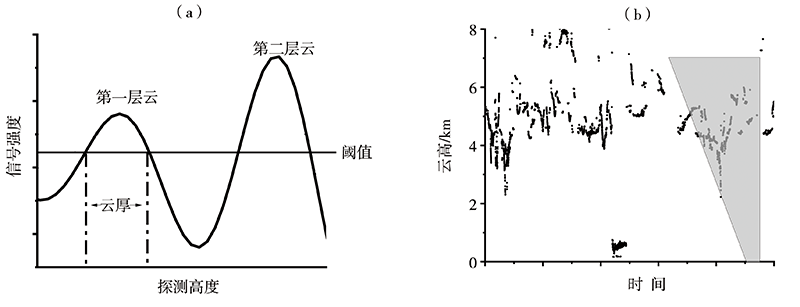
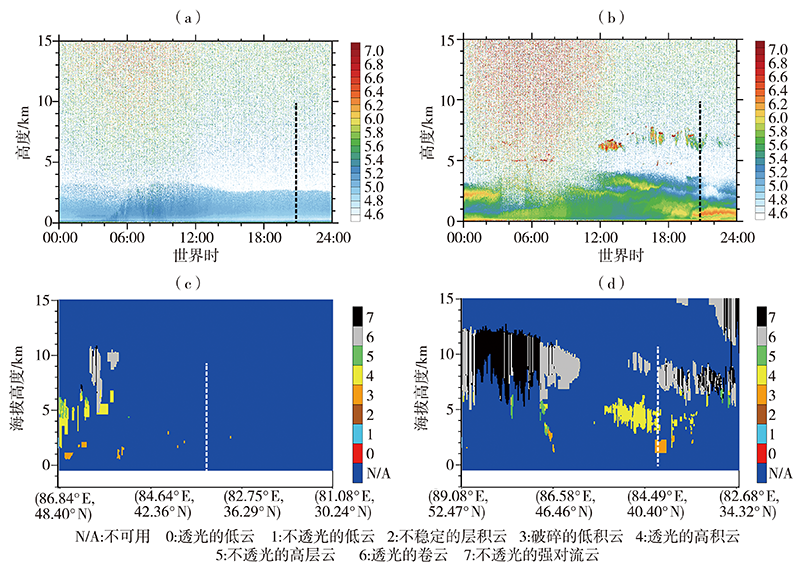
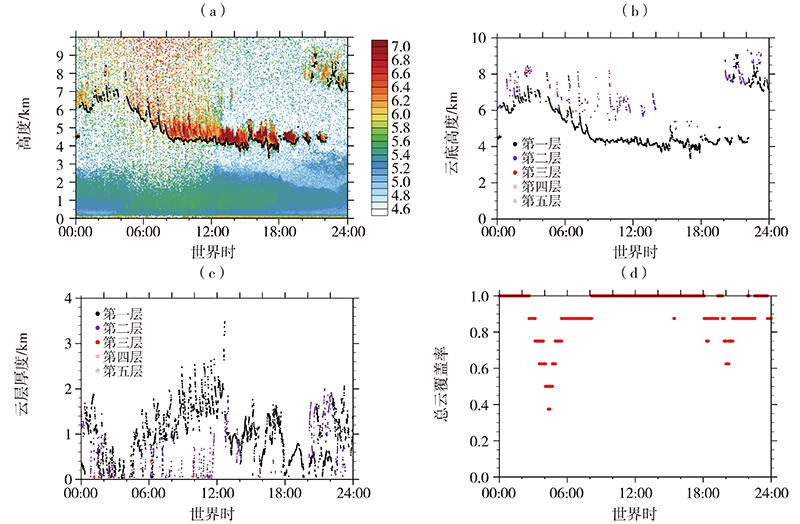
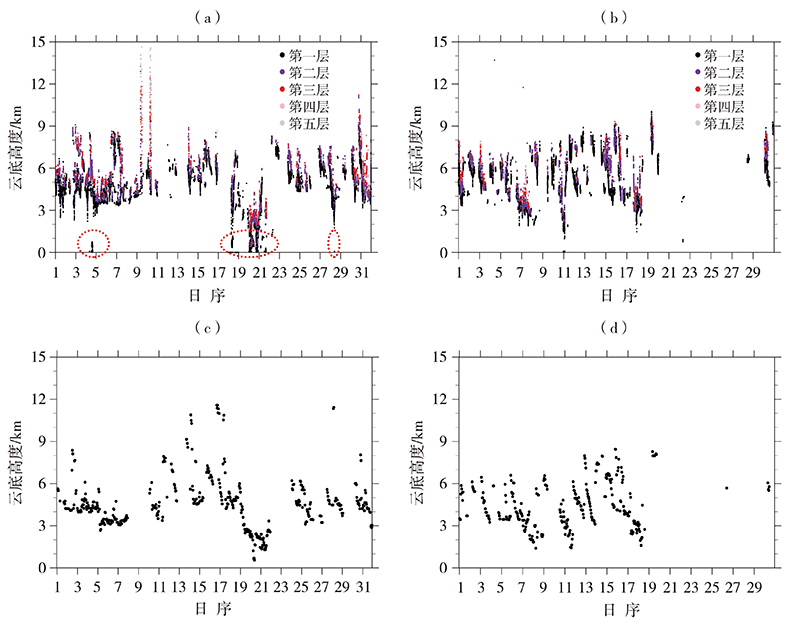
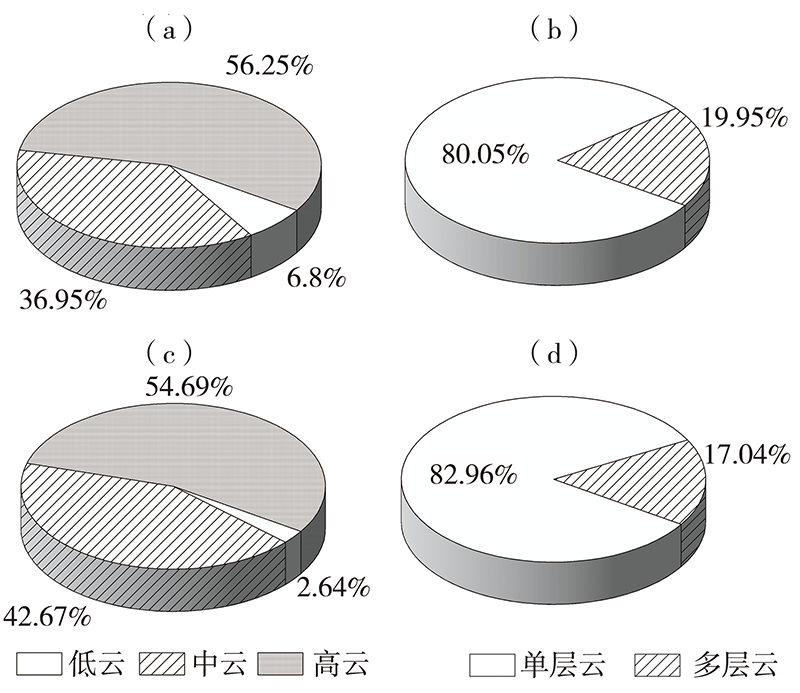
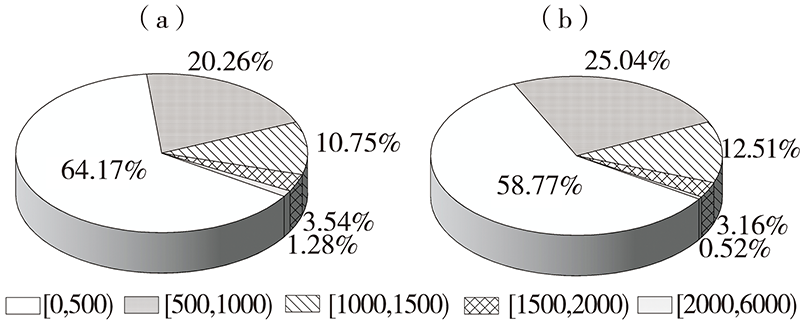
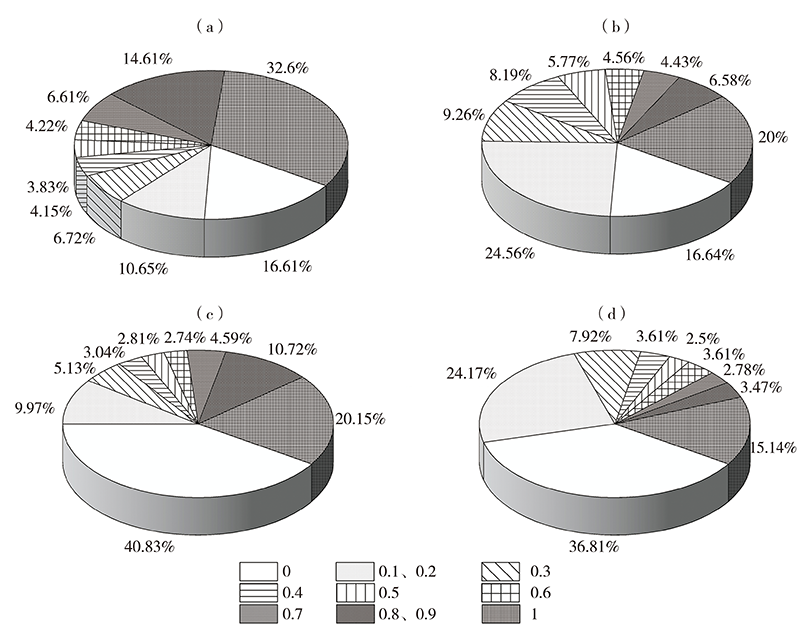
| [1] |
向华, 张峰, 江静, 等. 利用CFSR资料分析近30年全球云量分布及变化[J]. 气象, 2014, 40(5):555-561.
