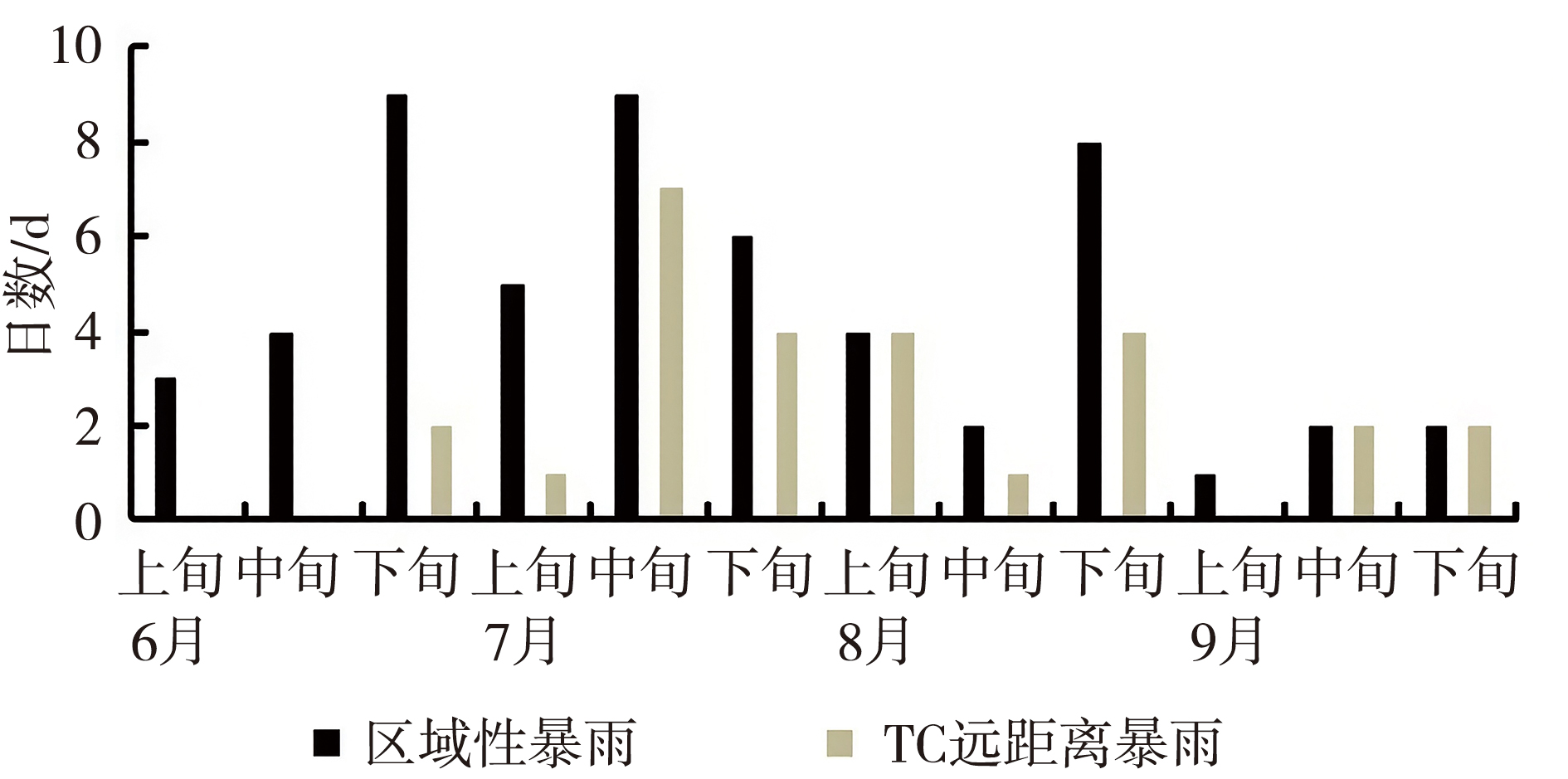
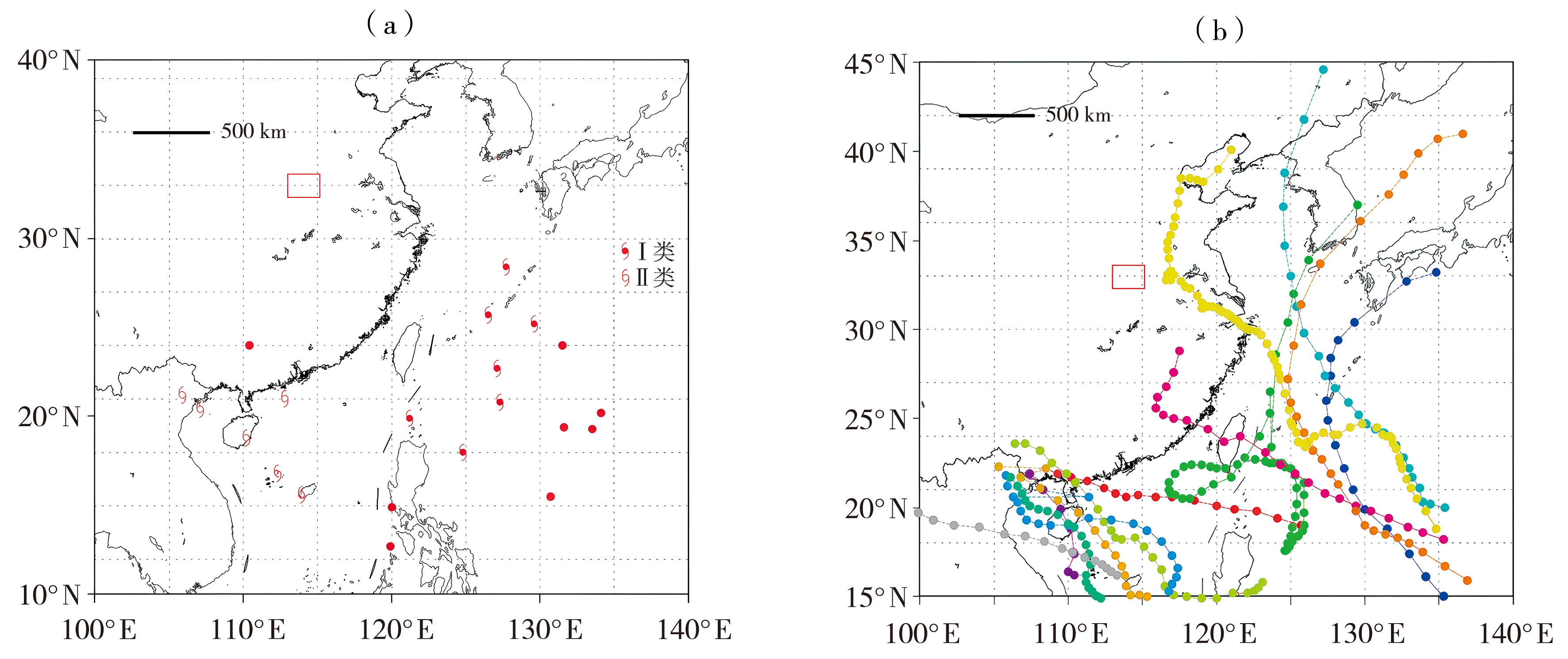
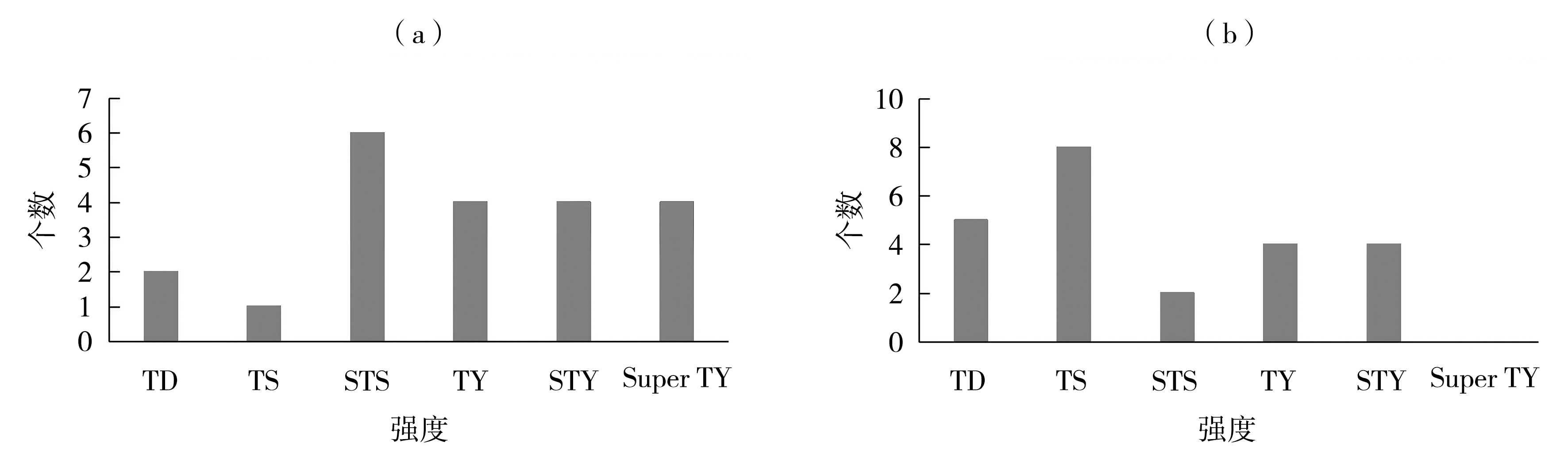
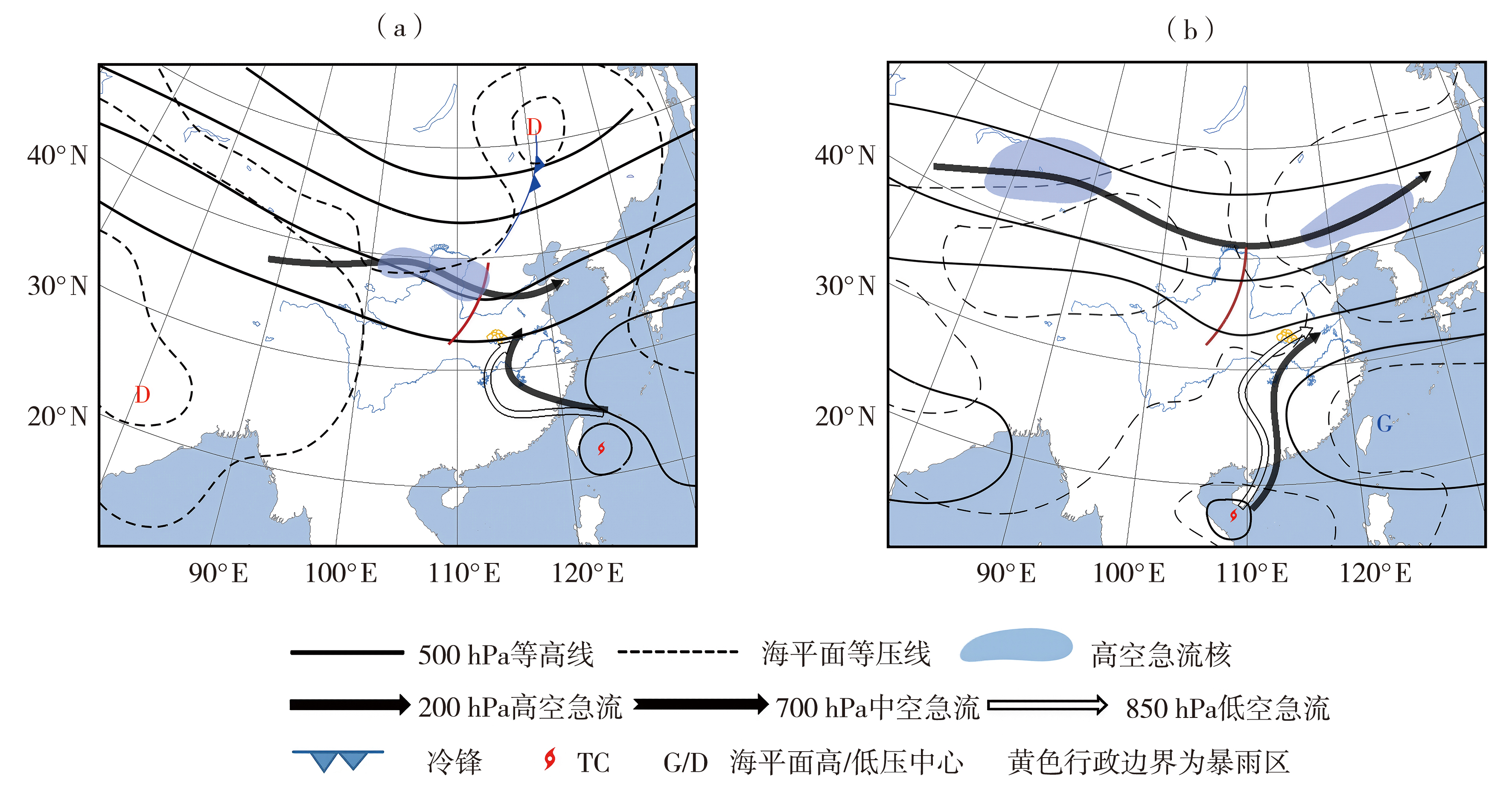
| [1] |
陈联寿, 2007. 登陆热带气旋暴雨的研究和预报[C]// 中国气象学会. 第十四届全国热带气旋科学讨论会论文集:3-7.
|
| [2] |
丛春华, 陈联寿, 雷小途, 等, 2012. 热带气旋远距离暴雨的研究[J]. 气象学报, 70(4):717-727.
