Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (4): 570-578.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-04-0570
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Aerosol types discrimination in semi-arid region of Northwest China using ground-based lidar data
LIAO Jiayan( ), ZHOU Tian(
), ZHOU Tian( ), HAN Biseng, HUANG Zhongwei, BI Jianrong
), HAN Biseng, HUANG Zhongwei, BI Jianrong
- College of Atmospheric Sciences, Lanzhou University, Key Laboratory of Semi-arid Climate Change, Ministry of Education, Lanzhou 730000, China
-
Received:2022-07-02Revised:2022-12-09Online:2023-08-31Published:2023-08-29
我国西北半干旱区气溶胶类型的地基激光雷达判别
- 兰州大学大气科学学院,半干旱气候变化教育部重点实验室,甘肃 兰州 730000
-
通讯作者:周天(1986—),男,博士,副教授,主要从事气溶胶及其气候效应研究。 E-mail:zhoutian@lzu.edu.cn。 -
作者简介:廖家艳(1999—),女,研究生,主要从事气溶胶及其气候效应研究。 E-mail:liaojy18@lzu.edu.cn。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(41975019);甘肃省科技计划项目(23JRRA1032)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LIAO Jiayan, ZHOU Tian, HAN Biseng, HUANG Zhongwei, BI Jianrong. Aerosol types discrimination in semi-arid region of Northwest China using ground-based lidar data[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(4): 570-578.
廖家艳, 周天, 韩璧森, 黄忠伟, 闭建荣. 我国西北半干旱区气溶胶类型的地基激光雷达判别[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(4): 570-578.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-04-0570
| 典型情形 | 是否穿透气溶胶层 | 体积线性退偏比 | 消光系数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 清洁大气 | 是 | 小 | 小 |
| 人为污染 | 是 | 小 | 大 |
| 沙尘 | 是 | 大 | 大 |
| 强沙尘暴 | 否 | 大 | 大 |
Tab.1 Dominant aerosol type selection criteria
| 典型情形 | 是否穿透气溶胶层 | 体积线性退偏比 | 消光系数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 清洁大气 | 是 | 小 | 小 |
| 人为污染 | 是 | 小 | 大 |
| 沙尘 | 是 | 大 | 大 |
| 强沙尘暴 | 否 | 大 | 大 |

Fig.2 Frequency distribution and probability density distribution of volume linear depolarization ratio and extinction coefficient of severe sandstorm events
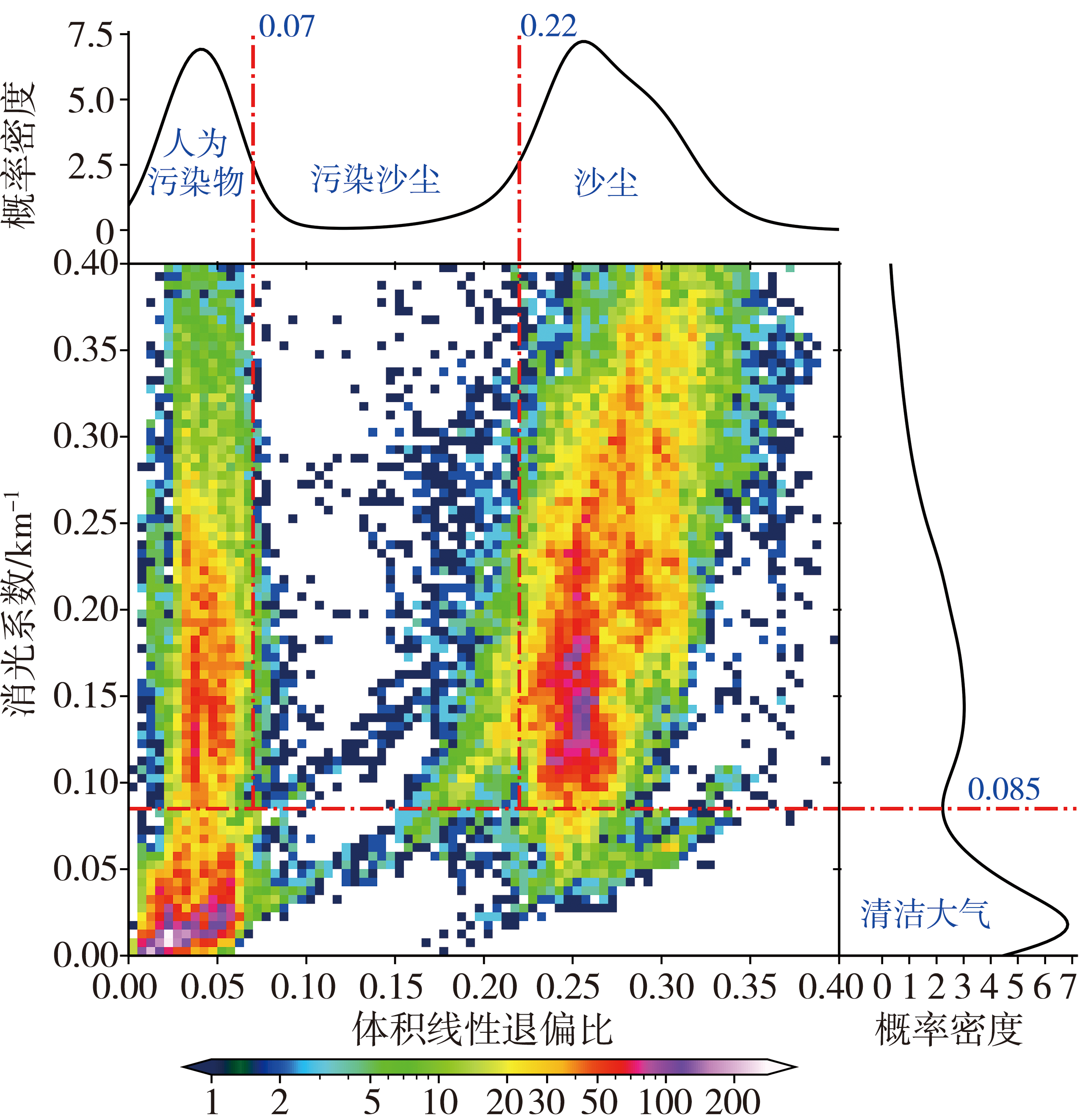
Fig.3 Frequency distribution and probability density distribution of volume linear depolarization ratio and extinction coefficient under the conditions of clean sky, air pollution and dust weathers

Fig.4 Time-height cross sections of backscatter ratio (a), aerosol depolarization ratio (b) and volume linear depolarization ratio (c) and the profiles of each variable at 23:00 UTC (d) on 9 December 2009
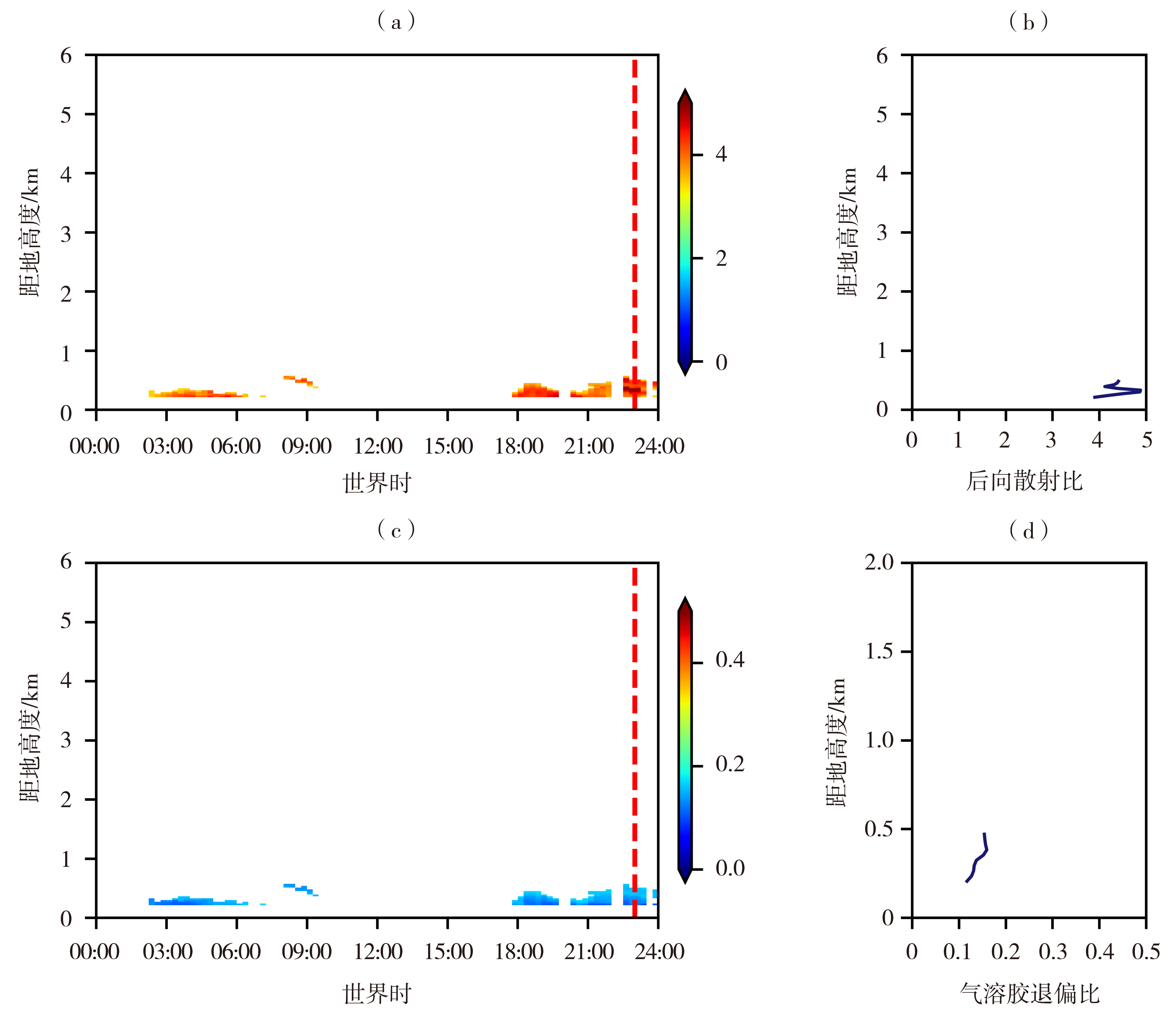
Fig.6 Time-height cross sections of backscatter ratio (a) and aerosol depolarization ratio (c) after data control of aerosol depolarization ratio and profiles of backscatter ratio (b) and aerosol depolarization ratio (d) at 23:00 UTC on 9 December 2009
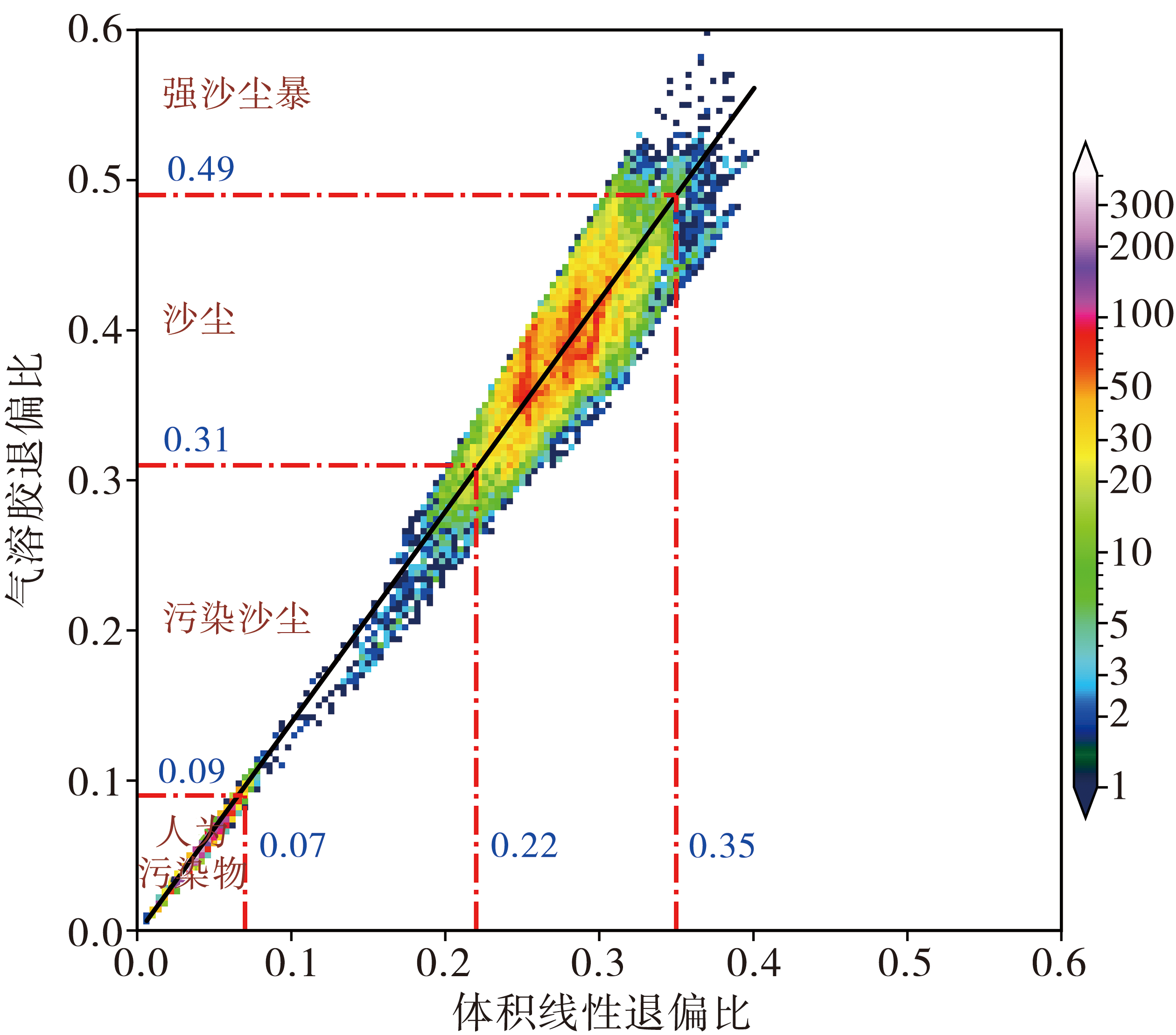
Fig.7 Frequency distribution and linear regression of volume linear depolarization ratio and aerosol depolarization ratio under four typical conditions
| 典型情形 | 消光系数/km-1 | 体积线性 退偏比 | 气溶胶 退偏比 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 清洁大气 | <0.085 | <0.07 | <0.09 |
| 人为污染 | >0.085 | <0.07 | <0.09 |
| 污染沙尘 | >0.085 | >0.07且<0.22 | >0.09且<0.31 |
| 沙尘 | >0.085 | >0.22 | >0.31 |
| 强沙尘暴 | >0.085 | >0.35 | >0.49 |
Tab.2 Discrimination threshold of aerosol types
| 典型情形 | 消光系数/km-1 | 体积线性 退偏比 | 气溶胶 退偏比 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 清洁大气 | <0.085 | <0.07 | <0.09 |
| 人为污染 | >0.085 | <0.07 | <0.09 |
| 污染沙尘 | >0.085 | >0.07且<0.22 | >0.09且<0.31 |
| 沙尘 | >0.085 | >0.22 | >0.31 |
| 强沙尘暴 | >0.085 | >0.35 | >0.49 |
| [1] | 毕鸿儒, 张越, 陈思宇, 等, 2022. 基于MIROC6模式探讨1850—2014年全球不同类型人为气溶胶的时空分布及辐射强迫[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 58(1): 111-117. |
| [2] | 毛毛, 孙昊飞, 2020. 随机取向沙尘气溶胶激光雷达退偏比特性研究[J]. 南京信息工程大学学报(自然科学版), 12(2): 256-260. |
| [3] | 任朝霞, 杨达源, 2007. 西北干旱区近50年气候变化特征与趋势[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 29(1): 99-102. |
| [4] | 姚玉璧, 肖国举, 王润元, 等, 2009. 近50年来西北半干旱区气候变化特征[J]. 干旱区地理, 32(2): 159-165. |
| [5] | 尹宏, 韩志刚, 1989. 气溶胶大气对太阳辐射的吸收[J]. 气象学报, 47(1): 118-123. |
| [6] | 周天, 黄忠伟, 黄建平, 等, 2013. 黄土高原地区云垂直结构的激光雷达遥感研究[J]. 干旱气象, 31(3): 246-253. |
| [7] |
ANDREAS B, TAKUJI N, 2002. Calculation of the calibration constant of polarization lidar and its dependency on atmospheric temperature[J]. Optics Express, 10(16): 805-817.
PMID |
| [8] |
BAARS H, SEIFERT P, ENGELMANN R, et al, 2017. Target categorization of aerosol and clouds by continuous multiwavelength-polarization lidar measurements[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 10(9): 3 175-3 201.
DOI URL |
| [9] | BOUCHER O, RANDALL D, ARTAXO P, et al, 2013. Climate Change 2013: the physical science basis: contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change[C]// Clouds and Aerosols. Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA: Cambridge University Press. |
| [10] |
BURTON S P, FERRARE R A, HOSTETLER C A, et al, 2012. Aerosol classification using airborne high spectral resolution lidar measurements-methodology and examples[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 5(1): 73-98.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
CHEN W N, TSAI F J, CHOU C C K, et al, 2007. Optical properties of Asian dusts in the free atmosphere measured by Raman lidar at Taipei, Taiwan[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 41(36): 7 698-7 714.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
CORDOBA-JABONERO C, SICARD M, ANSMANN A, et al, 2018. Separation of the optical and mass features of particle components in different aerosol mixtures by using POLIPHON retrievals in synergy with continuous polarized Micro-Pulse Lidar (P-MPL) measurements[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 11(8): 4 775-4 795.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
GROβ S, TESCHE M, FREUDENTHALER V, et al, 2011. Characterization of Saharan dust, marine aerosols and mixtures of biomass-burning aerosols and dust by means of multi-wavelength depolarization and Raman lidar measurements during SAMUM 2[J]. Tellus Series B-Chemical and Physical Meteorology, 63(4): 706-724.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
HAN B, ZHOU T, ZHOU X, et al, 2022. A new algorithm of atmospheric boundary layer height determined from polarization lidar[J]. Remote Sensing, 14(21): 5 436-5 460.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
JIN Y, KAI K, SHIBATA T, et al, 2010. Validation of the dust layer structure over the Taklimakan Desert, China by the CALIOP space-borne lidar using ground-based lidar[J]. Sola, 6(36): 121-124.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
KE J, SUN Y, DONG C, et al, 2022. Development of China’s first space-borne aerosol-cloud high-spectral-resolution lidar: retrieval algorithm and airborne demonstration[J]. Photonix, 3(1): 17-37.
DOI |
| [17] |
LIU D, WANG Z, LIU Z, et al, 2008. A height resolved global view of dust aerosols from the first year CALIPSO lidar measurements[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres, 113, D16214. DOI:10.1029/2007JD009776.
DOI |
| [18] | MA X, YU F, LUO G, 2012. Aerosol direct radiative forcing based on GEOS-Chem-APM and uncertainties[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 12(12): 5 563-5 581. |
| [19] |
MA Y, XIN J, MA Y, et al, 2017. Optical properties and source analysis of aerosols over a desert area in Dunhuang, Northwest China[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 34(8): 1 017-1 026.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
MAMOURI R E, ANSMANN A, 2014. Fine and coarse dust separation with polarization lidar[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 7(11): 3 717-3 735.
DOI URL |
| [21] | MYLONAKI M, GIANNAKAKI E, PAPAYANNIS A, et al., 2021. Aerosol type classification analysis using EARLINET multiwavelength and depolarization lidar observations[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 21(3): 2 211-2 227. |
| [22] |
OMAR A H, WINKER D M, KITTAKA C, et al, 2009. The CALIPSO automated aerosol classification and lidar ratio selection algorithm[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 26(10): 1 994-2 014.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
PAN X, UNO I, WANG Z, et al, 2017. Real-time observational evidence of changing Asian dust morphology with the mixing of heavy anthropogenic pollution[J]. Scientific Reports, 7(1): 335-343.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
PREWITT J M S, MENDELSOHN M L, 1966. The analysis of cell images[J]. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 128(3): 1 035-1 053.
DOI URL |
| [25] | QI S, HUANG Z, MA X, et al, 2021. Classification of atmospheric aerosols and clouds by use of dual-polarization lidar measurements[J]. Optics Express, 29(15): 23 461-23 476. |
| [26] | RAMASWAMY V, BOUCHER O, HAIGH J, et al, 2001. TAR Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis[C]// Radiative Forcing of Climate Change. Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA: Cambridge University Press: 353-405. |
| [27] |
SHIMIZU A, SUGIMOTO N, MATSUI I, et al, 2004. Continuous observations of Asian dust and other aerosols by polarization lidars in China and Japan during ACE-Asia[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres, 109, D19S17. DOI:10.1029/2002JD003253.
DOI |
| [28] |
SUGIMOTO N, NISHIZAWA T, SHIMIZU A, et al, 2011. Aerosol classification retrieval algorithms for EARTHCARE/ ATLID, CALIPSO/CALIOP, and ground-based lidars[C]// 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, BC, Canada: IEEE, 4 111-4 114. DOI: 10.1109/igarss.2011.6050137.
DOI |
| [29] |
TOLEDANO C, WIEGNER M, GROSS S, et al, 2011. Optical properties of aerosol mixtures derived from sun-sky radiometry during SAMUM-2[J]. Tellus Series B-Chemical and Physical Meteorology, 63(4): 635-648.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
ZACK G W, ROGERS W E, LATT S A, 1977. Automatic measurement of sister chromatid exchange frequency[J]. Journal of Histochemistry & Cytochemistry, 25(7): 741-753.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
ZHANG Z, HUANG J, CHEN B, et al, 2019. Three-year continuous observation of pure and polluted dust aerosols over northwest China using the ground-based lidar and sun photometer data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres, 124(2): 1 118-1 131.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
ZHOU T, XIE H, BI J, et al, 2018. Lidar measurements of dust aerosols during Three Field Campaigns in 2010, 2011 and 2012 over Northwestern China[J]. Atmosphere, 9(5): 173-193.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
ZHOU T, XIE H L, JIANG T, et al, 2021. Seasonal characteristics of aerosol vertical structure and autumn enhancement of non-spherical particle over the semi-arid region of northwest China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 244, 117912. DOI:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2020.117912.
DOI |
| [1] | QI Yue, ZHANG Qiang, HU Shujuan, WANG Runyuan, YANG Yang, LEI Jun, WANG Heling, ZHAO Hong, CHU Chao, JIN Rong. Response of photosynthetic parameters to leaf temperature of spring maize under drought stress [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(2): 215-222. |
| [2] | ZHANG Linhan, BI Jianrong, ZHANG Xueteng, LI Zhengpeng, ZHAO Changming, MA Xiaojun. Grassland soil respiration characteristics and their influencing factors in semi-arid region of Loess Plateau during the growing season in 2020 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(3): 354-363. |
| [3] | CAO Yueqian, ZHANG Wu, YAO Jingyu, WANG Wei. Variation of Cloud Fraction and Its Relationship with Solar Radiation over Semi-arid Region [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(4): 684-693. |
| [4] | ZHU Yan,ZUO Hongchao,GUO Yang,WU Jianjun. Characteristics of Abnormal Energy Balance Ratio in Semi - Arid Region of Loess Plateau [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2014, 32(5): 719-726. |
| [5] | DIAO Hong, WANG Run-Yuan, MA Feng-Li, SHU Jian-Lan. Effect of Stripe Rust Infection on Photosynthesis and Transpiration of Wheat in the Semi-arid Region [J]. J4, 2004, 22(4): 56-59. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||