Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 531-539.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-04-0531
• Column on “Regional High Temperature” • Previous Articles Next Articles
Spatio-temporal characteristics and circulation types of the regional high temperature processes in Liaoning during 1961-2023
SU Xiaoxuan1,2,3,4( ), YAN Qi1,2(
), YAN Qi1,2( ), LU Jinglong1, YU Yue1, FANG Yihe2,3,4,5, SUN Xiaolei1
), LU Jinglong1, YU Yue1, FANG Yihe2,3,4,5, SUN Xiaolei1
- 1. Liaoning Provincial Meteorological Observatory, Shenyang 110166, China
2. Key Laboratory of Northeast Cold Vortex Research, Shenyang 110166, China
3. Panjin National Climate Observatory, Panjin 124000, Liaoning, China
4. Institute of Atmosphere Environment, China Meteorological Administration, Shenyang 110166, China
5. Liaoning Provincial Climate Center, Shenyang 110166, China
-
Received:2024-11-06Revised:2025-01-14Online:2025-08-31Published:2025-09-08
1961—2023年辽宁区域性高温过程时空特征及其环流分型
苏小琁1,2,3,4( ), 阎琦1,2(
), 阎琦1,2( ), 陆井龙1, 于跃1, 房一禾2,3,4,5, 孙晓蕾1
), 陆井龙1, 于跃1, 房一禾2,3,4,5, 孙晓蕾1
- 1.辽宁省气象台,辽宁 沈阳 110166
2.东北冷涡研究重点开放实验室,辽宁 沈阳 110166
3.盘锦国家气候观象台,辽宁 盘锦 124000
4.中国气象局沈阳大气环境研究所,辽宁 沈阳 110166
5.辽宁省气候中心,辽宁 沈阳 110166
-
通讯作者:阎琦 -
作者简介:苏小琁(1997—),女,辽宁鞍山人,工程师,主要从事气候变化研究。E-mail: 2596853173@qq.com。 -
基金资助:中国气象局创新发展专项(CXFZ2023J014);中国气象局沈阳大气环境研究所联合开放基金项目(2023SYIAEKFMS12);辽宁省气象局科学技术研究项目(ZD202416)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
SU Xiaoxuan, YAN Qi, LU Jinglong, YU Yue, FANG Yihe, SUN Xiaolei. Spatio-temporal characteristics and circulation types of the regional high temperature processes in Liaoning during 1961-2023[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(4): 531-539.
苏小琁, 阎琦, 陆井龙, 于跃, 房一禾, 孙晓蕾. 1961—2023年辽宁区域性高温过程时空特征及其环流分型[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(4): 531-539.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-04-0531
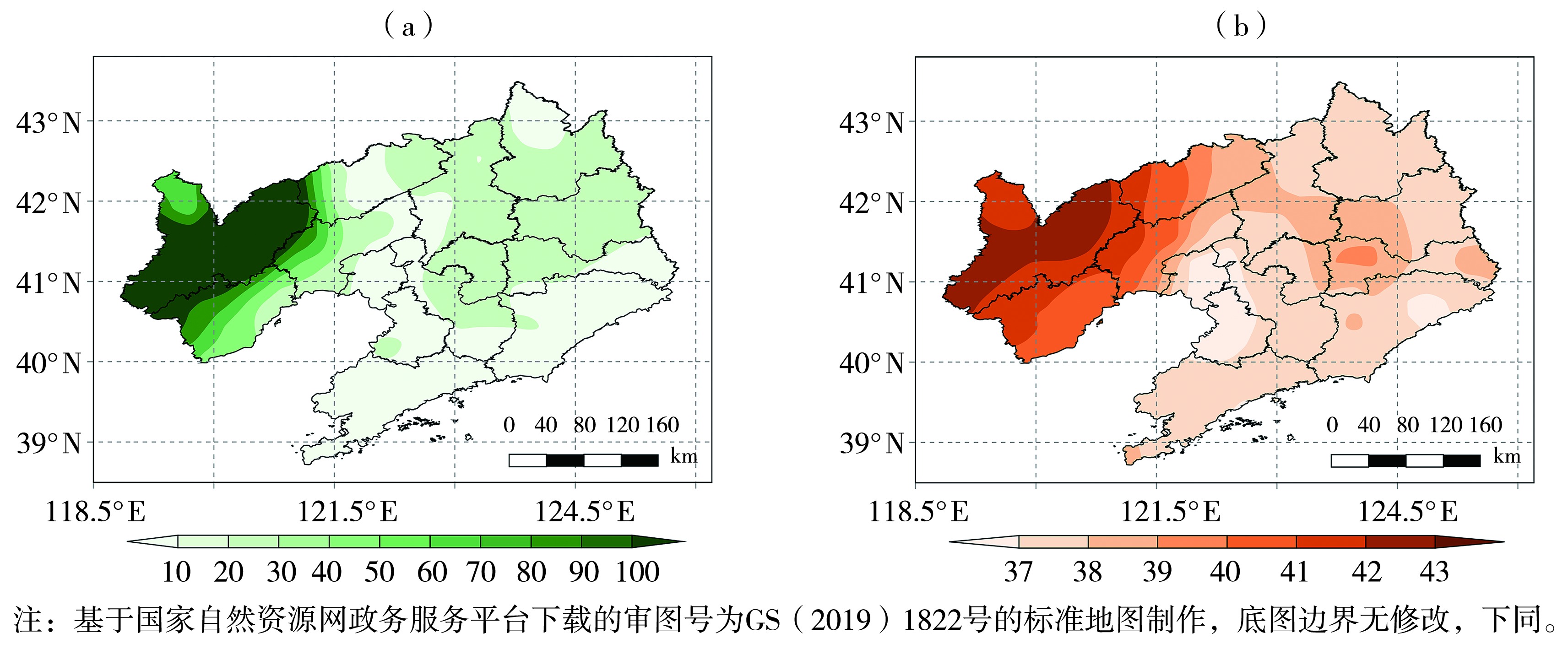
Fig.1 Spatial distribution of numbers of high temperature days (a, Unit: d) and extreme maximum temperature (b, Unit: ℃) in Liaoning from 1961 to 2023
| 时间 | 影响范围/站 | 强度/℃ | 持续时间/d | 综合强度 | 综合强度等级 | 排名 | 影响地区 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1961年7月2—4日 | 9 | 36.9 | 3 | 191.7 | 低 | 16 | 西部 |
| 1962年6月15—17日 | 12 | 36.1 | 3 | 216.6 | 低 | 14 | 西部、中部 |
| 1968年8月2—4日 | 9 | 35.9 | 3 | 186.5 | 低 | 18 | 西部 |
| 1972年7月10—14日 | 9 | 36.5 | 5 | 244.8 | 低 | 9 | 西部、中部 |
| 1979年5月27—29日 | 9 | 35.8 | 3 | 186.0 | 低 | 19 | 西部 |
| 1981年7月19—23日 | 7 | 36.6 | 5 | 216.5 | 低 | 15 | 西部 |
| 1994年6月16—18日 | 13 | 35.7 | 3 | 222.9 | 低 | 13 | 西部、北部 |
| 1997年6月13—15日 | 6 | 35.7 | 3 | 151.5 | 低 | 24 | 西部 |
| 1997年7月12—14日 | 14 | 36.4 | 3 | 235.9 | 低 | 11 | 西部、北部 |
| 2000年6月17—20日 | 19 | 36.0 | 4 | 313.8 | 中 | 6 | 全省大部 |
| 2000年7月5—10日 | 16 | 36.2 | 6 | 354.7 | 中 | 2 | 全省大部 |
| 2000年7月12—15日 | 15 | 38.3 | 4 | 296.7 | 中 | 7 | 西部、中部、北部 |
| 2001年6月2—5日 | 20 | 36.8 | 4 | 329.1 | 中 | 5 | 西部、中部、北部 |
| 2002年7月11—13日 | 9 | 36.7 | 3 | 190.7 | 低 | 17 | 西部 |
| 2004年6月9—11日 | 13 | 36.2 | 3 | 226.1 | 低 | 12 | 西部、中部 |
| 2009年8月11—16日 | 15 | 36.3 | 6 | 344.4 | 中 | 3 | 全省大部 |
| 2017年6月14—17日 | 21 | 37.0 | 4 | 339.1 | 中 | 4 | 全省大部 |
| 2018年7月22—24日 | 7 | 35.6 | 3 | 163.1 | 低 | 23 | 西部、北部 |
| 2018年7月28日—8月4日 | 30 | 36.5 | 8 | 565.5 | 高 | 1 | 全省大部 |
| 2018年8月9—11日 | 8 | 35.5 | 3 | 173.9 | 低 | 22 | 中部 |
| 2019年7月20—22日 | 14 | 36.6 | 3 | 237.2 | 低 | 10 | 西部、中部 |
| 2020年7月21—25日 | 12 | 36.2 | 5 | 280.4 | 中 | 8 | 西部、北部 |
| 2023年6月16—18日 | 8 | 36.8 | 3 | 180.3 | 低 | 20 | 西部 |
| 2023年6月30日—7月2日 | 8 | 36.8 | 3 | 180.3 | 低 | 20 | 西部 |
Tab.1 Statistics of regional high temperature processes in Liaoning from 1961 to 2023
| 时间 | 影响范围/站 | 强度/℃ | 持续时间/d | 综合强度 | 综合强度等级 | 排名 | 影响地区 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1961年7月2—4日 | 9 | 36.9 | 3 | 191.7 | 低 | 16 | 西部 |
| 1962年6月15—17日 | 12 | 36.1 | 3 | 216.6 | 低 | 14 | 西部、中部 |
| 1968年8月2—4日 | 9 | 35.9 | 3 | 186.5 | 低 | 18 | 西部 |
| 1972年7月10—14日 | 9 | 36.5 | 5 | 244.8 | 低 | 9 | 西部、中部 |
| 1979年5月27—29日 | 9 | 35.8 | 3 | 186.0 | 低 | 19 | 西部 |
| 1981年7月19—23日 | 7 | 36.6 | 5 | 216.5 | 低 | 15 | 西部 |
| 1994年6月16—18日 | 13 | 35.7 | 3 | 222.9 | 低 | 13 | 西部、北部 |
| 1997年6月13—15日 | 6 | 35.7 | 3 | 151.5 | 低 | 24 | 西部 |
| 1997年7月12—14日 | 14 | 36.4 | 3 | 235.9 | 低 | 11 | 西部、北部 |
| 2000年6月17—20日 | 19 | 36.0 | 4 | 313.8 | 中 | 6 | 全省大部 |
| 2000年7月5—10日 | 16 | 36.2 | 6 | 354.7 | 中 | 2 | 全省大部 |
| 2000年7月12—15日 | 15 | 38.3 | 4 | 296.7 | 中 | 7 | 西部、中部、北部 |
| 2001年6月2—5日 | 20 | 36.8 | 4 | 329.1 | 中 | 5 | 西部、中部、北部 |
| 2002年7月11—13日 | 9 | 36.7 | 3 | 190.7 | 低 | 17 | 西部 |
| 2004年6月9—11日 | 13 | 36.2 | 3 | 226.1 | 低 | 12 | 西部、中部 |
| 2009年8月11—16日 | 15 | 36.3 | 6 | 344.4 | 中 | 3 | 全省大部 |
| 2017年6月14—17日 | 21 | 37.0 | 4 | 339.1 | 中 | 4 | 全省大部 |
| 2018年7月22—24日 | 7 | 35.6 | 3 | 163.1 | 低 | 23 | 西部、北部 |
| 2018年7月28日—8月4日 | 30 | 36.5 | 8 | 565.5 | 高 | 1 | 全省大部 |
| 2018年8月9—11日 | 8 | 35.5 | 3 | 173.9 | 低 | 22 | 中部 |
| 2019年7月20—22日 | 14 | 36.6 | 3 | 237.2 | 低 | 10 | 西部、中部 |
| 2020年7月21—25日 | 12 | 36.2 | 5 | 280.4 | 中 | 8 | 西部、北部 |
| 2023年6月16—18日 | 8 | 36.8 | 3 | 180.3 | 低 | 20 | 西部 |
| 2023年6月30日—7月2日 | 8 | 36.8 | 3 | 180.3 | 低 | 20 | 西部 |
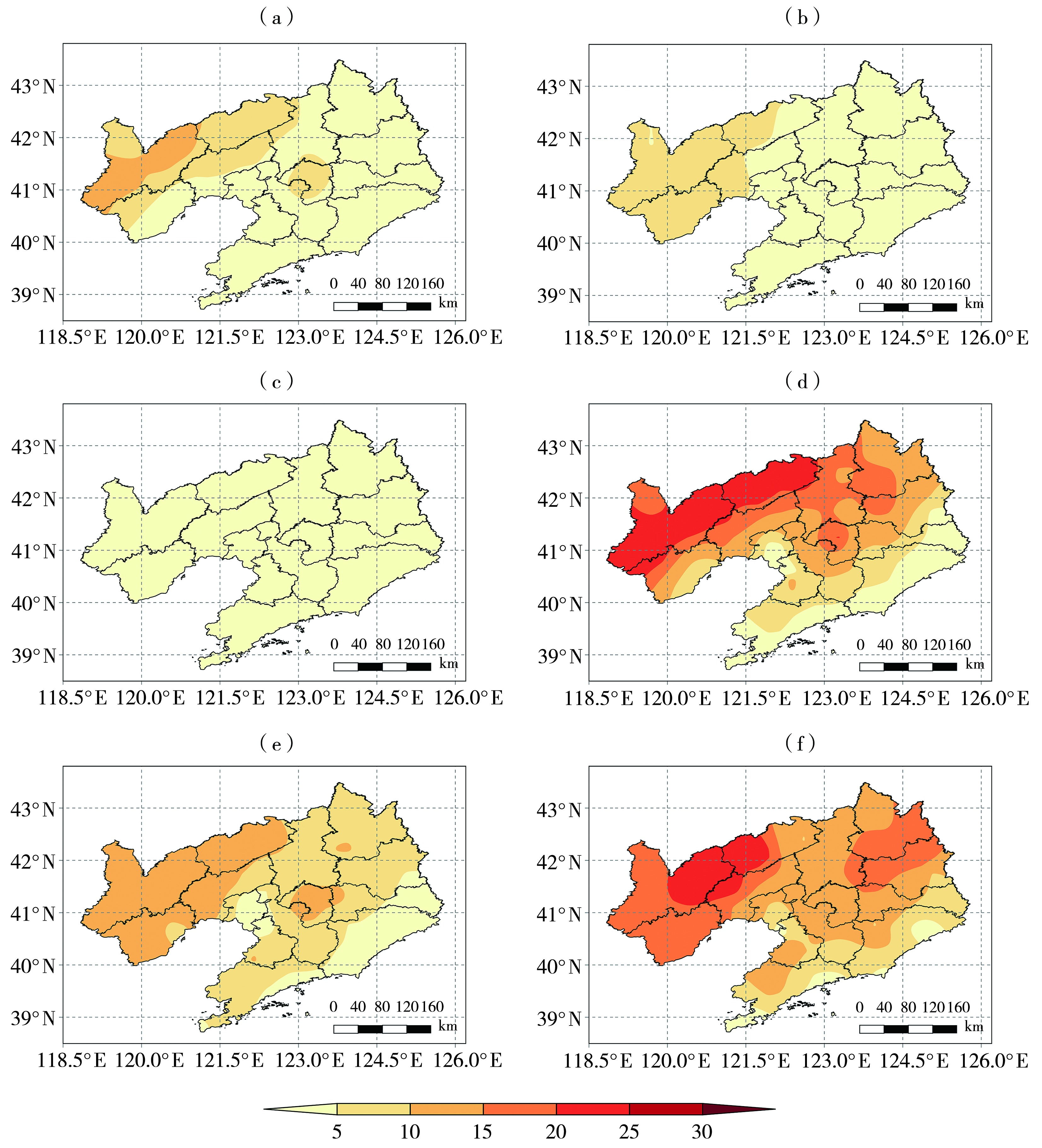
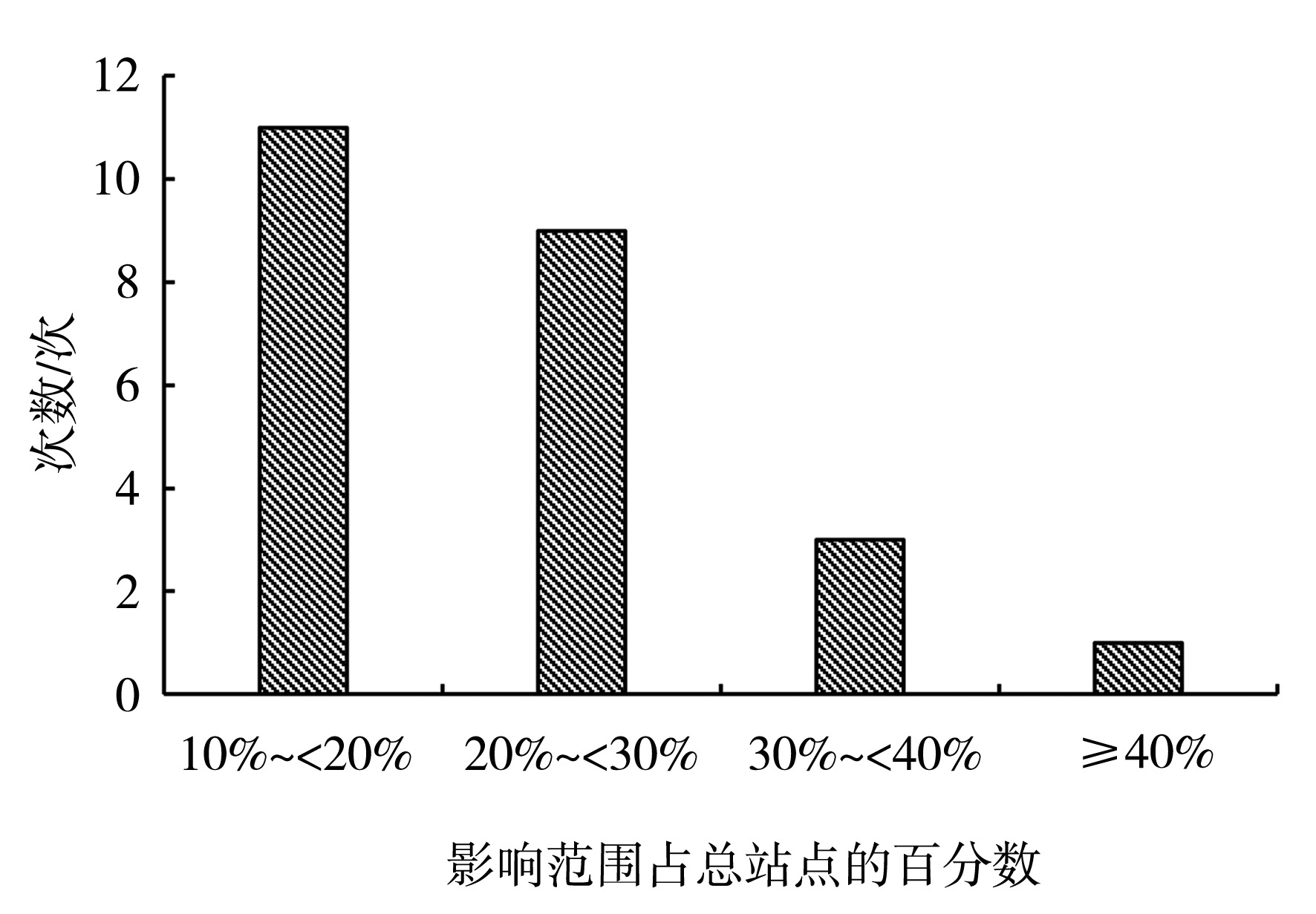
Fig.6 The percentage of regional high temperature processes occurring in Liaoning during 1961-1970 (a), 1971-1980 (b), 1981-1990 (c), 1991-2000 (d), 2001-2010 (e), and 2011-2020 (f) to the total number of high-temperature processes during 1961-2023(Unit: %)
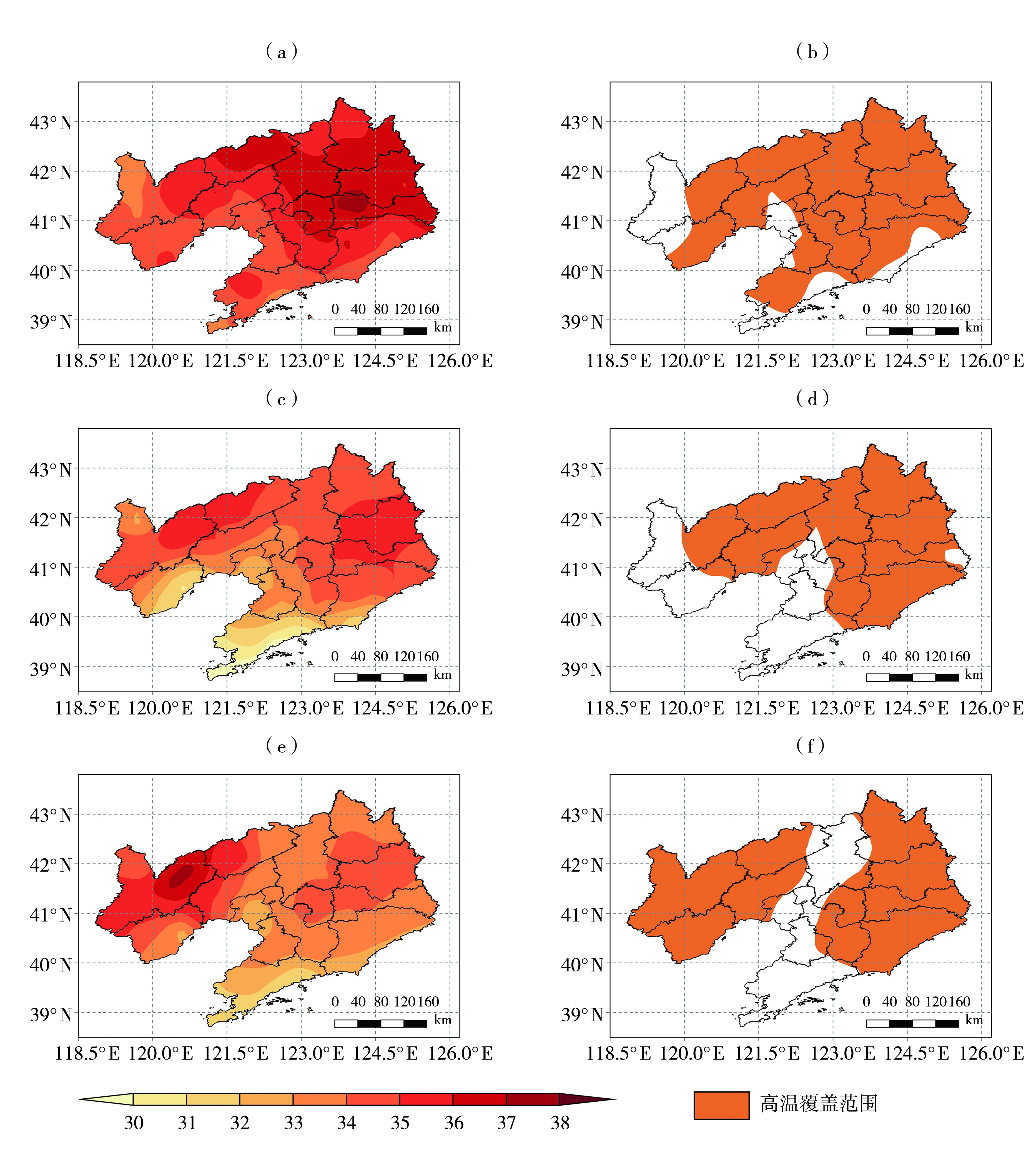
Fig.7 The daily average maximum temperatures (a, c, e, Unit: ℃) and the maximum coverage area of high temperature (b, d, f) during the process 1 (a, b), the process 2 (c, d), and the process 3 (e, f) in Liaoning
| 环流形势 | 5月 | 6月 | 7月 | 8月 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 暖高压脊型 | 1 | 8 | 10 | 2 |
| 纬向环流型 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| 合计 | 1 | 8 | 12 | 3 |
Tab.2
| 环流形势 | 5月 | 6月 | 7月 | 8月 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 暖高压脊型 | 1 | 8 | 10 | 2 |
| 纬向环流型 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| 合计 | 1 | 8 | 12 | 3 |
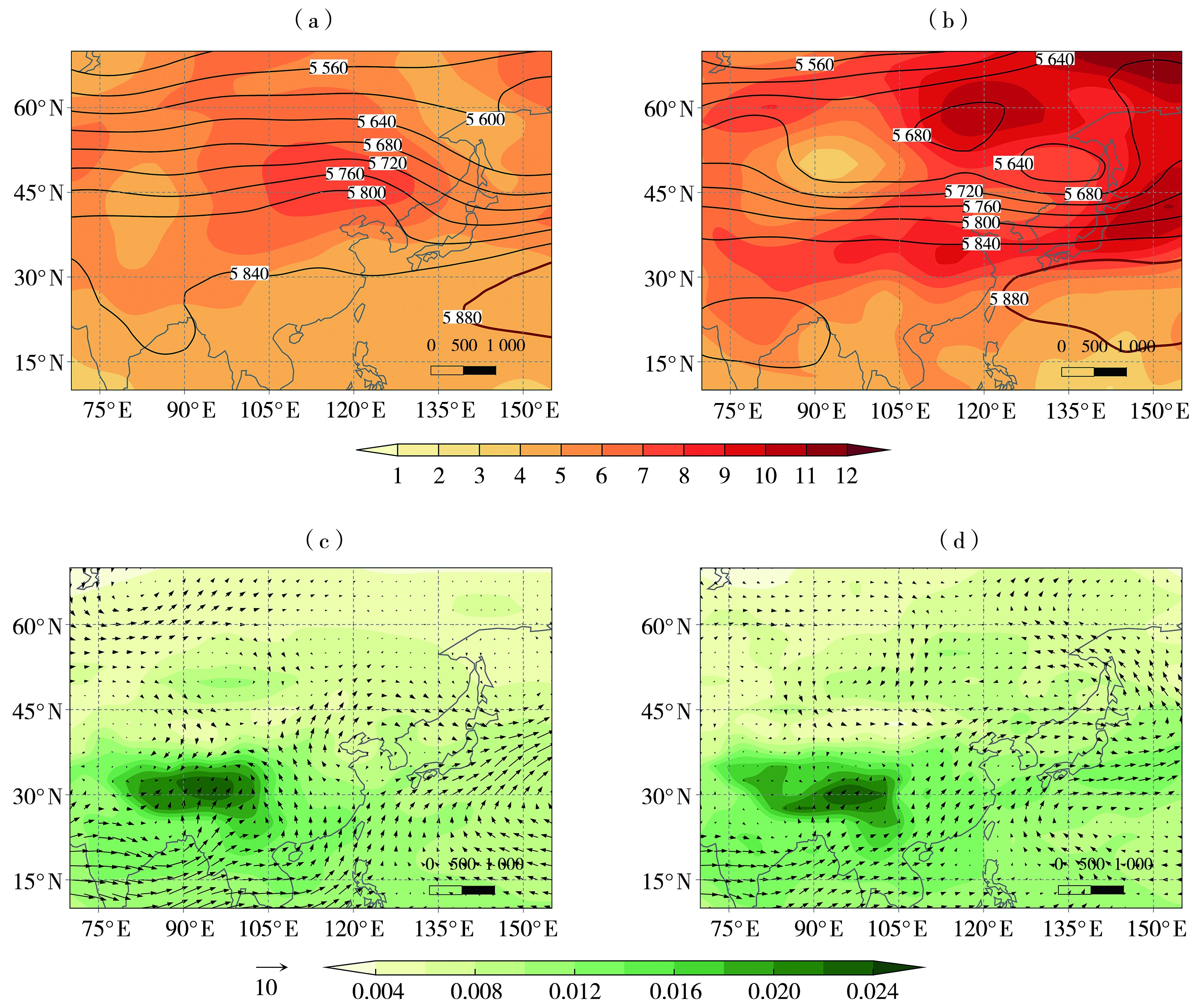
Fig.8 The 500 hPa geopotential height field (contours, Unit: gpm), temperature anomaly field (the color shaded, Unit: ℃) (a, b) and 850 hPa specific humidity (the color shaded, Unit: kg·kg-1) and wind field (arrow vectors, Unit: m·s-1) (c, d) during regional high temperature processes of the Liaoning under circulations of warm high pressure ridge pattern (a, c) and zonal circulation pattern (b, d)
| [1] | 邓斌, 肖长春, 姚魏, 等, 2019. 合肥市高温热浪对市民死亡及中暑的影响分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 13(4):124-127. |
| [2] | 段修荣, 罗伟, 王玲玲, 等, 2024. 2022年盛夏自贡市极端高温特征及气象服务技术总结[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 44(增刊1):104-113. |
| [3] |
范进进, 秦鹏程, 史瑞琴, 等, 2022. 气候变化背景下湖北省高温干旱复合灾害变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5):780-790.
DOI |
| [4] |
郝立生, 马宁, 何丽烨, 2022. 2022年长江中下游夏季异常干旱高温事件之环流异常特征[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5):721-732.
DOI |
| [5] | 胡颖, 殷娴, 陈剑桥, 等, 2022. 基于GIS的云南省1 km精细化暴雨灾害风险评估[J]. 气象科技, 50(5):742-750. |
| [6] | 焦敏, 李辑, 陈鹏狮, 等, 2019. 2018年夏季辽宁异常高温干旱的环流特征及成因[J]. 大气科学学报, 42(4):571-580. |
| [7] | 李庆祥, 黄嘉佑, 2011. 对我国极端高温事件阈值的探讨[J]. 应用气象学报, 22(2):138-144. |
| [8] |
李忆平, 张金玉, 岳平, 等, 2022. 2022年夏季长江流域重大干旱特征及其成因研究[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5):733-747.
DOI |
| [9] | 林爱兰, 谷德军, 彭冬冬, 等, 2021. 近60年我国东部区域性持续高温过程变化特征[J]. 应用气象学报, 32(3):302-314. |
| [10] |
林纾, 李红英, 黄鹏程, 等, 2022. 2022年夏季我国高温干旱特征及其环流形势分析[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5):748-763.
DOI |
| [11] |
毛炜峄, 陈鹏翔, 沈永平, 2016. 气候变暖背景下2015年夏季新疆极端高温过程及其影响[J]. 冰川冻土, 38(2):291-304.
DOI |
| [12] |
彭莉莉, 戴泽军, 罗伯良, 等, 2015. 2013年夏季西太平洋副高异常特征及其对湖南高温干旱的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 33(2):195-201.
DOI |
| [13] | 孙欣, 陈力强, 2016. 辽宁省高影响天气预报技术[M]. 沈阳: 辽宁科学技术出版社:114-116. |
| [14] |
孙昭萱, 张强, 孙蕊, 等, 2022. 2022年西南地区极端高温干旱特征及其主要影响[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5):764-770.
DOI |
| [15] | 唐恬, 金荣花, 彭相瑜, 等, 2014. 2013年夏季我国南方区域性高温天气的极端性分析[J]. 气象, 40(10):1207-1 215. |
| [16] | 王国复, 叶殿秀, 张颖娴, 等, 2018. 2017年我国区域性高温过程特征及异常大气环流成因分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 14(4):341-349. |
| [17] | 王荣, 王遵娅, 高荣, 等, 2023. 1961—2020年中国区域性高温过程的气候特征及变化趋势[J]. 地球物理学报, 66(2):494-504. |
| [18] |
王胜, 田红, 吴蓉, 等, 2022. 2022年安徽省区域性高温和干旱过程综合评估[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5):771-779.
DOI |
| [19] | 王文, 许金萍, 蔡晓军, 等, 2017. 2013年夏季长江中下游地区高温干旱的大气环流特征及成因分析[J]. 高原气象, 36(6):1595-1 607. |
| [20] |
王艳姣, 任福民, 闫峰, 2013. 中国区域持续性高温事件时空变化特征研究[J]. 地理科学, 33(3):314-321.
DOI |
| [21] | 肖风劲, 赵东, 尹红, 等, 2009. 东北干旱严重南方高温持续(2009年8月)[J]. 气象, 35(11):156-157. |
| [22] | 邢佩, 杨若子, 杜吴鹏, 等, 2020. 1961—2017年华北地区高温日数及高温热浪时空变化特征[J]. 地理科学, 40(8):1365-1 376. |
| [23] |
熊亚军, 于平, 扈海波, 2013. 国内高温气候变化事实及其灾害特征研究进展[J]. 干旱气象, 31(1):194-198.
DOI |
| [24] | 徐志强, 2009. 辽宁干旱严重部分地区农作物绝收[N/OL]. 国际在线,(2009-08-14)[2025-01-14]. https://news.sina.cn/sa/2009-08-14/detail-ikknscsk5082990.d.html. |
| [25] |
许婷婷, 杨霞, 周鸿奎, 2022. 1981—2019年新疆区域性高温天气过程时空特征及其环流分型[J]. 干旱气象, 40(2):212-221.
DOI |
| [26] | 杨萍, 封国林, 刘伟东, 等, 2010. 空间点过程理论在极端气候事件中的应用研究[J]. 应用气象学报, 21(3):352-359. |
| [27] | 杨毅, 2018. 持续高温致大连海参大面积死亡养殖户损失惨重[N/OL]. 中国新闻网,(2018-08-06)[2025-01-14]. https://www.chinanews.com.cn/sh/2018/08-06/8591201.shtml. |
| [28] | 叶殿秀, 尹继福, 陈正洪, 等, 2013. 1961—2010年我国夏季高温热浪的时空变化特征[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 9(1):15-20. |
| [29] | 叶培龙, 刘新伟, 赵文婧, 等, 2019. 2016年8月甘肃省持续性高温过程及其异常大气环流特征[J]. 高原气象, 38(6):1283-1 292. |
| [30] | 张君枝, 梁雅楠, 王冀, 等, 2023. 气候变化背景下京津冀极端高温事件变化特征研究[J]. 灾害学, 38(4):80-88. |
| [31] | 张夕迪, 孙军, 2018. 2018年7月大气环流和天气分析[J]. 气象, 44(10):1370-1 376. |
| [32] | 张迎新, 张守保, 2010. 2009年华北平原大范围持续性高温过程的成因分析[J]. 气象, 36(10):8-13. |
| [33] | 赵梓淇, 李丽光, 王宏博, 等, 2014. 1961—2010年辽宁高温日数和热浪特征[J]. 气象与环境学报, 30(5):57-61. |
| [34] | POUMADÈRE M, MAYS C, LE MER S, et al, 2005. The 2003 heat wave in France: Dangerous climate change here and now[J]. Risk Analysis, 25(6): 1 483-1 494. |
| [35] |
TOBÍAS A, DE OLALLA P G, LINARES C, et al, 2010. Short-term effects of extreme hot summer temperatures on total daily mortality in Barcelona, Spain[J]. International Journal of Biometeorology, 54(2): 115-117.
DOI PMID |
| [36] | WANG Y J, REN F M, ZHANG X B, 2014. Spatial and temporal variations of regional high temperature events in China[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 34(10): 3 054-3 065. |
| [1] | YAN Ruotong, DENG Fengdong, XU Dongbei, MAI Zhening. Analysis of the occurrence rules of the moving-out vortex over the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau and the differences in the development mechanism of typical cases in warm seasons [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(6): 910-921. |
| [2] | YI Xue, YANG Sen, LIU Mingyan, LI Tao, HOU Yiling, CUI Yan. Spatio-temporal Variation Characteristics of Vegetation Coverage and Its Response to Climate Change in Liaoning Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(2): 252-261. |
| [3] | SUI Yuxiu, YANG Jingtai, LI Yuqian, WANG Lei, ZHOU Meie, CAO Bo. Climatic Characteristics of Hails in Dalian Region of Liaoning Province from 1971 to 2018 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(2): 249-255. |
| [4] | ZHENG Meiqin, CHENG Yue, ZHANG Minkai, ZHOU Xiujun, LU Guirong. Climatic Characteristics of Typhoon Rainstorms Influencing Rizhao of Shandong Province During 1961-2015 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(4): 598-603. |
| [5] | KANG Guihong1, HAN Yongqing1, SUN Xingchi1, GE Xiang2. Climatic Characteristics and Circulation Situation of the First Rainstorm in Shandong Province During 1985-2014 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(6): 955-962. |
| [6] | ZHANG Linmei1,2, MA Yu3, TIAN Zhongfeng2. Climatic Characteristics of Extreme Precipitation Events in Summer and Their Circulation Patterns in Aletai of Xinjiang During 1961-2010 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(6): 970-978. |
| [7] | SHAO Jian1,2, PEI Xiaorong3, LIU Juan2,SHI Honglei2, WANG Shigong4, HU Wendong1. Temporal and Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Rainstorms in Ningxia During 1961-2013 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(4): 595-601. |
| [8] | DAI Zejun,LI Yizhi,LIU Zhixiong,PENG Lili,ZHANG Chao. Climatic Characteristics of Summer High Temperature in Hu nan Province in Last 53 Years [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2014, 32(5): 706-711. |
| [9] | ZHOU Heling,ZHANG Shaohui,YANG Yan. Climatic Characteristics of Thunderstorm Gale in Langfang of Hebei Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2014, 32(4): 588-592. |
| [10] | LI Haihua,LIU Dafeng. Climatic Characteristics of Winter Low - temperature Days in Altay Region of Xinjiang [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2013, 31(3): 505-510. |
| [11] | WANG Jianbing,AN Huayin,WANG Zhigui,WANG Chenfu,WANG Yaxi,CHEN Yang. The Climatic Characteristics of Continuous Autumn Rain in Gannan Plateau During 1981 - 2010 and the Main Circulation [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2013, 31(1): 70-77. |
| [12] | . Analysis of Causes for Severe Drought Event in July in Ningxia [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2012, 30(3): 332-338. |
| [13] | WANG Xuejun. Climatic Characteristics and Formation Mechanism of Fog in Jiuhua Mountain [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2012, 30(3): 374-379. |
| [14] | . Climatic Characteristics of Cold Wave Weather and Warming Winter in Hebei Province During 1962 - 2008 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2012, 30(2): 244-248. |
| [15] | JIN Li-Mei, SHI Jun. Climatic Character istics of Thunderstorm in Shangha i [J]. J4, 2010, 28(1): 54-58. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||