of box plot from bottom to top are the 5th (lower bound), 25th (lower quartile), median, 75th (upper quartile) and 95th (upper bound) percentiles, respectively. the same as below)
| 组 合 | 简 称 | 次数/次 |
|---|---|---|
| AQ与BSISO12&13 | B1-23-AQ | 38 |
| AQ与BSISO15&16 | B1-56-AQ | 41 |
| AQ与BSISO23&24 | B2-34-AQ | 46 |
| AQ与BSISO26&27 | B2-67-AQ | 32 |
| IAQ与BSISO12&13 | B1-23-IAQ | 35 |
| IAQ与BSISO15&16 | B1-56-IAQ | 40 |
| IAQ与BSISO23&24 | B2-34-IAQ | 53 |
| IAQ与BSISO26&27 | B2-67-IAQ | 30 |
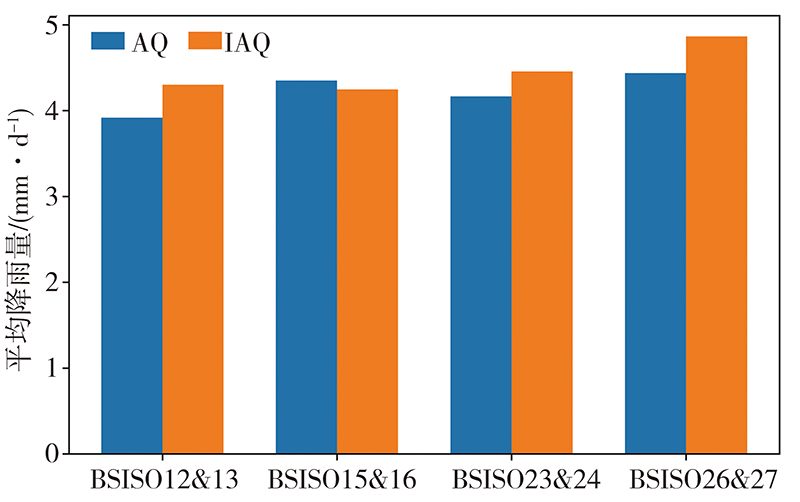
Tab.1 The times of combined events of QTPSM with BSISO in rainy season of southwestern China from 1981 to 2020
| 组 合 | 简 称 | 次数/次 |
|---|---|---|
| AQ与BSISO12&13 | B1-23-AQ | 38 |
| AQ与BSISO15&16 | B1-56-AQ | 41 |
| AQ与BSISO23&24 | B2-34-AQ | 46 |
| AQ与BSISO26&27 | B2-67-AQ | 32 |
| IAQ与BSISO12&13 | B1-23-IAQ | 35 |
| IAQ与BSISO15&16 | B1-56-IAQ | 40 |
| IAQ与BSISO23&24 | B2-34-IAQ | 53 |
| IAQ与BSISO26&27 | B2-67-IAQ | 30 |
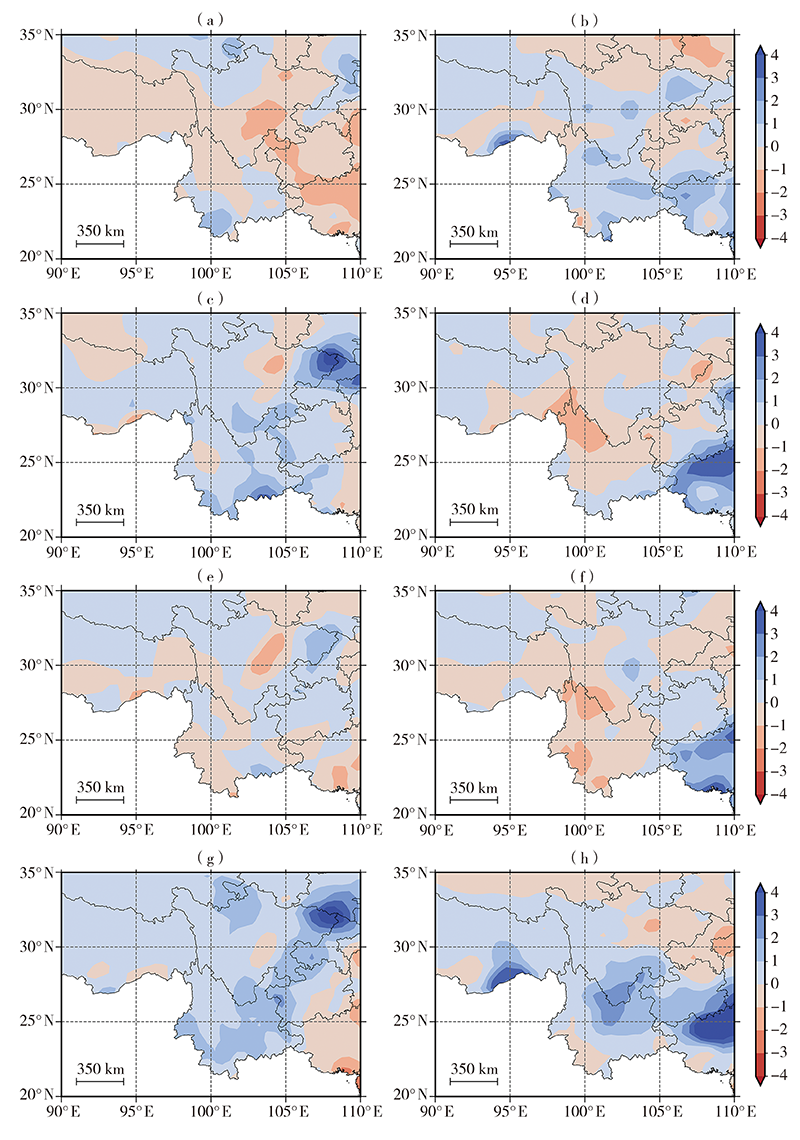
Fig.5 Precipitation anomaly in rainy season of southwestern China at different combined phase stages of QTPSM and BSISO from 1981 to 2020 (Unit: mm·d-1)(a) B1-23-AQ, (b) B1-23-IAQ, (c) B1-56-AQ, (d) B1-56-IAQ, (e) B2-34-AQ,(f) B2-34-IAQ, (g) B2-67-AQ, (h) B2-67-IAQ

Fig.6 Composites of 500 hPa (a, c, e, g), 850 hPa (b, d, f, h) geopotential height field (color shaded areas, Unit: dagpm) and wind field (arrows, Unit: m·s-1) anomaly in rainy season of southwestern China during the combined AQ from 1981 to 2020 (The color grid areas and arrows pass the significance test at 0.05 level, and the area enclosed by the red box is the southwestern China. the same as below) (a, b) B1-23-AQ, (c, d) B1-56-AQ, (e, f) B2-34-AQ, (g, h) B2-67-AQ
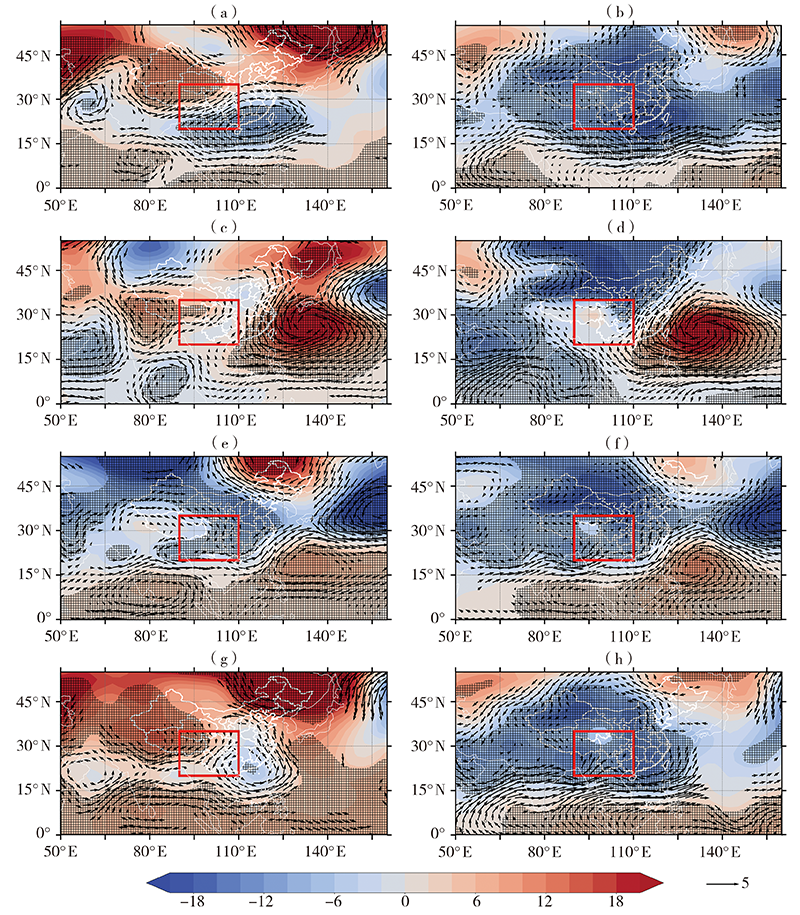
Fig.7 Composites of 500 hPa (a, c, e, g), 850 hPa (b, d, f, h) geopotential height field (color shaded areas, Unit: dagpm) and wind field (arrows, Unit: m·s-1) anomaly in rainy season of southwestern China during the combined IAQ from 1981 to 2020 (a, b) B1-23-IAQ, (c, d) B1-56-IAQ, (e, f) B2-34-IAQ, (g, h) B2-67-IAQ
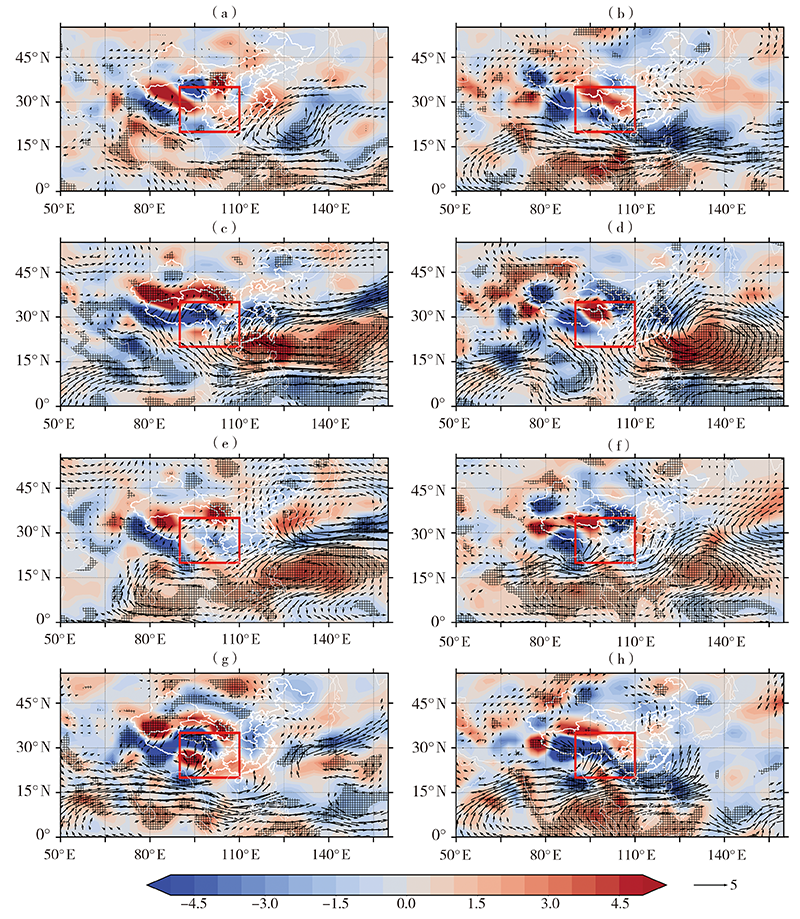
Fig.8 Composites of integrated water vapor flux divergence (color shaded areas, Unit: 10-5 kg·m-2·s-1) and 850 hPa water vapor flux (arrows, Unit: kg·hPa-1·m-1·s-1) anomaly fields in rainy season of southwestern China at different combined phase stages of QTPSM and BSISO from 1981 to 2020 (a) B1-23-AQ, (b) B1-23-IAQ, (c) B1-56-AQ, (d) B1-56-IAQ, (e) B2-34-AQ, (f) B2-34-IAQ, (g) B2-67-AQ, (h) B2-67-IAQ
| [1] | 黄珊, 杨扬, 王含嘉, 等. 中国西南地区地表感热和潜热通量时空变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(4): 601-611. |
| [2] | 晏红明, 李清泉, 孙丞虎, 等. 中国西南区域雨季开始和结束日期划分标准的研究[J]. 大气科学, 2013, 37(5): 1111-1128. |
| [3] | 郑凤琴, 钟利华, 罗小莉, 等. 利用天气关键区相似法预测西江流域6月延伸期强降水天气过程[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(3): 490-496. |
| [4] | ZHANG P F, LI G P, FU X H, et al. Clustering of Tibetan Plateau vortices by 10-30-day intraseasonal oscillation[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 2014, 142(1):290-300. |
| [5] | WANG M R, DUAN A M. Quasi-biweekly oscillation over the Tibetan Plateau and its link with the Asian summer monsoon[J]. Journal of Climate, 2015, 28(12):4921-4940. |
| [6] | YANG J, BAO Q, WANG B, et al. Characterizing two types of transient intraseasonal oscillations in the eastern Tibetan Plateau summer rainfall[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2017, 48(5/6):1749-1768. |
| [7] | 华维, 范广洲, 王炳赟. 近几十年青藏高原夏季风变化趋势及其对中国东部降水的影响[J]. 大气科学, 2012, 36(4):784-794. |
| [8] | 李菲, 段安民. 青藏高原夏季风强弱变化及其对亚洲地区降水和环流的影响——2008年个例分析[J]. 大气科学, 2011, 35(4):694-706. |
| [9] | WANG M R, WANG J, DUAN A M, et al. Coupling of the quasi‐biweekly oscillation of the Tibetan Plateau summer monsoon with the Arctic Oscillation[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2018, 45(15): 7756-7764. |
| [10] | 庞轶舒, 马振峰, 杨淑群, 等. 盛夏高原季风指数的探讨及其对四川盆地降水的影响[J]. 高原气象, 2017, 36(4):886-899. |
| [11] | 齐冬梅, 李英, 李跃清, 等. 2006年高原夏季风强弱变化及其与西南地区东部夏季气温和降水的关系[J]. 干旱气象, 2015, 33(4):555-565. |
| [12] | 王奕丹, 胡泽勇, 孙根厚, 等. 高原季风特征及其与东亚夏季风关系的研究[J]. 高原气象, 2019, 38(3):518-527. |
| [13] | LEE J Y, WANG B, WHEELER M C, et al. Real-time multivariate indices for the boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation over the Asian summer monsoon region[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2013, 40:493-509. |
| [14] | MOON J Y, WANG B, HA K J, et al. Teleconnections associated with Northern Hemisphere summer monsoon intraseasonal oscillation[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2013, 40: 2761-2774. |
| [15] | HSU P C, LEE J Y, HA K J. Influence of boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation on rainfall extremes in southern China[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2016, 36(3): 1403-1412. |
| [16] | REN P F, REN H L, FU J X, et al. Impact of boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation on rainfall extremes in southeastern China and its predictability in CFSv2[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2018, 123(9): 4423-4442. |
| [17] | HUNG C W, HSU H H. The first transition of the Asian summer monsoon, intraseasonal oscillation, and Taiwan Meiyu[J]. Journal of Climate, 2008, 21(7):1552-1568. |
| [18] | JIANG X, LI T, WANG B. Structures and mechanisms of the northward propagating boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation[J]. Journal of Climate, 2004, 17(5): 1022-1039. |
| [19] | LI T. Recent advance in understanding the dynamics of the Madden-Julian oscillation[J]. Journal of Meteorological Research, 2014, 28(1): 1-33. |
| [20] | LIU H B, YANG J, ZHANG D L, et al. Roles of synoptic to quasi-biweekly disturbances in generating the summer 2003 heavy rainfall in East China[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 2014, 142(2): 886-904. |
| [21] | OH H, HA K J. Thermodynamic characteristics and responses to ENSO of dominant intraseasonal modes in the East Asian summer monsoon[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2015, 44: 1751-1766. |
| [22] | 沈雨旸. 东亚季风区热带大气季节内振荡北传与我国南方夏季降水的关系[D]. 北京: 中国气象科学研究院, 2015. |
| [23] | 齐艳军, 张人禾, Tim Li, 等. 大气季节内振荡在印度夏季风建立和年际变化中的作用[J]. 科学通报, 2008, 53(23):2972-2975. |
| [24] | ZHOU J, WEN J, WANG X, et al. Analysis of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau monsoon evolution and its linkages with soil moisture[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8, 493, DOI: 10.3390/rs8060493 |
