干旱气象 ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (1): 25-33.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-01-0025
FY-4A闪电成像仪在干旱区应用评估及与多源数据对比
宋琳1,2( ), 张国平3(
), 张国平3( ), 王曙东3, 万夫敬2, 孙豪4
), 王曙东3, 万夫敬2, 孙豪4
- 1.青岛市气象灾害防御技术中心,山东 青岛 266003
2.青岛市气象灾害防御工程技术研究中心,山东 青岛 266003
3.中国气象局公共气象服务中心,北京 100081
4.南京信息工程大学气象灾害教育部重点实验室,气候与环境变化国际合作联合实验室,气象灾害预报预警与评估协同创新中心,中国气象局气溶胶与云降水重点开放实验室,江苏 南京 210044
Evaluation of FY-4A lightning mapping imager applied in arid region and its comparison with multi-source data
SONG Lin1,2( ), ZHANG Guoping3(
), ZHANG Guoping3( ), WANG Shudong3, WAN Fujing2, SUN Hao4
), WANG Shudong3, WAN Fujing2, SUN Hao4
- 1. Qingdao Meteorological Disaster Protection Technology Center, Qingdao 266003,China
2. Qingdao Meteorological Disaster Prevention Engineering Technology Research Center, Qingdao 266003, China
3. Public Meteorological Service Center of China Meteorological Administration, Beijing 100081, China
