干旱气象 ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 301-308.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-02-0301
青海共和盆地PM10质量浓度变化特征及其影响因子研究
- 1.青海省气象干部培训学院,青海 西宁 810001
2.青海省气象服务中心,青海 西宁 810001
3.青海省气候中心,青海 西宁 810001
4.青海省海南藏族自治州共和县气象局,青海 共和 813099
5.南京信息工程大学遥感与测绘工程学院,江苏 南京 210044
Study on the variation characteristics of PM10 mass concentration and its impact factors over the Gonghe Basin in Qinghai Province
NIE Hong1( ), BAO Guangyu2, DAI Sheng3, ZHANG Xiaoyun4, WANG Kai5
), BAO Guangyu2, DAI Sheng3, ZHANG Xiaoyun4, WANG Kai5
- 1. Qinghai Provincial Meteorological Cadre Training Institute, Xining 810001, China
2. Qinghai Provincial Meteorological Service Centre, Xining 810001, China
3. Qinghai Provincial Climate Centre, Xining 810001, China
4. Gonghe County Meteorological Bureau of Hainan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture of Qinghai Province, Gonghe 813099, Qinghai, China
5. School of Remote Sensing and Geomatics Engineering, Nanjing University of Information & Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
摘要:
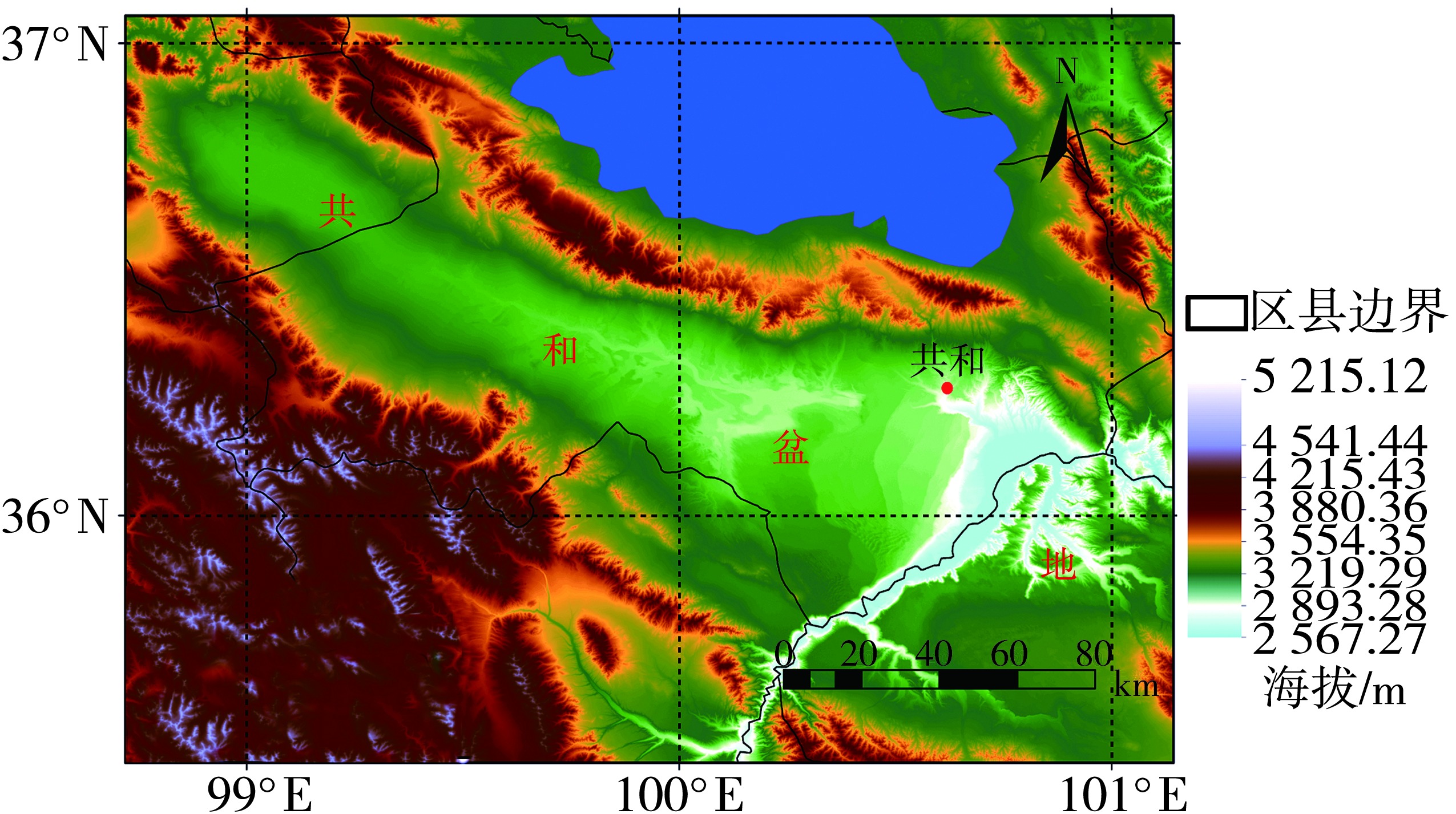
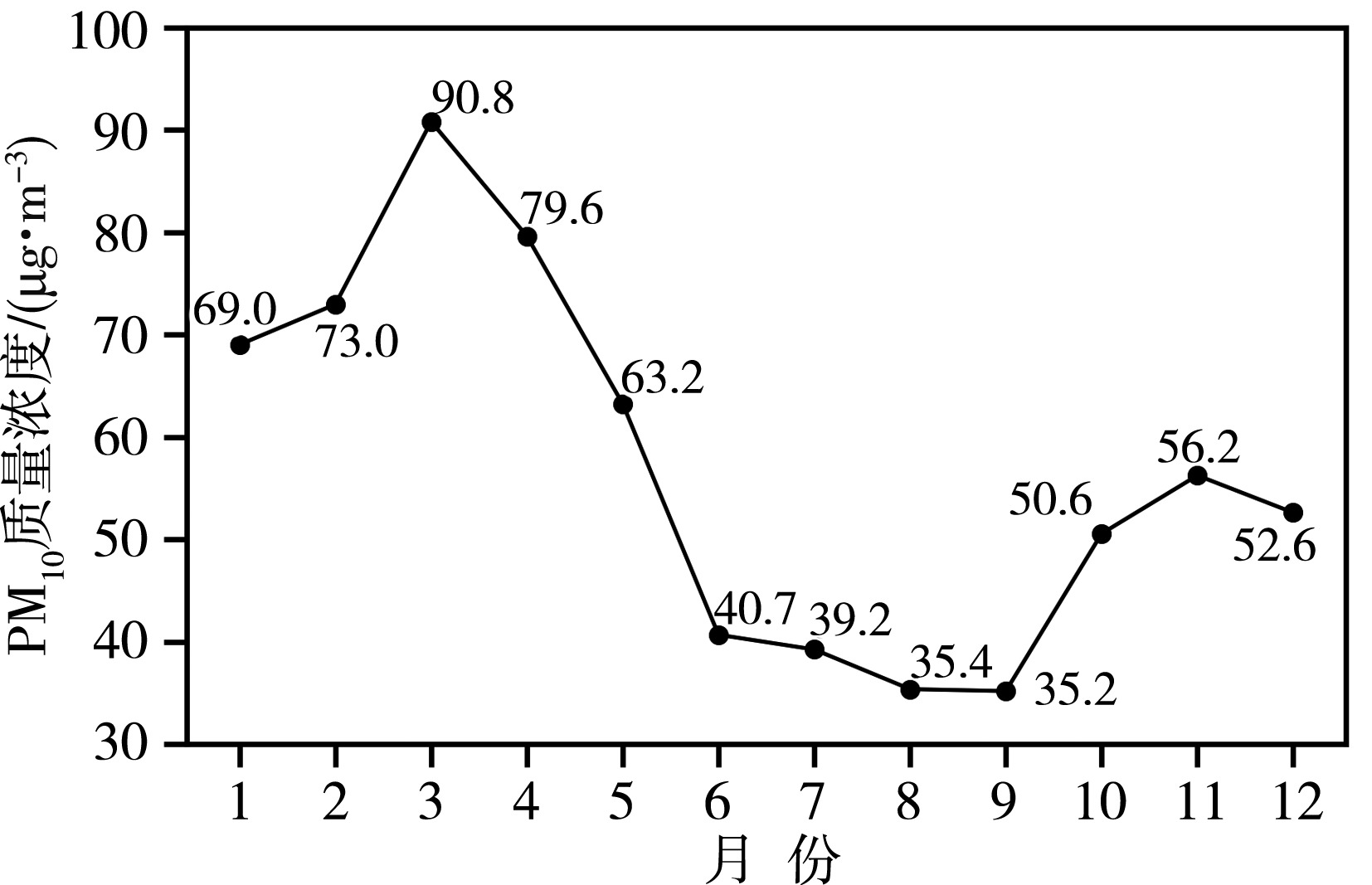
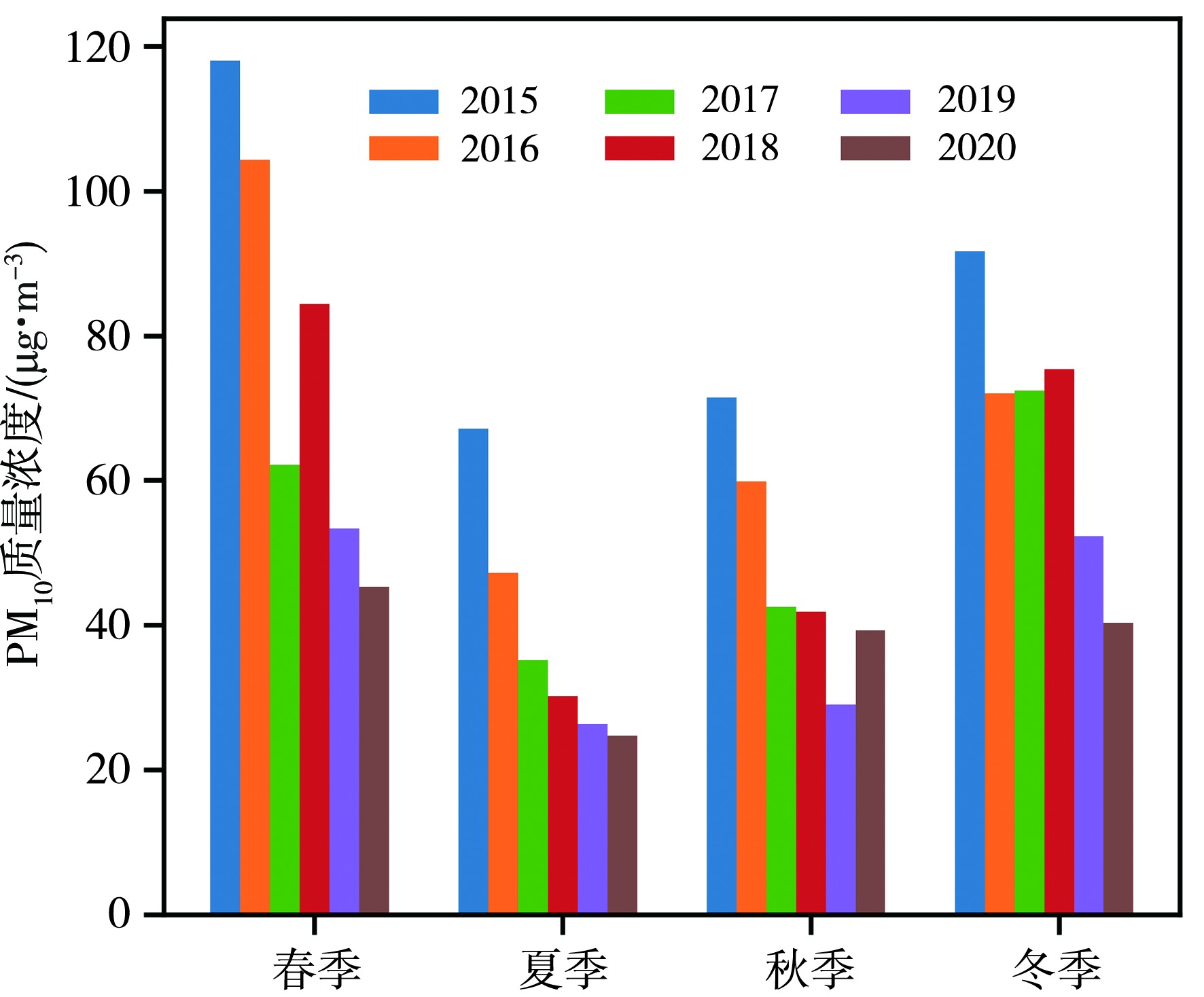
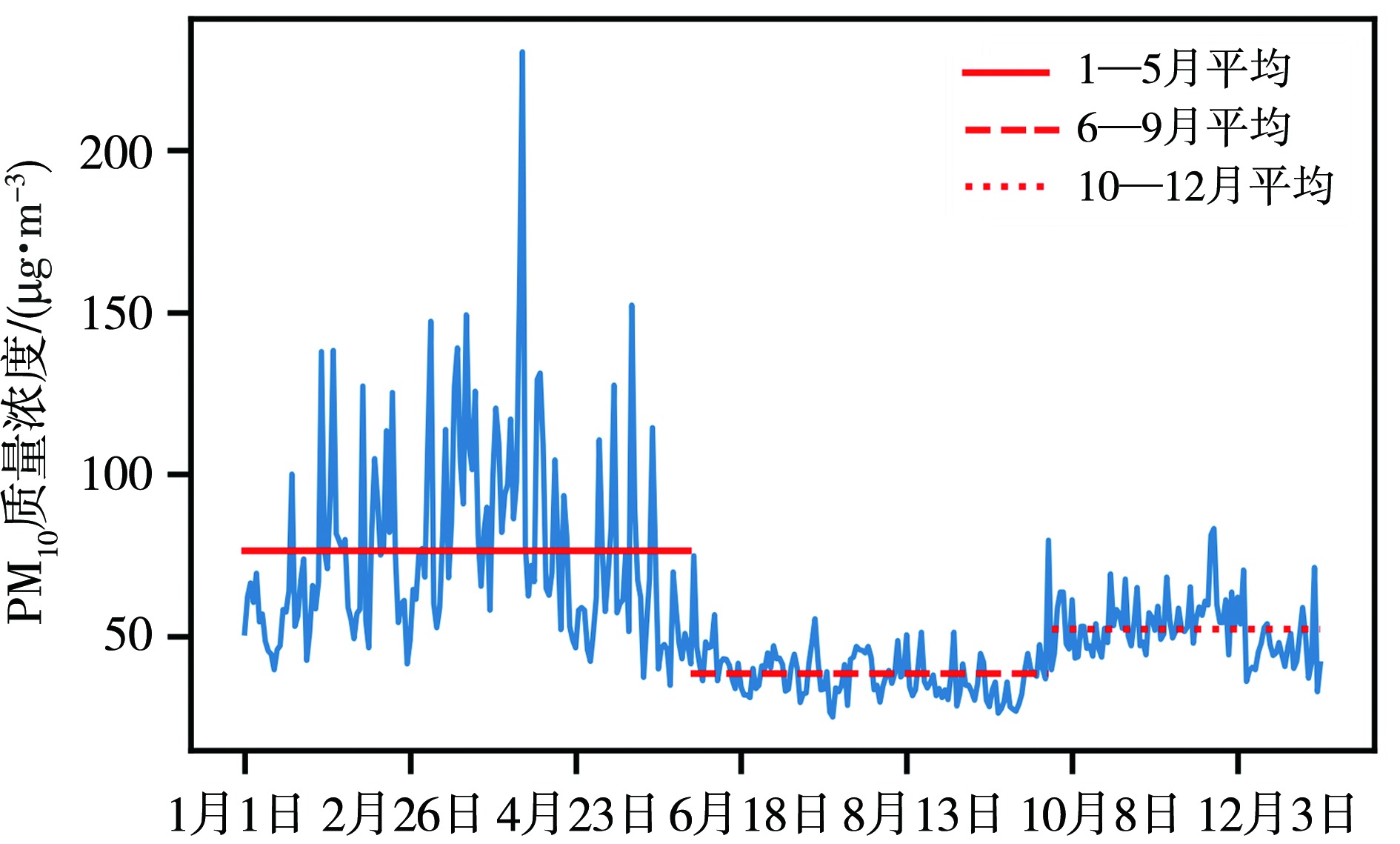
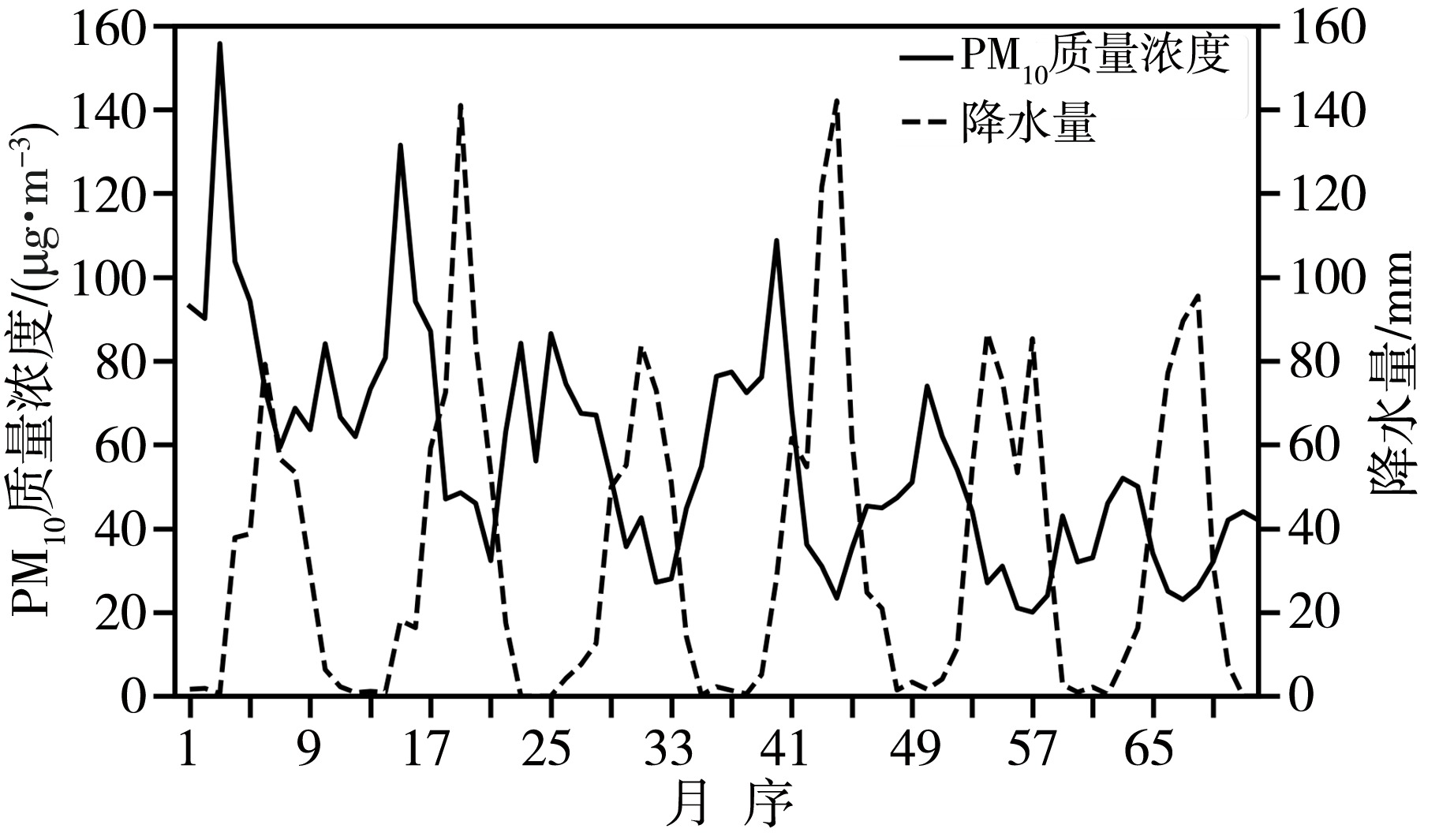
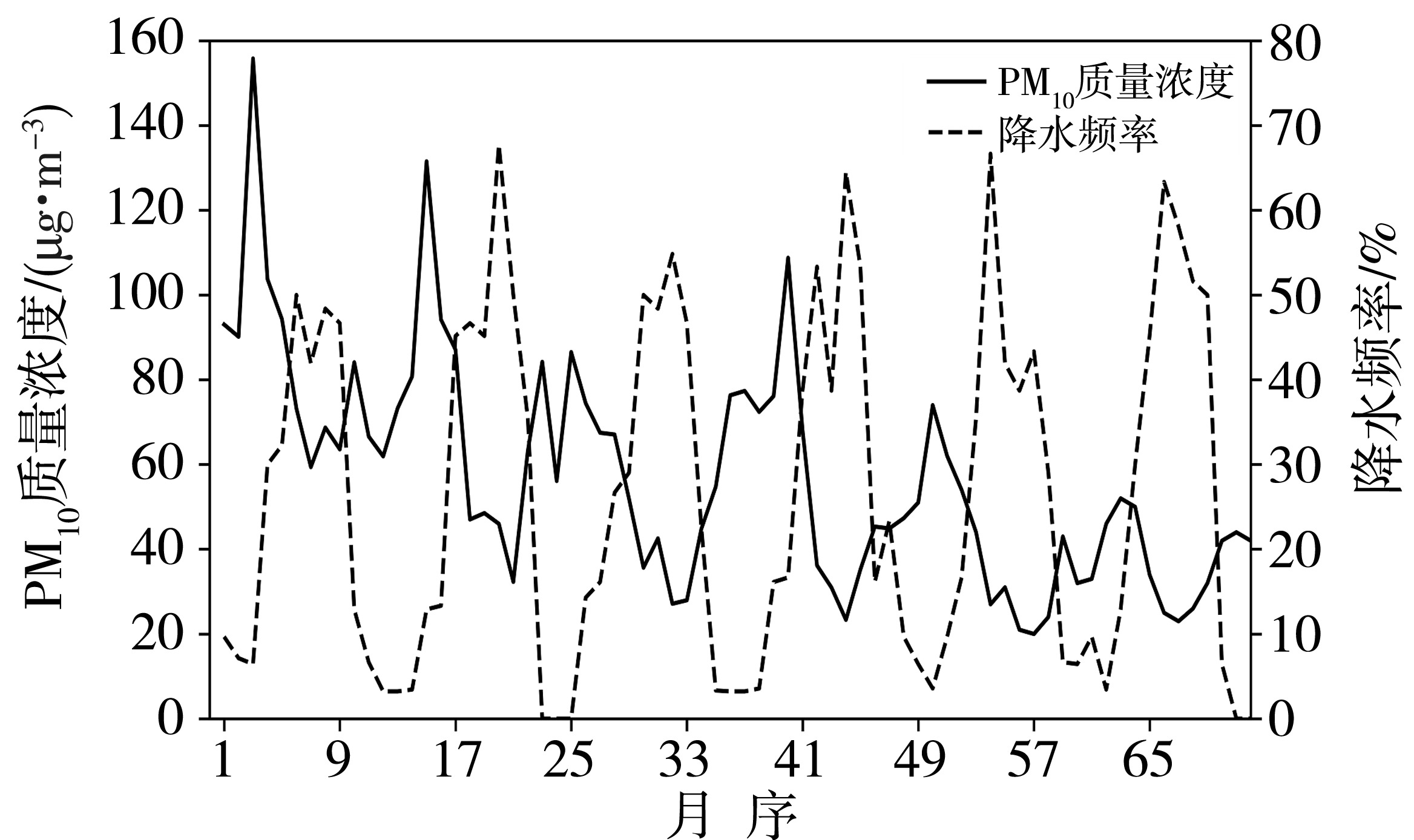
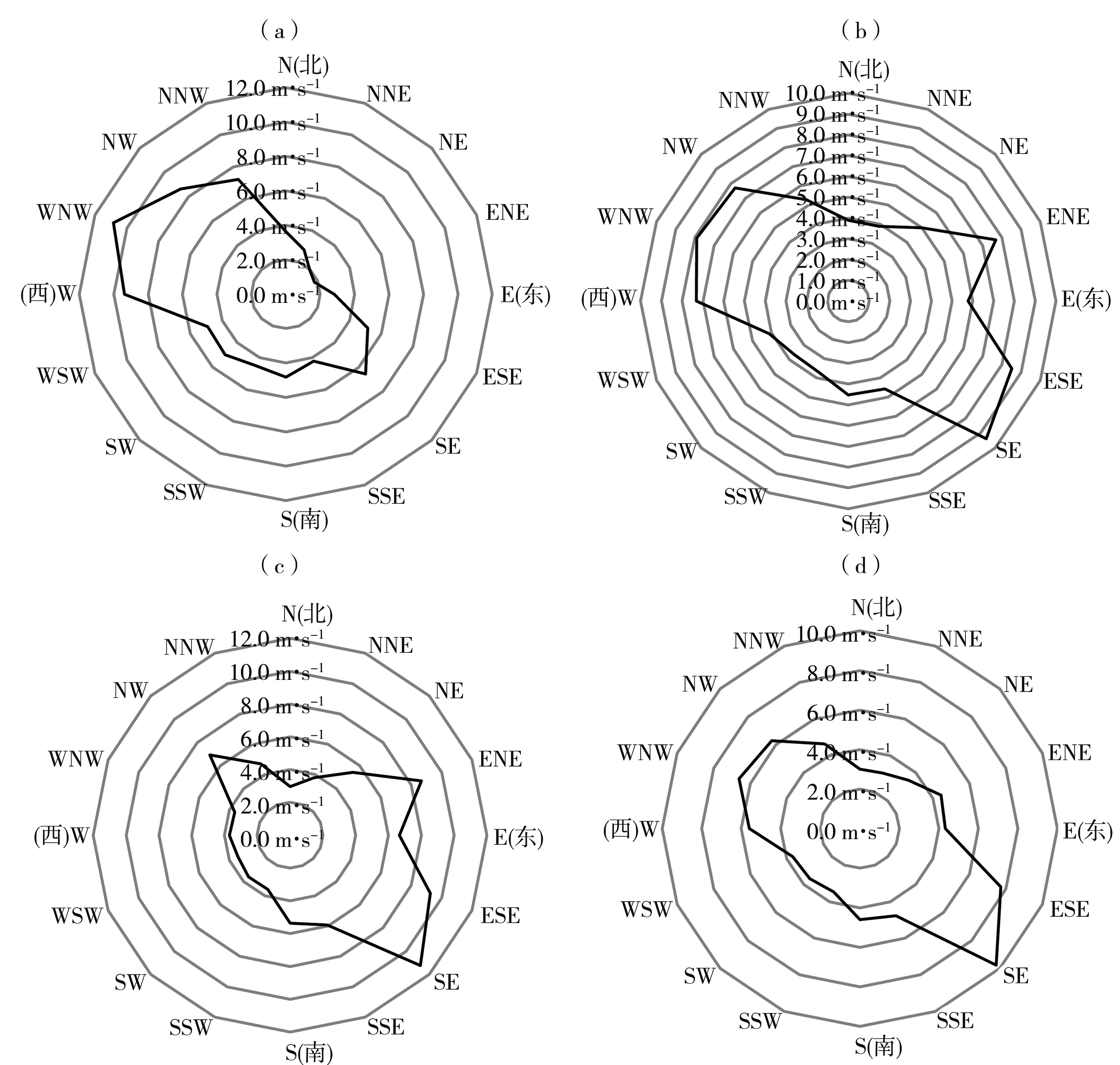
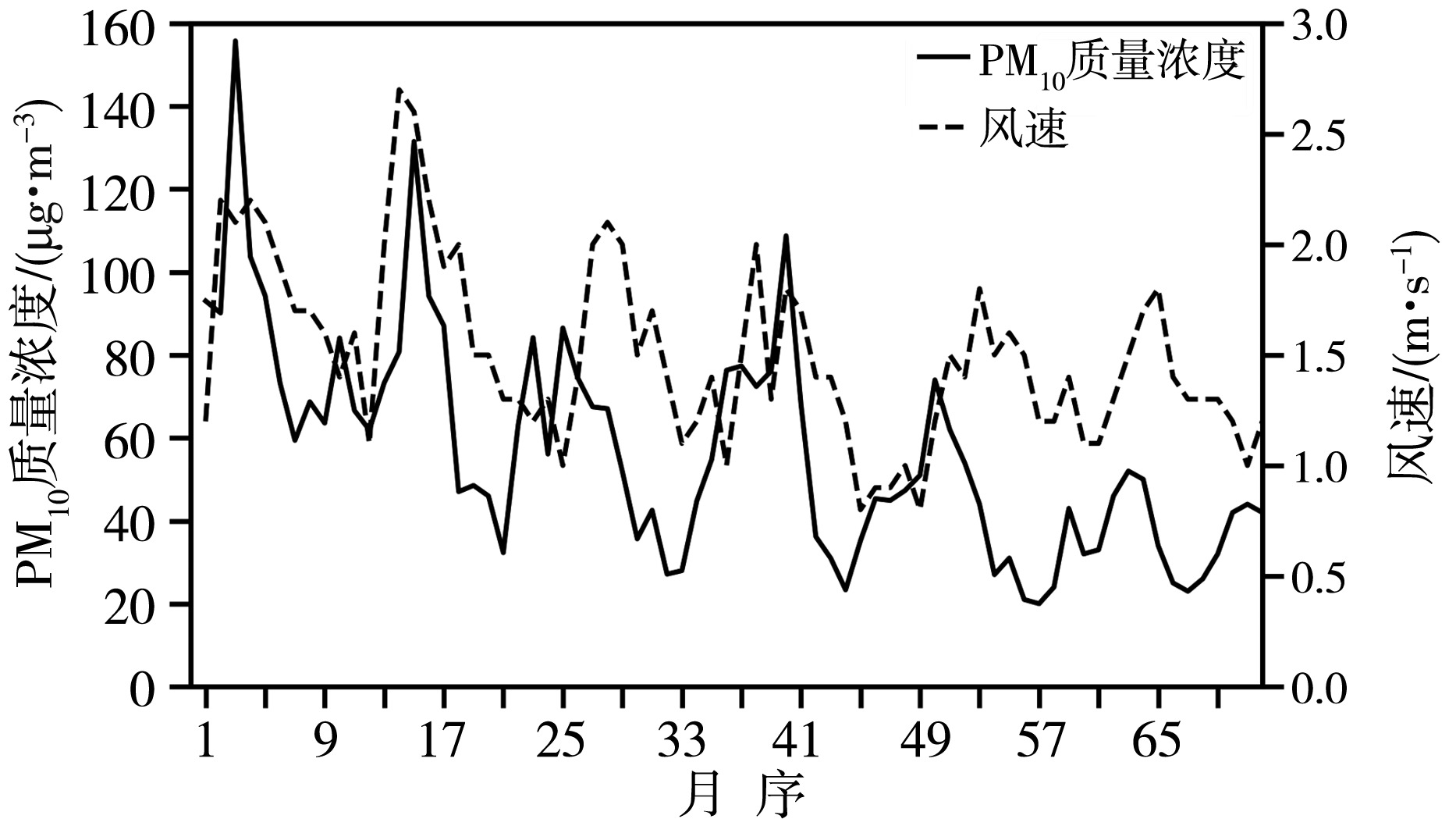
