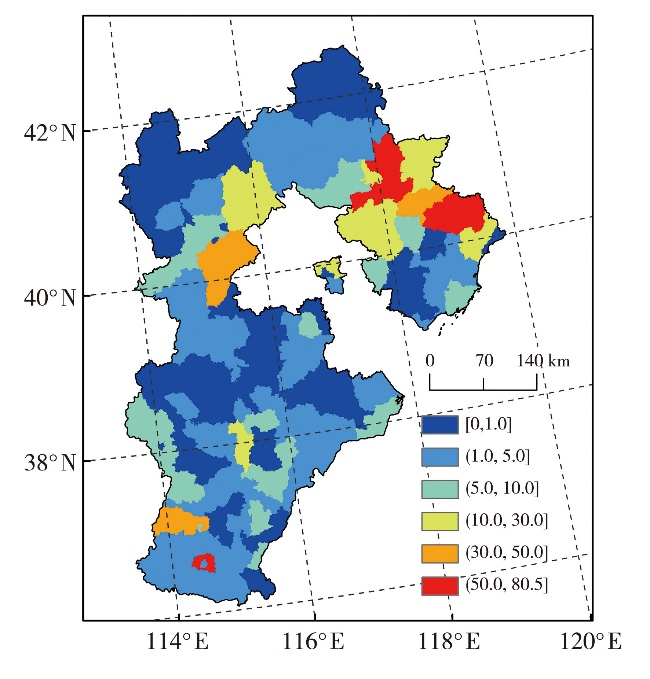
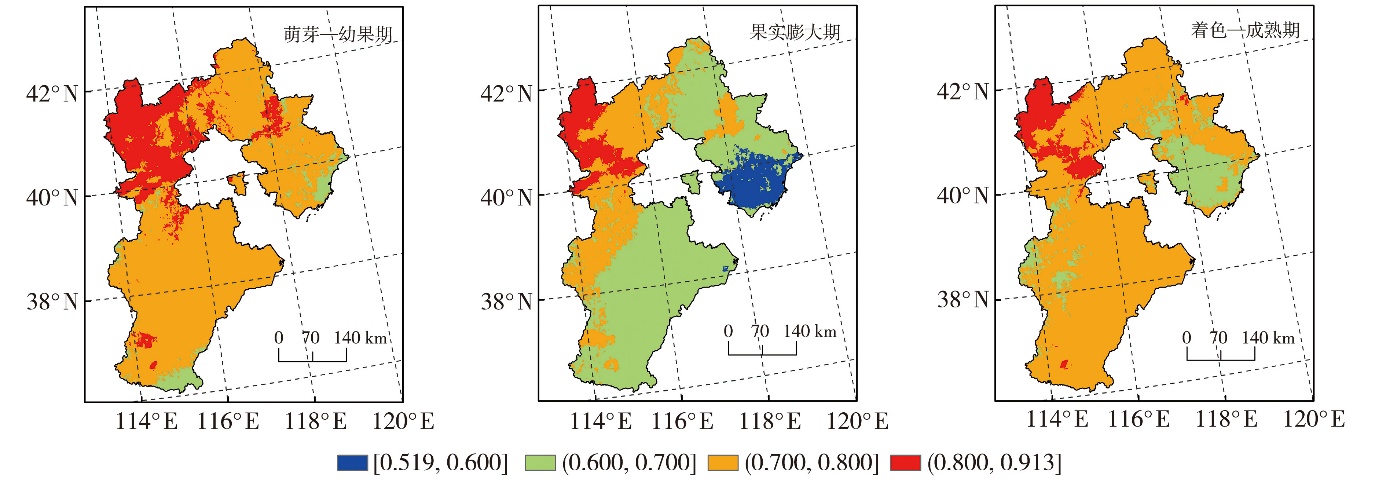
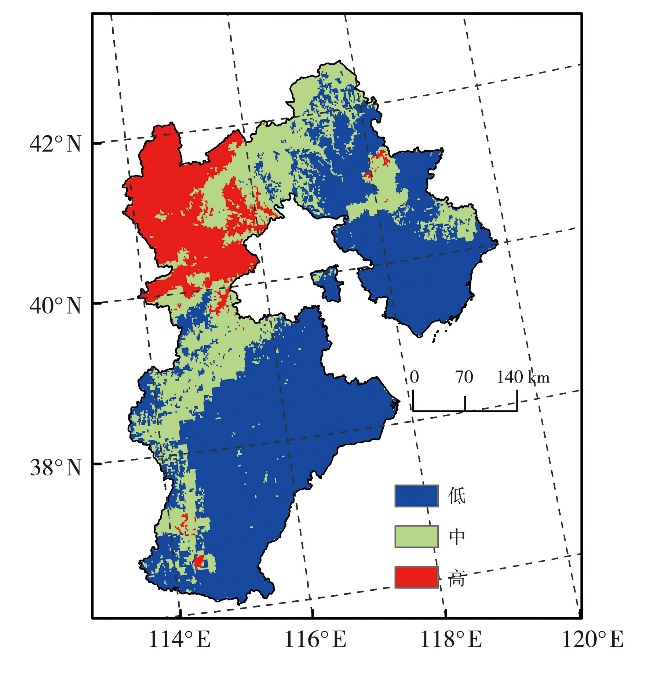
Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (3): 375-384.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-03-0375
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Risk assessment of drought disasters on apple cultivation in Hebei Province
NIE Zhenling1( ), WU Guoming2,3(
), WU Guoming2,3( ), DONG Hangyu2,3
), DONG Hangyu2,3
- 1. Handan Meteorological Bureau of Hebei Province,Handan 056001, Hebei, China
2. Hebei Provincial Institute of Meteorological Sciences, Shijiazhuang 050021, China
3. Key Laboratory of Meteorology and Ecological Environment of Hebei Province, Shijiazhuang 050021,China
-
Received:2025-02-07Revised:2025-04-09Online:2025-06-30Published:2025-07-12
干旱灾害对河北省苹果种植的风险评估
- 1.河北省邯郸市气象局,河北 邯郸 056001
2.河北省气象科学研究所,河北 石家庄 050021
3.河北省气象与生态环境重点实验室,河北 石家庄 050021
-
通讯作者:吴国明 -
作者简介:聂振岭(1970—),男,高级工程师,主要从事综合气象观测。E-mail: 176585736@qq.com。 -
基金资助:河北省气象局订单式项目(22kyd06)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
NIE Zhenling, WU Guoming, DONG Hangyu. Risk assessment of drought disasters on apple cultivation in Hebei Province[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(3): 375-384.
聂振岭, 吴国明, 董航宇. 干旱灾害对河北省苹果种植的风险评估[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(3): 375-384.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-03-0375
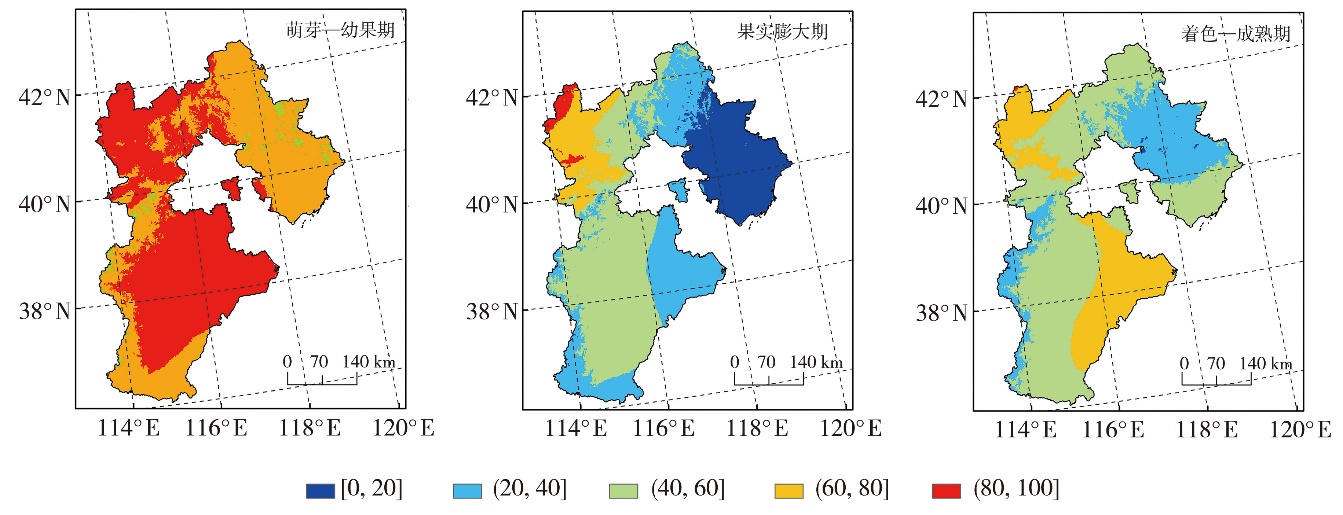
| 干旱等级 | 萌芽—幼果期 | 果实膨大期 | 着色—成熟期 | 全生育期 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 无旱 | WPLR≥-0.45 | WPLR≥-0.18 | WPLR≥-0.47 | WPLR≥-0.29 |
| 轻旱 | -0.56≤WPLR<-0.45 | -0.32≤WPLR<-0.18 | -0.58≤WPLR<-0.47 | -0.40≤WPLR<-0.29 |
| 中旱 | -0.66≤WPLR<-0.56 | -0.48≤WPLR<-0.32 | -0.70≤WPLR<-0.58 | -0.51≤WPLR<-0.40 |
| 重旱 | -0.78≤WPLR<-0.66 | -0.73≤WPLR<-0.48 | -0.85≤WPLR<-0.70 | -0.74≤WPLR<-0.51 |
| 特旱 | WPLR<-0.78 | WPLR<-0.73 | WPLR<-0.85 | WPLR<-0.74 |
Tab.1 Division of drought grade based on water profit and loss ratio
| 干旱等级 | 萌芽—幼果期 | 果实膨大期 | 着色—成熟期 | 全生育期 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 无旱 | WPLR≥-0.45 | WPLR≥-0.18 | WPLR≥-0.47 | WPLR≥-0.29 |
| 轻旱 | -0.56≤WPLR<-0.45 | -0.32≤WPLR<-0.18 | -0.58≤WPLR<-0.47 | -0.40≤WPLR<-0.29 |
| 中旱 | -0.66≤WPLR<-0.56 | -0.48≤WPLR<-0.32 | -0.70≤WPLR<-0.58 | -0.51≤WPLR<-0.40 |
| 重旱 | -0.78≤WPLR<-0.66 | -0.73≤WPLR<-0.48 | -0.85≤WPLR<-0.70 | -0.74≤WPLR<-0.51 |
| 特旱 | WPLR<-0.78 | WPLR<-0.73 | WPLR<-0.85 | WPLR<-0.74 |
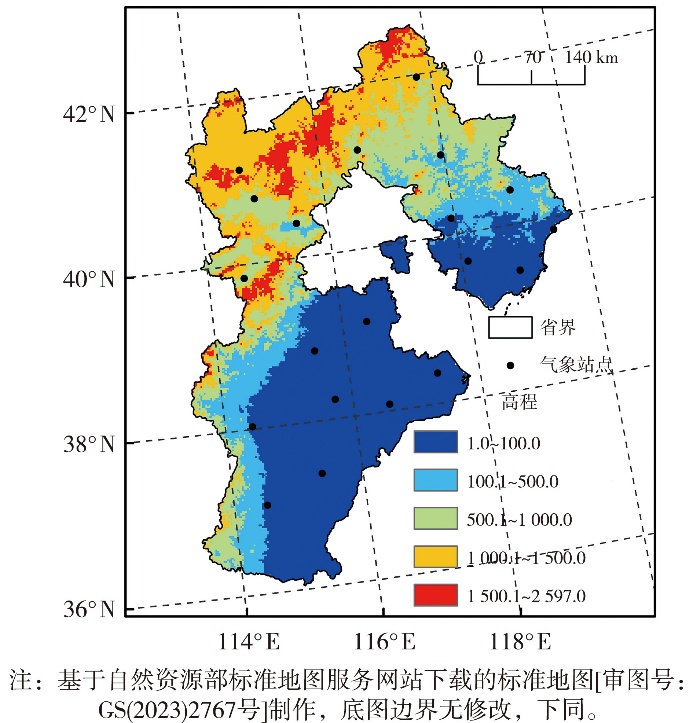
| 高程/m | 高程标准差 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1级(≤1 m) | 2级(>1~<10 m) | 3级(≥10 m) | |
| 1级(≤100) | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.7 |
| 2级(>100~300) | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.6 |
| 3级(>300~700) | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.5 |
| 4级(>700) | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.4 |
Tab.2 Different combination values of elevation and elevation standard deviation
| 高程/m | 高程标准差 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1级(≤1 m) | 2级(>1~<10 m) | 3级(≥10 m) | |
| 1级(≤100) | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.7 |
| 2级(>100~300) | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.6 |
| 3级(>300~700) | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.5 |
| 4级(>700) | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.4 |
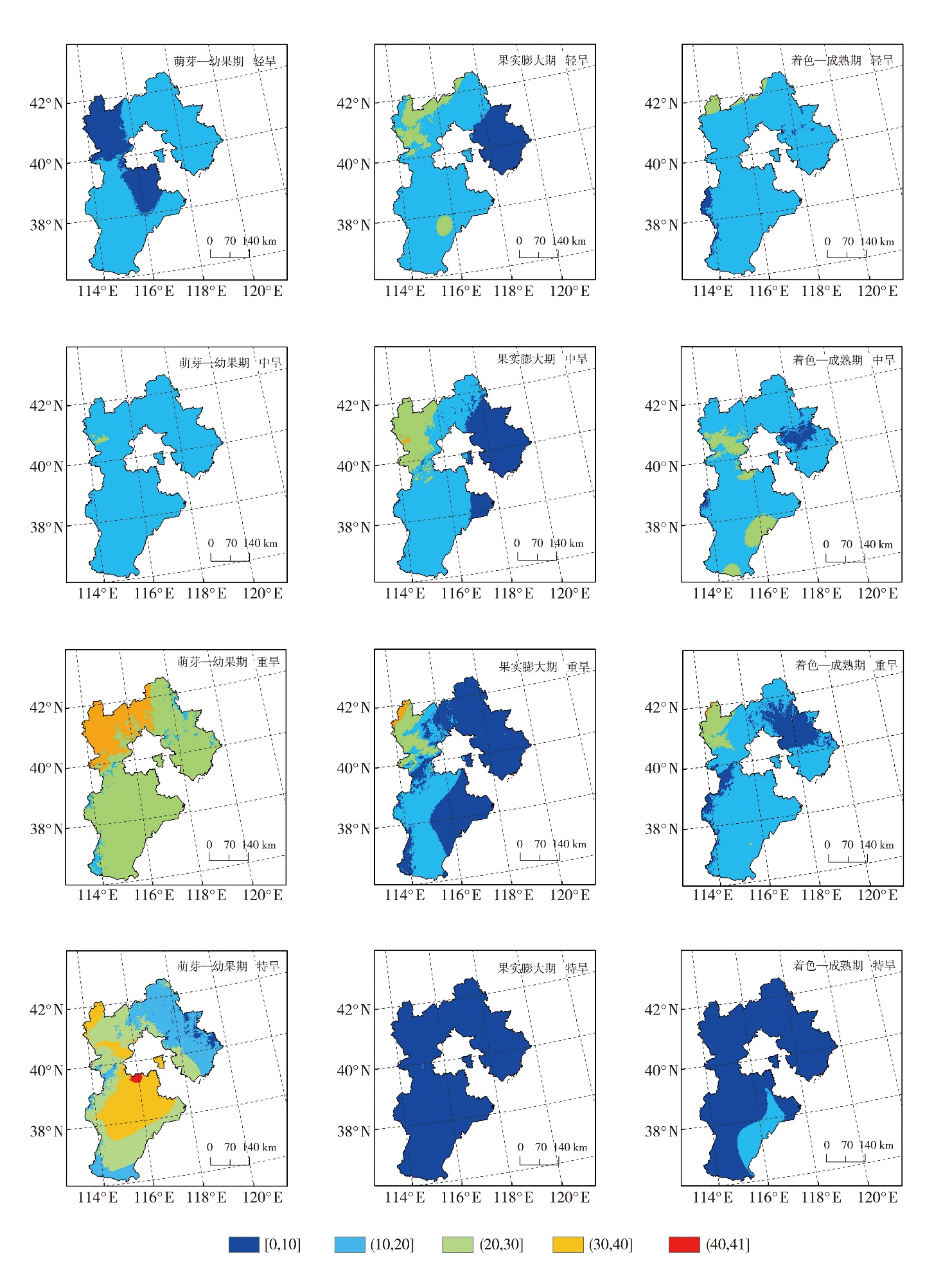