4. Key Laboratory of Meteorological Disaster, Ministry of Education (KLME), Joint International Research Laboratory of Climate and Environment Change (ILCEC), Collaborative Innovation Center on Forecast and Evaluation of Meteorological Disaster (CIC-FEMD), Key Laboratory for Aerosol-Cloud-Precipitation of China Meteorological Administration, Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
摘要:
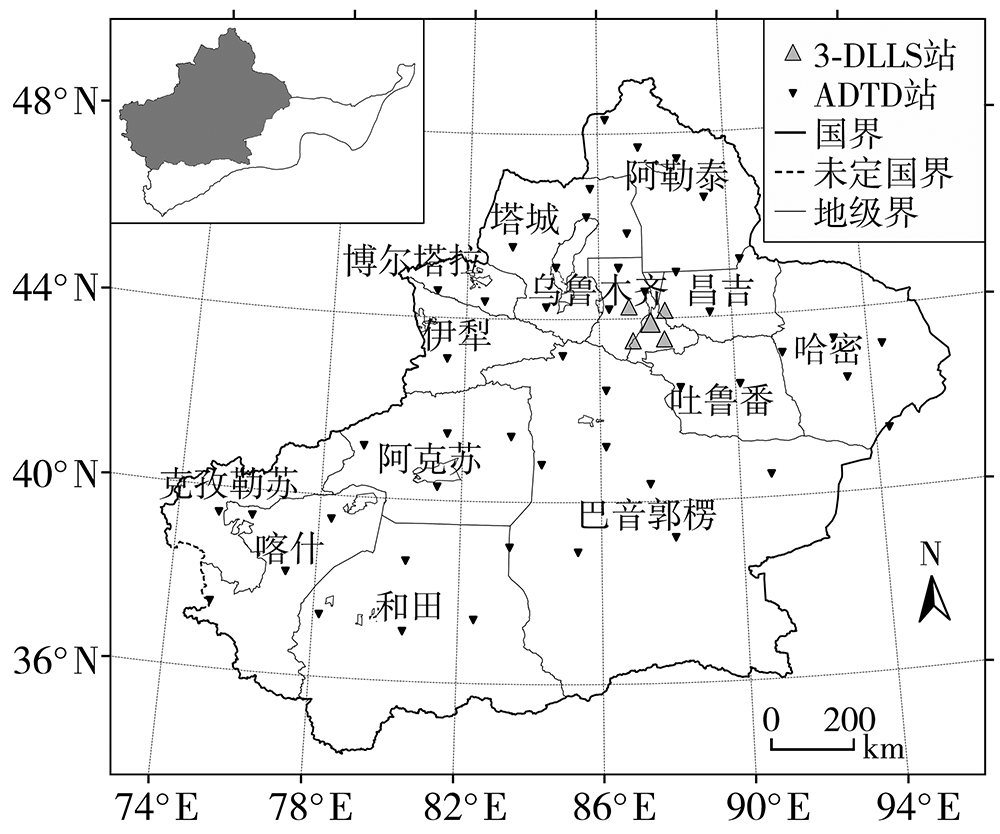
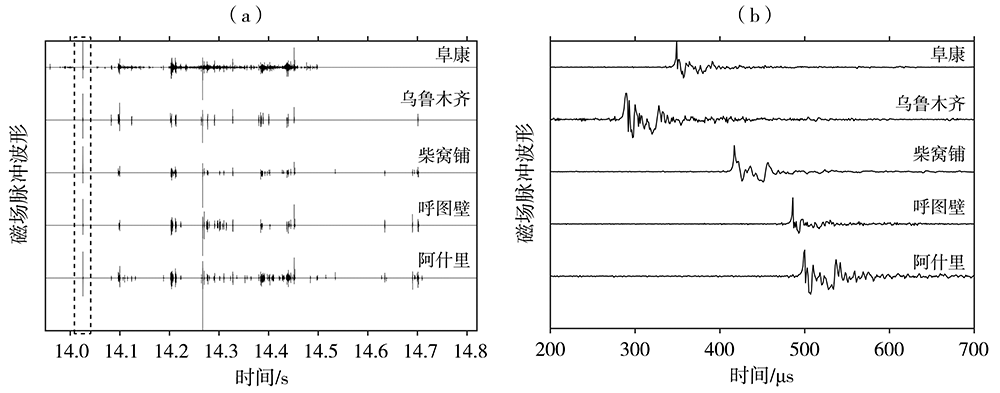
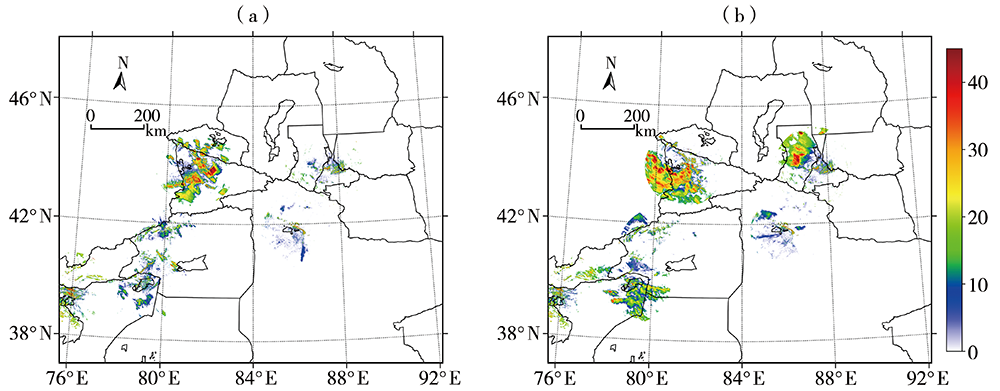