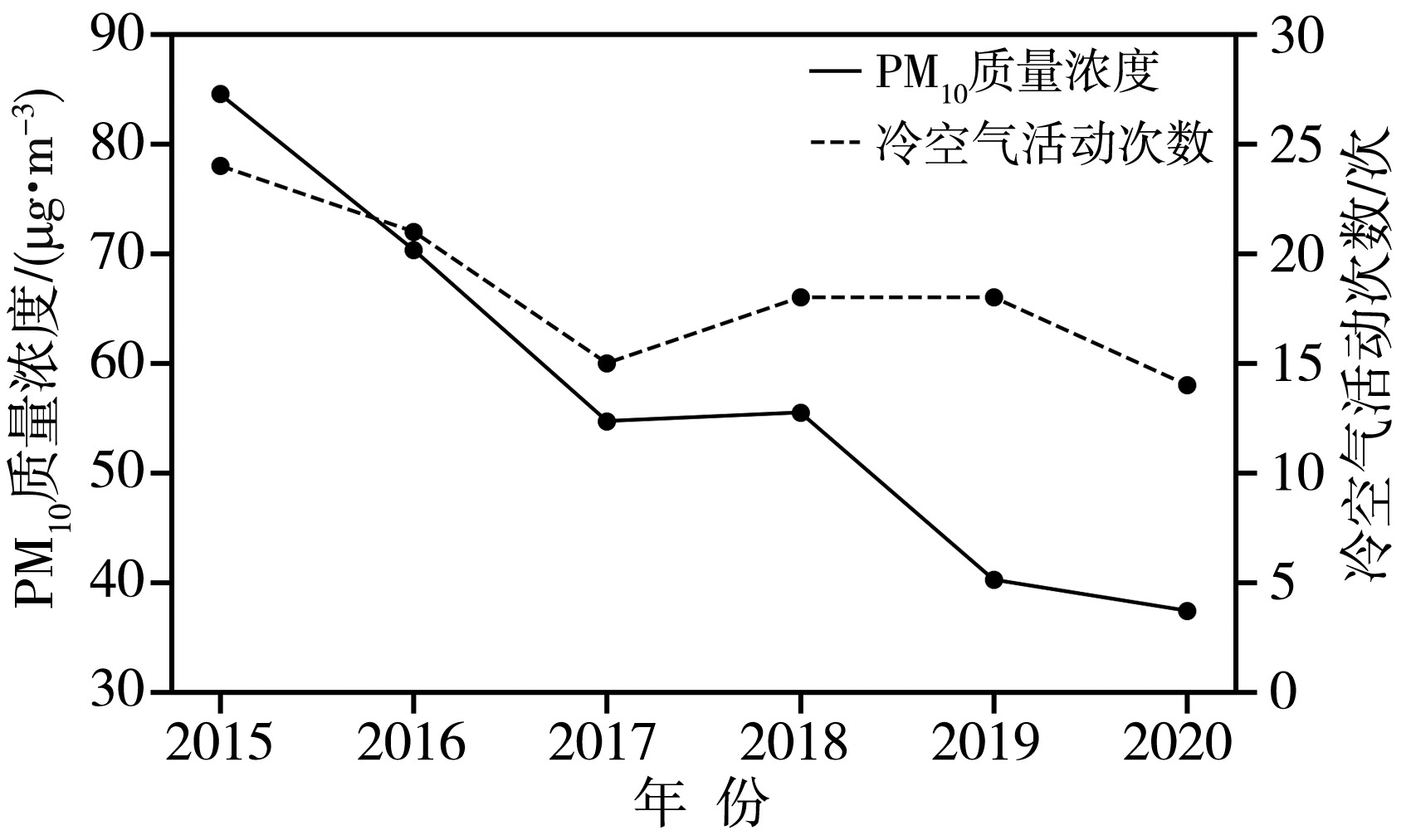
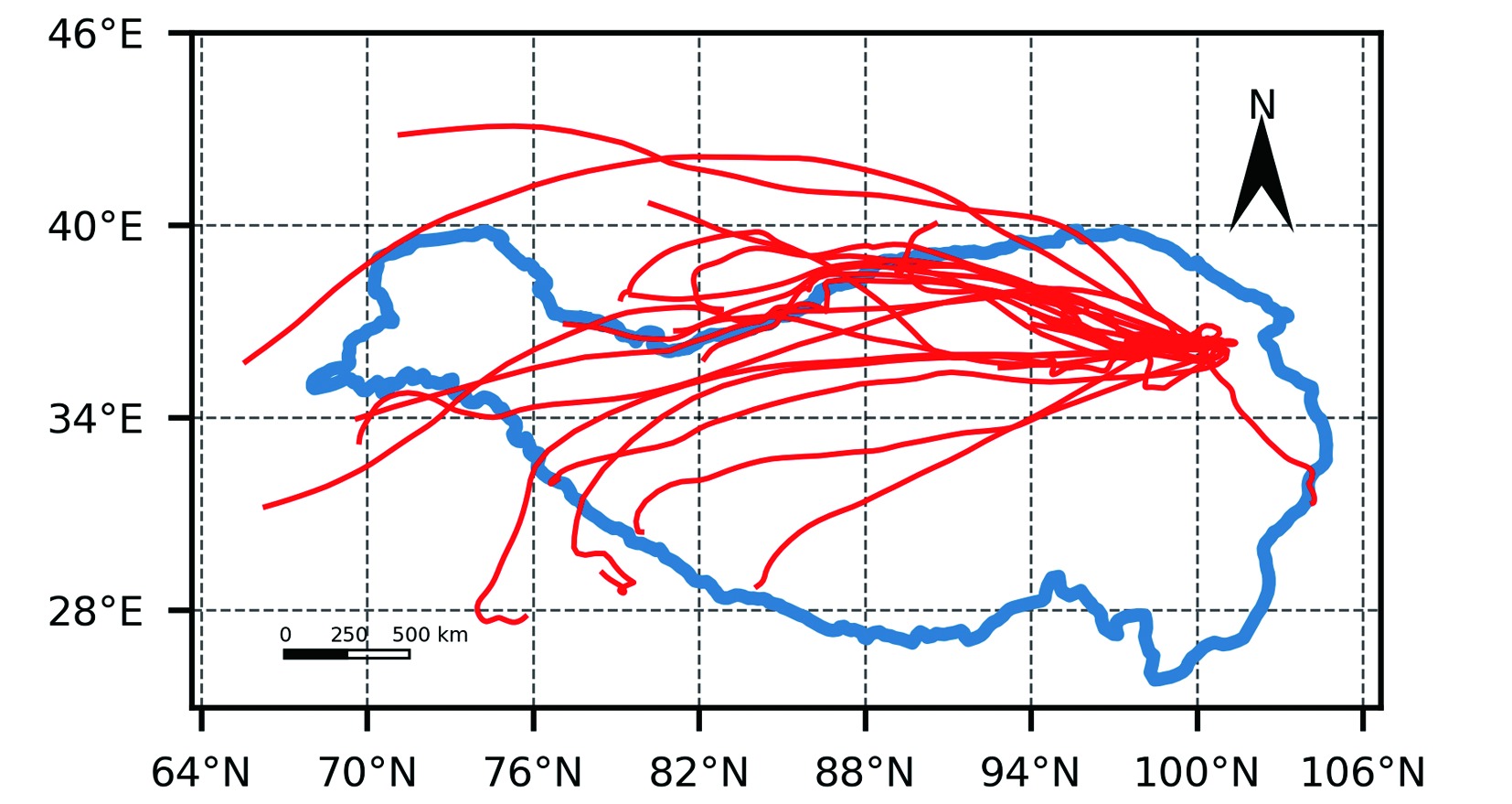
青藏高原作为生态脆弱区,大气颗粒物的质量浓度是生态安全的一项重要指标,研究其时间变化和影响因子的对该地区的环境和生态保护具有重要意义。利用2015—2020年海南州共和县气象局地面气象资料及海南州生态环境局监测点PM10质量浓度资料,分析共和盆地PM10质量浓度变化特征及其与气象因子的关系。结果表明,共和盆地年、春季、冬季PM10平均质量浓度下降趋势显著,夏季与秋季下降趋势不显著,平均月际分布呈双峰型。春季受偏东南风和偏西北风主导风向上的污染物水平输送的共同影响,PM10质量浓度居高不下,冬季受西风影响,PM10质量浓度次之,夏秋季盆地盛行东南风,污染物水平输送减弱,PM10质量浓度较低;月平均PM10质量浓度与月平均风速呈显著正相关,尤其春季更明显。冷空气活动是共和盆地PM10重污染过程的主要原因。共和盆地重污染过程气团路径主要有西南路径和西方路径。
中图分类号: