干旱气象 ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (3): 415-423.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-03-0415
基于CMIP6的福建省极端气温预估
陈笑晨1( ), 唐振飞1(
), 唐振飞1( ), 陈锡宽2, 郑潮宇1, 李欣欣1, 杨婷3
), 陈锡宽2, 郑潮宇1, 李欣欣1, 杨婷3
- 1.福建省气候中心,福建 福州 350008
2.江西省吉安市气象局,江西 吉安 343006
3.福建省气象服务中心,福建 福州 350008
-
收稿日期:2021-08-26修回日期:2021-12-27出版日期:2022-06-30发布日期:2022-06-28 -
通讯作者:唐振飞 -
作者简介:陈笑晨(1989—),男,硕士,工程师,主要从事气候预测和气候变化研究.E-mail: 930571818@qq.com。 -
基金资助:福建省气象局开放式基金项目“SSPs情景下福建省未来极端事件的模拟与预估”(2021KX01);福建省气象局开放式气象科学研究基金项目(2020K01)
Projection of extreme temperature in Fujian based on CMIP6 output
CEHN Xiaochen1( ), TANG Zhenfei1(
), TANG Zhenfei1( ), CHEN Xikuan2, ZHENG Chaoyu1, LI Xinxin1, YANG Ting3
), CHEN Xikuan2, ZHENG Chaoyu1, LI Xinxin1, YANG Ting3
- 1. Fujian Provincial Climate Center, Fuzhou 350008,China
2. Ji’an Meteorological Bureau of Jiangxi Province, Ji’an 343006,Jiangxi,China
3. Fujian Provincial Meteorological Service Center, Fuzhou 350008,China
-
Received:2021-08-26Revised:2021-12-27Online:2022-06-30Published:2022-06-28 -
Contact:TANG Zhenfei
摘要:
基于第六阶段耦合模式比较计划(Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6, CMIP6)模 拟数据和高分辨率逐日格点观测数据,分别采用分位数映射法和泰勒图对福建省极端气温指数模 拟值进行订正和评估,发现在历史参照期(1991—2010年)订正后的各极端气温指数模拟值与观测值更加接近。在此基础上,分析了SSP2-4.5和SSP5-8.5情景下福建省21世纪近期(2021—2040年)、中期(2051—2070年)和末期(2081—2100年)订正后的极端气温指数相对于历史参照期的时空变化特征。从时间变化来看,21世纪各时期,全省平均极端气温指数呈现升高趋势,且随着时间推移增幅不断加大。从空间变化来看,极端最高气温TXx呈现西北内陆增幅大、东南沿海增幅小的趋势,极端最低气温TNn空间分布与TXx类似,增幅略小,夏季日数Su增量在福建西南部为大值区,暖昼日数TX90p在福建东南部增幅最大。采用广义极值(generalized extreme value, GEV)分布研究了TXx重现期变化,发现SSP2-4.5情景下,21世纪3个时期增温较为匀速,而SSP5-8.5情景下增温呈加速趋势。在SSP5-8.5情景下,历史参照期20 a一遇的极端最高气温在21世纪末期每年都可能发生。
中图分类号:
引用本文
陈笑晨, 唐振飞, 陈锡宽, 郑潮宇, 李欣欣, 杨婷. 基于CMIP6的福建省极端气温预估[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(3): 415-423.
CEHN Xiaochen, TANG Zhenfei, CHEN Xikuan, ZHENG Chaoyu, LI Xinxin, YANG Ting. Projection of extreme temperature in Fujian based on CMIP6 output[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(3): 415-423.
| 序号 | 模式 | 研究机构 | 空间分辨率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BCC-CSM2-MR | 中国气象局国家气候中心 (BCC) | 1.125°×1.125° |
| 2 | EC-Earth3-Veg | 欧盟地球系统模式联盟 | 0.7°×0.7° |
| 3 | GFDL-ESM4 | 美国大气与海洋管理局地球物理流体动力实验室 (GFDL) | 1.0°×1.25° |
| 4 | IPSL-CM6A-LR | 法国皮埃尔-西蒙拉普斯研究所 (IPSL) | 1.26°×2.5° |
| 5 | MRI-ESM2-0 | 日本气象研究所(MRI) | 1.125°×1.125° |
| 6 | NorESM2-MM | 挪威气候中心 (NCC) | 0.94°×1.25° |
表1 6个CMIP6全球气候模式基本信息
Tab.1 Basic information of six CMIP6 global climate models
| 序号 | 模式 | 研究机构 | 空间分辨率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BCC-CSM2-MR | 中国气象局国家气候中心 (BCC) | 1.125°×1.125° |
| 2 | EC-Earth3-Veg | 欧盟地球系统模式联盟 | 0.7°×0.7° |
| 3 | GFDL-ESM4 | 美国大气与海洋管理局地球物理流体动力实验室 (GFDL) | 1.0°×1.25° |
| 4 | IPSL-CM6A-LR | 法国皮埃尔-西蒙拉普斯研究所 (IPSL) | 1.26°×2.5° |
| 5 | MRI-ESM2-0 | 日本气象研究所(MRI) | 1.125°×1.125° |
| 6 | NorESM2-MM | 挪威气候中心 (NCC) | 0.94°×1.25° |
| 名称 | 缩写 | 定义 | 单位 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 极端最高气温 | TXx | 每年日最高气温的最大值 | ℃ |
| 极端最低气温 | TNn | 每年日最低气温的最小值 | ℃ |
| 夏季日数 | Su | 每年日最高气温大于25 ℃的全部日数 | d |
| 暖昼日数 | TX90p | 每年日最高气温大于90百分位阈值的日数 | d |
表2 极端气温指数定义
Tab.1 The definition of extreme temperature indices
| 名称 | 缩写 | 定义 | 单位 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 极端最高气温 | TXx | 每年日最高气温的最大值 | ℃ |
| 极端最低气温 | TNn | 每年日最低气温的最小值 | ℃ |
| 夏季日数 | Su | 每年日最高气温大于25 ℃的全部日数 | d |
| 暖昼日数 | TX90p | 每年日最高气温大于90百分位阈值的日数 | d |
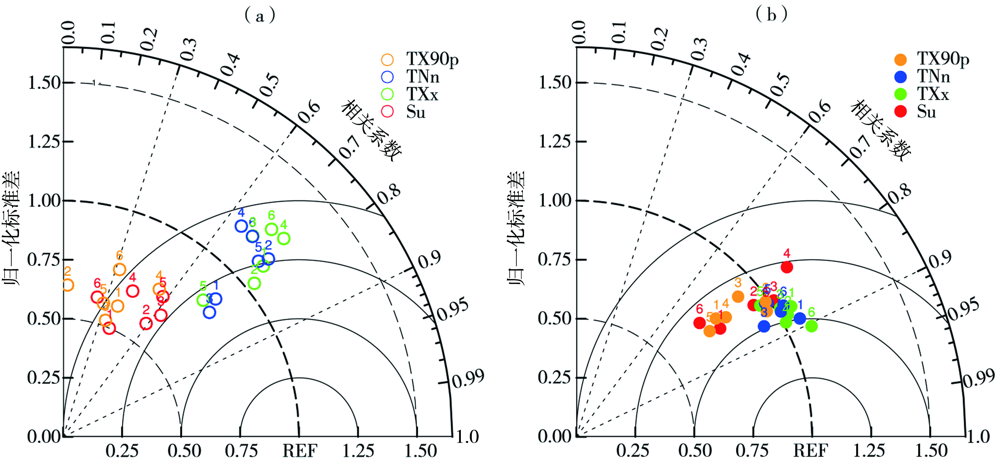
图1 历史参照期福建省4个极端气温指数模拟场相对于观测场的泰勒图 (a) QM偏差订正前,(b) QM偏差订正后(1~6对应表1中模式序号)
Fig.1 Taylor diagrams of simulated fields of four extreme temperature indices relative to observation fieldsin Fujian Province during historical reference period (a) before bias correction by QM method,(b) after bias correction by QM method(numbers 1 to 6 correspond to the model serial number in Table 1)

图2 历史参照期TXx(a)和TNn(b)(单位:℃),Su(c)和TX90p(d)(单位:d)模拟值经QM订正后空间分布
Fig.2 The spatial distribution of TXx (a) and TNn (b) (Unit:℃),Su (c) and TX90p (d) (Unit:d)simulations corrected by QM method during historical reference period
| 情景 | 时期 | TXx/ºC | TNn/ºC | Su/d | TX90p/d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21世纪近期 | 1.11 | 1.00 | 15.94 | 8.04 | |
| SSP2-4.5 | 21世纪中期 | 2.12 | 1.88 | 31.82 | 19.89 |
| 21世纪末期 | 2.76 | 2.38 | 38.57 | 27.34 | |
| 21世纪近期 | 1.20 | 1.22 | 18.89 | 9.55 | |
| SSP5-8.5 | 21世纪中期 | 2.93 | 2.78 | 41.18 | 28.60 |
| 21世纪末期 | 4.86 | 4.55 | 66.12 | 47.98 |
表3 SSP2-4.5和SSP5-8.5情景下21世纪不同时期福建极端气温指数相对于历史参照期的变化
Tab.3 The change of extreme temperature indices during different period in the 21st century relative to historical reference period in Fujian Province under SSP2-4.5 and SSP5-8.5 scenarios
| 情景 | 时期 | TXx/ºC | TNn/ºC | Su/d | TX90p/d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21世纪近期 | 1.11 | 1.00 | 15.94 | 8.04 | |
| SSP2-4.5 | 21世纪中期 | 2.12 | 1.88 | 31.82 | 19.89 |
| 21世纪末期 | 2.76 | 2.38 | 38.57 | 27.34 | |
| 21世纪近期 | 1.20 | 1.22 | 18.89 | 9.55 | |
| SSP5-8.5 | 21世纪中期 | 2.93 | 2.78 | 41.18 | 28.60 |
| 21世纪末期 | 4.86 | 4.55 | 66.12 | 47.98 |

图3 SSP2-4.5情景下21世纪近期(上)、中期(中)和末期(下)福建省TXx和TNn(单位:℃),Su和TX90p(单位:d)相对于历史参照期变化值的空间分布 (黑点通过α=0.05的显著性检验。下同)
Fig.3 Spatial distribution of change values of TXx and TNn (Unit:℃),Su and TX90p (Unit:d) in near-term (the top),mid-term (the middle) and late-term (the bottom)of the 21st century relative to historical reference period in Fujian Province under SSP2-4.5 scenario (The dark dots passed the 0.05 significance test. the same as below )

图4 SSP5-8.5情景下21世纪近期(上)、中期(中)和末期(下)福建省TXx和TNn(单位:℃),Su和TX90p(单位:d)相对于历史参照期变化值的空间分布
Fig.4 Spatial distribution of change values of TXx and TNn (Unit:℃),Su and TX90p (Unit:d) in near-term (the top),mid-term (the middle) and late-term (the bottom)of the 21st century relative to historical reference period in Fujian Province under SSP5-8.5 scenario

图5 SSP2-4.5(a)、SSP5-8.5(b)情景下21世纪不同时期福建省20、50、100 a一遇TXx相对于历史参照期的变化
Fig.5 The change of TXx of 20-year,50-year and 100-year return periods during different period in the 21st century relative to historical reference period in Fujian Province under SSP2-4.5 (a) and SSP5-8.5 (b) scenarios

图6 SSP2-4.5、SSP5-8.5情景下福建省历史参照期20 a一遇TXx在21世纪不同时期的重现期
Fig.6 The return period of TXx under 20-year return period in historical reference period in different periods in the 21st century under SSP2-4.5 and SSP5-8.5 scenarios
| [1] | IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Working Group I Contribution on the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental on Climate Change[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013. |
| [2] | 秦大河, THOMAS S. IPCC第五次评估报告第一工作组报告的亮点结论[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2014, 10(1): 1-6. |
| [3] |
EASTERLING D R, EVANS J L, GROISMAN P Y, et al. Observed variability and trends in extreme climate events: a brief review[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2000, 81(3): 417-425.
DOI URL |
| [4] | 蒋帅, 江志红, 李伟, 等. CMIP5模式对中国极端气温及其变化趋势的模拟评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2017, 13(1): 11-24. |
| [5] | 黄安宁, 张耀存. 海温季节和年际变化对东亚区域气候变率模拟的影响[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2004, 40(3): 319-329. |
| [6] | 任国玉, 封国林, 严中伟. 中国极端气候变化观测研究回顾与展望[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2010, 15(4): 337-353. |
| [7] | 冯晓莉, 多杰卓么, 李万志, 等. 1961—2018年青海高原极端气温指数时空变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(1): 28-37. |
| [8] | 武丽梅, 陈璐, 王凯,等. 中国大陆1983—2012年年极端气温时空变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2016, 34(6):945-951. |
| [9] | 江晓菲, 李伟, 游庆龙. 中国未来极端气温变化的概率预估及其不确定性[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018, 14(3): 228-236. |
| [10] | 唐宝琪, 延军平, 曹永旺. 福建省极端温度事件对气候变暖的响应[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2016, 21(9): 123-132. |
| [11] | 黄鹤楼, 丁烨毅, 涂小萍, 等. 城市化对宁波地区极端气温及人体舒适度的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(3): 396-403. |
| [12] |
CHEN H P, SUN J Q, LIN W Q, et al. Comparison of CMIP6 and CMIP5 models in simulating climate extremes[J]. Science Bulletin, 2020, 65(17): 1415-1418.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
MOSS R H, EDMONDS J A, HIBBARD K A, et al. The next generation of scenarios for climate change research and assessment[J]. Nature, 2010, 463(7282): 747-756.
DOI URL |
| [14] | 冯蜀青, 王海娥, 柳艳香, 等. 西北地区未来10 a气候变化趋势模拟预测研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(4): 557-564. |
| [15] | 伍清. 基于CMIP5资料的西南地区2020—2050年气温多模式集合预估[J]. 干旱气象, 2018, 36(6):971-978. |
| [16] | 周天军, 邹立维, 陈晓龙. 第六次国际耦合模式比较计划(CMIP6)评述[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15(5): 445-456. |
| [17] |
EYRING V, BONY S, MEEHL G A, et al. Overview of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6(CMIP6) experimental design and organization[J]. Geoscientific Model Development, 2016, 9: 1937-1958.
DOI URL |
| [18] | 周天军, 陈梓明, 邹立维, 等. 中国地球气候系统模式的发展及其模拟和预估[J]. 气象学报, 2020, 78(3): 332-350. |
| [19] | 张丽霞, 陈晓龙, 辛晓歌. CMIP6情景模式比较计划(Scenario MIP)概况与评述[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15(5): 519-525. |
| [20] | 赵宗慈, 罗勇, 黄建斌. 从检验 CMIP5气候模式看CMIP6地球系统模式的发展[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018, 14(6): 643-648. |
| [21] |
XIN X G, WU T W, ZHANG J, et al. Comparison of CMIP6 and CMIP5 simulations of precipitation in China and the East Asian summer monsoon[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2020, 40: 6423-6440.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
FU Y H, LIN Z D, WANG T. Simulated relationship between wintertime ENSO and East Asian summer rainfall: From CMIP3 to CMIP6[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2021, 38(2): 221-236.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
ZHU H H, JIANG Z H, LI J, et al. Does CMIP6 inspire more confidence in simulating climate extremes over China?[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2020, 37(10):1119-1132.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
JIANG D B, HU D, TIAN Z P, et al. Differences between CMIP6 and CMIP5 models in simulating climate over China and the East Asian monsoon[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2020, 37(10): 1102-1118.
DOI URL |
| [25] | 向竣文, 张利平, 邓瑶, 等. 基于CMIP6的中国主要地区极端气温/降水模拟能力评估及未来情景预估[J]. 武汉大学学报(工学版), 2021, 54(1): 46-57. |
| [26] | 陈丽娟, 王壬, 陈友飞. 1960—2014年福建省极端气候事件时空特征及变化趋势[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 2016, 14(6): 107-113. |
| [27] | 严平勇. 近40年来福建省极端气温时空变化特征[J]. 广东农业科学, 2009(8): 358-360. |
| [28] | 高晓丹, 陈彦, 李汉菁. 近58 a福州市极端气温变化趋势及重现期特征分析[J]. 农业灾害研究, 2021, 11(3): 41-42. |
| [29] | 吴佳, 高学杰. 一套格点化的中国区域日观测资料及与其他资料的对比[J]. 地球物理学报, 2013, 56(4): 1102-1111. |
| [30] |
ZHU H H, JIANG Z H, LI L. Projection of climate extremes in China, an incremental exercise from CMIP5 to CMIP6[J]. Science Bulletin, 2021, 66: 2528-2537.
DOI URL |
| [31] | HAN J, MIAO C, DUAN Q, et al. Variations in start date, end date, frequency and intensity of yearly temperature extremes across China during the period 1961-2017[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2020, 15, 045007. |
| [32] |
MISHRA V, BHATIA U, TIWARI A D. Bias-corrected climate projections for South Asia from coupled model intercomparison project-6[J]. Scientific Data, 2020, 7(1),338.DOI: 10.1038/s41597-020-00681-1.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
JIANG D, TIAN Z, LANG X. Reliability of climate models for China through the IPCC Third to Fifth Assessment Reports[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2016, 36(3): 1114-1133.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
ALEXANDER L V, ZHANG X, PETERSON T C, et al. Global observed changes in daily climate extremes of temperature and precipitation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 2006, 111, D05109. DOI: 10.1029/2015JD006290,2006.
DOI |
| [35] |
YIN H, SUN Y. Detection of anthropogenic influence on fixed threshold indices of extreme temperature[J]. Journal of Climate, 2018, 31: 6341-6352.
DOI URL |
| [36] | 童尧, 高学杰, 韩振宇, 等. 基于RegCM4的中国区域日尺度降水模拟误差订正[J]. 大气科学, 2017, 41(6): 1156-1166. |
| [37] |
TAYLOR K E. Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres, 2001, 106: 7183-7192.
DOI URL |
| [38] | 张昕怡, 方国华, 闻昕, 等. 中国格点化日降水极值统计模型及阈值的选取[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2017, 13(4): 346-355. |
| [39] | 丁裕国, 李佳耘, 江志红, 等. 极值统计理论的进展及其在气候变化研究中的应用[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2011, 7(4): 248-252. |
| [40] | HOSKING J R M. L-moments analysis and estimation of distributions using linear combinations of order statistics[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, 1990, 52(2): 105-122. |
| [41] | ZHOU T J, YU R C. Twentieth-century surface air temperature over China and the global simulated by coupled climate models[J]. Journal of Climate, 2006, 19(22): 5843-5858. |
| [42] | IPCC. Climate Change 2021:The Physical Science Basis.Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [M]. Cambridge:Cambridge University Press. In Press. |
| [43] |
SANTER B D, TAYLOR K E, GLECKLER P J, et al. Incorporating model quality information in climate change detection and attribution studies[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2009, 106(35): 14778-14783.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
KNUTTI R. The end of model democracy[J]. Climatic Change, 2010, 102(3/4): 395-404.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 曹晓云, 周秉荣, 周华坤, 乔斌, 颜玉倩, 赵彤, 陈奇, 赵慧芳, 于红妍. 气候变化对青藏高原植被生态系统的影响研究进展[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(6): 1068-1080. |
| [2] | 范进进, 秦鹏程, 史瑞琴, 李梦蓉, 杜良敏. 气候变化背景下湖北省高温干旱复合灾害变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(5): 780-790. |
| [3] | 吴斌, 钱业, 王瑞芳, 赵鑫, 金磊. 全球气候模式对影响西北太平洋台风强度的大尺度环境因子的模拟评估[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(3): 466-479. |
| [4] | 刘鸣彦, 房一禾, 孙凤华, 赵春雨, 侯依玲, 崔妍, 周晓宇. 气候变化和人类活动对太子河流域径流变化的贡献[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(2): 244-251. |
| [5] | 冯晓莉, 多杰卓么, 李万志, 申红艳, 陈冀青. 1961—2018年青海高原极端气温指数时空变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(1): 28-37. |
| [6] | 赵琳, 王长科, 艾婉秀. 北疆地区公众对气候变化认知与适应的性别差异分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(1): 168-174. |
| [7] | 李裕, 王小恒, 罗兴平, 康淑荷, 陈琛, 张强. 气候变化对半干旱地区作物微量元素利用率影响研究进展[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(6): 895-899. |
| [8] | 赵慧, 郭庆元, 马鹏程, 王丽娜, 刘丽伟, 刘卫平, 李常德. 陇东南地区近50 a极端低温事件演变特征及环流背景[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(6): 900-908. |
| [9] | 刘楚薇, 连鑫博, 黄建平. 我国臭氧污染时空分布及其成因研究进展[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(03): 355-361. |
| [10] | 孙银川1,2,王素艳1,2,李浩3,郑广芬1,王璠2,官景得1. 宁夏六盘山区夏季避暑旅游气候舒适度分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2018, 36(6): 1035-. |
| [11] | 张飞民,王澄海,谢国辉,孔维政. 气候变化背景下未来全球陆地风、光资源的预估[J]. 干旱气象, 2018, 36(5): 725-732. |
| [12] | 迪丽努尔·托列吾别克,李栋梁. 近115 a中亚干湿气候变化研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2018, 36(2): 185-195. |
| [13] | 滕水昌,张敏,滕杰,乔琴. 1951—2016年甘肃乌鞘岭气候变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2018, 36(1): 75-81. |
| [14] | 李艳丽,李永华,陈新均,杨文斌. 党河水库入库径流量的变化特征及对气候变化的响应[J]. 干旱气象, 2017, 35(6): 984-990. |
| [15] | 杨艳娟1,曹经福1,熊明明1,赵玉娟2. 影响海河流域参考作物蒸散量的气象因子定量分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2017, 35(3): 367-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