| 地点 | 年份 | 时段 | 灾情描述 | WPLR等级 | 差异程度 | 地点 | 年份 | 时段 | 灾情描述 | WPLR等级 | 差异程度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 唐山 | 2004 | I | 中旱 | 无旱 | 2 | 承德 | 2004 | I | 重旱 | 重旱 | 0 |
| 沧州 | 2004 | I | 无旱 | 无旱 | 0 | 秦皇岛 | 2004 | I | 中旱 | 中旱 | 0 |
| 衡水 | 2004 | I | 无旱 | 无旱 | 0 | 廊坊 | 2004 | I | 中旱 | 中旱 | 0 |
| 邯郸 | 2004 | I | 无旱 | 轻旱 | 1 | 保定 | 2004 | I | 中旱 | 中旱 | 0 |
| 石家庄 | 2004 | I | 重旱 | 重旱 | 0 | 张家口 | 2007 | II | 重旱 | 重旱 | 0 |
| 邢台 | 2004 | I | 重旱 | 重旱 | 0 | 张家口 | 2010 | II | 重旱 | 重旱 | 0 |
| 张家口 | 2004 | I | 重旱 | 重旱 | 0 | 张家口 | 2012 | II | 较重 | 重旱 | 0 |
Tab.3 Verification of the difference between the occurrence of apple drought and the actual situation in Hebei Province
| 地点 | 年份 | 时段 | 灾情描述 | WPLR等级 | 差异程度 | 地点 | 年份 | 时段 | 灾情描述 | WPLR等级 | 差异程度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 唐山 | 2004 | I | 中旱 | 无旱 | 2 | 承德 | 2004 | I | 重旱 | 重旱 | 0 |
| 沧州 | 2004 | I | 无旱 | 无旱 | 0 | 秦皇岛 | 2004 | I | 中旱 | 中旱 | 0 |
| 衡水 | 2004 | I | 无旱 | 无旱 | 0 | 廊坊 | 2004 | I | 中旱 | 中旱 | 0 |
| 邯郸 | 2004 | I | 无旱 | 轻旱 | 1 | 保定 | 2004 | I | 中旱 | 中旱 | 0 |
| 石家庄 | 2004 | I | 重旱 | 重旱 | 0 | 张家口 | 2007 | II | 重旱 | 重旱 | 0 |
| 邢台 | 2004 | I | 重旱 | 重旱 | 0 | 张家口 | 2010 | II | 重旱 | 重旱 | 0 |
| 张家口 | 2004 | I | 重旱 | 重旱 | 0 | 张家口 | 2012 | II | 较重 | 重旱 | 0 |
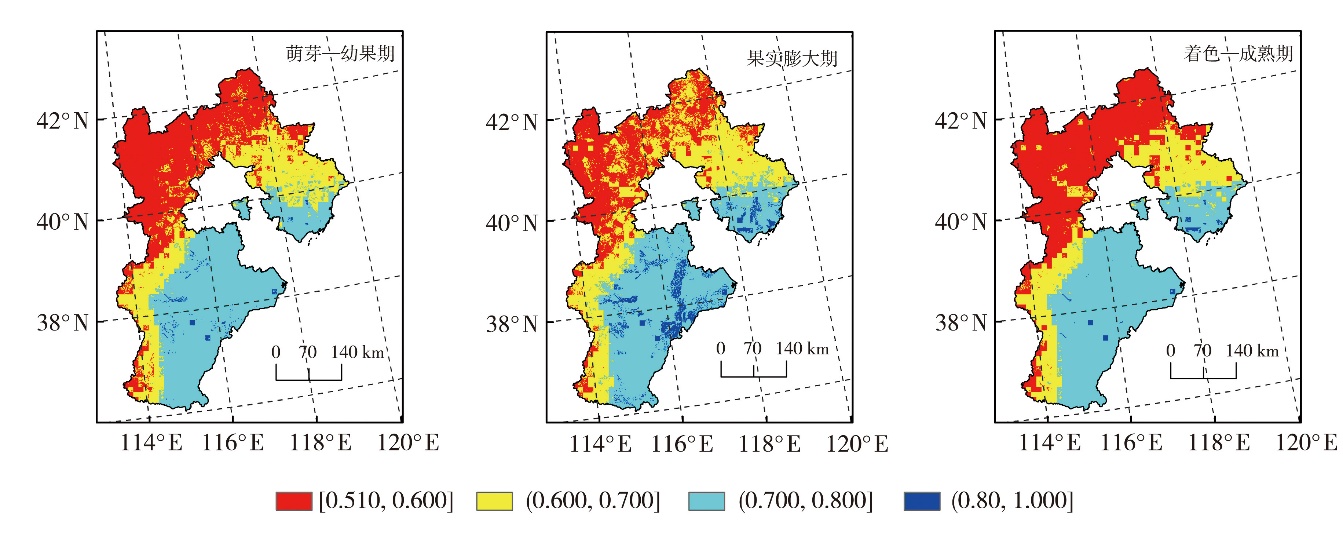
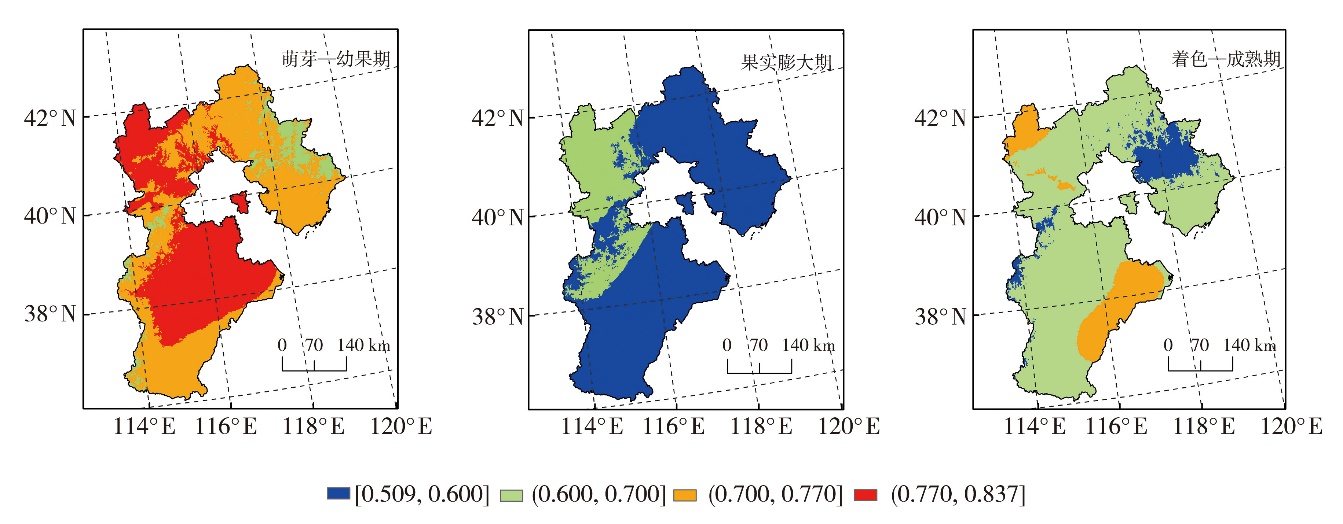
Fig.5 Spatial distribution of environmental sensitivity index of drought disaster in different growth stages of apple in Hebei Province from 1980 to 2023
| [1] | 程雪, 孙爽, 张方亮, 等, 2020. 我国北方地区苹果干旱时空分布特征[J]. 应用气象学报, 31(1):63-73. |
| [2] | 高歌, 李莹, 陈涛, 等, 2023. 2004—2019年中国干旱多承灾体灾损风险特征评估[J]. 气象, 49(5):611-623. |
| [3] |
郭守生, 张铖玉, 马昕芮, 等, 2024. 气候变化背景下青海省春小麦水分盈亏率时空分布特征[J]. 中国农学通报, 40(20):122-129.
DOI |
| [4] | 河北省统计局, 2012. 河北农村统计年鉴2011[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社. |
| [5] | 贺洁, 王让会, 刘春伟, 2024. 基于SPAC系统的阿克苏地区农业干旱灾害风险评估与区划[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 42(5): 255-262. |
| [6] |
贾桂梅, 李春强, 王蓉蓉, 等, 2024. 河北省苹果生长季极端干旱时空特征[J]. 农学学报, 14(11):64-71.
DOI |
| [7] | 金垚, 王锐婷, 邹雨伽, 等, 2022. 基于水分亏缺指数的四川省水稻干旱灾害综合风险评价[J]. 西南大学学报:自然科学版, 44(11):51-61. |
| [8] | 李聪, 孙菀, 刘佳, 等, 2020. 河南省大豆干旱风险区划研究[J]. 湖北农业科学, 59(12):51-55. |
| [9] | 李万志, 张调风, 马有绚, 等, 2021. 基于灾害风险因子的青海省干旱灾害风险区划[J]. 干旱气象, 39(3):480-485. |
| [10] | 刘焕莉, 范增禄, 韩明稚, 等, 2020. 基于ANUSPLIN的京津冀区域逐日气温格点数据集建立方法研究[J]. 海洋气象学报, 40(3):111-120. |
| [11] | 梅茹玉, 毛克彪, 杜宝裕, 等, 2022. 河北省冬小麦—夏玉米干旱灾害风险评估[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 43(7): 216-231. |
| [12] |
穆佳, 吴迪, 刘洋, 等, 2024. 吉林省玉米干旱风险对产量的影响分析[J]. 干旱气象, 42(4): 498-506.
DOI |
| [13] | 钱永兰, 吕厚荃, 张艳红, 2010. 基于ANUSPLIN软件的逐日气象要素插值方法应用与评估[J]. 气象与环境学报, 26(2):7-15. |
| [14] | 邱美娟, 郭春明, 王冬妮, 等, 2018. 基于作物水分亏缺指数的吉林省玉米不同生育时段干旱特征分析[J]. 灾害学, 33(2): 89-98. |
| [15] | 邱美娟, 刘布春, 刘园, 等, 2021. 中国北方苹果种植需水特征及降水适宜性[J]. 应用气象学报, 32(2):175-187. |
| [16] | 宋珂, 2024. 山东省夏玉米干旱灾害风险评估[D]. 廊坊: 防灾科技学院. |
| [17] | 隋刚, 郝兵元, 彭林, 2010. 利用高程标准差表达地形起伏程度的数据分析[J]. 太原理工大学学报, 41(4):381-384. |
| [18] | 孙可可, 陈进, 许继军, 等, 2013. 基于EPIC模型的云南元谋水稻春季旱灾风险评估方法[J]. 水利学报, 44(11): 1 326-1 332. |
| [19] | 索相敏, 李学营, 王献革, 等, 2014. 高温干旱对苹果生产的影响及对策[J]. 现代农村科技(16):46. |
| [20] | 王景红, 柏秦凤, 梁轶, 等, 2014. 陕西苹果干旱指数研究及基于县域单元的苹果干旱风险分布[J]. 气象科技, 42(3): 516-523. |
| [21] | 王景红, 梁轶, 柏秦凤, 等, 2013. 陕西猕猴桃高温干旱灾害风险区划研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 29(7): 105-110. |
| [22] | 王静, 2023. 中国苹果生产空间布局优化研究[D]. 杨陵: 西北农林科技大学. |
| [23] |
王莺, 张强, 王劲松, 等, 2022. 21世纪以来干旱研究的若干新进展与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 40(4):549-566.
DOI |
| [24] |
王莺, 张强, 韩兰英, 2016. 基于信息扩散理论的中国南方水旱灾害风险特征[J]. 干旱气象, 34(6):919-926.
DOI |
| [25] | 乌日娜, 张兴东, 曹永强, 等, 2022. 辽宁省玉米旱灾时空分布特征及综合风险评价[J]. 生态学报, 42(16):6731-6 744. |
| [26] |
吴叔阳, 郑博福, 汪江, 等, 2024. 2022年江西省极端干旱对柑橘种植经济损失的遥感评估[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 39(2):337-349.
DOI |
| [27] | 肖楠舒, 刘布春, 殷红, 等, 2022. 基于作物水分亏缺指数的环渤海地区鲜食葡萄干旱风险评估[J]. 中国农业气象, 43(5): 380-391. |
| [28] | 徐新良, 2018a. 中国月度NDVI、 EVI 250 m数据集. 资源环境科学数据注册与出版系统(http://www.resdc.cn/DOI).DOI:10.12078/2018060602) |
| [29] | 徐新良, 2018b. 基于DEM提取的中国流域、河网数据集. 资源环境科学数据注册与出版系统() |
| [30] | 杨王华, 刘志娟, 巩敬锦, 等, 2024. 东北地区未来春玉米干旱风险时空分布及对气候变化的响应[J]. 中国农业科学, 57(12):2336-2 349. |
| [31] | 余锐, 侯灵, 云翔, 等, 2023. 基于百分位数法的广东气温变化特征研究[J]. 广东气象, 45(5):17-21. |
| [32] | 袁喆, 徐翔宇, 许继军, 等, 2023. 基于灾损拟合分析的区域干旱灾害风险区划方法及应用:以湖南省为例[J]. 中国防汛抗旱, 33(3):24-29. |
| [33] | 臧建升, 温克刚, 2008. 《中国气象灾害大典:河北卷》[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [34] | 张玮玮, 张眉, 吴杨, 等, 2020. 复杂地形下浙江夏季气候要素空间插值方法评价[J]. 干旱气象, 38(4): 674-682. |
| [35] |
张玉翠, 谭江红, 闫彩霞, 2024. 湖北省区域性高温、干旱及其复合事件变化特征及危险性评估[J]. 干旱气象, 42(6): 825-835.
DOI |
| [36] | 张玥滢, 2020. 苹果水旱灾害风险评价与保险产品研发[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院. |
| [37] |
赵鸿, 蔡迪花, 王鹤龄, 等, 2023. 干旱灾害对粮食安全的影响及其应对技术研究进展与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 41(2): 187-206.
DOI |
| [38] | 赵佳琪, 张强, 朱秀迪, 等, 2021. 中国旱灾风险定量评估[J]. 生态学报, 41(3): 1 021-1 031. |
| [39] | 中国气象局, 2004—2012. 中国气象灾害年鉴[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [40] | 中华人民共和国国家统计局, 2023. 中国统计年鉴2023[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社. |
| [41] | 中华人民共和国水利部, 2024. 中国水旱灾害防御公报2023[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社. |
| [42] | 邹海平, 陈汇林, 李伟光, 等, 2015. 海南岛冬种瓜菜暴雨洪涝灾害风险评估与区划[J]. 中国农业气象, 36(1): 100-107. |
| [43] | ALLEN R G, PEREIRA L S, RAES D, et al, 1998. Crop evapotranspiration: Guidelines for computing crop water requirements[M]. FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 56. Rome:Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. |
| [44] | DOORENBOS J, KASSAM A H, 1979. Yield response to water[Z]. FAO Irrigation and Drainage, Paper 33, Rome: 193. |
| [45] | IPCC, 2021. Climate Change 2021:The Physical Science Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change[M]. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. |
| [46] | LIU Z C, ZHOU W, WANG X, 2024. Extreme meteorological drought events over China(1951-2022):Migration patterns, diversity of temperature extremes, and decadal variations[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 41(12): 2 313-2 336. |
| [47] | NIU K J, HU Q F, ZHAO L, et al, 2019. Analysis of agricultural drought risk based on information distribution and diffusion methods in the main grain production areas of China[J]. Atmosphere, 10(12):764. DOI:10.3390/atmos10120764. |
| [48] | SU B D, HUANG J L, FISCHER T, et al, 2018. Drought losses in China might double between the 1.5 ℃ and 2.0 ℃ warming[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 115(42): 10 600-10 605. |
| [49] | SU X Y, HUANG G, WANG L, et al, 2024. Global drought changes and attribution under carbon neutrality scenario[J]. Climate Dynamics, 62(8):7851-7 868. |
| [50] | ZHANG Q, YAO Y B, WANG Y, et al, 2019. Characteristics of drought in Southern China under climatic warming, the risk, and countermeasures for prevention and control[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 136(3):1157-1 173. |
| [1] | ZHOU Jianqin, LI Meng, TAO Yun, DOU Xiaodong, WANG Yuyouting. Study on the evolutionary characteristics of agricultural drought disasters and the relationship with climatic factors in Yunnan [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(1): 21-31. |
| [2] | DENG Guowei, SUN Jun, LAI Jiang, ZHANG Ling. Grey correlation analysis of drought and yield at different growth stages of rice in Sichuan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(5): 814-822. |
| [3] | LE Zhangyan, SHI Minghua, LI De, HUO Zhiguo, DU Zixuan, TAN Yanjing. Risk assessment of low temperature disaster in winter for facility agriculture in Henan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(4): 667-676. |
| [4] | ZHANG Xiaopei, FAN Zhichao. Research on Safety Risk Assessment Method of Ground Weather Modification Operation Based on SCA-LEC Model [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(6): 1037-1042. |
| [5] | QIU Meijuan, LIU Buchun, LIU Yuan, PANG Jingyi, WANG Keyi, WANG Yaming, ZHANG Yueying. Spatial-temporal Distribution Characteristics of Precipitation Suitability in Main Apple Producing Areas in China from 1971 to 2017 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(5): 810-819. |
| [6] | MA Lei, LIU Yao, WU Wanli, GOU Xiaohui, SU Zhansheng, . Risk Assessment of Gale Disaster on Expressways in Ningxia Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(03): 504-510. |
| [7] | MU Chenying, JI Ruipeng, YIN Hong, ZHANG Yu, LI Juan,XU Quanhui, ZHANG Siyao. Variation Characteristics of Heat Index of Spring Maize in Different Growth Periods in Shenyang [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(5): 828-834. |
| [8] | WANG Jie, FU Guiqin, WU Huiqin, QI Yuchao, ZHAO Zengbao. Temporal-spatial Distribution Characteristics of Power Grid Disaster Accidents and Risk Assessment in Northern Hebei [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(5): 879-883. |
| [9] | ZHAO Nianwu, GUO Lianyun,ZHAO Henghe. Variation Characteristics of Climate Factors During Potato Growth Period and Their Effect on Yield in the Alpine Semiarid Zone [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(6): 1024-1030. |
| [10] | DU Zixuan1,2, LIU Zhongyang1,2, LIU Jing3, CAO Shuchao2 . Temporal and Spatial Distribution and Risk Assessment of Few Sunshine Disasters for Cucumber in He’nan Facility Agriculture [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(4): 694-701. |
| [11] | ZHANG Cunjie,WANG Sheng,SONG Yanling,CAI Wenyue. Research of Drought Risk Assessment for Winter Wheat in Northern China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2014, 32(6): 883-893. |
| [12] | FU Guiqin,ZHANG Wenzong . Characteristic Analysis and Risk Assessment of Electrified Wire Netting Accidents Caused by Meteorological Disasters in Hebei Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2014, 32(3): 460-464. |
| [13] | YANG Xiaoli. Risk Assessment of Agricultural Insurance on Apple FreezingInjury at Blooming Stage in Pingliang of Gansu Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2014, 32(2): 281-285. |
| [14] | SHI Jie,YAO Yubi,LEI Jun. Risk Assessment and Division of Drought Disaster Based on GIS in Dingxi City [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2014, 32(2): 305-309. |
| [15] | WANG Ying,LI Yaohui,ZHAO Funian,HU Tiantian. Risk Assessment of Agriculture Drought Disaster in Gansu Province Based on Information Diffusion Principle [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2013, 31(1): 43-48. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||