Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (5): 813-823.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2024-05-0813
• Technical Report • Previous Articles
Research on risk assessment and early warning method for geological hazards induced by heavy precipitation in Longnan power grid
SUN Tao1( ), LI Yue2, WANG Jin3, LI Xiaoqin4(
), LI Yue2, WANG Jin3, LI Xiaoqin4( ), HE Jinmei4, ZHAO Wenjing4, LYU Meixia4
), HE Jinmei4, ZHAO Wenjing4, LYU Meixia4
- 1. State Grid Gansu Electric Power Company, Lanzhou 730030, China
2. State Grid Lanzhou Power Supply Company, Lanzhou 730070, China
3. State grid Gansu Electric Power Company Electric Power Science Research Institute, Lanzhou 730070, China
4. Meteorological Service Center of Gansu Province, Lanzhou 730020, China
-
Received:2024-05-24Revised:2024-08-30Online:2024-10-31Published:2024-11-17
强降水诱发陇南电网地质灾害风险评估及预警方法研究
孙涛1( ), 李玥2, 王津3, 李晓琴4(
), 李玥2, 王津3, 李晓琴4( ), 何金梅4, 赵文婧4, 吕玫霞4
), 何金梅4, 赵文婧4, 吕玫霞4
- 1.国网甘肃省电力公司,甘肃 兰州 730030
2.国网兰州供电公司,甘肃 兰州 730070
3.国网甘肃省电力公司电力科学研究院,甘肃 兰州 730070
4.甘肃省气象服务中心,甘肃 兰州 730020
-
通讯作者:李晓琴(1994—),女,甘肃武威人,主要从事专业气象服务。E-mail:lxqin369@163.com 。 -
作者简介:孙涛(1982—),男,甘肃兰州人,高级工程师,主要从事电力气象应用研究。E-mail: suntao821115@163.com。 -
基金资助:甘肃省青年科技基金项目(22JR5RA756);甘肃省重点研发计划-工业类项目(23YFGA0016);甘肃省气象局人才专项(2425rczx-G-QNQHRC-08);甘肃省科技计划项目(23JRRA1574);甘肃省气象局气象科研重点项目(Zd2022-04)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
SUN Tao, LI Yue, WANG Jin, LI Xiaoqin, HE Jinmei, ZHAO Wenjing, LYU Meixia. Research on risk assessment and early warning method for geological hazards induced by heavy precipitation in Longnan power grid[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(5): 813-823.
孙涛, 李玥, 王津, 李晓琴, 何金梅, 赵文婧, 吕玫霞. 强降水诱发陇南电网地质灾害风险评估及预警方法研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(5): 813-823.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2024-05-0813

Fig.2 Distribution of annual average precipitation days (a) and precipitation amount (b), annual average frequency of rainstorm and above (c) and their precipitation amount (d), annual average short-time strong precipitation frequency (e) and precipitation amount (f) in Longnan from 2018 to 2022
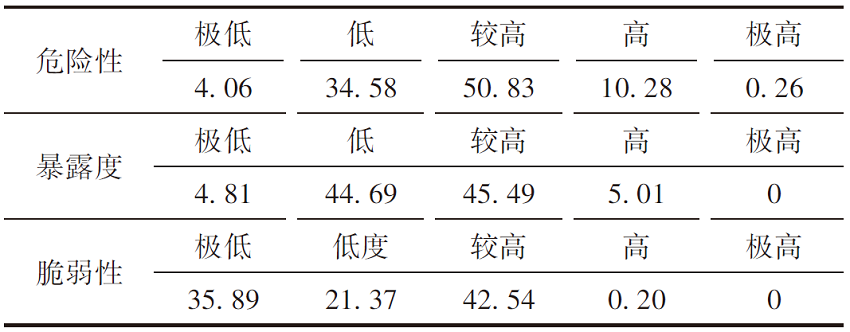
| 危险性 | 极低 | 低 | 较高 | 高 | 极高 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.89 | 31.62 | 56.53 | 9.87 | 0.09 | |
| 暴露度 | 极低 | 低 | 较高 | 高 | 极高 |
| 1.32 | 31.28 | 20.79 | 39.74 | 6.87 | |
| 脆弱性 | 极低 | 低度 | 较高 | 高 | 极高 |
| 35.47 | 23.59 | 36.41 | 4.14 | 0.01 |
Tab.1
| 危险性 | 极低 | 低 | 较高 | 高 | 极高 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.89 | 31.62 | 56.53 | 9.87 | 0.09 | |
| 暴露度 | 极低 | 低 | 较高 | 高 | 极高 |
| 1.32 | 31.28 | 20.79 | 39.74 | 6.87 | |
| 脆弱性 | 极低 | 低度 | 较高 | 高 | 极高 |
| 35.47 | 23.59 | 36.41 | 4.14 | 0.01 |
| 评价因子 | 分级 | (Ni/N)/% | 信息量值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 高程/m | ≤2 000 | 8.22 | 1.52 |
| >2 000~2 500 | 23.33 | 0.36 | |
| >2 500~3 000 | 37.01 | 0.24 | |
| >3 000~3 500 | 23.57 | -0.15 | |
| >3 500~4 000 | 6.57 | -0.79 | |
| >4 000 | 1.30 | -1.79 | |
| 曲率 | <0 | 9.58 | 0.70 |
| 0 | 39.71 | -0.23 | |
| >0 | 50.71 | -0.67 | |
| 坡度/(°) | ≤15 | 8.23 | -0.02 |
| >15~25 | 66.38 | -0.15 | |
| >25~35 | 41.21 | -0.15 | |
| >35~45 | 26.01 | 0.42 | |
| >45 | 9.89 | 0.79 | |
| 坡向 | 北 | 20.24 | -0.13 |
| 东北 | 12.26 | 0.01 | |
| 东 | 8.76 | -0.25 | |
| 东南 | 10.16 | -0.14 | |
| 南 | 17.30 | 0.44 | |
| 西南 | 10.66 | -0.03 | |
| 西 | 9.01 | -0.15 | |
| 西北 | 11.59 | 0.09 | |
| NDVI | ≤0.25 | 12.45 | 10.45 |
| >0.25~0.50 | 59.55 | 2.90 | |
| >0.50~0.75 | 19.25 | -1.00 | |
| >0.75~1.00 | 8.75 | -0.50 |
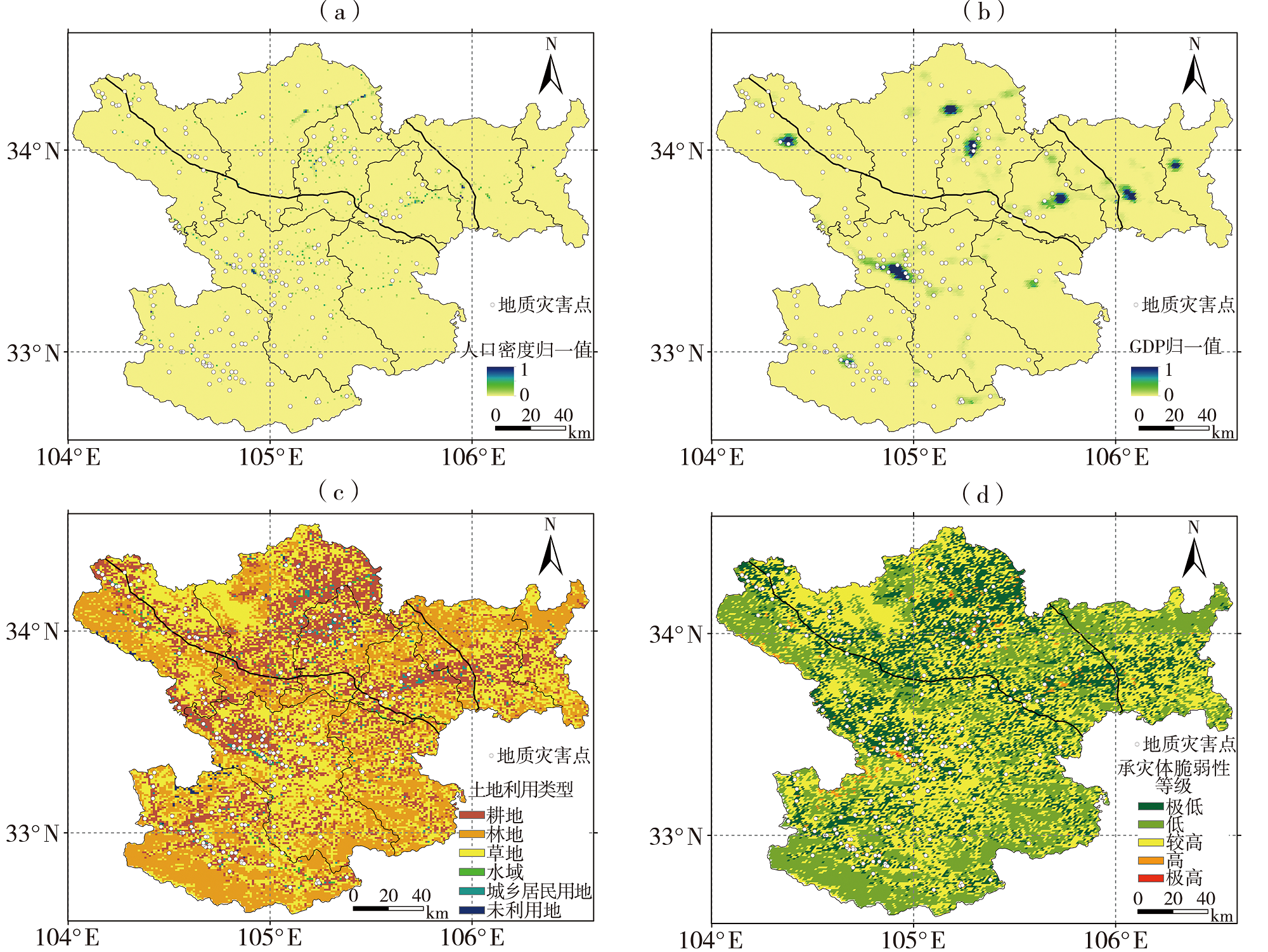
Tab.2 Geological hazard exposure degree valuation factor classification and information quantity values
| 评价因子 | 分级 | (Ni/N)/% | 信息量值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 高程/m | ≤2 000 | 8.22 | 1.52 |
| >2 000~2 500 | 23.33 | 0.36 | |
| >2 500~3 000 | 37.01 | 0.24 | |
| >3 000~3 500 | 23.57 | -0.15 | |
| >3 500~4 000 | 6.57 | -0.79 | |
| >4 000 | 1.30 | -1.79 | |
| 曲率 | <0 | 9.58 | 0.70 |
| 0 | 39.71 | -0.23 | |
| >0 | 50.71 | -0.67 | |
| 坡度/(°) | ≤15 | 8.23 | -0.02 |
| >15~25 | 66.38 | -0.15 | |
| >25~35 | 41.21 | -0.15 | |
| >35~45 | 26.01 | 0.42 | |
| >45 | 9.89 | 0.79 | |
| 坡向 | 北 | 20.24 | -0.13 |
| 东北 | 12.26 | 0.01 | |
| 东 | 8.76 | -0.25 | |
| 东南 | 10.16 | -0.14 | |
| 南 | 17.30 | 0.44 | |
| 西南 | 10.66 | -0.03 | |
| 西 | 9.01 | -0.15 | |
| 西北 | 11.59 | 0.09 | |
| NDVI | ≤0.25 | 12.45 | 10.45 |
| >0.25~0.50 | 59.55 | 2.90 | |
| >0.50~0.75 | 19.25 | -1.00 | |
| >0.75~1.00 | 8.75 | -0.50 |
| 等级 | 成县 | 宕昌县 | 徽县 | 康县 | 礼县 | 两当县 | 文县 | 武都区 | 西和县 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 危险性 | 极低 | 0.37 | 13.22 | / | 0.08 | 0.66 | / | 5.52 | 9.44 | 0.49 |
| 低 | 0.56 | 40.63 | 0.29 | 0.84 | 8.17 | 0.91 | 56.43 | 29.53 | 4.99 | |
| 较高 | 71.92 | 45.79 | 88.47 | 22.99 | 75.13 | 94.72 | 19.43 | 38.86 | 70.92 | |
| 高 | 27.15 | 0.31 | 11.23 | 76.09 | 14.71 | 4.37 | 18.62 | 22.18 | 23.48 | |
| 极高 | / | 0.05 | / | / | 1.33 | / | / | / | 0.12 | |
| 暴露度 | 极低 | 2.62 | 0.31 | 1.42 | 0.17 | 1.09 | 0.35 | 1.67 | 2.21 | 1.10 |
| 低 | 40.16 | 18.63 | 40.50 | 39.53 | 37.38 | 30.90 | 20.26 | 29.03 | 44.38 | |
| 较高 | 14.70 | 30.23 | 18.12 | 13.85 | 17.19 | 21.88 | 29.00 | 18.16 | 15.62 | |
| 高 | 41.21 | 36.79 | 38.37 | 44.09 | 42.02 | 43.06 | 32.81 | 44.52 | 37.53 | |
| 极高 | 1.31 | 14.05 | 1.60 | 2.36 | 2.32 | 3.82 | 16.26 | 6.08 | 1.37 | |
| 极低 | 36.71 | 31.05 | 35.51 | 41.19 | 30.61 | 35.59 | 32.30 | 41.02 | 34.79 | |
| 低 | 23.67 | 22.81 | 24.76 | 23.56 | 21.61 | 28.83 | 20.51 | 28.74 | 18.04 | |
| 脆弱性 | 较高 | 34.78 | 40.65 | 36.08 | 33.22 | 42.94 | 34.68 | 41.43 | 26.65 | 38.40 |
| 高 | 4.83 | 5.49 | 3.65 | 2.03 | 4.71 | 0.90 | 5.76 | 3.36 | 8.25 | |
| 极高 | / | / | / | / | 0.14 | / | / | 0.23 | 0.52 |
Tab.4
| 等级 | 成县 | 宕昌县 | 徽县 | 康县 | 礼县 | 两当县 | 文县 | 武都区 | 西和县 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 危险性 | 极低 | 0.37 | 13.22 | / | 0.08 | 0.66 | / | 5.52 | 9.44 | 0.49 |
| 低 | 0.56 | 40.63 | 0.29 | 0.84 | 8.17 | 0.91 | 56.43 | 29.53 | 4.99 | |
| 较高 | 71.92 | 45.79 | 88.47 | 22.99 | 75.13 | 94.72 | 19.43 | 38.86 | 70.92 | |
| 高 | 27.15 | 0.31 | 11.23 | 76.09 | 14.71 | 4.37 | 18.62 | 22.18 | 23.48 | |
| 极高 | / | 0.05 | / | / | 1.33 | / | / | / | 0.12 | |
| 暴露度 | 极低 | 2.62 | 0.31 | 1.42 | 0.17 | 1.09 | 0.35 | 1.67 | 2.21 | 1.10 |
| 低 | 40.16 | 18.63 | 40.50 | 39.53 | 37.38 | 30.90 | 20.26 | 29.03 | 44.38 | |
| 较高 | 14.70 | 30.23 | 18.12 | 13.85 | 17.19 | 21.88 | 29.00 | 18.16 | 15.62 | |
| 高 | 41.21 | 36.79 | 38.37 | 44.09 | 42.02 | 43.06 | 32.81 | 44.52 | 37.53 | |
| 极高 | 1.31 | 14.05 | 1.60 | 2.36 | 2.32 | 3.82 | 16.26 | 6.08 | 1.37 | |
| 极低 | 36.71 | 31.05 | 35.51 | 41.19 | 30.61 | 35.59 | 32.30 | 41.02 | 34.79 | |
| 低 | 23.67 | 22.81 | 24.76 | 23.56 | 21.61 | 28.83 | 20.51 | 28.74 | 18.04 | |
| 脆弱性 | 较高 | 34.78 | 40.65 | 36.08 | 33.22 | 42.94 | 34.68 | 41.43 | 26.65 | 38.40 |
| 高 | 4.83 | 5.49 | 3.65 | 2.03 | 4.71 | 0.90 | 5.76 | 3.36 | 8.25 | |
| 极高 | / | / | / | / | 0.14 | / | / | 0.23 | 0.52 |
| 强降水过程时间 | 地质灾害气象风险预警 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有一定风险 | 较高风险 | 高风险 | 极高风险 | 预警准确率 | |
| 2022-07-15 | 27.27 | 18.18 | 22.73 | 4.55 | 72.73 |
| 2022-08-27 | 42.86 | 14.29 | 14.29 | 0 | 71.44 |
| 2023-07-12 | 22.53 | 25.82 | 18.68 | 5.49 | 72.52 |
| 2023-07-27 | 11.36 | 21.59 | 29.55 | 17.05 | 79.55 |
Tab.5
| 强降水过程时间 | 地质灾害气象风险预警 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有一定风险 | 较高风险 | 高风险 | 极高风险 | 预警准确率 | |
| 2022-07-15 | 27.27 | 18.18 | 22.73 | 4.55 | 72.73 |
| 2022-08-27 | 42.86 | 14.29 | 14.29 | 0 | 71.44 |
| 2023-07-12 | 22.53 | 25.82 | 18.68 | 5.49 | 72.52 |
| 2023-07-27 | 11.36 | 21.59 | 29.55 | 17.05 | 79.55 |
| [1] | 陈强, 王建, 熊小伏, 等, 2020. 一种降雨诱发滑坡灾害下输电杆塔的监测与预警方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 48 (3): 147-155. |
| [2] | 陈长坤, 戴琦乐, 余荣付, 等, 2024. 基于灾害演化网络的泥石流风险评估方法研究[J]. 灾害学, 39(2): 62-66. |
| [3] | 邓创, 刘友波, 刘俊勇, 等, 2016. 考虑降雨诱发次生地质灾害的电网风险评估方法[J]. 电网技术, 40(12): 3 825-3 834. |
| [4] | 狄靖月, 许凤雯, 李焕连, 等, 2022. 暴雨诱发恩施州地质灾害成因分析[J]. 气象, 48(10): 1 321-1 332. |
| [5] | 杜国梁, 张永双, 高金川, 等, 2016. 基于GIS的白龙江流域甘肃段滑坡易发性评价[J]. 地质力学学报, 22 (1): 1-11. |
| [6] | 冯军, 尚学军, 樊明, 等, 2006. 陇南地质灾害降雨区划及临界雨量研究[J]. 干旱气象, 24(4): 20-24. |
| [7] | 郭富赟, 宋晓玲, 谢煜, 等, 2015. 甘肃地质灾害气象预警技术方法探讨[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 26(1): 127-133. |
| [8] | 胡倩, 岳大鹏, 赵景波, 等, 2019. 甘肃省近50年暴雨变化特征及其灾害效应[J]. 水土保持通报, 39(4): 68-75. |
| [9] | 胡现振, 付少杰, 迟宏庆, 等, 2023. 基于层次分析-信息量耦合模型的地质灾害风险评价:以河北省武安市为例[J]. 中国地质调查, 10 (5): 109-117. |
| [10] | 李宇梅, 杨寅, 狄靖月, 等, 2020. 全国地质灾害气象风险精细化网格预报方法及其应用[J]. 气象, 46(10): 1 310-1 319. |
| [11] | 刘康, 田臣龙, 徐凤琳, 2023. 基于信息量-层次分析耦合模型的泗水县地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 中国地质调查, 10 (2): 77-86. |
| [12] | 刘书豪, 2021. 降雨条件下的输电线路滑坡风险评估与预警技术研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学. |
| [13] | 卢佳燕, 李为乐, 刘刚, 等, 2019. 米林震后地质灾害空间分布特征及易发性分析[J]. 自然灾害学报, 28 (2): 183-190. |
| [14] |
马莉, 杨晓军, 王勇, 等, 2023. 1990—2019年甘肃汛期极端小时降水特征[J]. 高原气象, 42(4): 993-1 004.
DOI |
| [15] | 牛全福, 熊超, 雷姣姣, 等, 2023. 基于FFPI模型的甘肃陇南山区山洪灾害风险评价[J]. 自然灾害学报, 32(4): 36-47. |
| [16] | 裴静, 2022. 陇南市地质灾害危险性评价与分区研究[D]. 兰州: 西北师范大学. |
| [17] | 全国气象防灾减灾标准化技术委员会, 2018. 强对流天气等级: QX/T 416—2018[S]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [18] | 全国气象防灾减灾标准化技术委员会, 2019. 暴雨诱发的地质灾害气象风险预警等级: QX/T 487—2019[S]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [19] | 全国气象防灾减灾标准化技术委员会, 2012. 降水量等级: GB/T 28592—2012[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| [20] | 全国自然资源与国土空间规划标准化技术委员会, 2023. 地质灾害气象风险预警规范: DZ/T 0449—2023[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| [21] |
石延召, 刘维成, 傅朝, 等, 2024. 甘肃陇南两次暴雨天气过程对比分析[J]. 干旱气象, 42(1): 107-116.
DOI |
| [22] | 苏军锋, 张锋, 黄玉霞, 等, 2021. 甘肃陇南市短时强降水时空分布特征及中尺度分析[J]. 干旱气象, 39(6): 966-973. |
| [23] | 孙蕊, 丁雨虹, 郭海燕, 等, 2022. 基于GIS的四川省降水诱发型滑坡泥石流风险区划[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 42(3): 111-116. |
| [24] | 谭洋洋, 杨洪耕, 徐方维, 等, 2016. 降雨型滑坡诱发电网连锁故障风险评估模型研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 16(33): 8-13. |
| [25] | 汤奕, 徐香香, 陈彬, 等, 2020. 降雨滑坡灾害对输电杆塔故障的时空强在线预警[J]. 中国电力, 53(1): 56-65. |
| [26] | 田广旭, 陈俊, 2013. 甘肃省陇南市自然灾害监测预警指挥系统[J]. 干旱气象, 31(2): 437-440. |
| [27] | 王莲芬, 许树柏, 1990. 层次分析法引论[M]. 北京: 中国人民大学出版社. |
| [28] |
王莺, 王健顺, 张强, 2022. 中国草原干旱灾害风险特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 31(8): 1-12.
DOI |
| [29] | 王莹, 张晓月, 张琪, 等, 2019. 暴雨灾害风险及其对农业影响的评估[J]. 气象科学, 39(1): 137-142. |
| [30] | 邬礼扬, 殷坤龙, 曾韬睿, 等, 2024. 不同栅格尺寸下输电线路地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 43(1): 241-252. |
| [31] | 熊木齐, 孟兴民, 庆丰, 等, 2016. 甘肃省陇南市白龙江流域泥石流灾害事件与降水特征的关系[J]. 兰州大学学报: 自然科学版, 52(3): 295-300. |
| [32] | 薛永安, 王玉洁, 朱婧聪, 等, 2022. 县域国土空间斜坡地质灾害敏感性评价研究[J]. 自然灾害学报, 31(4): 219-230. |
| [33] | 肖瑞迪, 范立张, 张明达, 等, 2024. 云南怒江州地质灾害时空变化特征及其与降水的关系[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 44(2):127-132. |
| [34] |
杨丽杰, 曹彦超, 刘维成, 等, 2022. 陇东黄土高原旱区短时强降水的时空分布特征及地形影响研究[J]. 干旱气象, 40(6): 945-953.
DOI |
| [35] | 杨思慧, 袁淑杰, 施红霞, 等, 2023. 基于逻辑回归的若尔盖气象地质灾害预警研究[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 43(4):101-108. |
| [36] |
姚玉璧, 王莺, 王劲松, 2016. 气候变暖背景下中国南方干旱灾害风险特征及对策[J]. 生态环境学报, 25(3): 432-439.
DOI |
| [37] | 张君霞, 黄武斌, 李安泰, 等, 2023. 甘肃省主要地质灾害精细化气象风险预警预报[J]. 干旱区地理, 46(9): 1 443-1 452. |
| [38] | 赵焕臣, 许树柏, 和金生, 1986. 层次分析法:一种简易的新决策方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| [39] | 赵良军, 李虎, 刘玉锋, 等, 2017. 新疆伊犁果子沟地质灾害风险评价及其致灾因子[J]. 干旱区研究, 34(3): 693-700. |
| [40] | 赵倩, 夏晓玲, 唐延婧, 等, 2020. 贵州省主要输电线路沿线强降雨时空分布特征[J]. 人民长江, 51(7): 100-105. |
| [41] | 赵庆云, 宋松涛, 杨贵名, 等, 2014. 西北地区暴雨时空变化及异常年夏季环流特征[J]. 兰州大学学报: 自然科学版, 50(4): 517-522. |
| [42] | GE Y F, CHEN H Z, ZHAO B B, et al, 2018. A comparison of five methods in landslide susceptibility assessment: a case study from the 330-kV transmission line in Gansu Region, China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 77(19): 1-15. |
| [43] | IPCC, 2012. Summary for Policymakers[M]// Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation. A Special Report of Working Groups I and II of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press: 1-19. |
| [44] | ZHAO B B, GE Y F, CHEN H Z, 2021. Landslide susceptibility assessment for a transmission line in Gansu Province, China by using a hybrid approach of fractal theory, information value, and random forest models[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 80(12): 1-23. |
| [45] | ZHANG Q, YAO Y B, WANG Y, et al, 2019. Characteristics of drought in Southern China under climatic warming, the risk, and countermeasures for prevention and control[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 136(3/4): 1 157-1 173. |
| [1] | DUAN Yunxia, CUI Jin, LI Deqin, WANG Yue, BAN Weilong, LIU Qing. Comparative analysis of the characteristics of dry intrusions during two heavy rainfall processes under Northeast Cold Vortex background [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(3): 357-366. |
| [2] | WANG Binyan, WANG Jiajin, XIAO Dixiang, LONG Keji. Evaluation of forecasting ability of four numerical models for heavy precipitation processes in Sichuan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(2): 315-323. |
| [3] | XIAO Yiqing, MA Yongyong, CHEN Xiaoting, AN Dawei, HUANG Shaoni. A short-time heavy precipitation process triggered by a cold front in the Hanjiang Basin of southern Shaanxi and its precipitation forecast verification [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 972-983. |
| [4] | XIAO An, YIN Xiaofei, LIU Xianyao. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of diurnal variation of precipitation in Jiangxi Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(5): 840-848. |
| [5] | XU Min, SHEN Fang, LIU Qiqi, LI Na, WANG Jie. Formation conditions and characteristics of heavy precipitation with quasi-linear MCSs [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(4): 596-604. |
| [6] | SHEN Xiaoyan, SHEN Yanling, QUAN Chen, DU Huali, YAN Yuqian. Verification and comparison of different methods to prediction performance of model products during the heavy precipitations in 2020 in Qinghai Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(2): 333-343. |
| [7] | YANG Tao, YANG Lianmei, ZHANG Yunhui, ZHUANG Xiaocui, HUANG Yan. Circulation Configuration of Synoptic System and Radar Echo Characteristics of Shorttime Heavy Rainfall in Xinjiang [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(4): 631-640. |
| [8] | XIAO Wei, FU Zhao, XU Lili, LIU Weicheng, DI Xiaohong, ZHENG Xin, YANG Xiumei. Comparison of Dynamic Characteristics of Two Short-time Heavy Precipitation Processes of Baroclinic-Frontogenesis in the Early Flood Period of Southeast Gansu [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(4): 641-651. |
| [9] | ZHANG Wulong, KANG Lan, ZHOU Wei, YIN Hang, . Extreme Short-time Heavy Precipitation Forecast Based on GRAPES-MESO Model [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(3): 507-513. |
| [10] | ZHENG Zheng, PAN Lingjie, QIAN Yanzhen, ZHAO Changyu, HUANG Xuanxuan, XIAO Wangxing. Evolution Characteristics of Extreme Heavy Precipitation in Coast of Zhejiang Province Caused by Typhoon Lekima [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(2): 269-278. |
| [11] | SU Junfeng, ZHANG Feng, HUANG Yuxia, LIU Li, ZHANG Qiuyu, WEI Qingxia, ZHANG Yan. Spatial-temporal distribution characteristics and mesoscale analysis of short-time heavy precipitation in Longnan of Gansu Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(06): 966-973. |
| [12] | DONG Xuguang, QIU Can, LIU Huanbin, CHEN Yanchun, YE Dianxiu, LI Shengli. Characteristics of Hourly Heavy Precipitation Changes in Jinan Area [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(6): 892-898. |
| [13] | GAO Song, CHEN Guichuan, WU Zheng, DU Qin, ZHAO Lei, HUYAN Lidou. A Case Analysis of Rainstorm in Sichuan-Chongqing Region Under the Influence of Southwest Vortex [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(4): 597-612. |
| [14] | GUO Jie, SONG Wenwen, ZHENG Hao, LIU Xinchao, . Analysis on Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Areal Precipitation in Dadu River Basin and Rainy Season Transition Indexes [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(3): 370-. |
| [15] | GUO Qu1, CHEN Jia2, LI Rui3, HE Huigen1. Climatic Characteristics of Short Duration Heavy Precipitation in Chongqing [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(6): 944-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||