干旱气象 ›› 2021, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (5): 785-795.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2021)-05-0785
2018年2月琼州海峡一次持续性海雾过程特征分析
- 1.海南省气象台,海南 海口 570203
2.海南省南海气象防灾减灾重点实验室,海南 海口 570203
-
收稿日期:2021-03-31修回日期:2021-08-24出版日期:2021-10-30发布日期:2021-11-08 -
通讯作者:张春花 -
作者简介:冯箫(1988— ),女,硕士,工程师,主要从事海南省天气气候方面的研究. E-mail:fxloran@foxmail.com 。 -
基金资助:中国气象局预报员专项(CMAYBY2020-101);海南省气象局科研项目(HNQXJS201801)
Characteristics of a Persistent Sea Fog Process over the Qiongzhou Strait in February 2018
FENG Xiao1,2( ),LI Xun1,2,YANG Wei1,2,ZHANG Chunhua1,2(
),LI Xun1,2,YANG Wei1,2,ZHANG Chunhua1,2( )
)
- 1. Hainan Meteorological Observatory, Haikou 570203, China
2. Key Laboratory of South China Sea Meteorological Disaster Prevention and Mitigation of Hainan Province, Haikou 570203, China
-
Received:2021-03-31Revised:2021-08-24Online:2021-10-30Published:2021-11-08 -
Contact:Chunhua ZHANG
摘要:
基于逐小时地面常规观测资料、L波段探空资料、风廓线雷达风场资料和日本葵花气象卫星数据及ERA-Interim再分析资料,对2018年2月15—25日琼州海峡持续性海雾过程进行诊断分析。结果表明:此次持续性海雾过程分为4个阶段、3种类型,即15—17日辐射雾、18—20日和24—25日平流雾、22日锋面雾。辐射雾期间,琼州海峡为均压型环流控制,夜间气温降低,水汽处于饱和状态,1000 m以下存在双层逆温结构,雾顶出现在第一逆温层底部。两次平流雾期间,琼州海峡为入海变性高压脊后部偏强的东到东南风控制,气温(相对湿度)长时间维持不变(饱和),但18—20日的低空湿平流较24—25日强,水汽辐合层较厚,且比湿持续增大,致使平流雾持续时间较长;600 m以下较大的垂直风切变使雾层混合均匀,雾顶可发展至1000 m以上。锋面雾期间,徐闻站为4 m·s-1以上的偏北风且伴有弱降水,琼州海峡附近低空为湿平流(水汽辐合)中心和冷暖平流交汇的锋区。海雾各阶段,气-海温差在-2~3 ℃之间,当气-海温差增大时,海雾消散。
中图分类号:
引用本文
冯箫,李勋,杨薇,张春花. 2018年2月琼州海峡一次持续性海雾过程特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(5): 785-795.
FENG Xiao,LI Xun,YANG Wei,ZHANG Chunhua. Characteristics of a Persistent Sea Fog Process over the Qiongzhou Strait in February 2018[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(5): 785-795.
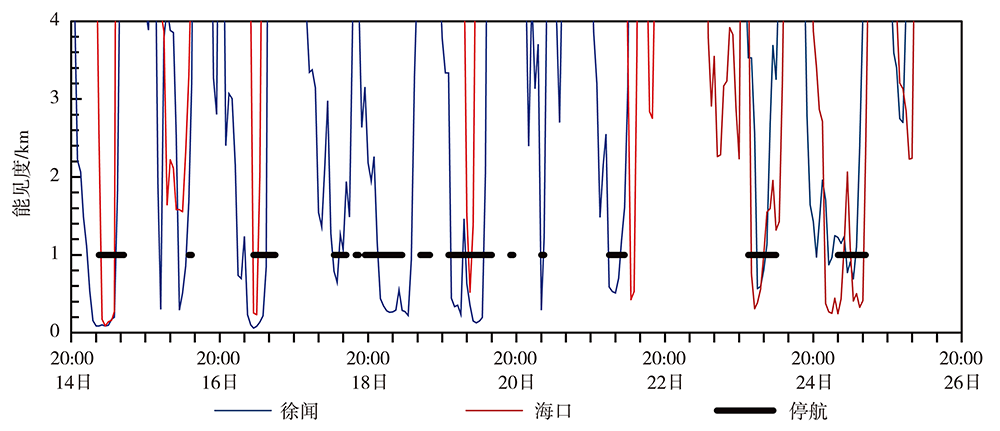
图2 2018年2月14日20:00至26日20:00徐闻、海口站大气能见度逐小时演变及琼州海峡停航时间
Fig.2 The hourly evolution of atmospheric visibility at Xuwen and Haikou stations and suspending time of ships in the Qiongzhou Strait from 20:00 BST 14 to 20:00 BST 26 February 2018

图3 2018年2月15日04:00至22日02:00琼州海峡上空海雾的演变 (a) 15日04:00,(b) 15日06:00,(c) 15日09:00,(d) 19日04:00,(e) 19日06:00, (f) 19日09:00,(g) 21日22:00,(h) 22日00:00,(i) 22日02:00
Fig.3 The evolution of sea fogs over the Qiongzhou Strait from 04:00 BST 15 to 02:00 BST 22 February 2018 (a) 04:00 BST 15 February, (b) 06:00 BST 15 February, (c) 09:00 BST 15 February, (d) 04:00 BST 19 February, (e) 06:00 BST 19 February, (f) 09:00 BST 19 February, (g) 22:00 BST 21 February, (h) 00:00 BST 22 February, (i) 02:00 BST 22 February
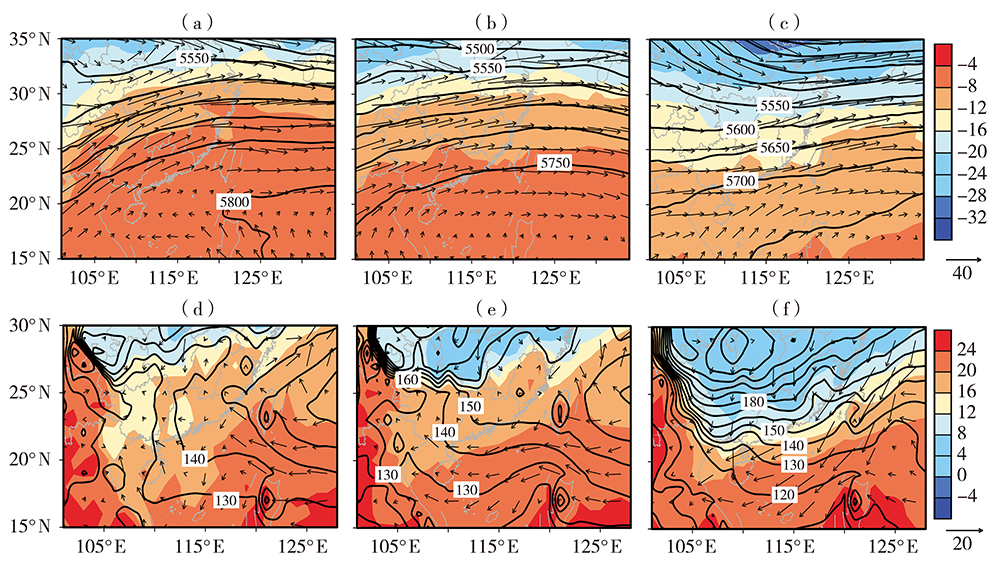
图4 2018年2月15(a、d)、19(b、e)、22(c、f)日08:00琼州海峡500 hPa(a、b、c)和1000 hPa(d、e、f)位势高度场(等值线,单位:gpm)、风场(矢量,单位:m·s-1)和温度场(阴影,单位:℃)空间分布
Fig.4 The spatial distribution of 500 hPa (a, b, c) and 1000 hPa (d, e, f) geopotential height field (contours, Unit: gpm), wind field (vectors, Unit: m·s-1) and air temperature field (shadows, Unit: ℃) over the Qiongzhou Strait at 08:00 BST 15 (a, d), 19 (b, e) and 22 (c, f) February 2018
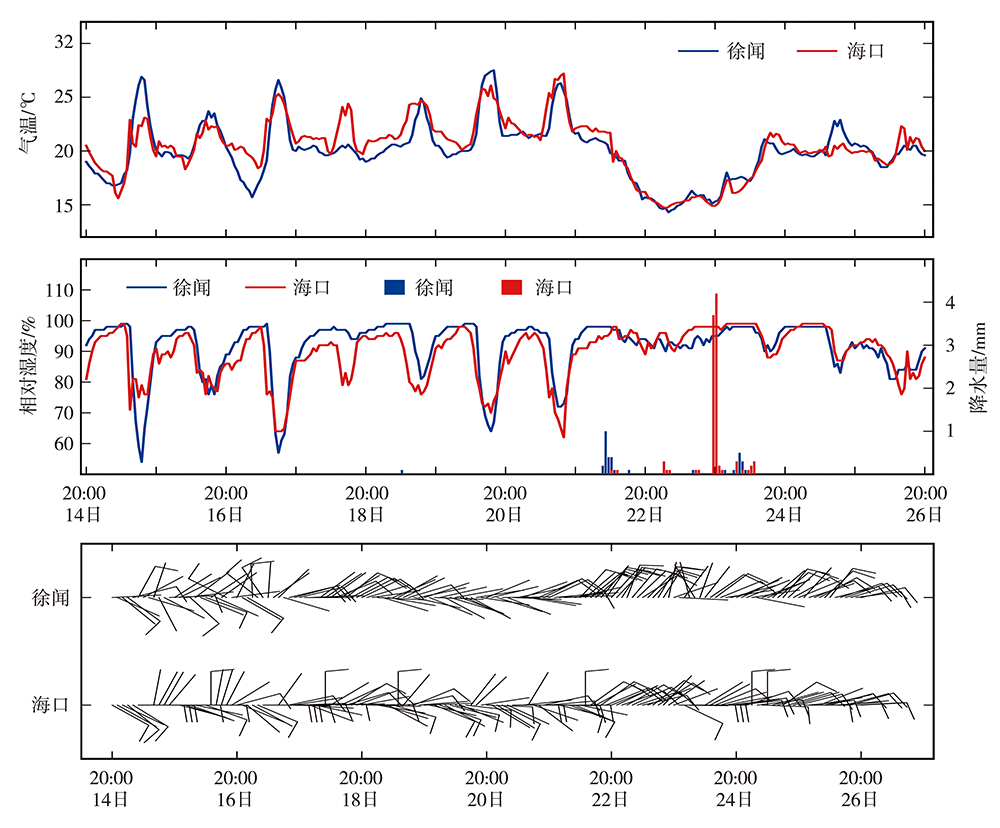
图5 2018年2月14日20:00至26日20:00徐闻、海口2站气温、相对湿度、降水量的逐小时演变及风向风速逐2 h演变
Fig.5 The hourly evolution of air temperature, relative humidity and precipitation and 2-hour evolution of wind speed and wind direction at Xuwen and Haikou stations from 20:00 BST 14 to 20:00 BST 26 February 2018
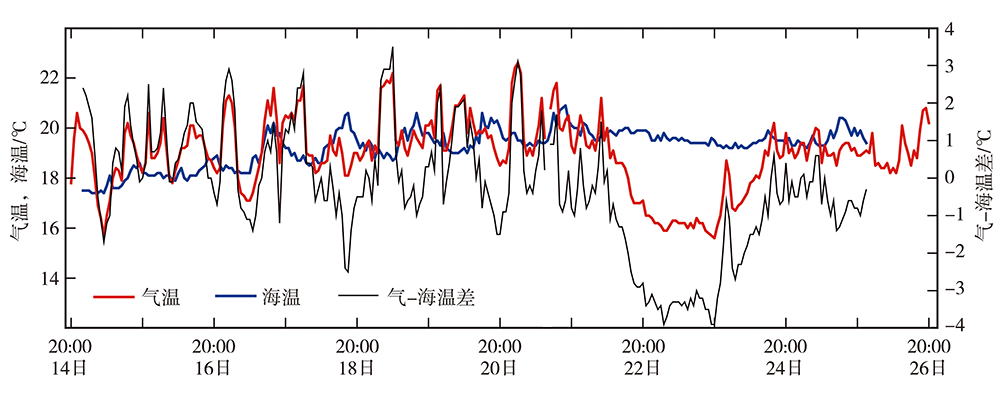
图6 2018年2月14日20:00至26日20:00秀英港海温、观海台气温和气-海温差的逐小时演变
Fig.6 The hourly evolutions of sea surface temperature at Xiuying harbour station, air temperature at Guanhaitai station and air-sea temperature difference from 20:00 BST 14 to 20:00 BST 26 February 2018
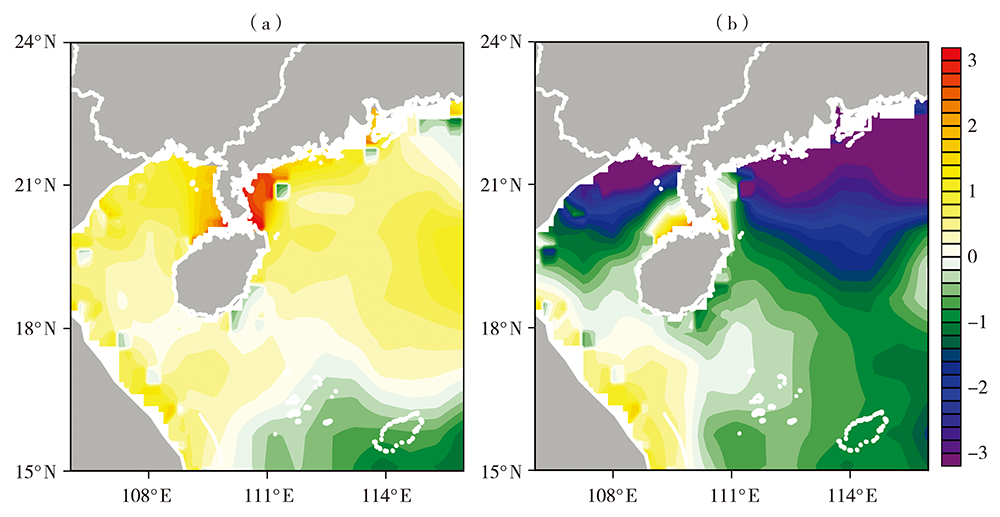
图7 2018年2月19(a)和22(b)日08:00琼州海峡气-海温差空间分布(单位:℃) (灰色区域为陆地)
Fig.7 The spatial distributions of difference between air temperature and sea surface temperature in the Qiongzhou Strait at 08:00 BST 19 (a) and 22 (b) February 2018 (Unit: ℃) (the gray areas for the land)
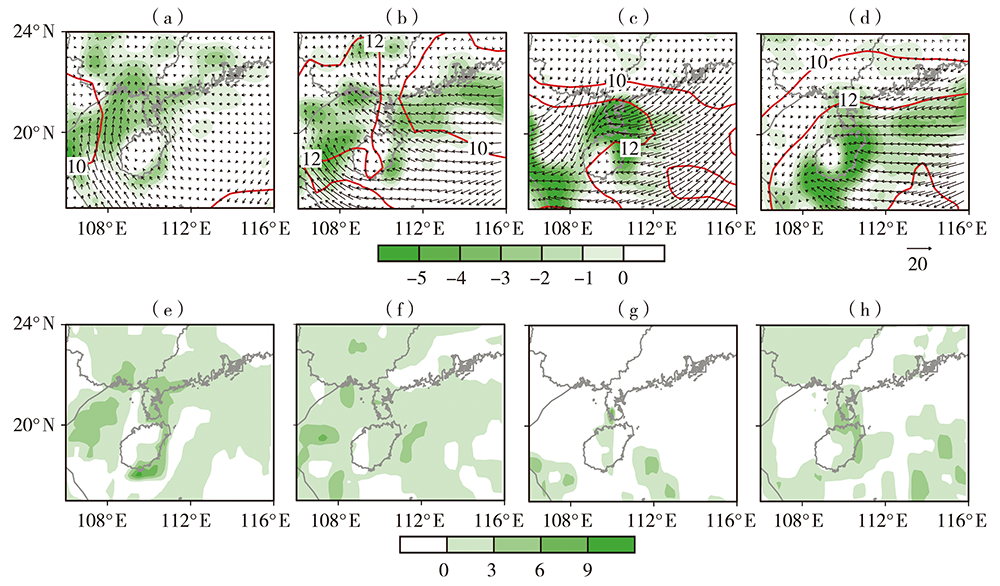
图8 2018年2月15(a、e)、19(b、f)、22(c、g)、24(d、h)日08:00琼州海峡1000 hPa比湿(红色等值线,单位:g·kg-1)、水汽通量(矢量,单位:g·hPa-1·cm-1·s-1)及其散度(填色,单位:10-5 g·hPa-1·cm-2·s-1)(a、b、c、d)和1000 hPa水汽平流项(e、f、g、h,单位:10-5 g·kg-1·s-1)分布
Fig.8 The distributions of 1000 hPa specific humidity (red contours, Unit: g·kg-1), water vapor flux (vectors, Unit: g·hPa-1·cm-1·s-1) and its divergence (shadows, Unit: 10-5 g·hPa-1·cm-2·s-1) (a, b, c, d) and 1000 hPa water vapor advection term (e, f, g, h, Unit: 10-5 g·kg-1·s-1) over the Qiongzhou Strait at 08:00 BST 15 (a, e), 19 (b, f), 22 (c, g) and 24 (d, h) February 2018
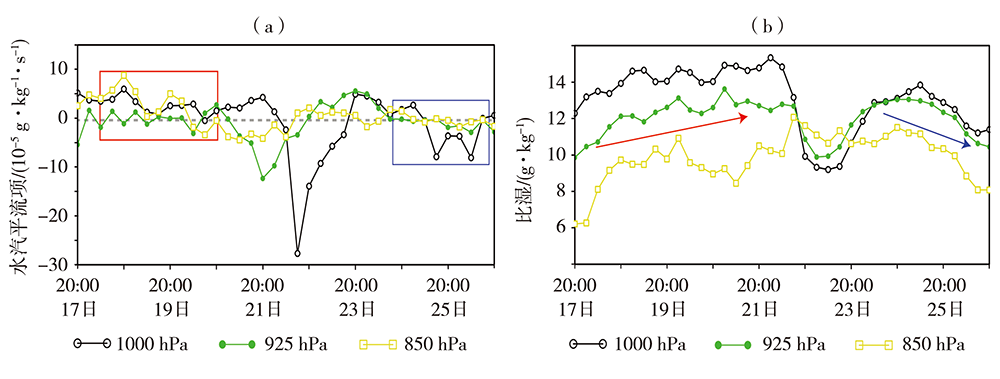
图9 2018年2月17—26日琼州海峡(109.20°E—110.26°E、19.95°N—20.35°N)不同高度层平均水汽平流项(a)和比湿(b)逐6 h演变[红色(蓝色)方框、箭头分别表示18—20日(24—25日)持续湿平流(湿平流转为干平流)和比湿增加(下降)过程]
Fig.9 The 6-hour evolutions of mean water vapor advection term (a) and specific humidity (b) at different levels over the Qiongzhou Strait (109.20°E-110.26°E, 19.95°N-20.35°N) from 17 to 26 February 2018 [The red (blue) box and arrow indicated continuous wet advection (wet advection transfering to dry advection) and specific humidity increase (decrease) process from 18 to 20 (24 to 25) February 2018, respectively]
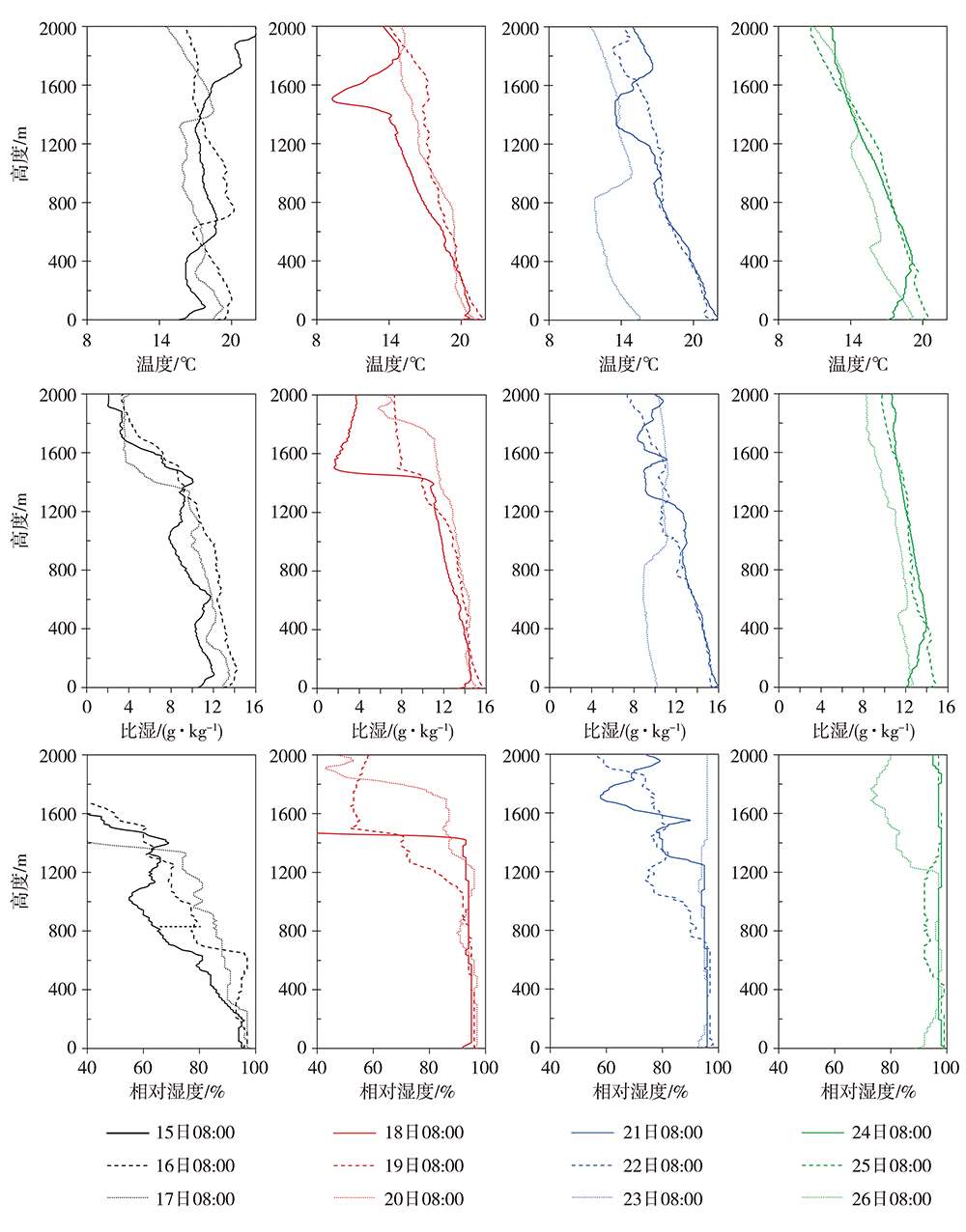
图10 2018年2月15—26日08:00海口探空站温度(上)、比湿(中)和相对湿度(下)的垂直廓线
Fig.10 The vertical profiles of temperature (the top), specific humidity (the middle) and relative humidity (the below) at Haikou sounding station at 08:00 BST from 15 to 26 February 2018

图11 2018年2月15日(a)、19日(b)和22日(c)08:00沿110.26°E的温度平流(填色,单位:10-5 K·s-1)及垂直环流(流线)经向垂直剖面
Fig.11 The meridional vertical sections of temperature advection (shadows, Unit: 10-5 K·s-1) and vertical circulation (streamlines) along 110.26°E at 08:00 BST 15 (a), 19 (b) and 22 (c) February 2018
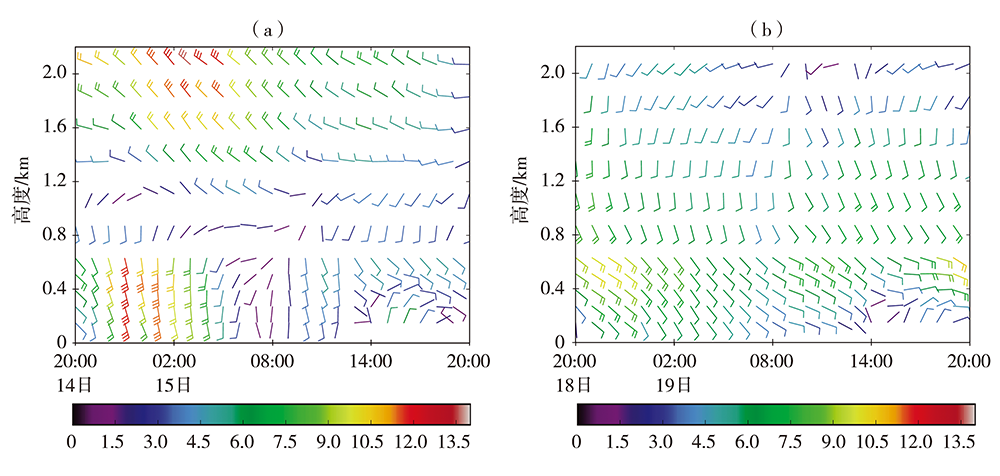
图12 2018年2月14日20:00至15日20:00(a)和18日20:00至19日20:00(b)海口站风场(风羽,单位:m·s-1)时间-高度剖面 (风速达12 m·s-1以上为低空急流)
Fig.12 The time-height section of wind field (barbs, Unit: m·s-1) at Haikou station from 20:00 BST 14 to 20:00 BST 15 (a) and 20:00 BST 18 to 20:00 BST 19 (b) February 2018 (The wind speed of low-level jet was more than 12 m·s-1)
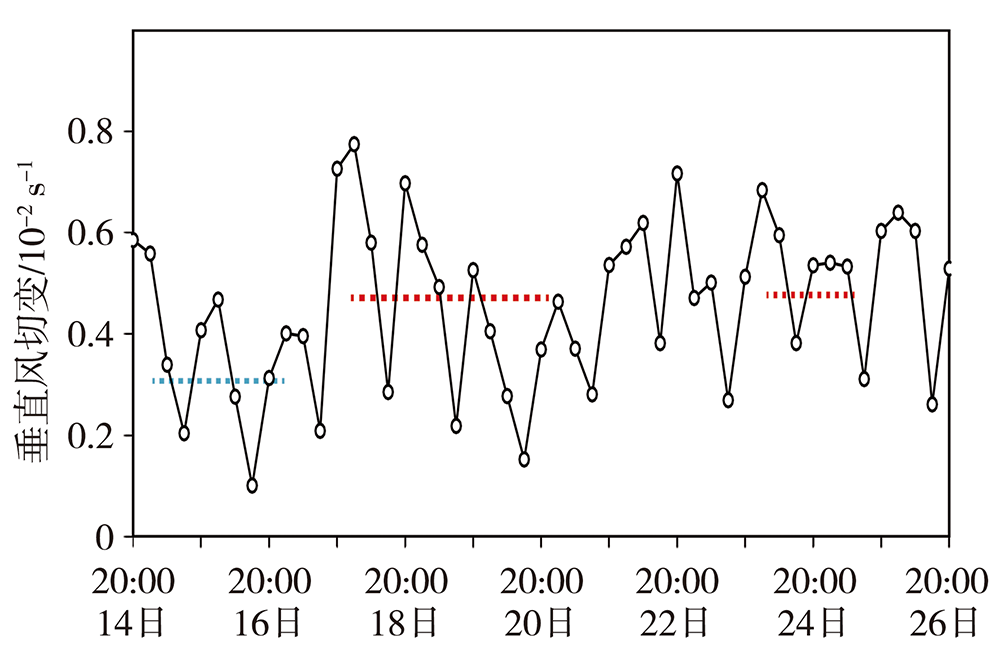
图13 2018年2月14—26日海口站地面与600 m高度垂直风切变的逐小时演变[蓝、红色虚线分别为辐射雾(15—17日)、平流雾(18—20日、24—25日)期间垂直风切变的平均值]
Fig.13 The hourly evolution of vertical wind shear between surface and 600 m height at Haikou station from 14 to 26 February 2018 [the blue (red) dot line indicated the average value of vertical wind shear during radiation (advection) fog from 15 to 17 (18 to 20 and 24 to 25) February, respectively]
| [1] | 王彬华. 海雾[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1983: 352. |
| [2] | 田永杰, 邓玉娇, 陈武喝, 等. 基于FY-2E数据白天海雾检测算法的改进[J]. 干旱气象, 2016, 34(4):738-742. |
| [3] | ZHANG Y, FAN S X, ZHANG S T, et al. Microstructures and temporal variation characteristics during a sea fog event along the west coast of the Taiwan Strait[J]. Journal of Tropical Meteorology, 2017, 23(2):155-165. |
| [4] | 王冠岚, 孙莎莎, 孙柏堂, 等. 2018年6月青岛海域一次海雾过程分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 2021, 44(1):29-35. |
| [5] | 李美琪, 郭蕊, 贾小卫, 等. 冀中南一次持续性大雾过程成因及维持机制[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(4):591-600. |
| [6] | 黄翊, 彭新东. 边界层湍流参数化改进对雾的模拟影响[J]. 大气科学, 2017, 41(3):533-543. |
| [7] | HUANG H J, HUANG B, YI L, et al. Evaluation of the global and regional assimilation and prediction system for predicting sea fog over the South China Sea[J]. Advance in Atmospheric Sciences, 2019, 36:623-642. |
| [8] | 王冠岚, 孙莎莎, 孙柏堂, 等. 2018年6月青岛海域一次海雾过程分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 2021, 44(1):29-35. |
| [9] | 杨悦, 高山红. 黄海海雾天气特征与逆温层成因分析[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 45(6):19-30. |
| [10] | HUANG J, WANG B, WANG X, et al. The spring Yellow Sea fog: synoptic and air-sea characteristics associated with different airflow paths[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2018, 37(1):20-29. |
| [11] | 徐峰, 牛生杰, 张羽, 等. 雷州半岛雾的气候特征及生消机理[J]. 大气科学学报, 2011, 34(4):423-432. |
| [12] | 郭丽君, 郭学良, 栾天, 等. 云辐射效应在华北持续性大雾维持和发展中的作用[J]. 气象学报, 2019, 77(1):111-128. |
| [13] | 黄彬, 王皘, 陆雪, 等. 黄渤海一次持续性大雾过程的边界层特征及生消机理分析[J]. 气象, 2014, 40(11):1324-1337. |
| [14] |
TELFORD J W, CHAI S K. Marine fog and its dissipation over warm water[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 1993, 50(19):3336-3349.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
HUANG J, WANG X, ZHOU W, et al. The characteristics of sea fog with different airflow over the Huanghai Sea in boreal spring[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2010, 29(4):3-12.
DOI URL |
| [16] | 黄彬, 许健民, 史得道, 等. 黄渤海一次持续性海雾过程形变特征及其成因分析[J]. 气象, 2018, 44(10):1342-1351. |
| [17] | 焦圣明, 朱承瑛, 朱毓颖, 等. 江苏地区一次罕见持续性强浓雾过程的成因分析[J]. 气象学报, 2016, 74(2):200-212. |
| [18] | 马翠平, 吴彬贵, 李江波, 等. 一次持续性大雾边界层结构特征及诊断分析[J]. 气象, 2014, 40(6):715-722. |
| [19] | 陆春松, 牛生杰, 杨军, 等. 南京冬季平流雾的生消机制及边界层结构观测分析[J]. 南京气象学院学报, 2008, 31(4):520-529. |
| [20] | 王玮, 黄玉芳, 孙建玲. 2008年11月初大雾过程边界问题分析[J]. 气象, 2009, 35(11):117-122. |
| [21] | 史得道, 吴振玲, 罗凯, 等. 2015-04-28渤海海雾形成过程中的海气相互作用分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 2018, 34(3):324-331. |
| [22] | 涂石飞, 韩利国, 徐峰, 等. 华南海雾研究进展[J]. 海洋气象学报, 2019, 39(4):12-20. |
| [23] | HUANG H J, LIU H N, JIANG W M, et al. Characteristics of the boundary layer structure of sea fog on the coast of southern China[J]. Advance in Atmospheric Sciences, 2011, 28(6):1377-1389. |
| [24] |
HUANG H J, LIU H N, HUANG J, et al. Atmospheric boundary layer structure and turbulence during sea fog on the southern China coast[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 2015, 143(5):1907-1923.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
SUN J X, HUANG H J, ZHANG S P, et al. How sea fog influences inland visibility on the southern China coast[J]. Atmosphere, 2018, 9(9):344.
DOI URL |
| [26] | 屈凤秋, 刘寿东, 易燕明, 等. 一次华南海雾过程的观测分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 2008, 24(5):490-496. |
| [27] | 刘少军, 吴胜安, 李伟光, 等. 基于FY-3B卫星资料的中国南海海区1—3月海雾时空分布特征研究[J]. 海洋气象学报, 2017, 37(4):85-90. |
| [28] | 黄彬, 宋晚郊, 刘爽, 等. 2018年春节期间琼州海峡持续性大雾监测分析[J]. 海洋气象学报, 2020, 40(4):52-59. |
| [29] | 许向春, 张春花, 林建兴, 等. 琼州海峡沿岸雾统计特征及天气学预报指标[J]. 气象科技, 2009, 37(3):323-329. |
| [30] |
FUELL K K, GUYER B J, KANN D, et al. Next generation satellite RGB dust imagery leads to operational changes at NWS Alburquerque[J]. Journal of Operational Meteorology, 2016, 4(6):75-91.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
HAN J H, SUH M S, YU H Y, et al. Development of fog detection algorithm using GK2A/AMI and ground data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(19):3181.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 阙志萍, 凌婷, 吴凡, 陈云辉. 江西一次连续大暴雨的水汽特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(1): 76-86. |
| [2] | 徐丽娜, 李忠, 胡亚男, 谷新波. 2019年冬季呼和浩特市大气污染频发的气象条件分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(1): 112-118. |
| [3] | 刘光普, 黄思源, 梁莺, 任雍, 周亭亭. 毫米波雷达在港口海雾观测和能见度反演中的应用[J]. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(6): 993-1004. |
| [4] | 刘 畅,杨成芳. 山东省极端降雪天气事件特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2017, 35(6): 957-967. |
| [5] | 田永杰1,邓玉娇2,陈武喝1,王捷纯2. 基于FY-2E数据白天海雾检测算法的改进[J]. 干旱气象, 2016, 34(4): 738-742. |
| [6] | 汤鹏宇,何宏让,阳向荣. 大连海雾特征及形成机理初步分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2013, 31(1): 62-69. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||