|
| [3] |
丁治英, 赵晓慧, 邢蕊, 等, 2014. 2000—2009年夏季东亚热带气旋远距离暴雨统计分析及个例的数值模拟[J]. 热带气象学报, 30(2):229-238.
|
| [4] |
范学峰, 吴蓁, 席世平, 2007. AERE台风远距离降水形成机制分析[J]. 气象, 33(8):12-16.
|
| [5] |
葛战旗, 2017. 2013年8月沙澧河流域一次连续暴雨过程成因分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 40(4):90-99.
|
| [6] |
侯建忠, 王川, 鲁渊平, 等, 2006. 台风活动与陕西极端暴雨的相关特征分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 22(2):203-208.
|
| [7] |
靳冰凌, 芦阿咪, 张璞, 等, 2022. “21·7”豫北极端暴雨天气成因分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 45(2):65-74.
|
| [8] |
李改琴, 梁海河, 王树文, 等, 2007. 台风海棠远距离暴雨中尺度系统特征[J]. 气象, 33(8):17-22.
|
| [9] |
李明, 高维英, 杜继稳, 等, 2011. 远距离台风影响下的陕西大暴雨分析[J]. 干旱区研究, 28(3):514-523.
|
| [10] |
彭力, 赵强, 乔丹杨, 等, 2022. 有无台风影响下陕西西北涡暴雨特征对比分析[J]. 干旱气象, 40(6):981-992.
|
| [11] |
戚佳明, 2014. 基于HYSPLIT模型的大气CO2传输研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学.
|
| [12] |
寿绍文, 2019. 中国暴雨的天气学研究进展[J]. 暴雨灾害, 38(5):450-463.