|
| [2] |
RAMANATHAN V, CESS R D, HARRISON E F, et al. Cloud-radiative forcing and climate: results from the earth radiation budget experiment.[J]. Science, 1989, 243(4887):57-63.
|
| [3] |
LI J, JIAN B, HUANG J, et al. Long-term variation of cloud droplet number concentrations from space-based lidar[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2018, 213:144-161.
|
| [4] |
张小曳, 廖宏, 王芬娟. 对IPCC第五次评估报告气溶胶-云对气候变化影响与响应结论的解读[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2014, 10(1):37-39.
|
| [5] |
PAN H, WANG M, KUMAR K R, et al. Seasonal and vertical distributions of aerosol type extinction coefficients with an emphasis on the impact of dust aerosol on the microphysical properties of cirrus over the Taklimakan desert in Northwest China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2019, 203:216-227.
|
| [6] |
LINDZEN R S, CHOU M D, HOU A Y. Does the earth have an adaptive infrared iris?[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2001, 82(3):417-432.
|
| [7] |
LIN B, WIELICKI B A, CHAMBERS L H, et al. The iris hypothesis: a negative or positive cloud feedback?[J]. Journal of Climate, 2002, 15(1):3-7.
|
| [8] |
丁守国, 石广玉, 赵春生. 利用ISCCP D2资料分析近20年全球不同云类云量的变化及其对气候可能的影响[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(11):1105-1111.
|
| [9] |
COSTA-SURÓS M, CALBÓ J, GONZÁLEZ J A, et al. Behavior of cloud base height from ceilometer measurements[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2013, 127:64-76.
|
| [10] |
张华, 陈勇航, 宣越建, 等. 东亚地区云对地球辐射收支和降水变化的影响研究[J]. 中国基础科学, 2017(5):18-22.
|
| [11] |
吕巧谊, 张玉轩, 李积明. 南半球中高纬度区域不同类型云的辐射特性[J]. 气象学报, 2017, 75(4):596-606.
|
| [12] |
汪宏七, 赵高祥. 云和辐射 (I):云气候学和云的辐射作用[J]. 大气科学, 1994, 18(增刊1):910-932.
|
| [13] |
施雅风, 沈永平, 胡汝骥. 西北气候由暖干向暖湿转型的信号、影响和前景初步探讨[J]. 冰川冻土, 2002, 24(3):219-226.
|
| [14] |
商沙沙, 廉丽姝, 马婷, 等. 近54 a中国西北地区气温和降水的时空变化特征[J]. 干旱区研究, 2018, 35(1):68-76.
|
| [15] |
周雪英, 贾健, 刘国强, 等. 1997—2017年塔克拉玛干沙漠腹地降水特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(1):187-194.
|
| [16] |
王德旺, 曲明星, 黄宁立, 等. 基于云雷达反射率因子的云宏观参量反演[J]. 干旱气象, 2016, 34(6):1071-1077.
|
| [17] |
MING H, WANG M, WEI M, et al. Study on the clouds detected by a millimeter-wave cloud radar over the hinterland of the Taklimakan desert in April-June 2018[J]. Journal of Meteorological Research, 2021, 35(6):1074-1090.
|
| [18] |
朱泽恩, 郑创, 葛觐铭, 等. 利用KAZR云雷达对SACOL站云宏观特性的研究[J]. 科学通报, 2017, 62(8):824-835.
|
| [19] |
曹越前, 张武, 药静宇, 等. 半干旱区云量变化特征及其与太阳辐射关系的研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2015, 33(4):684-693.
|
| [20] |
陶法, 胡树贞. 地基自动云观测技术对比分析[J]. 气象水文海洋仪器, 2017(4):5-12.
|
| [21] |
DANSO D K, ANQUETIN S, DIEDHIOU A, et al. Spatio‐temporal variability of cloud cover types in West Africa with satellite‐based and reanalysis data[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 2019, 145(725):3715-3731.
|
| [22] |
范思睿, 王维佳, 林丹. 基于ISCCP云资料的中国地区不同类型云的时空分布[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(2):213-225.
|
| [23] |
陈勇航, 陈艳, 黄建平, 等. 中国西北地区云的分布及其变化趋势[J]. 高原气象, 2007, 26(4):741-748.
|
| [24] |
翁笃呜, 韩爱梅. 我国卫星总云量与地面总云量分布的对比分析[J]. 应用气象学报, 1998, 9(1):32-37.
|
| [25] |
陈勇航, 彭宽军, 史玉光, 等. 天山山区与塔克拉玛干沙漠云水资源的对比分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 2009, 32(6):886-891.
|
| [26] |
叶培龙, 王天河, 尚可政, 等. 基于卫星资料的中国西部地区云垂直结构分析[J]. 高原气象, 2014, 33(4):977-987.
|
| [27] |
HERVO M. CEILINEX 2015: Validation of calibration methods during the ceilometer inter-comparison[C]// EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts. Vienna: EGU General Assembly, 2016: EPSC 2016-4785.
|
| [28] |
WIEGNER M, GEISS A. Aerosol profiling with the Jenoptik ceilometer CHM15kx[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2012, 5(8):1953-1964.
|
| [29] |
HEESE B, FLENTJE H, ALTHAUSEN D, et al. Ceilometer lidar comparison: backscatter coefficient retrieval and signal-to-noise ratio determination[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques Discussions, 2010, 3(6):1763-1770.
|
| [30] |
PATTANTYÚS-BRAHÁM M.The international ceilometer intercomparison campaign CeiLinEx 2015 WMO-TECO 2016 [C]// WMO TECO. Madrid:WMO, 2016.
|
| [31] |
WIEGNER M, MADONNA F, BINIETOGLOU I, et al. What is the benefit of ceilometers for aerosol remote sensing? An answer from EARLINET[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2014, 7(7): 1979-1997.
|
| [32] |
STACHLEWSKA I S, PIDOWSKI M, MIGACZ S, et al. Ceilometer observations of the boundary layer over Warsaw, Poland[J]. Acta Geophysica, 2012, 60(5):1386-1412.
|
| [33] |
HAEFFELIN M, ANGELINI F, MORILLE Y, et al. Evaluation of mixing-height retrievals from automatic profiling lidars and ceilometers in view of future integrated networks in Europe[J]. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 2012, 143(1):49-75.
|
| [34] |
HERSBACH H, BELL B, BERRISFORD P, et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 2020, 146(730):1999-2049.
|
| [35] |
刘刚, 史伟哲, 尤睿. 美国云和气溶胶星载激光雷达综述[J]. 航天器工程, 2008, 17(1):78-84.
|
| [36] |
方乐锌, 李昀英, 孙国荣, 等. 基于CloudSat-CALIPSO资料的全球不同类型云的水平和垂直分布特征[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2016, 21(5):547-556.
|
| [37] |
刘屹岷, 燕亚菲, 吕建华, 等. 基于CloudSat/CALIPSO卫星资料的青藏高原云辐射及降水的研究进展[J]. 大气科学, 2018, 42(4):144-155.
|
| [38] |
郑建宇, 刘东, 王志恩, 等. CloudSat/CALIPSO卫星资料分析云的全球分布及其季节变化特征[J]. 气象学报, 2018, 76(3):420-433.
|
| [39] |
CHEPFER H, BONY S, WINKER D, et al. The GCM-oriented calipso cloud product (CALIPSO‐GOCCP)[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2010, 115, D00H16. DOI:10.1029/2009JD012251.
|
| [40] |
WANG T, FETZER E J, WONG S, et al. Validation of MODIS cloud mask and multilayer flag using CloudSat‐CALIPSO cloud profiles and a cross‐reference of their cloud classifications[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 2016, 121(19):11 620-11 635.
|
| [41] |
WANG Y, ZHAO C, DONG Z, et al. Improved retrieval of cloud base heights from ceilometer using a non-standard instrument method[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2018, 202:148-155.
|
| [42] |
中国气象局. 地面气象观测规范[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2003.
|
| [43] |
李汉林, 何清, 金莉莉. 塔克拉玛干沙漠腹地和北缘典型天气近地层风速廓线特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(6):965-978.
|
 ), BI Jianrong1,2,3(
), BI Jianrong1,2,3( ), ZUO Dapeng1,3, ZHANG Linhan1,3, YANG Fan1,4,5
), ZUO Dapeng1,3, ZHANG Linhan1,3, YANG Fan1,4,5
 ), 闭建荣1,2,3(
), 闭建荣1,2,3( ), 左大鹏1,3, 张琳焓1,3, 杨帆1,4,5
), 左大鹏1,3, 张琳焓1,3, 杨帆1,4,5