干旱气象 ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (3): 463-473.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-03-0463
印度双低涡对青藏高原西部一次典型暴雪过程的影响
张入财1( ), 王君2(
), 王君2( ), 陈超辉3, 付伟基4, 魏璐璐5
), 陈超辉3, 付伟基4, 魏璐璐5
- 1.中国人民解放军31308部队,四川 成都 610031
2.河南省气象学会,河南省气象科学研究所,河南 郑州 450003
3.国防科技大学气象海洋学院,湖南 长沙 410073
4.中国人民解放军96606部队,河南 洛阳 471000
5.河南省三门峡市气象局,河南 三门峡 472000
Influence of Indian double vortexes on a typical snowstorm event in the west of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau
ZHANG Rucai1( ), WANG Jun2(
), WANG Jun2( ), CHEN Chaohui3, FU Weiji4, WEI Lulu5
), CHEN Chaohui3, FU Weiji4, WEI Lulu5
- 1. No. 31308 of PLA, Chengdu 610031, China
2. Henan Provincial Meteorological Society, Henan Institute of Meteorological Sciences, Zhengzhou 450003, China
3. College of Meteorology and Oceanography, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
4. No. 96606 of PLA, Luoyang 471000, Henan, China
5. Sanmenxia Meteorological Office of Henan Province, Sanmenxia 472000, Henan, China
摘要:
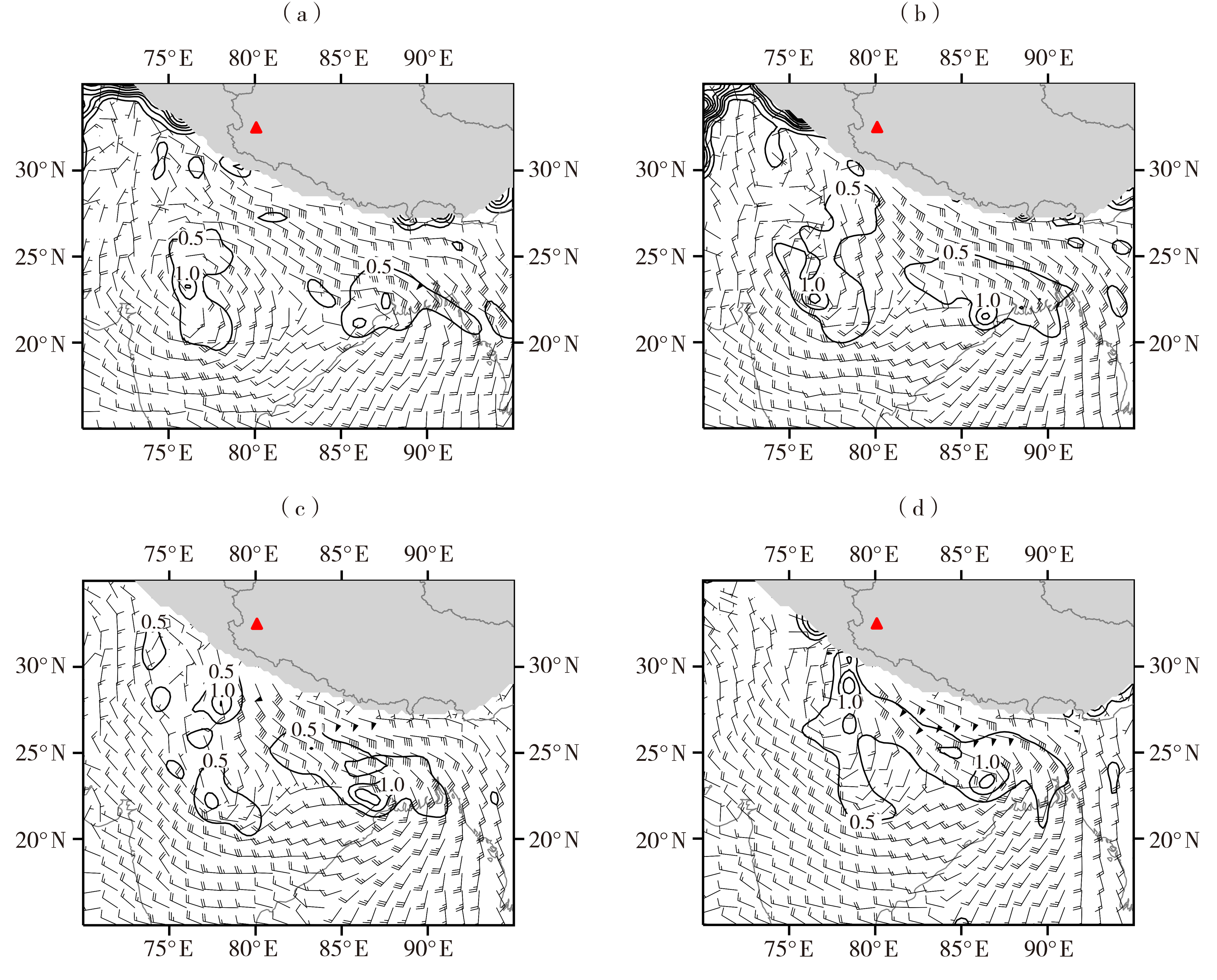
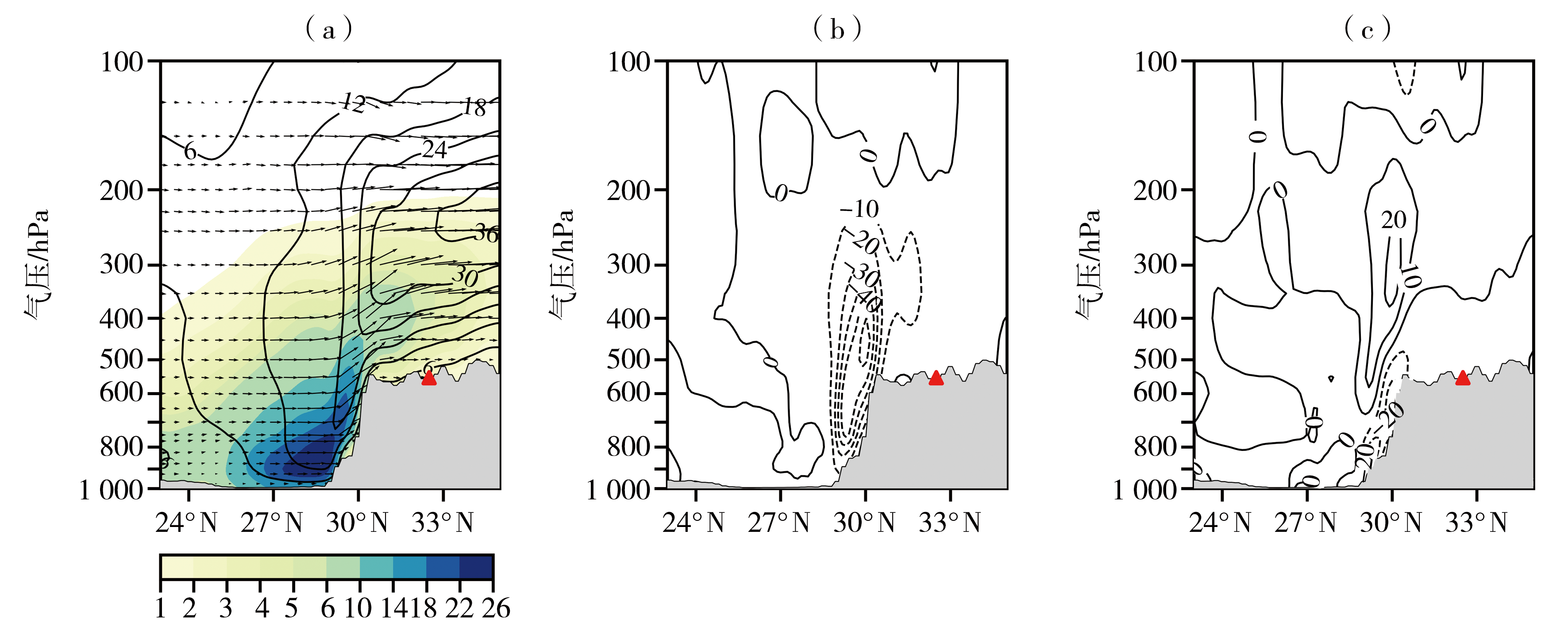
利用地面气象观测数据、欧洲中期天气预报中心ERA5再分析资料和FY-4A卫星云顶亮温数据,对2021年10月18—19日青藏高原西部暴雪过程进行综合分析,研究印度北部低涡对强降雪天气的贡献。结果表明:本次强降雪过程在南支槽东移和印度低涡异常活跃的背景下产生,南支槽前高空急流和印度北部东西向两个低涡为高原西部强降雪提供了有利的环流背景;降雪期间,印度北部至喜马拉雅山脉以南地区东南风低空急流大爆发,建立了一条由孟加拉湾向西输送的水汽通道,使得孟加拉湾水汽能够向西输送;生成于印度西北地区的对流层低涡系统一方面阻挡水汽继续向西输送,有利于孟加拉湾的水汽在低涡东部聚集,另一方面增强低涡东部偏南气流与高原大地形之间的强迫作用,使得大量水汽能够源源不断地从对流层低层沿高原南坡陡峭地形向上爬升至高原,为强降雪天气提供充足水汽条件;高空位涡侵入是印度西北地区的低涡系统生成发展的重要原因。总的来看,印度北部的低涡系统在此次高原西部降雪天气中起了重要作用,在高原地区降雪预报业务中,有必要加强对低纬度地区对流层低层低涡系统的跟踪监测。
中图分类号: