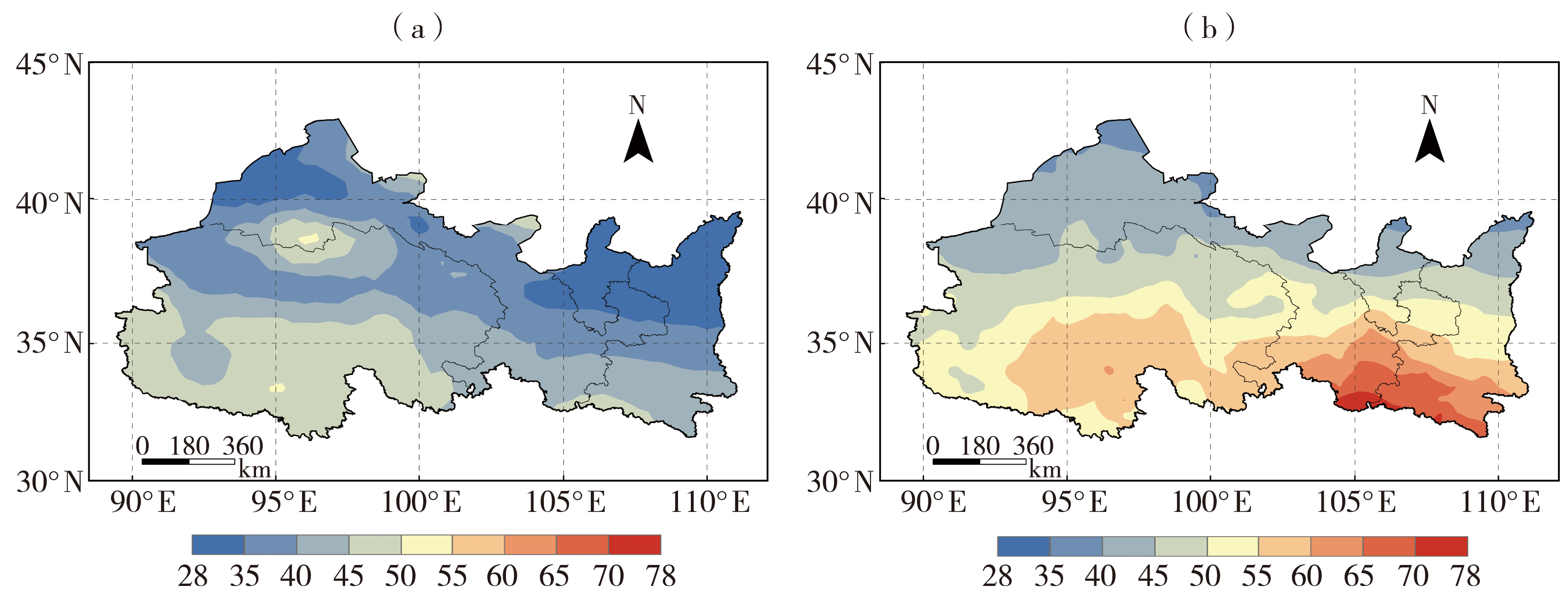
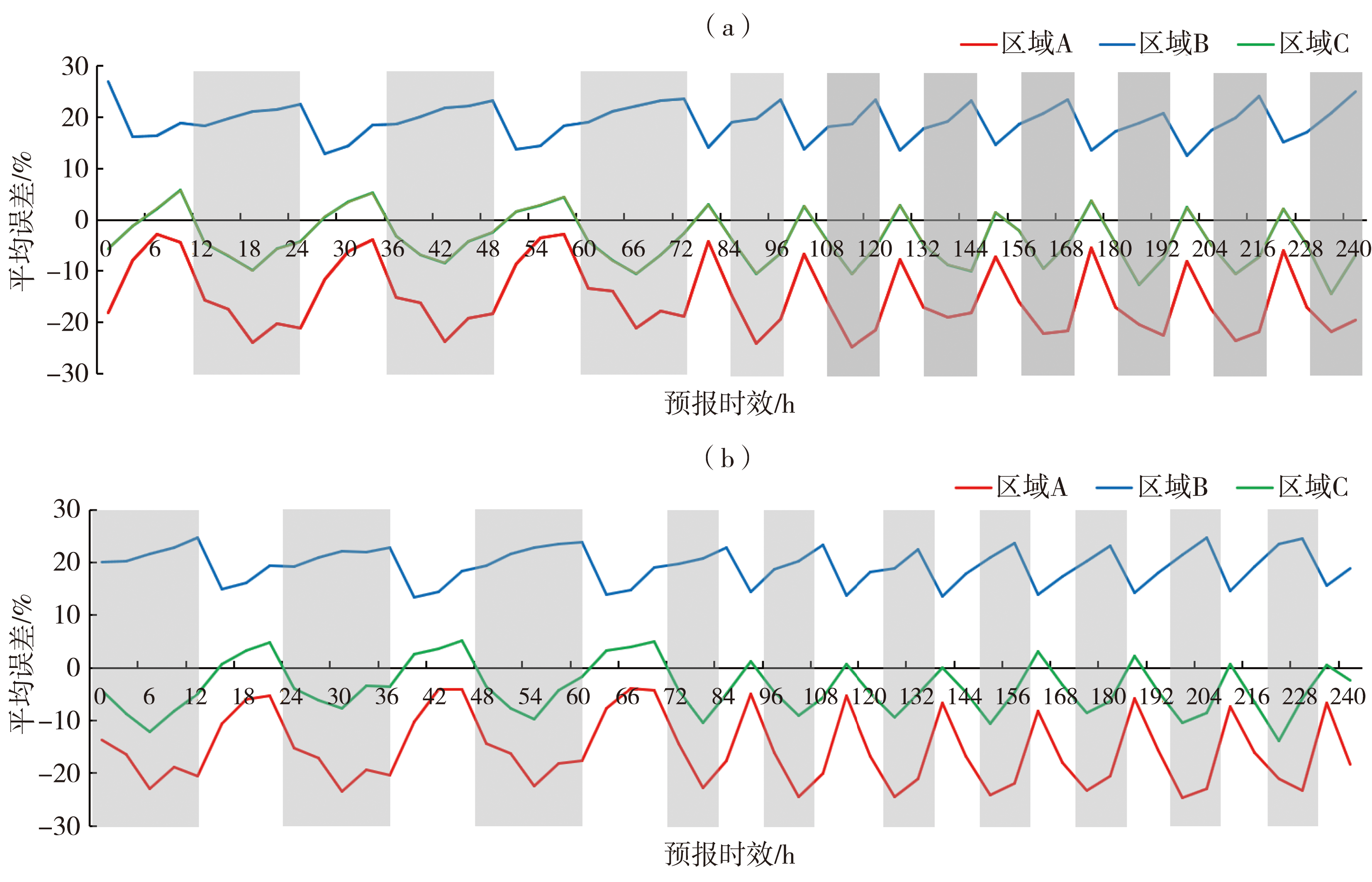
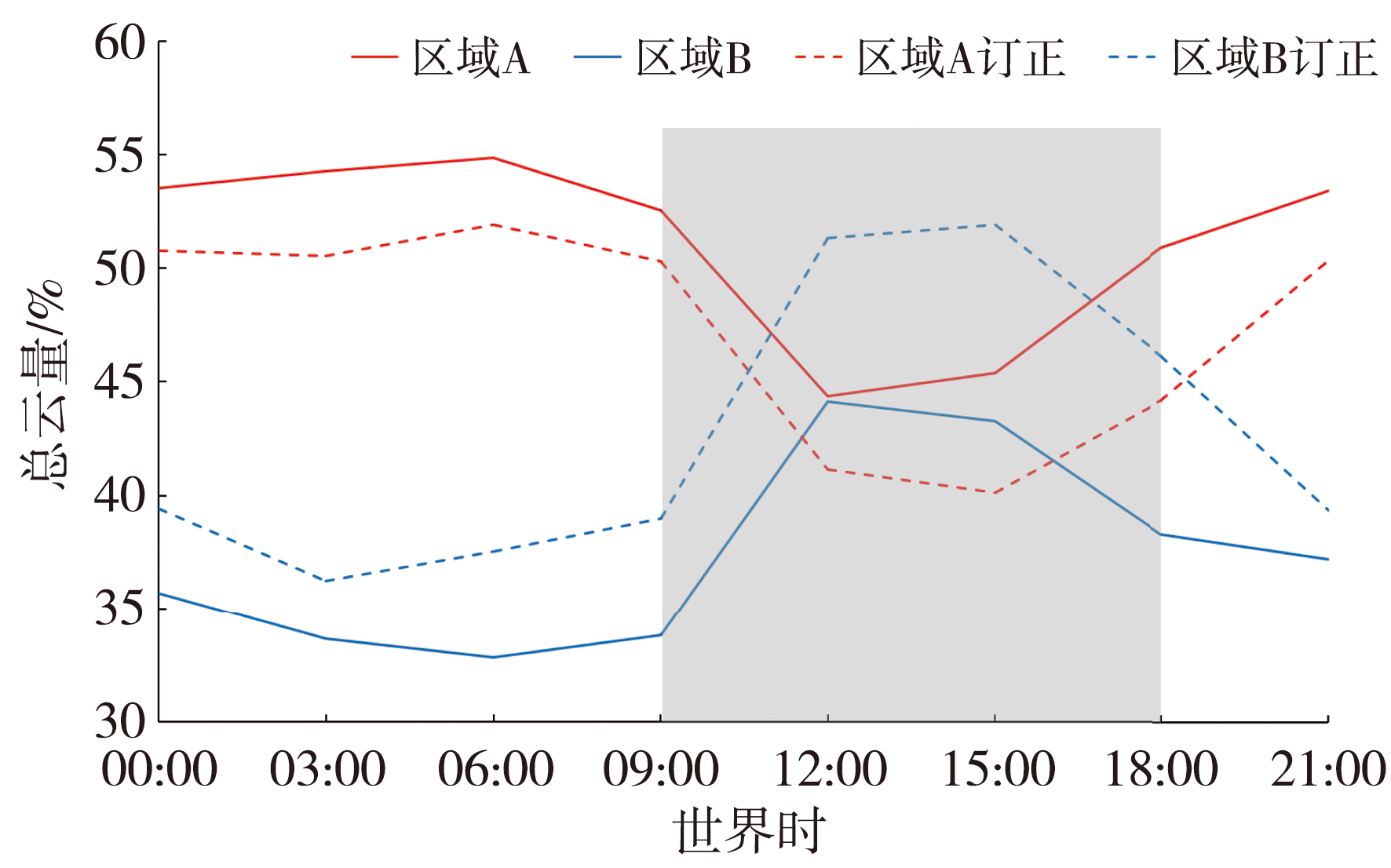
| [1] |
曹越前, 张武, 药静宇, 等, 2015. 半干旱区云量变化特征及基与太阳-辐射关系的研究[J]. 干旱气象, 33(4): 684-693.
DOI
|
| [2] |
陈勇航, 黄建平, 陈长和, 等, 2005. 西北地区空中云水资源的时空分布特征[J]. 高原气象, 24(6): 905-912.
|
| [3] |
范思睿, 王维佳, 林丹, 2020. 基于ISCCP云资料的中国地区不同类型云的时空分布[J]. 干旱气象, 38(2): 213-225.
|
| [4] |
高太长, 刘磊, 赵世军, 2010. 全天空测云技术现状及进展[J]. 应用气象学报, 21(1):101-109.
|
| [5] |
李栋梁, 邵鹏程, 王慧, 等, 2013. 中国东亚副热带夏季风北边缘带研究进展[J]. 高原气象, 32(1): 305-314.
DOI
|
| [6] |
李娅, 郭建侠, 曹云昌, 等, 2018. FY-2G云量产品与地面观测云量对比分析[J]. 高原气象, 37(2): 514-523.
DOI
|
| [7] |
廖国男, 1985. 大气辐射导论[M]. 北京: 气象出版社.
|
| [8] |
刘健, 崔鹏, 肖萌, 2017. FY-2G卫星冬夏云量产品偏差分析[J]. 应用气象学报, 28(2): 177-188.
|
| [9] |
刘俏华, 姚秀萍, 陈明诚, 2021. 基于OLR资料的青藏高原地区对流活动研究[J]. 大气科学, 45(2): 456-470.
|
| [10] |
刘玉兰, 孙银川, 桑建人, 等, 2011. 影响太阳能光伏发电功率的环境气象因子诊断分析[J]. 水电能源科学, 29(12): 200-202.
|
| [11] |
吕学梅, 朱虹, 王金东, 等, 2014. 气象因素对光伏发电量的影响分析[J]. 可再生能源, 32(10):1 423-1 428.
|
| [12] |
强安丰, 汪妮, 魏加华, 等, 2020. 近50年三江源地区云水资源分布及降水效率研究[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报, 28(3): 574-593.
|
| [13] |
孙朋杰, 陈正洪, 成驰, 等, 2013. 太阳能光伏电站发电量变化特征及其与气象要素的关系[J]. 水电能源科学, 31(11): 249-252.
|
| [14] |
王宝鉴, 黄玉霞, 王劲松, 等, 2006. 祁连山云和空中水汽资源的季节分布与演变[J]. 地球科学进展, 21(9): 948-955.
DOI
|
| [15] |
王宝鉴, 黄玉霞, 魏栋, 等, 2017. TRMM卫星对青藏高原东坡一次大暴雨强降水结构的研究[J]. 气象学报, 75(6): 966-980.
|
| [16] |
王澄海, 张晟宁, 李课臣, 等, 2021. 1961—2018年西北地区降水的变化特征[J]. 大气科学, 45(4): 713-724.
|
| [17] |
王平, 陈怡蓓, 何艳红, 等, 2018. ECMWF高分辨率数值模式对广安地区气温预报性能检验分析[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 38(4): 41-44.
|
| [18] |
王遂缠, 李栋梁, 王谦谦, 2005. 青藏高原东北侧夏季降水的气候特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 23(2): 13-18.
|
| [19] |
汪宏七, 赵高祥, 1994. 云和辐射 (I): 云气候学和云的辐射作用[J]. 大气科学, 18(增刊1): 910-932.
|
| [20] |
吴伟, 2011. 基于CloudSat及MODIS卫星云产品对GRAPES全球模式和WRF模式云微物理方案的对比检验[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学.
|
| [21] |
肖玉华, 王佳津, 蒋丽娟, 等, 2019. GRAPES-GFS在西南地区的预报稳定性及其误差与地形的关系[J]. 暴雨灾害, 38(1): 59-65.
|
| [22] |
宜树华, 刘洪利, 李维亮, 等, 2003. 中国西北地区云时空分布特征的初步分析[J]. 气象, 29(1): 7-11.
|
| [23] |
余忠水, 拉巴, 周洪莉, 等, 2018. 近40年西藏高原云量与降水分布及耦合变化特征[J]. 西藏科技, 2018(9): 51-57.
|
| [24] |
张超, 孙绩华, 巩远发, 等, 2018. ECMWF高分辨率网格对云南区域降水预报性能的定量检验[J]. 成都信息工程大学学报, 2018(6): 93-108.
|
| [25] |
张宁瑾, 肖天贵, 假拉, 2018. 1979—2016年青藏高原降水时空特征[J]. 干旱气象, 36(3): 373-382.
|
| [26] |
张强, 张存杰, 白虎志, 等, 2010. 西北地区气候变化新动态及对干旱环境的影响——总体暖干化, 局部出现暖湿迹象[J]. 干旱气象, 28(1): 1-7.
|
| [27] |
张寅, 罗亚丽, 管兆勇, 2012. NCEP全球预报系统在ARM SGP站点预报大气温度、湿度和云量的检验[J]. 大气科学, 36(1):170-184.
|
| [28] |
郑晓辉, 徐国强, 魏荣庆, 2013. GRAPES新云量计算方案的引进和影响试验[J]. 气象, 39(1): 57-66.
|
| [29] |
GAO S T, XIAO F L, 2009. Dependence of the accuracy of precipitation and cloud simulation on temporal and spatial scales[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, (6): 1 108-1 114.
|
| [30] |
ISAKSEN L, JANSSEN P A E M, 2004. Impact of ERS scatterometer winds in ECMWF's assimilation system[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 130(600): 1 793-1 814.
|
| [31] |
LEUTBECHER M, LOCK S J, OLLINAHO P, et al. Stochastic representations of model uncertainties at ECMWF: state of the art and future vision[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 2017, 143 (707): 2 315-2 339.
|
| [32] |
MORADI I, ARKIN P, FERRARO R, et al, 2016. Diurnal variation of tropospheric relative humidity in tropical regions[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 16(11): 6 913-6 929.
|
| [33] |
SKJERDAL, SUNDVOR M, 2009. Variability of precipitation in complex terrain and the investigation of representativeness of a single point measurement for the Matre Hydro System, Western Norway[J]. Vdp Matematikk Og Naturvitenskap Geofag Meteorologi.
|
| [34] |
ZHANG G J, ZUROCAVC-JEVTIC D, BOER E R, 1999. Spatial characteristics of the tropical cloud systems: comparison between model simulation and satellite observations[J]. Tellus A, 51(5): 922-936.
DOI
URL
|
 ), 沙宏娥1,2,3(
), 沙宏娥1,2,3( ), 秦豪君3, 吕巧谊4, 刘丽伟1, 傅朝3
), 秦豪君3, 吕巧谊4, 刘丽伟1, 傅朝3
 ), SHA Hong’e1,2,3(
), SHA Hong’e1,2,3( ), QIN Haojun3, LYU Qiaoyi4, LIU Liwei1, FU Zhao3
), QIN Haojun3, LYU Qiaoyi4, LIU Liwei1, FU Zhao3