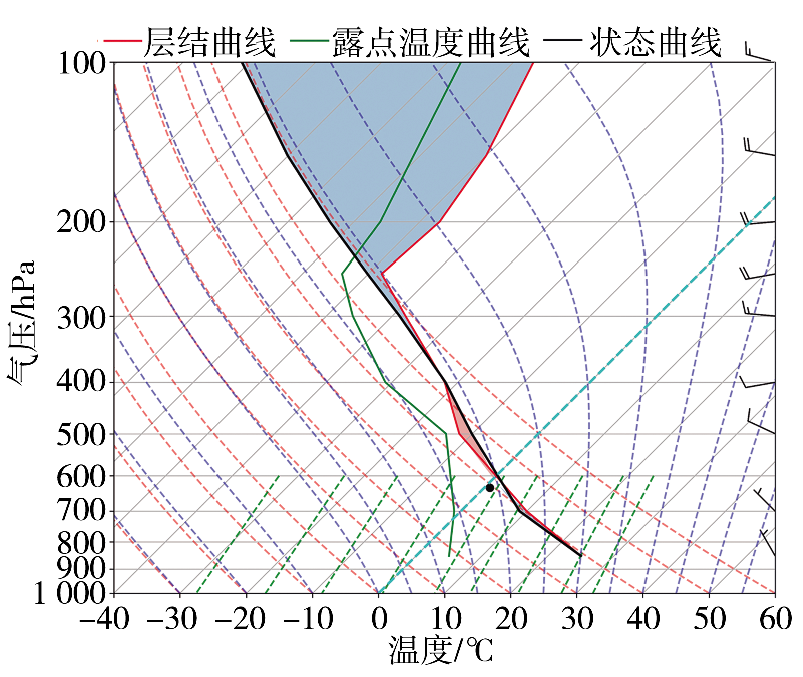
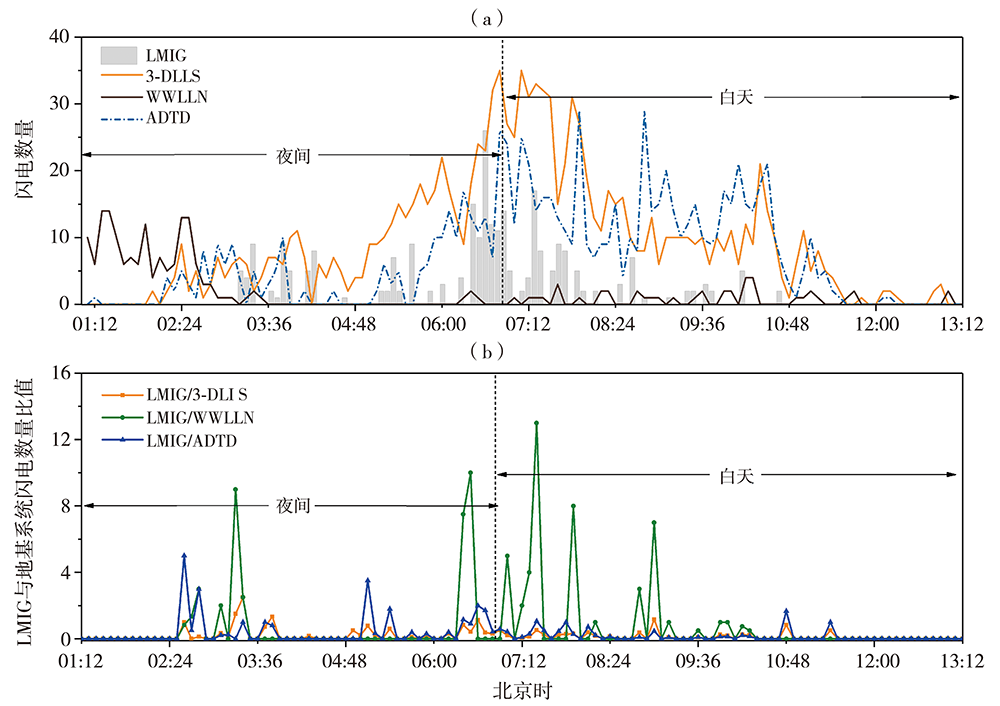
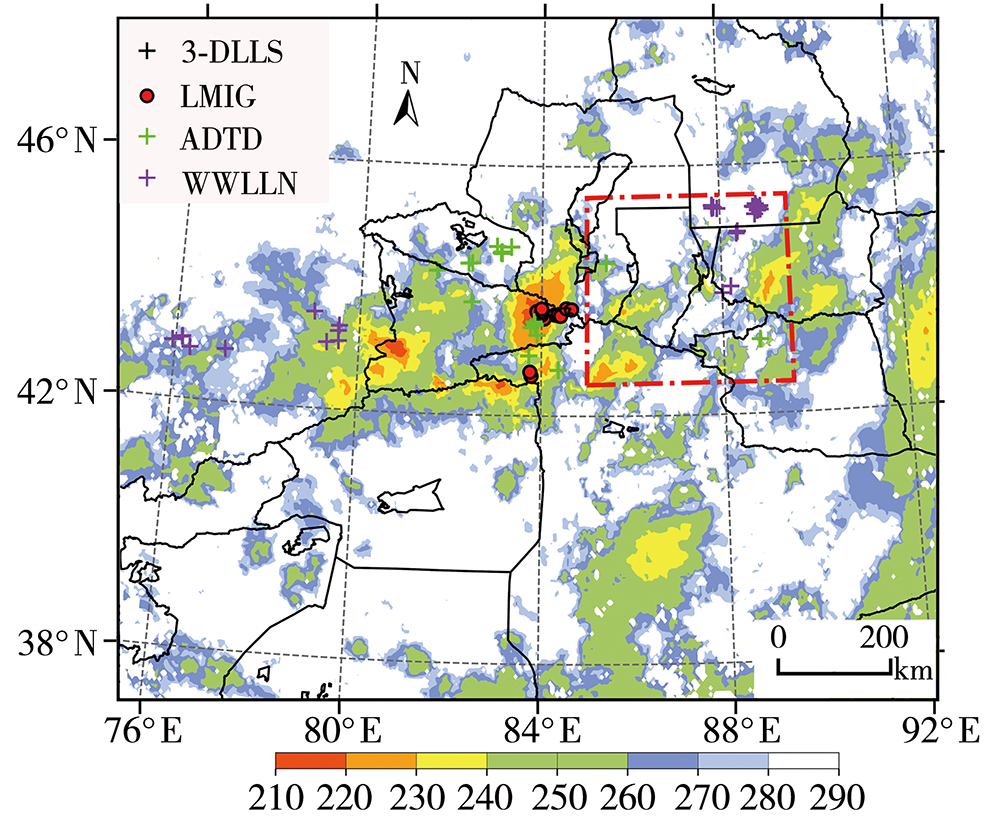
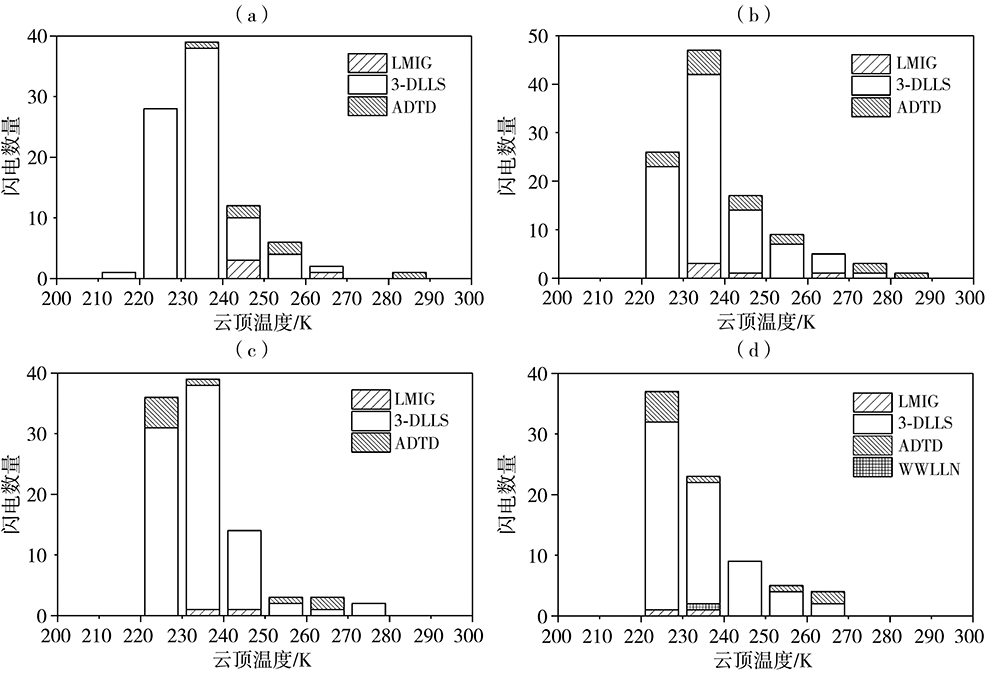
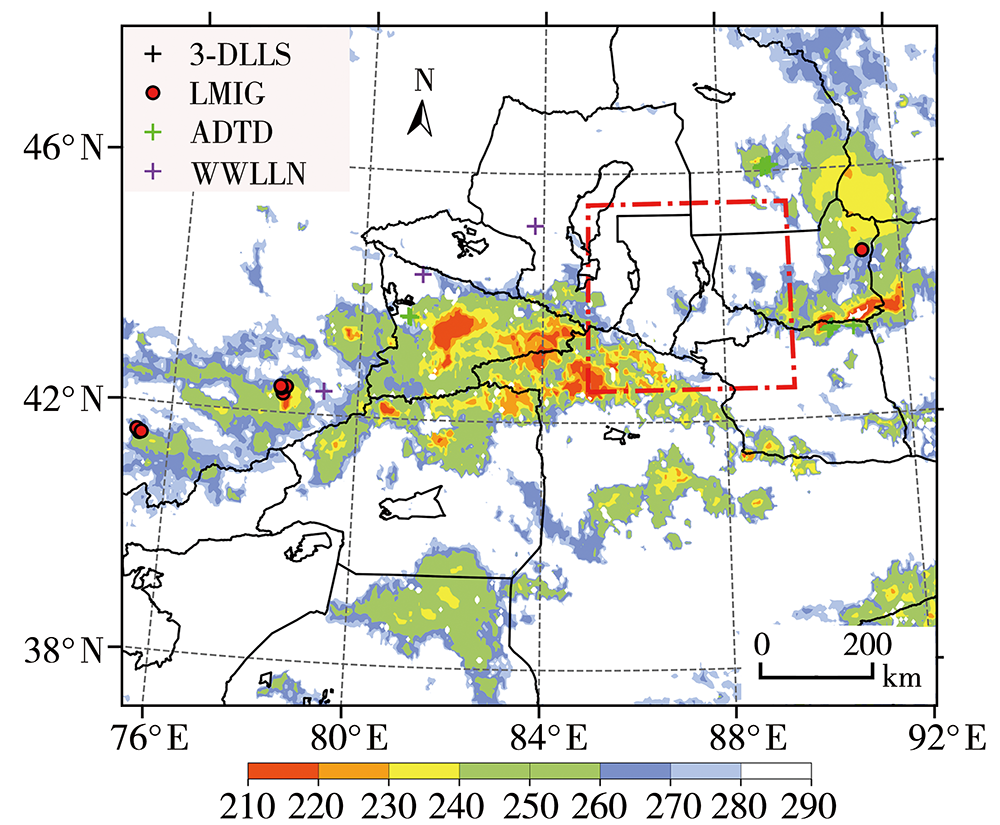
为加强多源闪电数据在干旱区的融合应用,利用新疆民航三维地基闪电探测系统(3-Dimension Lightning Location System,3-DLLS)、全球闪电定位网(World-Wide Lightning Location Network,WWLLN)和气象部门ADTD(Advanced Time of Arrival and Direction System)、FY-4A闪电成像仪(Lightning Mapping Imager,LMI)等多源闪电资料,针对新疆地区2019年11次典型雷暴过程,开展FY-4A LMI探测性能的初步评估,并结合FY-4A云顶温度(Cloud Top Temperature,CTT)资料,详细分析2019年7月21日强雷暴过程的闪电特征,探寻CTT与闪电活动的相关关系。结论如下:(1)FY-4A LMI闪电“组”(LMI Group,LMIG)数量约为3-DLLS的1/5、WWLLN的1.02倍、ADTD的1/3。白天,在太阳背景光影响下FY-4A LMI的探测效率有所下降,即使日出后雷暴系统有所加强,但LMIG数量并无增加趋势。(2)在2019年7月21日强雷暴过程中,3-DLLS探测的闪电时空分布与ADTD重合度较高,而WWLLN的闪电定位与前两者在时空上存在一定偏差,这主要是各系统的探测原理(WWLLN主要探测的是强地闪,ADTD主要监测地闪回击,而3-DLLS探测的是全闪)及测站布局和数量不同所致。(3)在强雷暴过程不同发展阶段,闪电发生区域的FY-4A CTT值差异较大,初始阶段、旺盛阶段和消散阶段闪电区域对应的CTT值分别为260~280 K、230~240 K和240~260 K。
中图分类号: