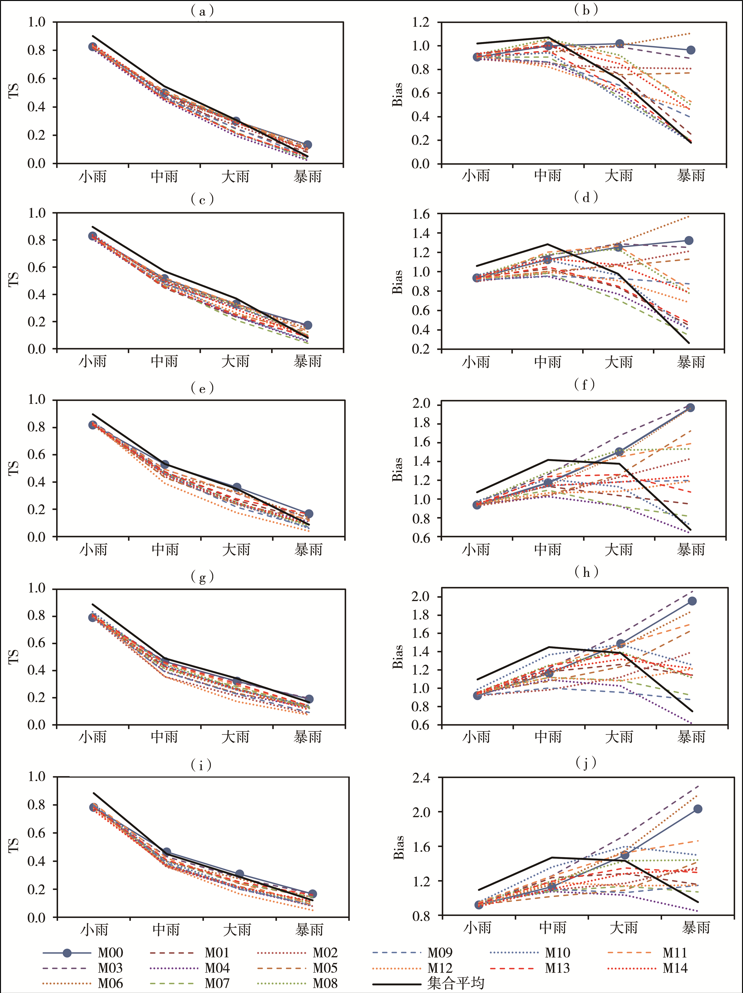
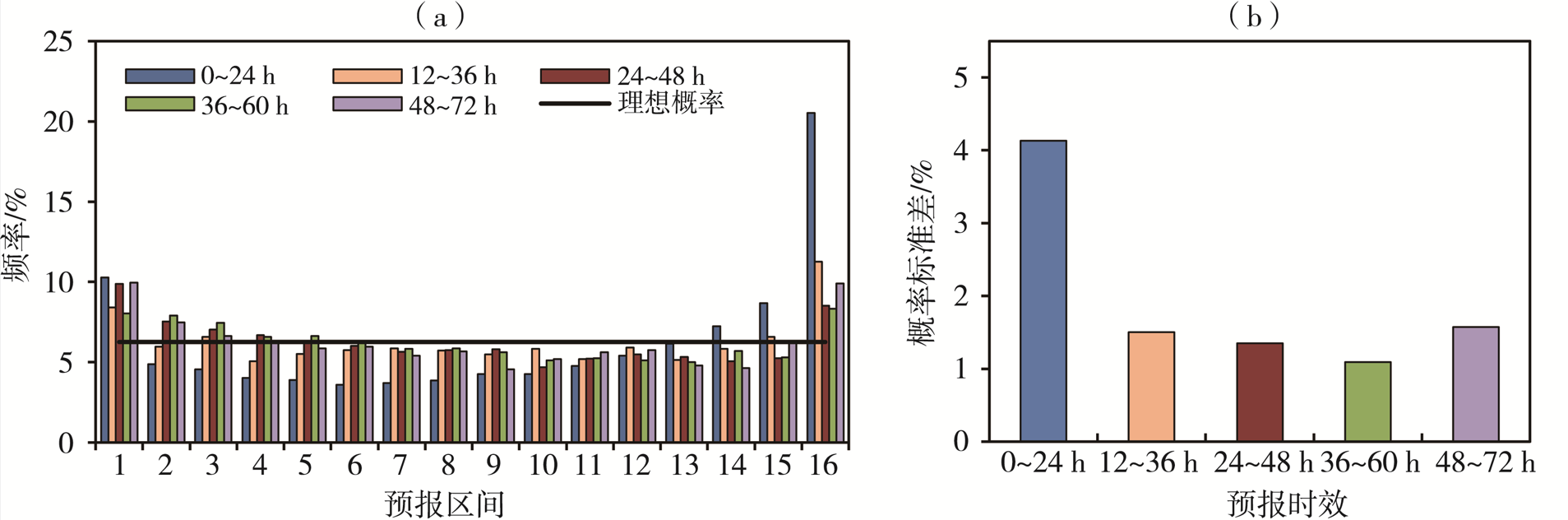
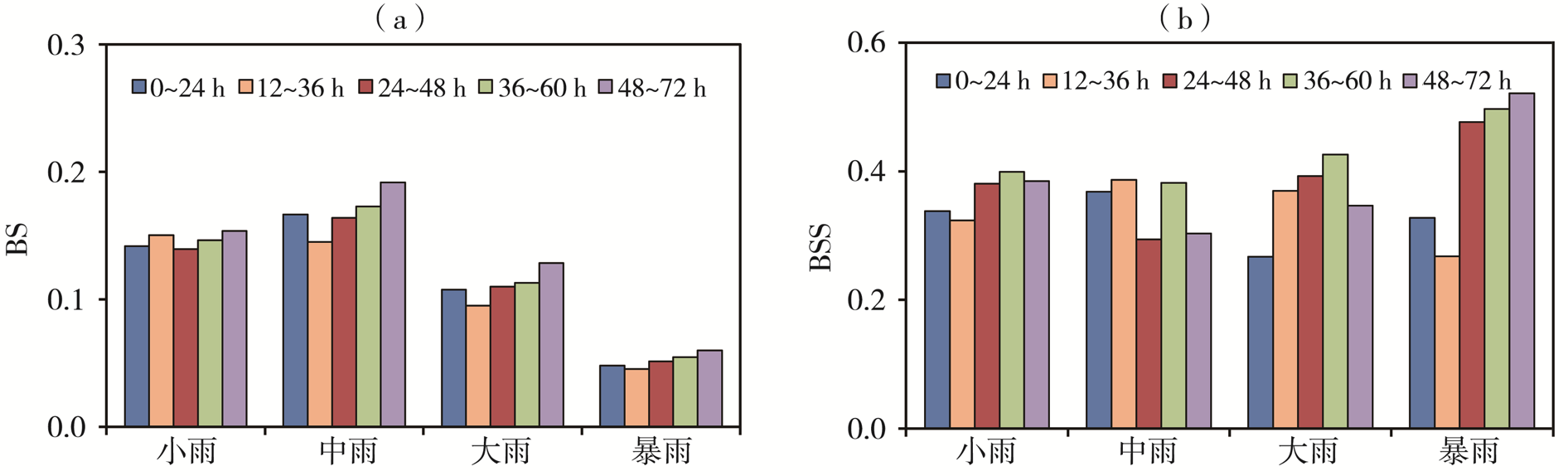
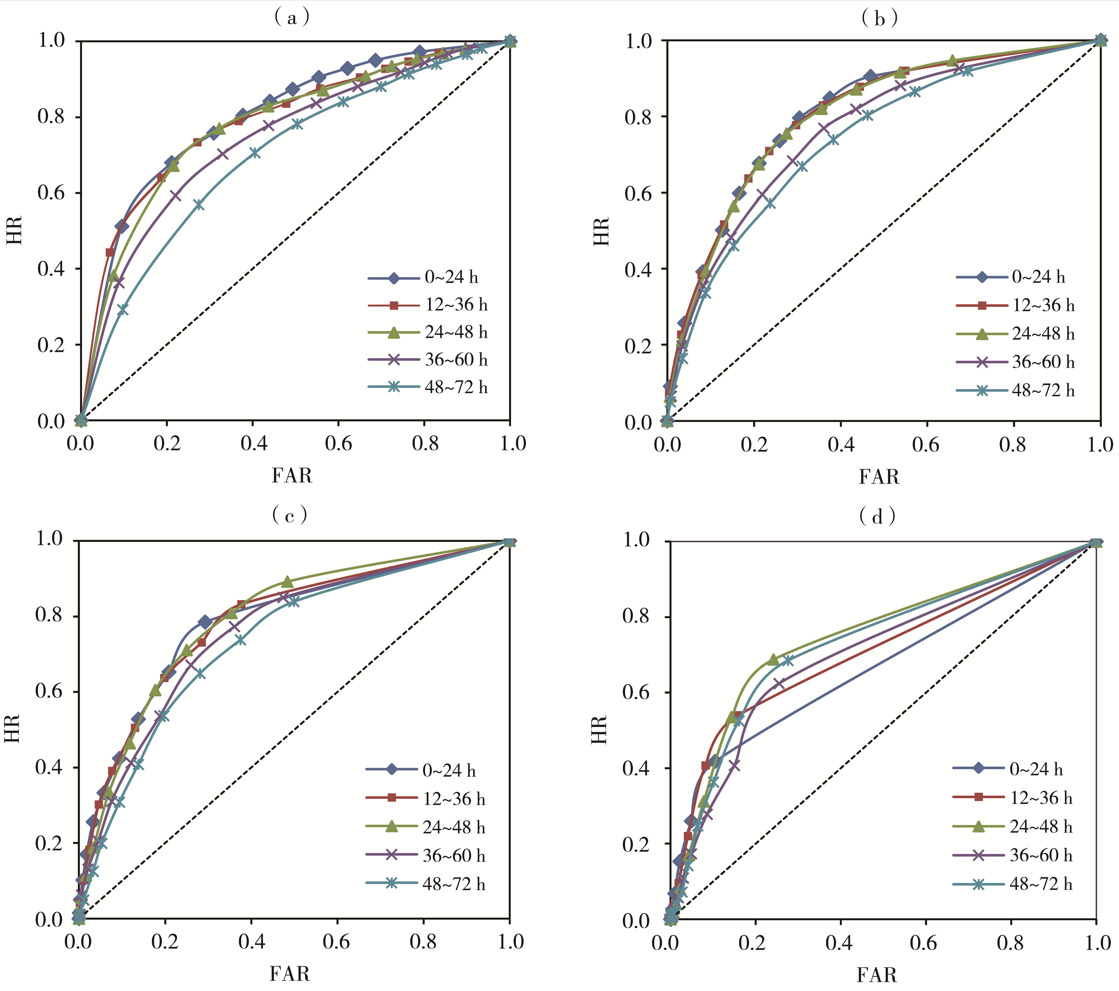
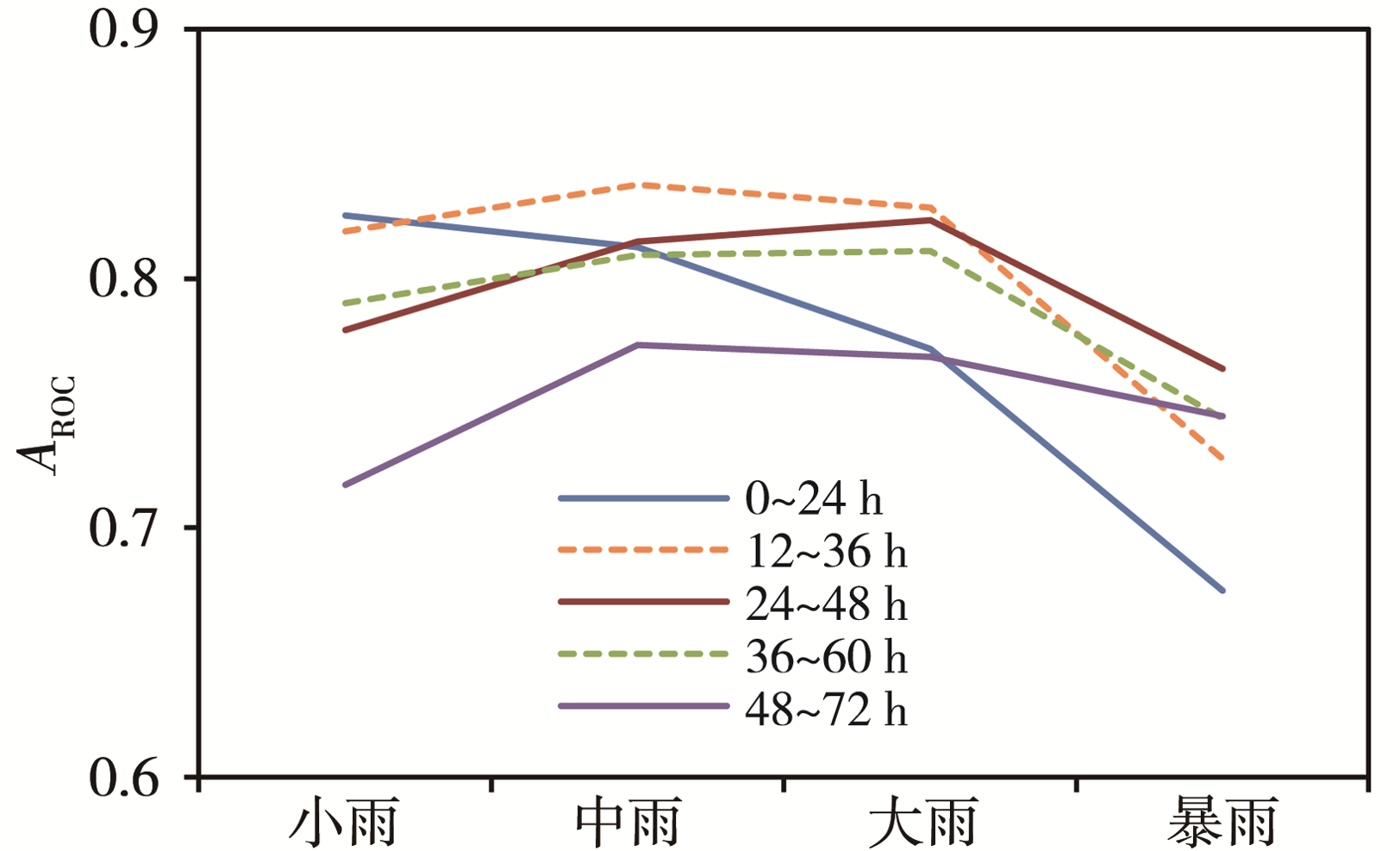
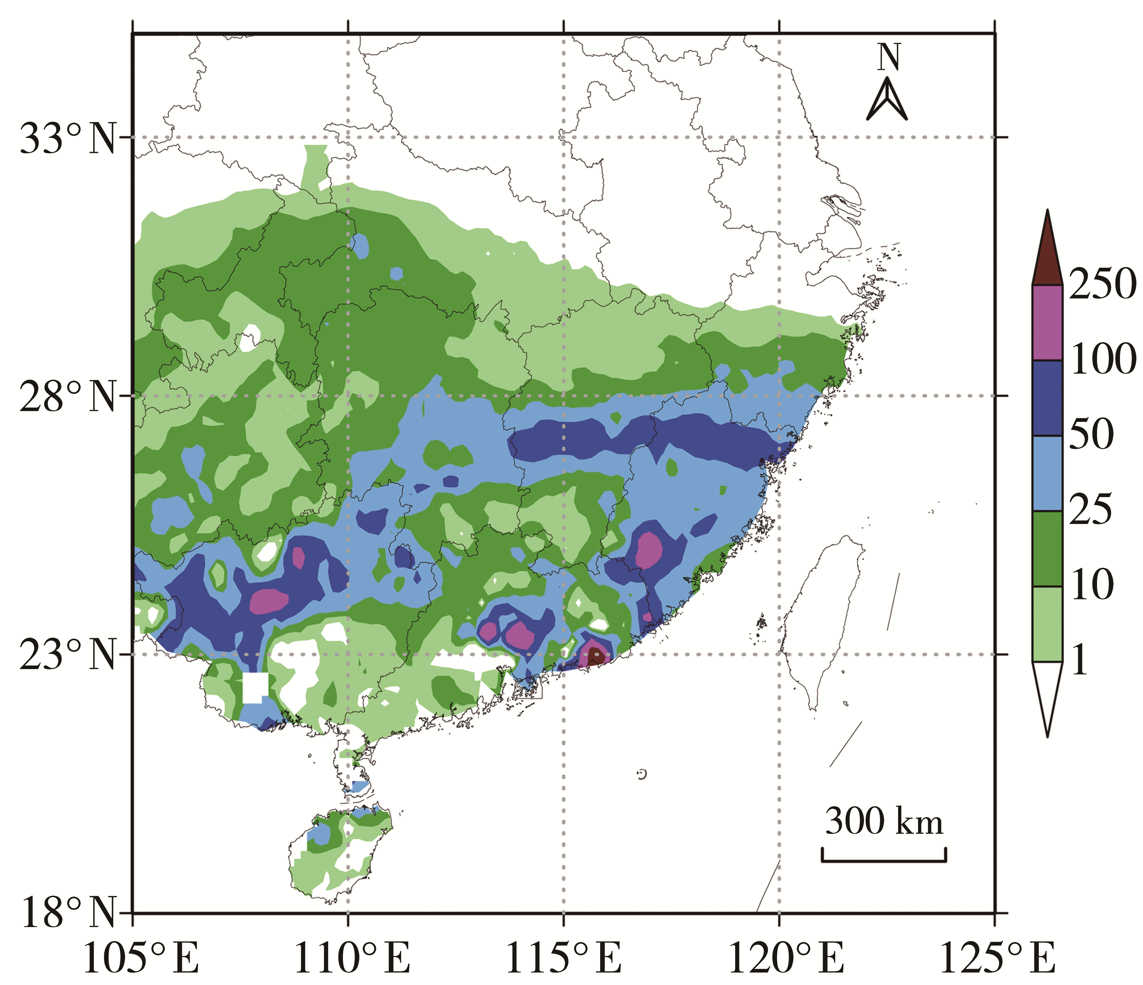
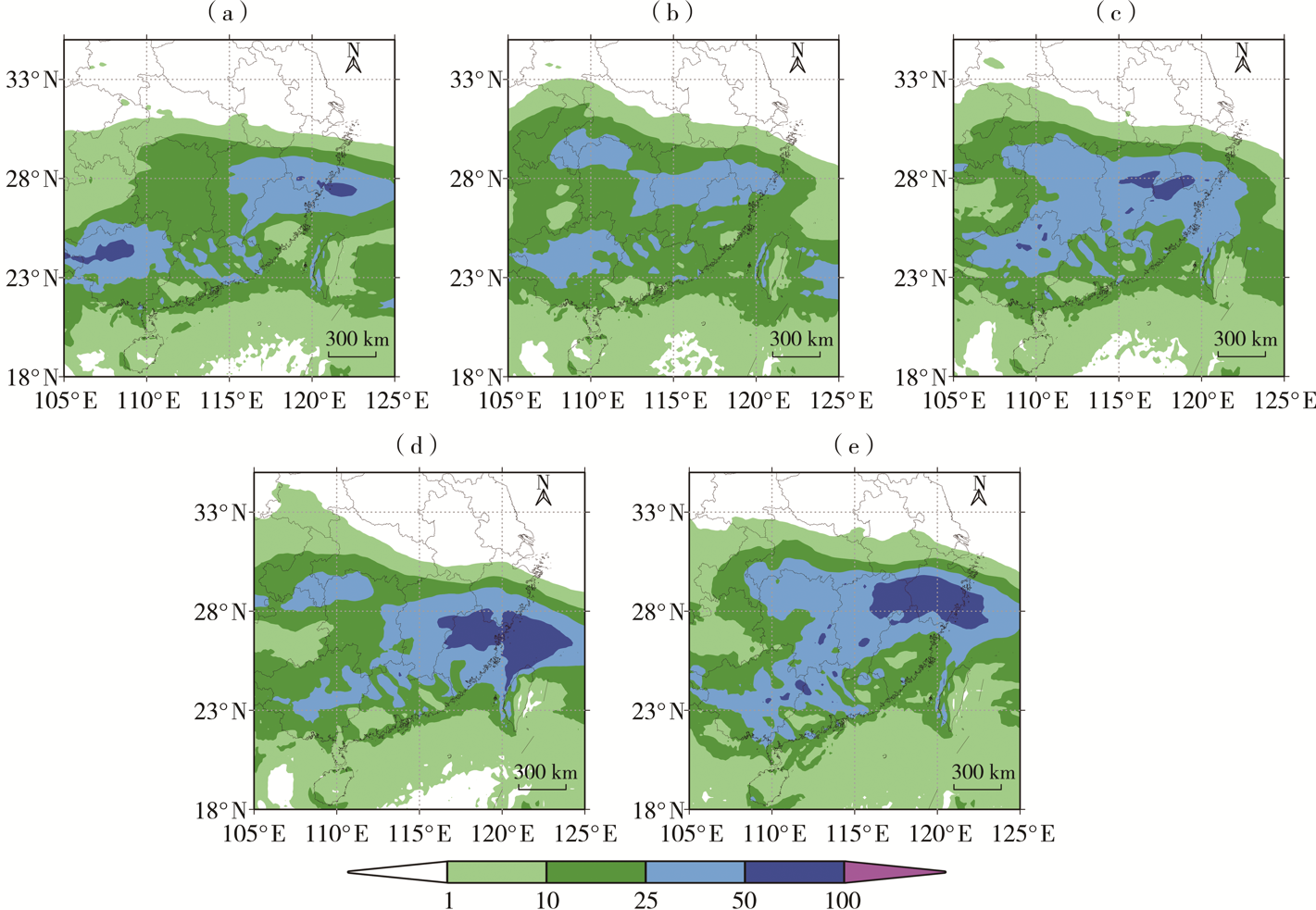
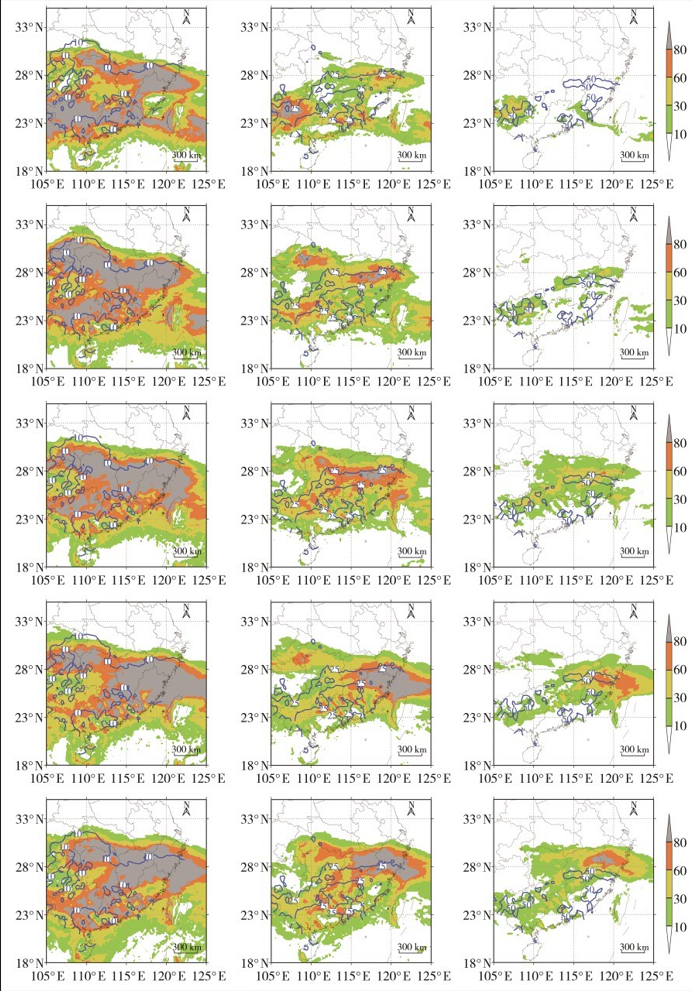
| [1] |
陈博宇, 代刊, 郭云谦, 2015. 2013年汛期ECMWF集合统计量产品的降水预报检验与分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 34(1): 64-73.
|
| [2] |
陈静, 陈德辉, 颜宏, 2002. 集合数值预报发展与研究进展[J]. 应用气象学报, 13(4): 497-507.
|
| [3] |
陈静, 薛纪善, 颜宏, 2005. 一种新型的中尺度暴雨集合预报初值扰动方法研究[J]. 大气科学, 29(5): 717-726.
|
| [4] |
陈圣劼, 刘梅, 张涵斌, 等, 2019. 集合预报产品在江苏省暴雨预报中的应用评估[J]. 气象, 45(7): 893-907.
|
| [5] |
邓国, 龚建东, 邓莲堂, 等, 2010. 国家级区域集合预报系统研发和性能检验[J]. 应用气象学报, 21(5): 513-523.
|
| [6] |
董甫, 张玲, 张海鹏, 等, 2020. 基于WRF模式的强天气过程集合预报综述[J]. 干旱气象, 38(5): 699-708.
|
| [7] |
杜钧, 2002. 集合预报的现状和前景[J]. 应用气象学报, 13(1): 16-28.
|
| [8] |
杜钧, 陈静, 2010. 单一值预报向概率预报转变的基础:谈谈集合预报及其带来的变革[J]. 气象, 36(11): 1-11.
|
| [9] |
杜钧, 李俊, 2014. 集合预报方法在暴雨研究和预报中的应用[J]. 气象科技进展, 4(5): 6-20.
|
| [10] |
杜钧, 周斌斌, 2016. 雾的集合预报与集合预报的检验[J]. 气象科技进展, 6(3):41-47.
|
| [11] |
李俊, 杜钧, 陈超君, 2014. 降水偏差订正的频率(或面积)匹配方法介绍和分析[J]. 气象, 40(5): 580-588.
|
| [12] |
李俊, 杜钧, 陈超君, 2015. “频率匹配法”在集合降水预报中的应用研究[J]. 气象, 41(6): 674-684.
|
| [13] |
李俊, 王明欢, 公颖, 等, 2010. AREM短期集合预报系统及其降水预报检验[J]. 暴雨灾害, 29(1): 30-37.
|
| [14] |
谭燕, 2006. 中尺度强降水天气集合预报技术的研究[D]. 北京: 中国气象科学研究院.
|
| [15] |
王婧卓, 陈法敬, 陈静, 等, 2021. GRAPES区域集合预报对2019年中国汛期降水预报评估[J]. 大气科学, 45(3): 664-682.
|
| [16] |
王婧卓, 陈静, 庄照荣, 等, 2018. GRAPES区域集合预报模式的初值扰动增长特征[J]. 大气科学, 42(2): 367-382.
|
| [17] |
王静, 陈静, 钟有亮, 等, 2017. GRAPES-REPS西南低涡预报检验评估[J]. 气象, 43(4): 385-401.
|
| [18] |
王叶红, 赵玉春, 2020. 边界层参数化方案对“莫兰蒂”台风(1614)登陆阶段影响的数值模拟研究[J]. 大气科学, 44(5): 935-959.
|
| [19] |
吴秋霞, 史历, 翁永辉, 等, 2007. AREMS/973模式系统对2004年中国汛期降水实时预报检验[J]. 大气科学, 31(2): 298-310.
|
| [20] |
闫慧, 赵桂香, 2020. 山西一次持续暴雨天气过程诊断与集合预报检验[J]. 干旱气象, 38(1): 137-147.
|
| [21] |
张涵斌, 陈静, 智协飞, 等, 2014. GRAPES区域集合预报系统应用研究[J]. 气象, 40(9): 1 076-1 087.
|
| [22] |
赵琳娜, 刘琳, 刘莹, 等, 2015. 观测降水概率不确定性对集合预报概率Brier技巧评分结果的分析[J]. 气象, 41(6): 685-694.
|
| [23] |
钟有亮, 陈静, 王静, 等, 2017. GRAPES区域集合预报系统对登陆台风预报的检验评估[J]. 热带气象学报, 33(6): 953-964.
|
| [24] |
BRIER G W, 1950. Verification of forecasts expressed in terms of probability[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 78(1): 1-3.
DOI
URL
|
| [25] |
CANDILLE G, TALAGRAND O, 2008. Impact of observational error on the validation of ensemble prediction systems[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 134(633): 959-971.
DOI
URL
|
| [26] |
DONALDSON R J, DYER R M, KRAUS M J, 1975. An objective evaluator of techniques for predicting severe weather events[C]// Preprints: Ninth Conference on Severe Local Storms. Norman: American Meteorological Society:321-326.
|
| [27] |
HUO Z H, DUAN W S, ZHOU F F, 2019. Ensemble forecasts of tropical cyclone track with orthogonal conditional nonlinear optimal perturbations[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 36(2): 231-247.
DOI
|
| [28] |
MASON I, 1979. On reducing probability forecasts to yes/no forecasts[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 107(2): 207-211.
DOI
URL
|
| [29] |
MURPHY A H, 1973. A new vector partition of the probability score[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 12(4): 595-600.
DOI
URL
|
| [30] |
SCHAEFER J T, 1990. The critical success index as an indicator of warning skill[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 5(4): 570-575.
DOI
URL
|
| [31] |
SWETS J A, 1986. Indices of discrimination or diagnostic accuracy: their ROCs and implied models[J]. Psychological Bulletin, 99(1): 100-117.
PMID
|
| [32] |
TALAGRAND O, VAUTARD R, STRAUSS B, 1997. Evaluation of probabilistic prediction systems[C]// Proceedings: ECMWF Workshop on Predictability, Berkshire, United Kingdom: ECMWF: 1-25.
|
| [33] |
WANG J Z, CHEN J, DU J, et al, 2018. Sensitivity of ensemble forecast verification to model Bias[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 146(3): 781-796.
DOI
URL
|
| [34] |
WANG Y H, ZHAO Y C, CUI C G, 2007. Numerical research on effects upon precipitation forecast of Doppler-radar estimated precipitation and retrieved wind field under different model initial schemes[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 21(1): 98-113.
|
| [35] |
ZHANG H B, CHEN J, ZHI X F, et al, 2015. A comparison of ETKF and downscaling in a regional ensemble prediction system[J]. Atmosphere, 6(3): 341-360.
DOI
URL
|