| [25] | 陈悦, 李文铠, 郭维栋. 青藏高原季风的季节内振荡特征[J]. 高原气象, 2019, 38(6):1158-1171. |
| [26] | DOUGUEDROIT A. The variations of dry spells in Marseilles from 1865 to 1984[J]. Journal of Climatology, 1987, 7(6): 541-551. |
| [27] | ROMERO R, GUIJARRO J A, RAMIS C, et al. A 30-year (1964-1993) daily rainfall data base for the Spanish Mediterranean.regions: first exploratory study[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 1998, 18: 541-560. |
| [28] | GE F, SIELMANN F, ZHU X H, et al. The link between Tibetan Plateau monsoon and Indian summer precipitation: a linear diagnostic perspective[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2017, 49(11/12): 4201-4215. |
| [1] | ZHANG Qiang. Scientific interpretation of severe drought in the Yangtze River Basin [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(4): 545-548. |
| [2] | WANG Ying, ZHANG Qiang, WANG Jinsong, HAN Lanying, WANG Suping, ZHANG Liang, YAO Yubi, HAO Xiaocui, WANG Sheng. New progress and prospect of drought research since the 21st century [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(4): 549-566. |
| [3] | ZHANG Guohong. Relationship between autumn sea ice in the Barents Sea and change of temperature in February in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region of China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(2): 187-194. |
| [4] | WANG Yaoting, MENG Chunlei, MIAO Shiguang, ZHENG Zuofang, LI Qingchun. Estimation of Anthropogenic Heat Emission in Beijing Based on Population and Energy Consumption Data [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(1): 89-99. |
| [5] | DONG Junling, LIU Chao, SU Aifang. Impact of Urbanization on a Torrential Rain Process in Zhengzhou Region [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(6): 922-932. |
| [6] | HE Yongli, DING Lei, LI Dongdong, HUANG Jianping, LI Changyu, BI Lu. Research Review on the Contrast of Land and Ocean Warming Features Under the Global Warming [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(5): 703-712. |
| [7] | LIU Xuetao, XIE Yiran, XU Yingjie, SUN Jihua. Temporal and Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Lightning Activity over Yunnan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(5): 729-735. |
| [8] | YAN Kailin, YU Miao, GUO Li, LIAO Hong. Relationships Between Precipitation Anomaly in Meiyu Period in the Yangtze-Huaihe Region and Surface Sensible Heat Flux over East Asia [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(5): 771-780. |
| [9] | ZHU Ping, YU Xiaoding, WANG Zhenhui, XIAO Jianshe. Temporal and Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Disastrous Convective Weather over the Qinghai Plateau [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(3): 377-. |
| [10] | ZHAO Caiping, ZHOU Jinhong, LI Zhaoqi, LI Yanhong. Influence of Urbanization on the Change of Rainstorm in Taiyuan [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(1): 109-118. |
| [11] | LUO Yu, MA Zhenfeng, CHEN Chao, LIU Jia, LI Xiaolan, YANG Rong. Variation Characteristics of Extreme Precipitation in Midsummer in Sichuan and Relationship with Tibetan Plateau Summer Monsoon [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(5): 733-742. |
| [12] | PEI Shaoyang, ZHOU Dan, BAO Guangyu, SHEN Yanling. Spatial and Temporal Variation Characteristics of Highway Visibility in Qinghai Province and Its Influencing Factors [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(6): 1004-1010. |
| [13] | CHEN Yan, GUO Shichang, LIU Yu, JU Jianhua, REN Juzhang, ZHANG Huizhu. Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of the Onset Date of Rainy Season in Yunnan and Its Relationship with ENSO [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(4): 545-551. |
| [14] | SHANG Lin, GU Weizong, TANG Zidong, MENG Xiangxin, LUO Jiali, CUI Qiang. Decadal Variation of the Relationship Between Summer Precipitation in Shandong Province and Previous Winter SST over the Equatorial Central and Eastern Pacific [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(4): 552-558. |
| [15] | ZHANG Yanting, HUANG Jianping, GUAN Xiaodan, GUO Ruixia. Quantitative Assessment of Global Human Activity’s Influence on Climate [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(2): 182-189. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||