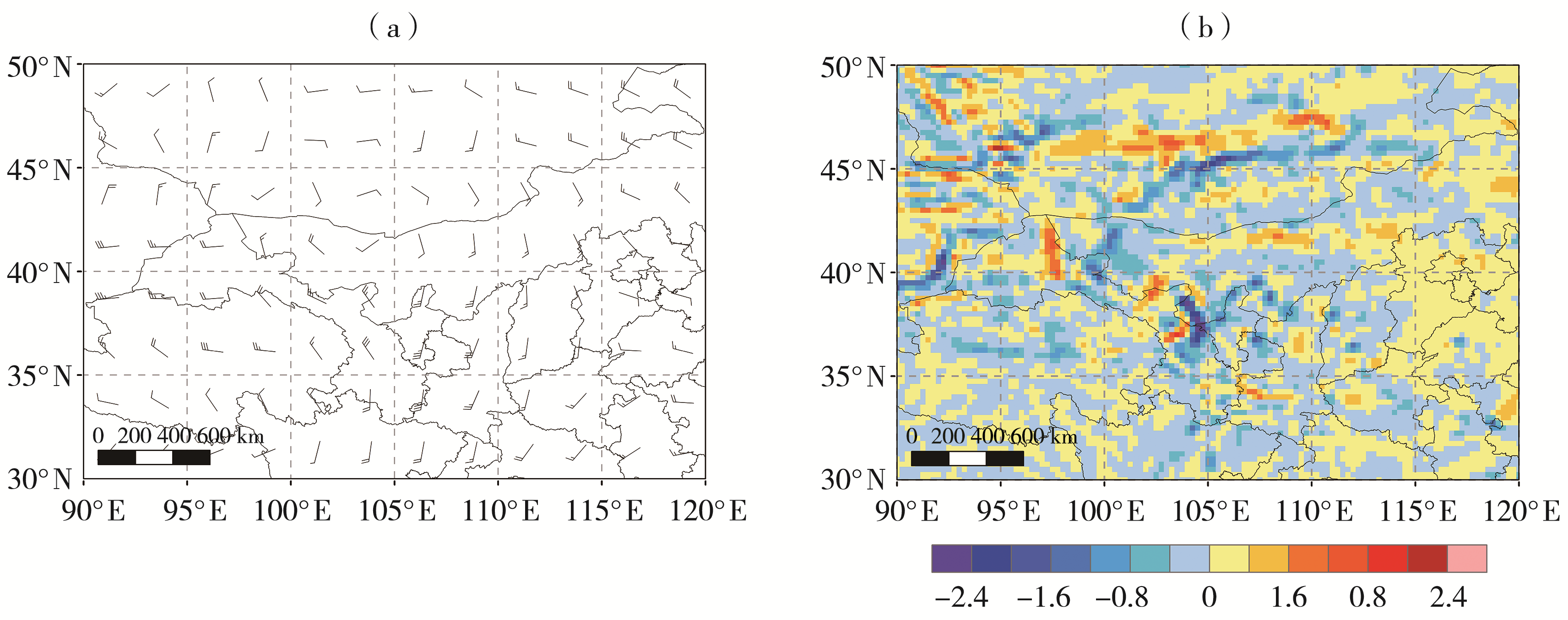
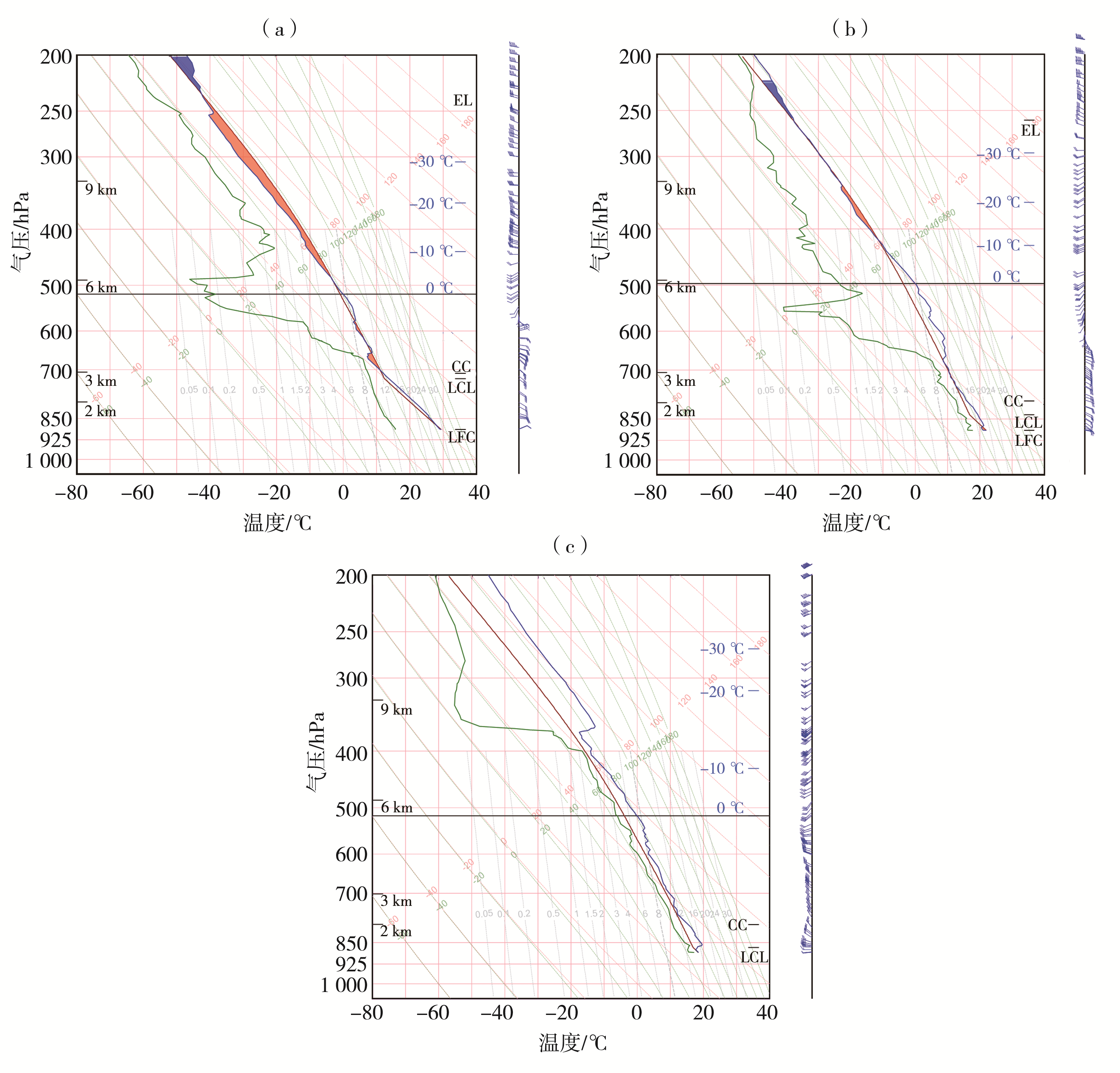
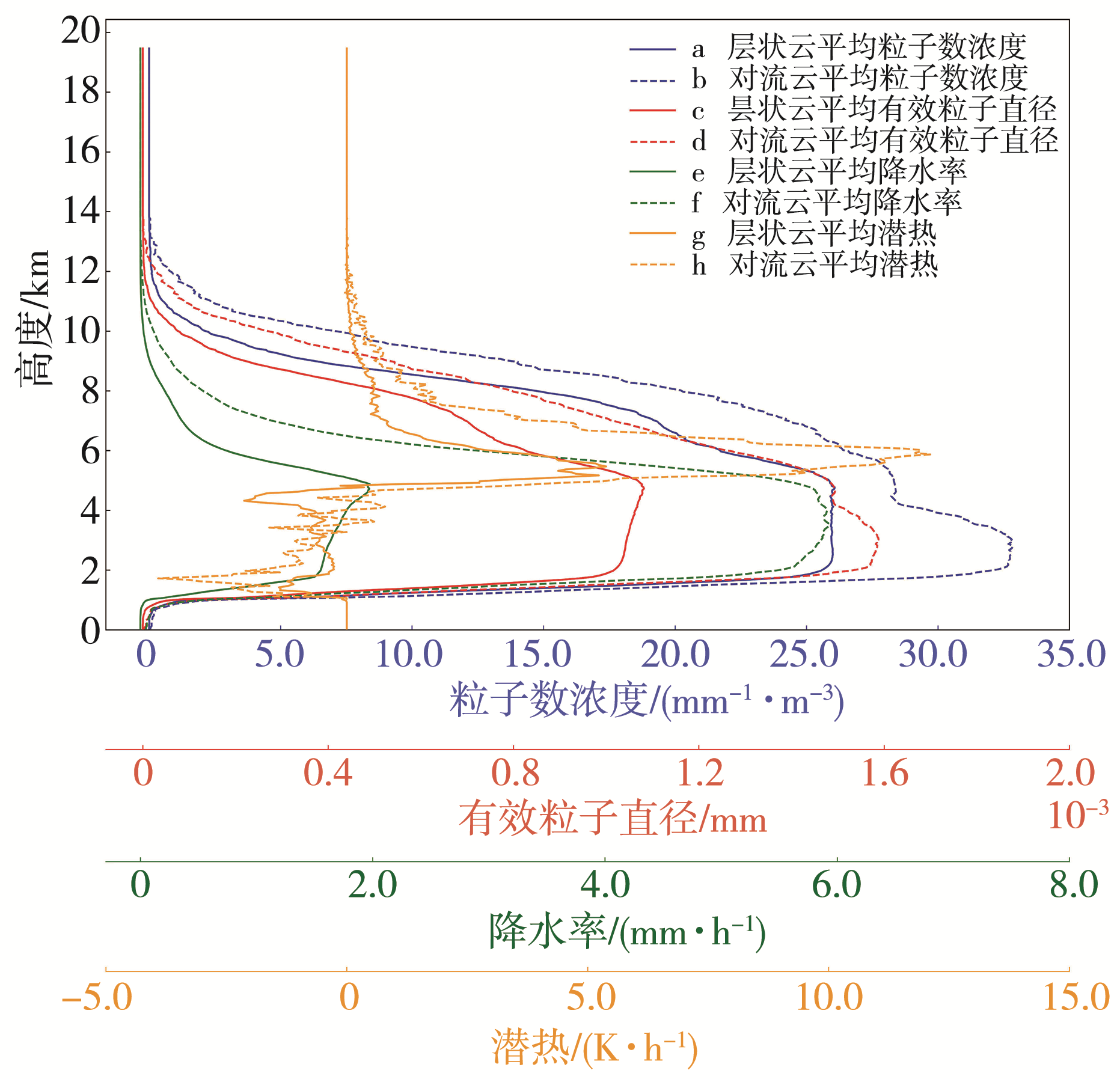
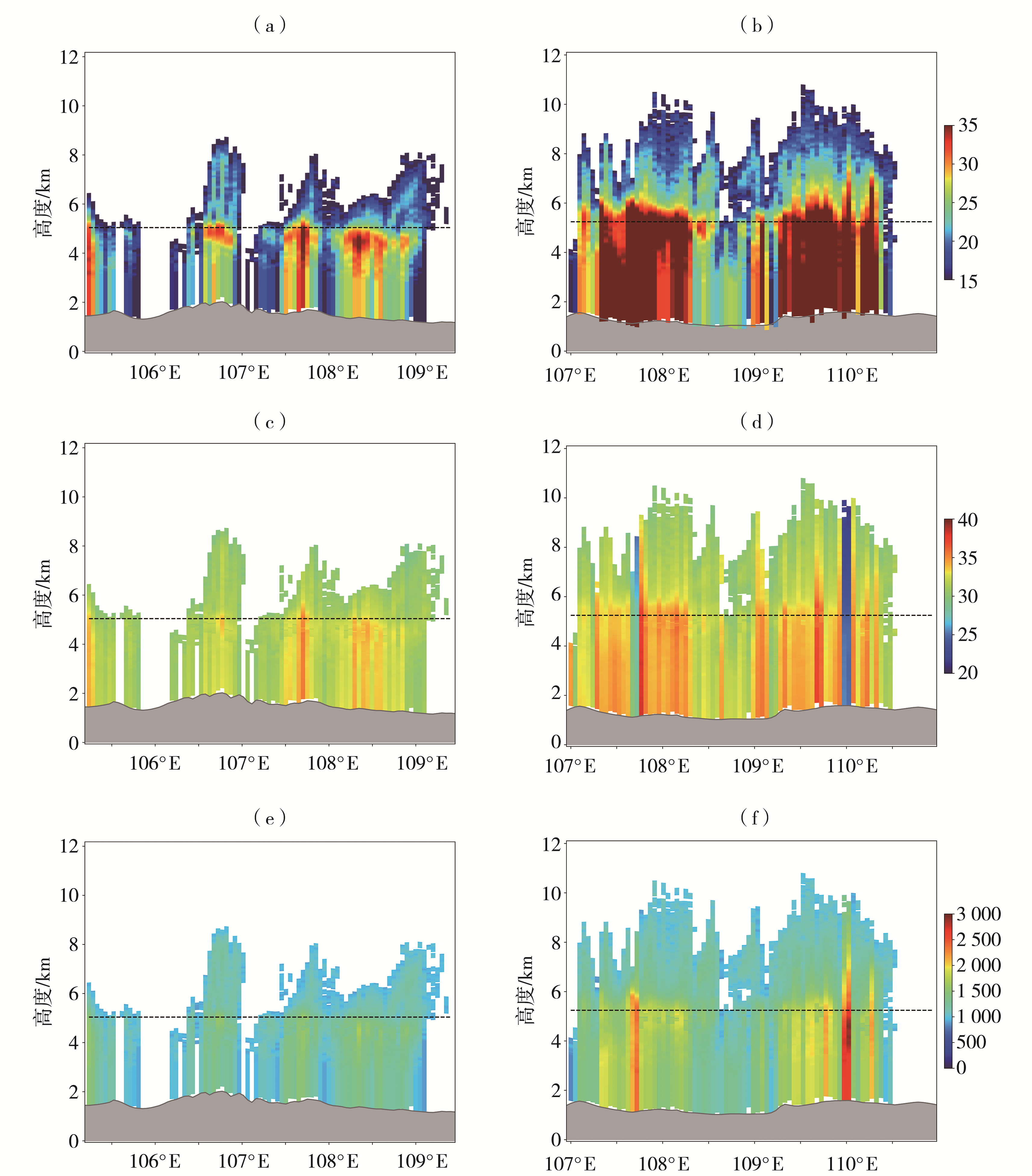
| [1] |
常煜, 韩经纬, 2015. 一次阻塞形势下的内蒙古暴雨过程特征分析[J]. 高原气象, 34(3):741-752.
DOI
|
| [2] |
陈贝, 黄楚惠, 高文良, 等, 2024. 四川盆地西部2020年8月14—18日致洪强降水过程的地形影响分析[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 44(4):41-53.
|
| [3] |
邓欣柔, 吴莹, 2022. 基于GPM探测资料的台风降水水平结构分析[J]. 地球物理学进展, 37(5):1 799-1 806.
|
| [4] |
丁一汇, 2019. 中国暴雨理论的发展历程与重要进展[J]. 暴雨灾害, 38(5):395-406.
|
| [5] |
冯启祯, 肖辉, 姚振东, 2019. 利用地面双偏振雷达检验GPM_DPR降水测量华北地区适用性初探[J]. 成都信息工程大学学报, 34(4):323-332.
|
| [6] |
傅云飞, 罗晶, 罗双, 等, 2022. GPM卫星DPR和GMI探测的2018年5月重庆超级单体云团降水结构特征分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 41(1):1-14.
|
| [7] |
龚乃虎, 1999. 关于冰晶雪花融化问题的研究:进展与展望[J]. 高原气象, 18(3):368-376.
|
| [8] |
谷松岩, 卢乃锰, 吴琼, 等, 2022. FY-3气象卫星降水探测能力分析与展望[J]. 海洋气象学报, 42(2):1-10.
|
| [9] |
谷松岩, 张鹏, 陈林, 等, 2023. 中国首颗降水测量卫星(风云三号G星)的探测能力概述与展望[J]. 暴雨灾害, 42(5):489-498.
|
| [10] |
胡庆芳, 张野, 李伶杰, 等, 2022. GPM近实时反演数据对河南省2021年“7·20”极端暴雨的比较分析[J]. 水科学进展, 33(4):567-580.
|
| [11] |
李晨蕊, 伏晶, 刘维成, 等, 2022. 应用FY卫星产品分析陇东半干旱区特大暴雨事件云特征[J]. 干旱气象, 40(6):954-967.
DOI
|
| [12] |
李国平, 2025. 四川盆地周边山地夜间暴雨的特征与机理研究新进展[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 19(3):1-9.
|
| [13] |
李山山, 王晓芳, 李国平, 等, 2023. 短时强降水和持续性强降水的雨滴谱特征对比[J]. 暴雨灾害, 42(1):1-12.
|
| [14] |
马洁, 廉陆鹞, 刘原峰, 等, 2024. 黄河流域1960—2022年干湿格局变化特征[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 43(12):65-73.
|
| [15] |
毛璐, 谢彦辉, 刘瑞霞, 等, 2022. FY-3C微波湿度计辐射率资料同化对RMAPS-ST系统的降水预报影响[J]. 高原气象, 41(4):896-908.
DOI
|
| [16] |
沈程锋, 李国平, 2022. 基于GPM资料的四川盆地及周边地区夏季地形降水垂直结构研究[J]. 高原气象, 41(6):1 532-1 543.
|
| [17] |
陶诗言, 1980. 中国之暴雨[M]. 北京: 科学出版社:25-88.
|
| [18] |
王宝鉴, 黄玉霞, 魏栋, 等, 2017. TRMM卫星对青藏高原东坡一次大暴雨强降水结构的研究[J]. 气象学报, 75(6):966-980.
|
| [19] |
王德旺, 刘黎平, 仲凌志, 等, 2012. 毫米波雷达资料融化层亮带特征的分析及识别[J]. 气象, 38(6):712-721.
|
| [20] |
王君, 2019. 豫北两次特大暴雨事件的物理量极端性和中尺度特征[J]. 干旱气象, 37(3):419-429.
|
| [21] |
王立羽, 傅云飞, 2022. 基于GPM与ERA5数据的北太平洋冬季风暴路径降水个例分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 41(5):525-535.
|
| [22] |
魏娟娟, 万瑜, 潘宁, 等, 2024. 伊犁河谷春季极端暴雨水汽特征与不稳定机制分析[J]. 干旱气象, 42(3):395-404.
DOI
|
| [23] |
吴琼, 尹红刚, 陈林, 等, 2024. 星载雷达降水反演算法敏感性分析[J]. 气象学报, 82(2):236-246.
|
| [24] |
奚雪松, 高俊刚, 郝媛媛, 等, 2023. 多维复合空间视角下的黄河生态带构建:以黄河流域内蒙古段为例[J]. 自然资源学报, 38(3):721-741.
DOI
|
| [25] |
谢雅洁, 刘曙光, 周正正, 2024. 汶川县降雨时空分布特征及设计暴雨频率分析[J]. 人民长江, 55(1):105-112.
|
| [26] |
杨忠东, 张鹏, 谷松岩, 等, 2017. FY-3卫星应用和发展[J]. 上海航天, 34(4):1-7.
|
| [27] |
袁敏, 李玫, 闫美林, 等, 2023. GPM卫星探测四川“5·21”特大暴雨的降水结构特征分析[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 43(4):35-41.
|
| [28] |
袁征, 张志高, 闫瑾, 等, 2024. 1960—2020年黄河流域不同等级降水时空特征[J]. 干旱区研究, 41(8):1 259-1 271.
|
| [29] |
张奡祺, 傅云飞, 2018. GPM卫星双频测雨雷达探测降水结构的个例特征分析[J]. 大气科学, 42(1):33-51.
|
| [30] |
张桂莲, 仲夏, 韩经纬, 等, 2018. 内蒙古中西部地区一次极端大暴雨特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 36(1):17-26.
DOI
|
| [31] |
张晋茹, 杨莲梅, 刘凡, 等, 2023. 基于Ka波段云雷达观测的中国西天山降雨云宏微观物理特征研究[J]. 大气科学, 47(3):756-768.
|
| [32] |
张鹏, 杨虎, 邱红, 等, 2012. 风云三号卫星的定量遥感应用能力[J]. 气象科技进展, 2(4):6-11.
|
| [33] |
周泓, 闵颖, 许彦艳, 等, 2024. 滇中地区不同影响系统下3次短时强降水过程的大气环境特征和雷达特征分析[J]. 高原气象, 43(1):166-183.
DOI
|
| [34] |
周晋红, 王秀明, 田晓婷, 等, 2024. 山西极端暴雨环流特征及水汽异常研究[J]. 干旱气象, 42(3):426-436.
DOI
|
| [35] |
CHEN K Y, CHEN Z X, XIAN Z P, et al, 2023. Impacts of the all-sky assimilation of FY-3C and FY-3D MWHS-2 radiances on analyses and forecasts of typhoon hagupit[J]. Remote Sensing, 15(9): 2279. DOI:10.3390/rs15092279.
|
| [36] |
CHEN K Y, FAN J, XIAN Z P, 2021. Assimilation of MWHS-2/FY-3C 183 GHz channels using a dynamic emissivity retrieval and its impacts on precipitation forecasts: A southwest Vortex case[J]. Advances in Meteorology, 2021(1): 6427620. DOI:10.1155/2021/6427620.
|
| [37] |
FABRY F, ZAWADZKI I, 1995. Long-term radar observations of the melting layer of precipitation and their interpretation[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 52(7): 838-851.
DOI
URL
|
| [38] |
FANG H L, ZHANG X, SHI L J, et al, 2022. Evaluation of Arctic Sea ice drift products based on FY-3, HY-2, AMSR2, and SSMIS radiometer data[J]. Remote Sensing, 14(20): 5161. DOI:10.3390/rs14205161.
|
| [39] |
HOU A Y, KAKAR R K, NEECK S, et al, 2014. The global precipitation measurement mission[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 95(5): 701-722.
DOI
|
| [40] |
KOZU T, KAWANISHI T, KUROIWA H, et al, 2001. Development of precipitation radar onboard the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 39(1): 102-116.
DOI
URL
|
| [41] |
LI Y P, LIN X, XU R H, et al, 2023. Radiometric calibration analysis for thermal infrared data from MERSI-LL onboard the dust-dawn orbiting satellite FY3E[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 17: 1 813-1 823.
DOI
URL
|
| [42] |
LIU R X, LU Q F, CHEN M, et al, 2021. Impact of assimilating FY-3C MWHS2 data in the RMAPS-ST forecast system on its rainfall forecasts[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 14(4): 100059. DOI:10.1016/j.aosl.2021.100059.
|
| [43] |
OSMANAJ L, SPIRIDONOV I, JAKIMOVSKI B, et al, 2025. Three-dimensional cloud-resolving modeling of the flash-flood heavy rainfall event over Kosovo[J]. Acta Geophysica, 73(2): 2 029-2 045.
DOI
|
| [44] |
WILLIS P T, HEYMSFIELD A J, 1989. Structure of the melting layer in mesoscale convective system stratiform precipitation[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 46(13): 2 008-2 025.
DOI
URL
|
| [45] |
XIA R D, ZHANG D L, 2019. An observational analysis of three extreme rainfall episodes of 19-20 July 2016 along the Taihang Mountains in North China[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 147(11): 4 199-4 220.
DOI
URL
|
| [46] |
XIE Y H, MAO L, CHEN M, et al, 2022. Evaluation and assimilation of FY-3C/D MWHS-2 radiances in the RMAPS-ST[J]. Remote Sensing, 14(2): 275. DOI:10.3390/rs14020275.
|
 ), LI Yunpeng2(
), LI Yunpeng2( ), LI Haiyan3, SI Yaobin4
), LI Haiyan3, SI Yaobin4