|
| [13] |
司福意, 张一平, 赵海青, 等, 2021. 豫北“7·9”特大暴雨的形成与极端性探析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 44(1):65-73.
|
| [14] |
苏爱芳, 吕晓娜, 崔丽曼, 等, 2021. 郑州“7·20”极端暴雨天气的基本观测分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 40(5):445-454.
|
| [15] |
苏爱芳, 席乐, 吕晓娜, 等, 2022. 豫北“21·7”极端暴雨过程特征及成因分析[J]. 气象, 48(5):556-570.
|
| [16] |
苏洋, 闫军, 薛宏宇, 2023. 宁夏两次台风远距离暴雨过程对比分析[J]. 宁夏大学学报:自然科学版, 44(3):301-308.
|
| [17] |
孙其明, 胡石建, 赵义军, 2023. 2021年夏季河南极端降雨水汽来源分析与西太平洋副热带高压的可能作用[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 54(1):16-29.
|
| [18] |
汪小康, 崔春光, 王婧羽, 等, 2022. “21·7”河南特大暴雨水汽和急流特征诊断分析[J]. 气象, 48(5):533-544.
|
| [19] |
王红燕, 陈海山, 王军, 等, 2020. 登陆台风“温比亚”(1818)引发豫东特大暴雨的特征分析[J]. 中国科技论文, 15(5):563-576.
|
| [20] |
王静, 武建华, 罗凯丽, 等, 2012. 驻马店市致洪暴雨特征分析与物理量场预报模型[C]// 中国气象学会. 第29届中国气象学会年会论文集:1-7.
|
| [21] |
王军, 吴迪, 王超杰, 等, 2022. “21·7”河南极端降水的远距离台风作用分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 45(2):75-85.
|
| [22] |
王军, 席乐, 王超杰, 等, 2021. “温比亚”引发河南特大暴雨的中尺度系统特征分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 44(4):16-23.
|
| [23] |
王明星, 张仁健, 郑循华, 2000. 温室气体的源与汇[J]. 气候与环境研究, 5(1):75-79.
|
| [24] |
王瑞祥, 2021. 2018年18号台风“温比亚”引发的豫东极端降水诊断分析[J]. 河南科技, 40(8):139-142.
|
| [25] |
王新敏, 赵培娟, 李保生, 等, 2002. 影响河南的登陆台风分析[J]. 河南气象, 25(2):14-16.
|
| [26] |
闫军, 王黎娟, 纪晓玲, 等, 2020. 影响宁夏的热带气旋远距离暴雨特征和预报概念模型[J]. 热带气象学报, 36(1):32-41.
|
| [27] |
杨德南, 黄丽娜, 林莉, 等, 2019. 1710号台风“海棠”登陆后漳州市远距离暴雨的能量特征[J]. 干旱气象, 37(1):76-89.
|
| [28] |
杨晓霞, 陈联寿, 刘诗军, 等, 2008. 山东省远距离热带气旋暴雨研究[J]. 气象学报, 66(2):236-250.
|
| [29] |
张树民, 吴海英, 黄绮君, 等, 2024. 副热带高压内部台风远距离暴雨特征和机制个例分析[J]. 气象科技, 52(4):535-548.
|
| [30] |
张雅斌, 武麦凤, 侯建忠, 等, 2014. 陕西4次台风远距离暴雨过程的水汽条件对比[J]. 干旱气象, 32(5):788-797.
|
| [31] |
郑世林, 赵培娟, 吴蓁, 等, 2020. 台风倒槽导致河南不同强度降水的对比分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 43(2):11-20.
|
| [32] |
AYAT H, EVANS J P, SHERWOOD S C, et al, 2022. Intensification of subhourly heavy rainfall[J]. Science, 378(6620): 655-659.
|
| [33] |
VILLARINI G, LAVERS D A, SCOCCIMARRO E, et al, 2014. Sensitivity of tropical cyclone rainfall to idealized global-scale forcings[J]. Journal of Climate, 27(12): 4 622-4 641.
|