干旱气象 ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (3): 413-422.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-03-0413
2014—2020年关中地区近地面臭氧污染特征及气象条件分析
黄蕾1,3( ), 王丽1,3, 杜萌萌1,3(
), 王丽1,3, 杜萌萌1,3( ), 刘慧2, 金丽娜1
), 刘慧2, 金丽娜1
- 1.陕西省西安市气象局,陕西 西安 710016
2.陕西省气象台,陕西 西安 710014
3.秦岭和黄土高原生态环境气象重点实验室,陕西 西安 710016
Characteristics of near-ground ozone pollution and relationships with meteorological conditions in Guanzhong region from 2014 to 2020
HUANG Lei1,3( ), WANG Li1,3, DU Mengmeng1,3(
), WANG Li1,3, DU Mengmeng1,3( ), LIU Hui2, JIN Lina1
), LIU Hui2, JIN Lina1
- 1. Xi’an Meteorological Bureau of Shaanxi Province, Xi’an 710016, China
2. Shaanxi Provincial Meteorological Observatory, Xi’an 710014, China
3. Key Laboratory of Eco-Environment and Meteorology for the Qinling Mountains and Loess Plateau, Xi’an 710016, China
摘要:
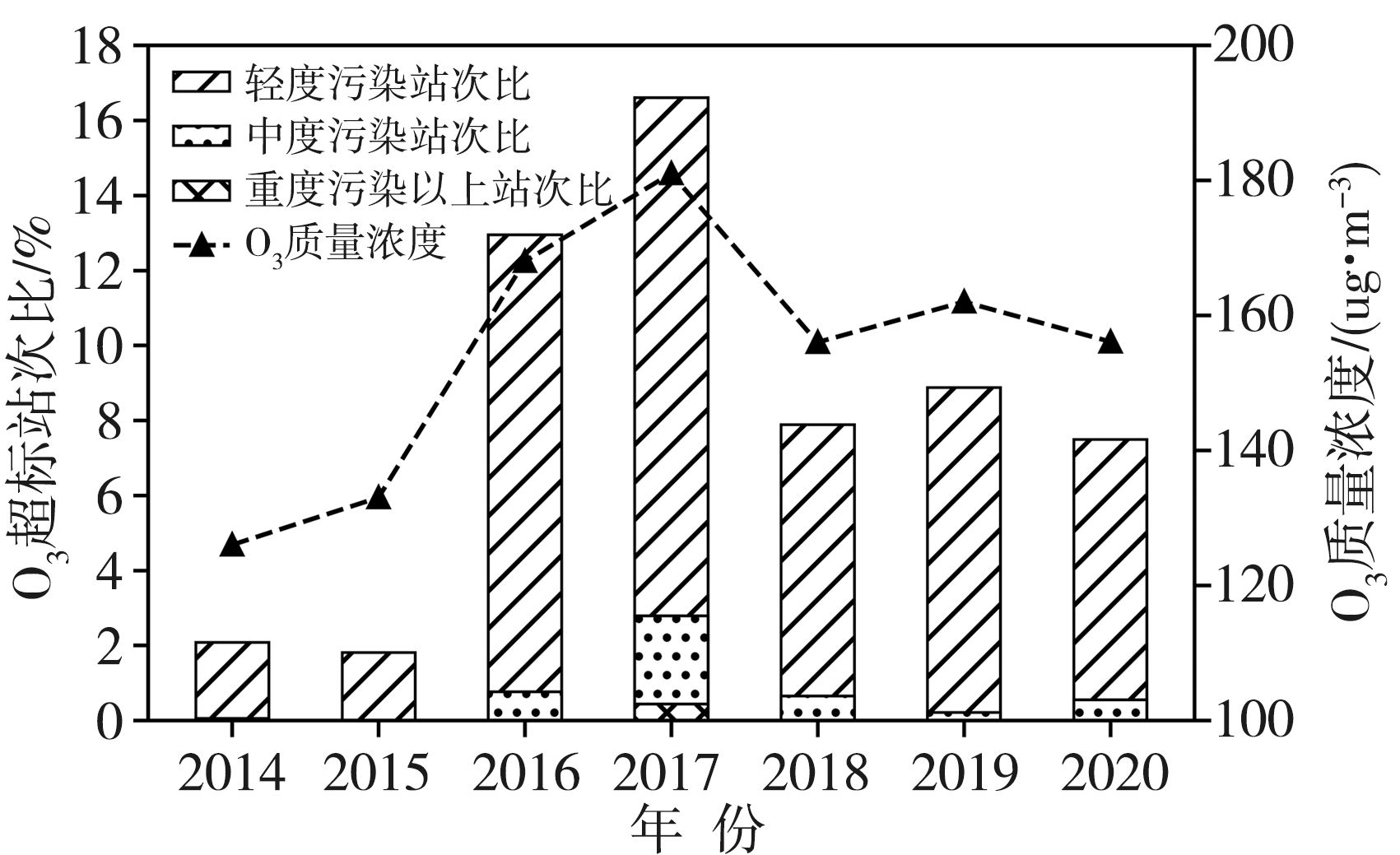
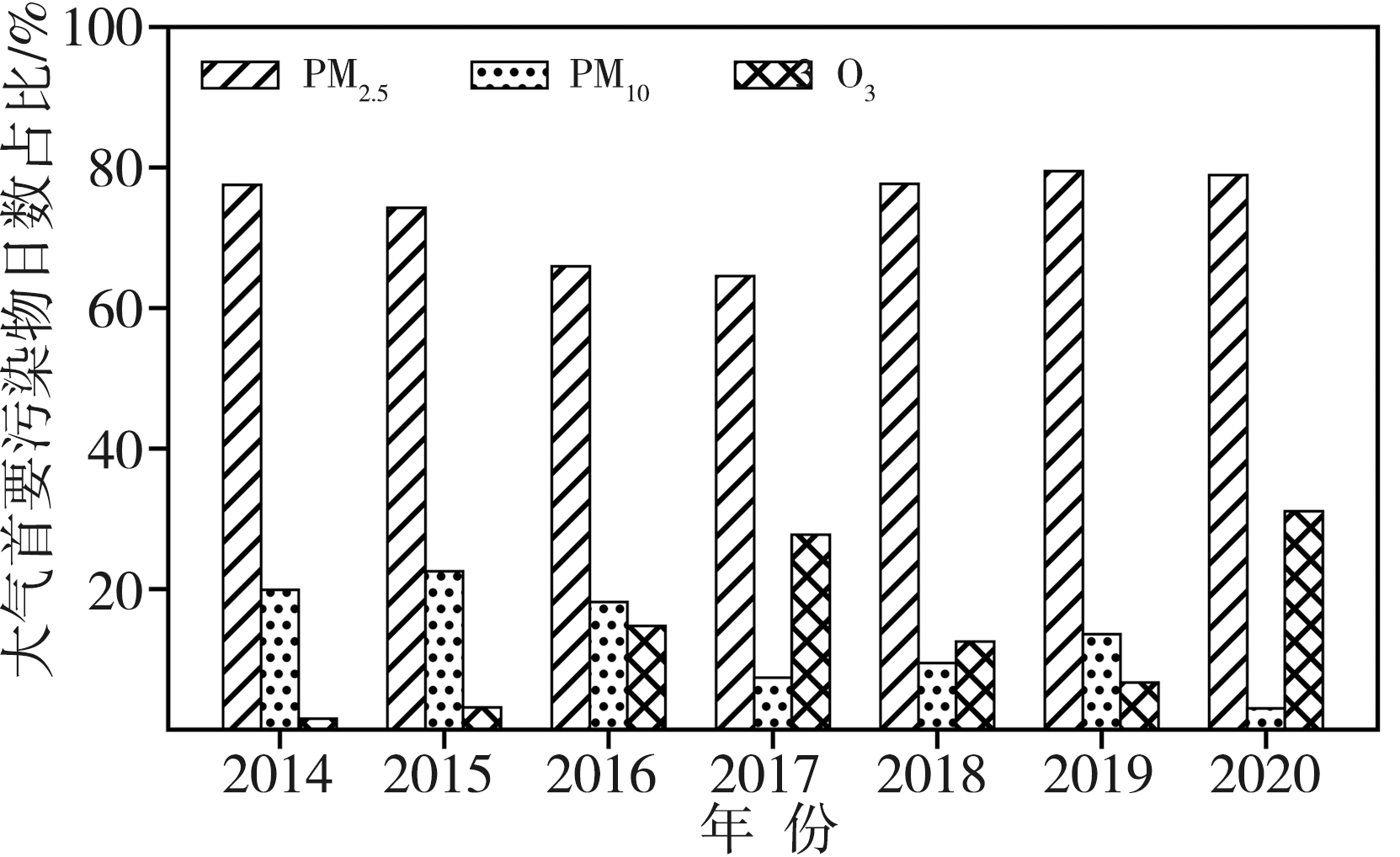
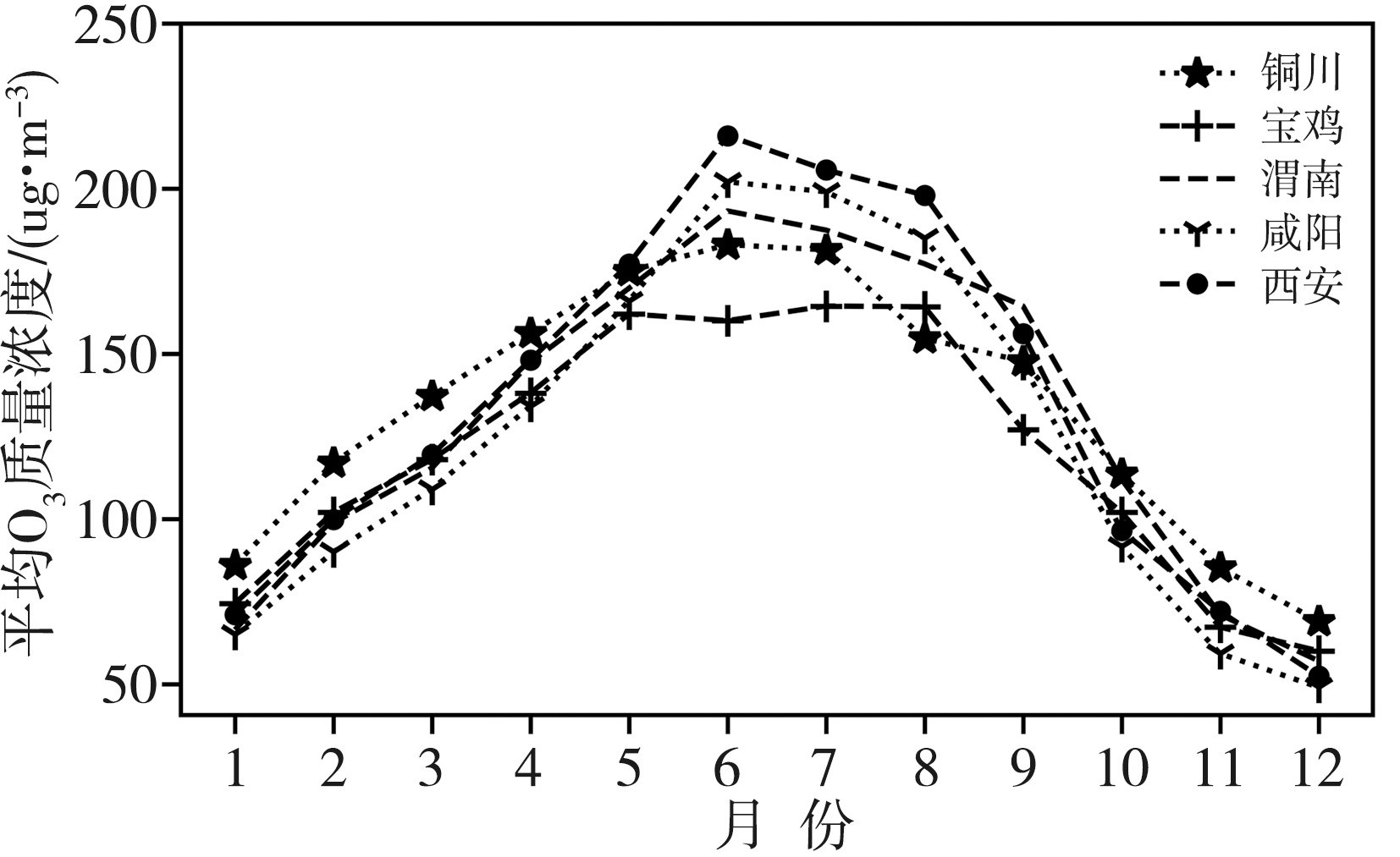
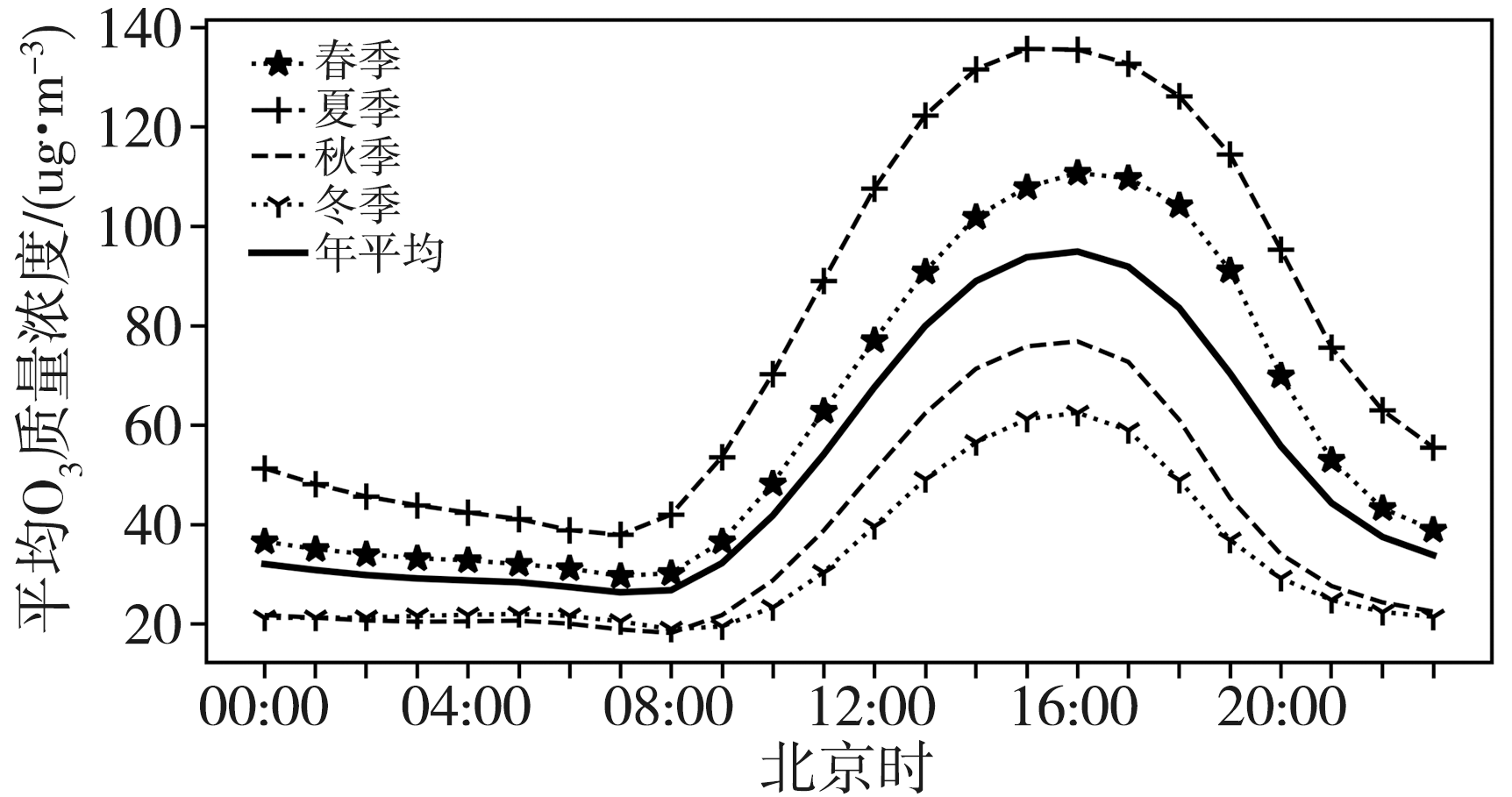
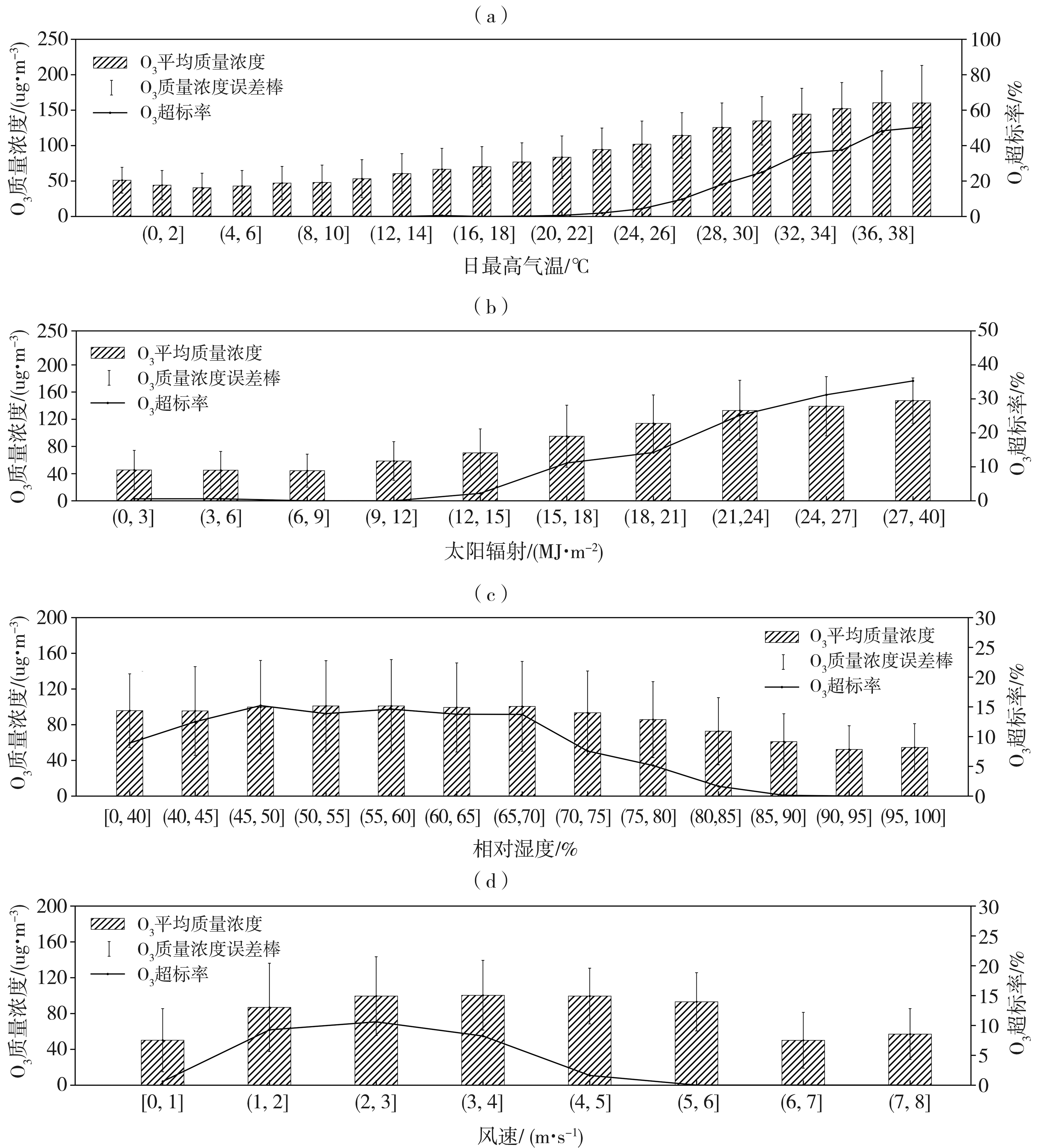
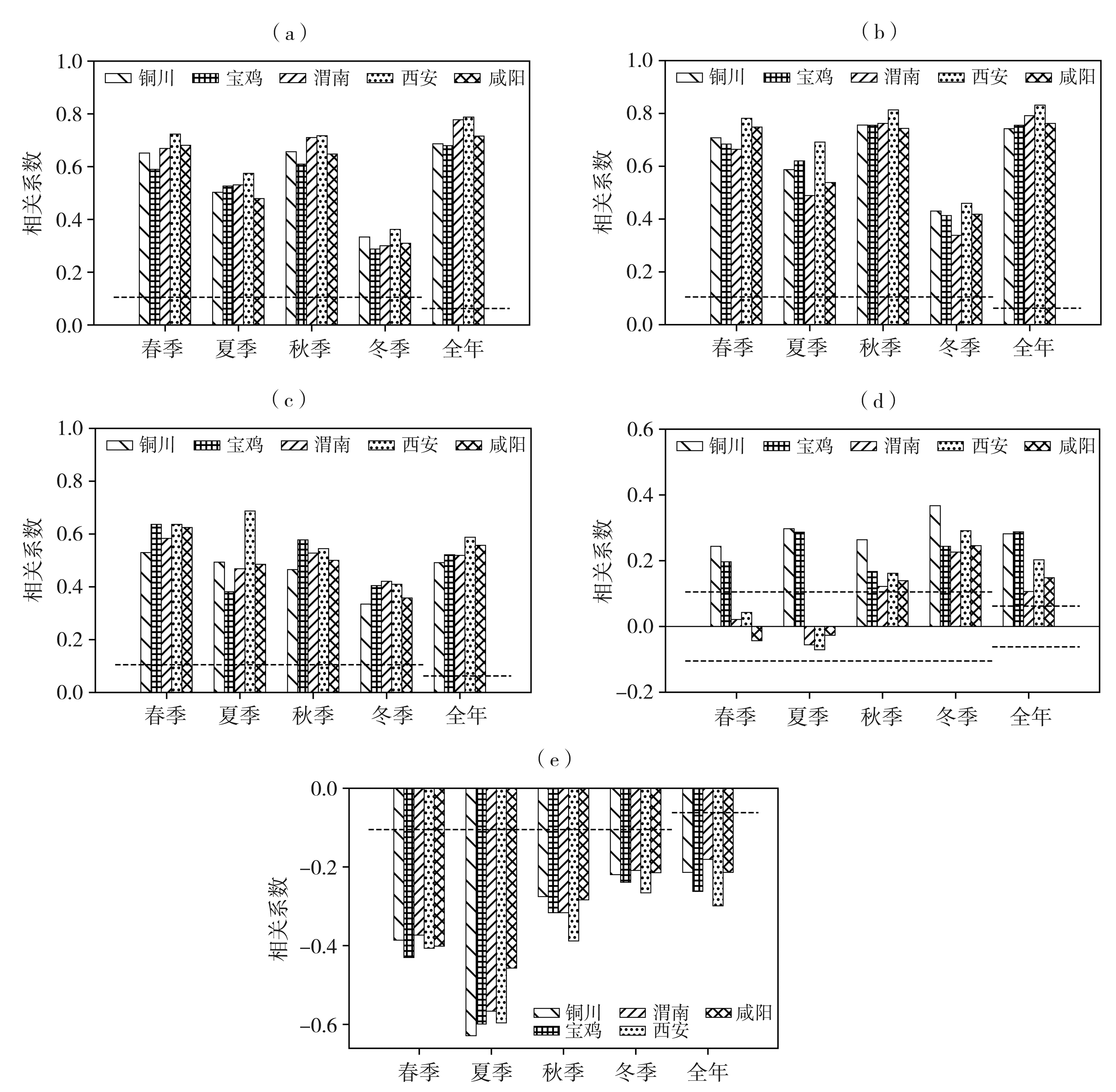
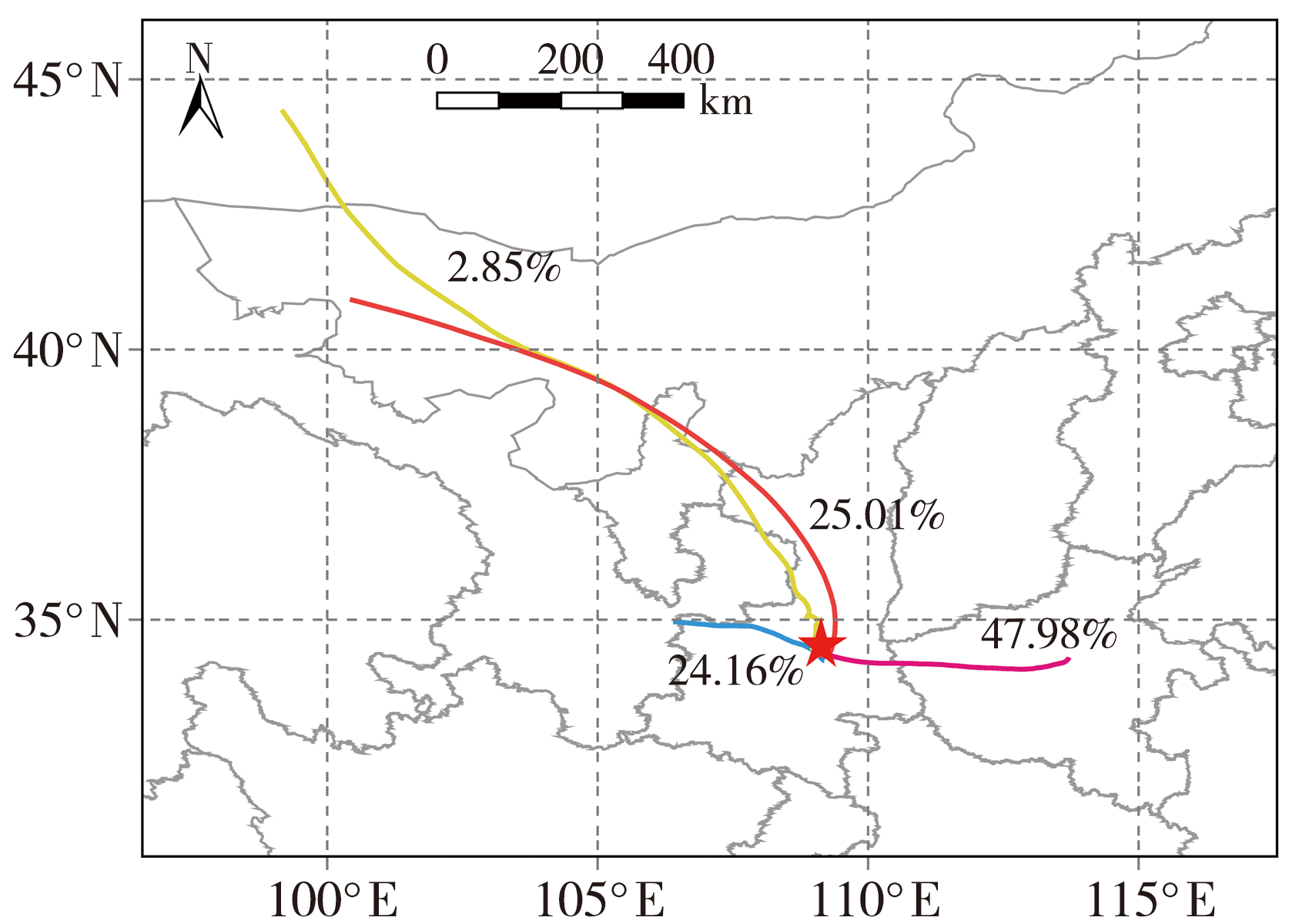
关中作为西北地区最重要的城市群落,近年来O3污染逐渐成为影响当地空气质量的突出问题,探究其变化特征和影响因素对该地区大气环境治理有重要意义。基于2014—2020年关中地区5地市国控环境监测站O3质量浓度逐小时观测资料和国家气象站地面气象要素逐小时观测资料,对比分析关中地区近地面O3污染特征及其气象影响因素。结果表明:(1)近7 a来,O3已逐渐取代PM10成为关中地区仅次于PM2.5的大气首要污染物,以O3为首要污染物的天数占比总体呈波动增加态势。(2)关中地区O3质量浓度呈典型的单峰型月际、日变化,夏季(6—8月)浓度较高,且浓度值自西安、咸阳、渭南、铜川、宝鸡依次减小;07:00—08:00为谷值,15:00—16:00为峰值。(3)当最高气温大于36 ℃、相对湿度为45%~70%、平均风速为2~3 m·s-1时,关中地区O3易超标,且最高气温越高,O3超标率越大;西安、铜川、咸阳、渭南O3污染的有利风向为东北风(NE),而宝鸡则为东南风(SE)或西北风(NW)。(4)源自河南中西部的偏东路径是影响西安夏季O3质量浓度最主要的传输路径,除本省相邻城市影响外,河南中西部、山西南部运城及湖北北部也是西安O3污染主要的潜在贡献源区。
中图分类号: