Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (3): 450-462.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-03-0450
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Macro and micro physical structure characteristics of a low trough cold front cloud system in southern North China based on aircraft detection
FU Jiao( ), WANG Shuyi, DONG Xiaobo(
), WANG Shuyi, DONG Xiaobo( ), WANG Xiaoqing, YANG Jiashuai, ZHANG Jiannan
), WANG Xiaoqing, YANG Jiashuai, ZHANG Jiannan
- Hebei Provincial Weather Modification Center, Shijiazhuang 050021, China
-
Received:2021-09-09Revised:2022-05-22Online:2023-06-30Published:2023-07-02 -
Contact:DONG Xiaobo
基于飞机探测的华北南部低槽冷锋云系宏微物理结构特征
付娇( ), 王姝怡, 董晓波(
), 王姝怡, 董晓波( ), 王晓青, 杨佳帅, 张健南
), 王晓青, 杨佳帅, 张健南
- 河北省人工影响天气中心,河北 石家庄 050021
-
通讯作者:董晓波 -
作者简介:付娇(1988—),女,河北灵寿人,工程师,主要从事云物理与人工影响天气研究。E-mail:fj_ryb@126.com。 -
基金资助:河北省省级科技计划(20375402D);科技部国家重点研发计划项目(2017YFB0504002)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
FU Jiao, WANG Shuyi, DONG Xiaobo, WANG Xiaoqing, YANG Jiashuai, ZHANG Jiannan. Macro and micro physical structure characteristics of a low trough cold front cloud system in southern North China based on aircraft detection[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(3): 450-462.
付娇, 王姝怡, 董晓波, 王晓青, 杨佳帅, 张健南. 基于飞机探测的华北南部低槽冷锋云系宏微物理结构特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(3): 450-462.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-03-0450
| 仪器名称 | 测量内容 | 测量范围(通道) | 分辨率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| CDP | 云滴粒子数浓度、尺度谱、云中含水量等 | 2~50 μm (30通道) | 各通道分辨率不同 |
| CIP | 大云滴、冰雪晶粒子数浓度、尺度谱、粒子图像等 | 25~1 550 μm (62通道) | 25 μm |
| HVPS | 冰雪晶、雨滴粒子数浓度、尺度谱、粒子图像等 | 150~19 200 μm (61通道) | 各通道分辨率不同 |
| CPI | 云与降水粒子图像 | 10~2 000 μm (—) | 2.3 μm |
| 热线含水量仪 | 液态水含量和总含水量 | 0.05~3 g·m-3(—) | |
| AIMMS-20 | 经纬度 | ||
| 海拔 | 0~13.7 km,精度18.3 m(—) | 1 m | |
| 温度 | -50~50 ℃(—) | 0.01 ℃ |
Tab.1 Airborne instrumentations and their operational parameters
| 仪器名称 | 测量内容 | 测量范围(通道) | 分辨率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| CDP | 云滴粒子数浓度、尺度谱、云中含水量等 | 2~50 μm (30通道) | 各通道分辨率不同 |
| CIP | 大云滴、冰雪晶粒子数浓度、尺度谱、粒子图像等 | 25~1 550 μm (62通道) | 25 μm |
| HVPS | 冰雪晶、雨滴粒子数浓度、尺度谱、粒子图像等 | 150~19 200 μm (61通道) | 各通道分辨率不同 |
| CPI | 云与降水粒子图像 | 10~2 000 μm (—) | 2.3 μm |
| 热线含水量仪 | 液态水含量和总含水量 | 0.05~3 g·m-3(—) | |
| AIMMS-20 | 经纬度 | ||
| 海拔 | 0~13.7 km,精度18.3 m(—) | 1 m | |
| 温度 | -50~50 ℃(—) | 0.01 ℃ |
| 飞行时间 | 飞行高度/m(飞行方式) | 飞行区域 | 机上宏观记录 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10:20:51—10:30:30 | 844~866(水平飞行)① | 赵县 | 赵县高度限制东移 |
| 10:32:21—10:34:27 | 557~575(水平飞行)② | 赵县 | |
| 10:34:31—11:24:14 | 582~6 781(盘旋上升) | 赵县 | 因为限制高度,探测点向东偏移,5 942 m高度出云见蓝天 |
| 10:54:49—10:57:04 | 3 603~3 617(水平飞行)③ | 赵县 | |
| 11:09:57—11:17:04 | 5 445~5 542(水平飞行)④ | 赵县、宁晋、柏乡 | |
| 11:41:14—12:20:07 | 5 705~5 847(水平飞行)⑤ | 高邑、柏乡、临城、赞皇 |
Tab.2 Flight overview
| 飞行时间 | 飞行高度/m(飞行方式) | 飞行区域 | 机上宏观记录 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10:20:51—10:30:30 | 844~866(水平飞行)① | 赵县 | 赵县高度限制东移 |
| 10:32:21—10:34:27 | 557~575(水平飞行)② | 赵县 | |
| 10:34:31—11:24:14 | 582~6 781(盘旋上升) | 赵县 | 因为限制高度,探测点向东偏移,5 942 m高度出云见蓝天 |
| 10:54:49—10:57:04 | 3 603~3 617(水平飞行)③ | 赵县 | |
| 11:09:57—11:17:04 | 5 445~5 542(水平飞行)④ | 赵县、宁晋、柏乡 | |
| 11:41:14—12:20:07 | 5 705~5 847(水平飞行)⑤ | 高邑、柏乡、临城、赞皇 |

Fig.1 The time-height cross section of radar combination reflectivity along the flight trajectory (Unit: dBZ) (Numbers ①-⑤ correspond to Tab.2; Dotted boxes a and b stand for vertical detection period, the flying heights are 582-5 451 m and 5 451-6 781 m, respectively)
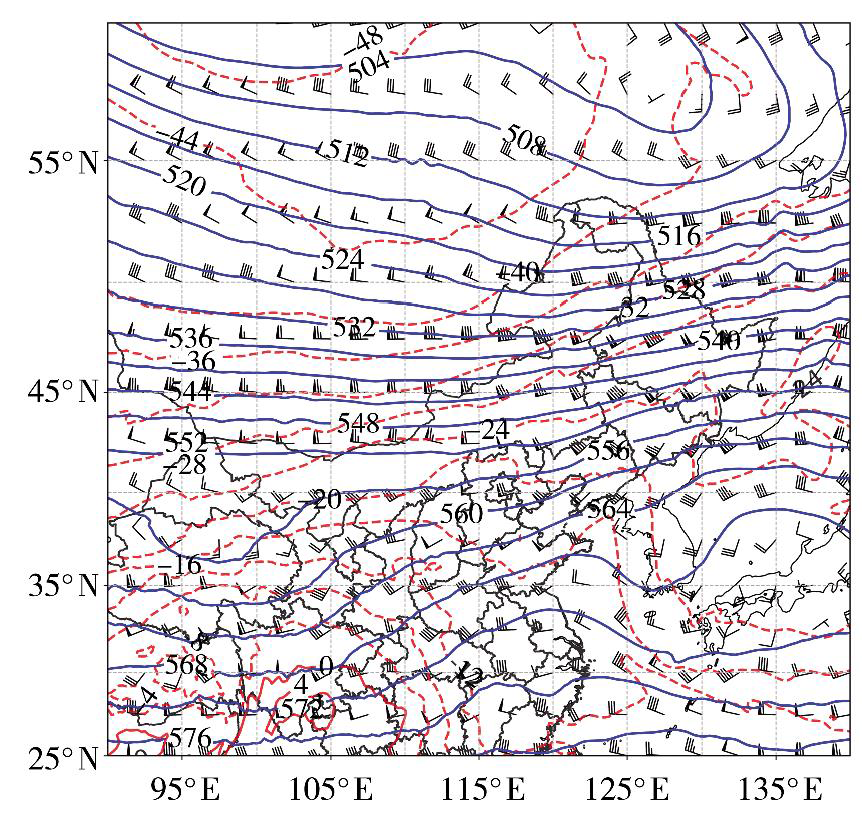
Fig.2 The 500 hPa geopotential height (the blue solid contours, Unit: dagpm), temperature (the red dashed isolines, Unit: ℃) and wind field (wind vectors, Unit: m·s-1) at 08:00 on February 28, 2021
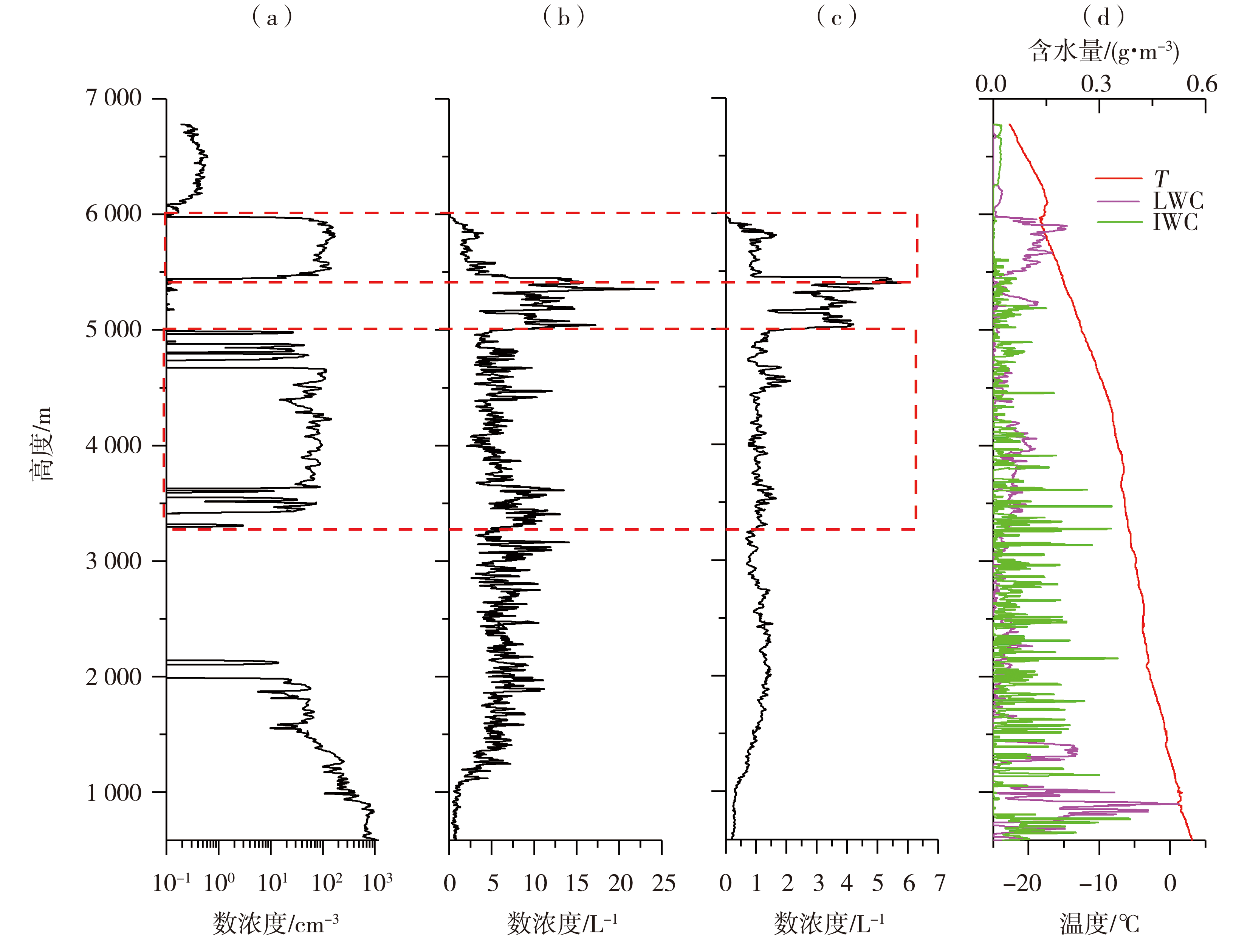
Fig.3 Vertical distribution of cloud particle number concentration detected by CDP (a), CIP (b), HVPS (c) and water content and temperature (d) over Zhaoxian (The red dotted boxes represent the strong seeding areas)

Fig.5 Cloud top height (a, Unit: km) and cloud top temperature (b, Unit: °C) retrieved by FY-2F satellite at 11:00 on February 28, 2021 (The purple box area shows the position of the cloud observed by aircraft at 11:20)

Fig.6 The particle spectrum detected by three types of probe at different level (a) 5 802m, (b) 5 714 m, (c) 5 541 m, (d) 4 651 m, (e) 4 472 m, (f) 4 206 m, (g) 4 025 m, (h)1 387 m, (i) 1 249 m, (j) 997 m
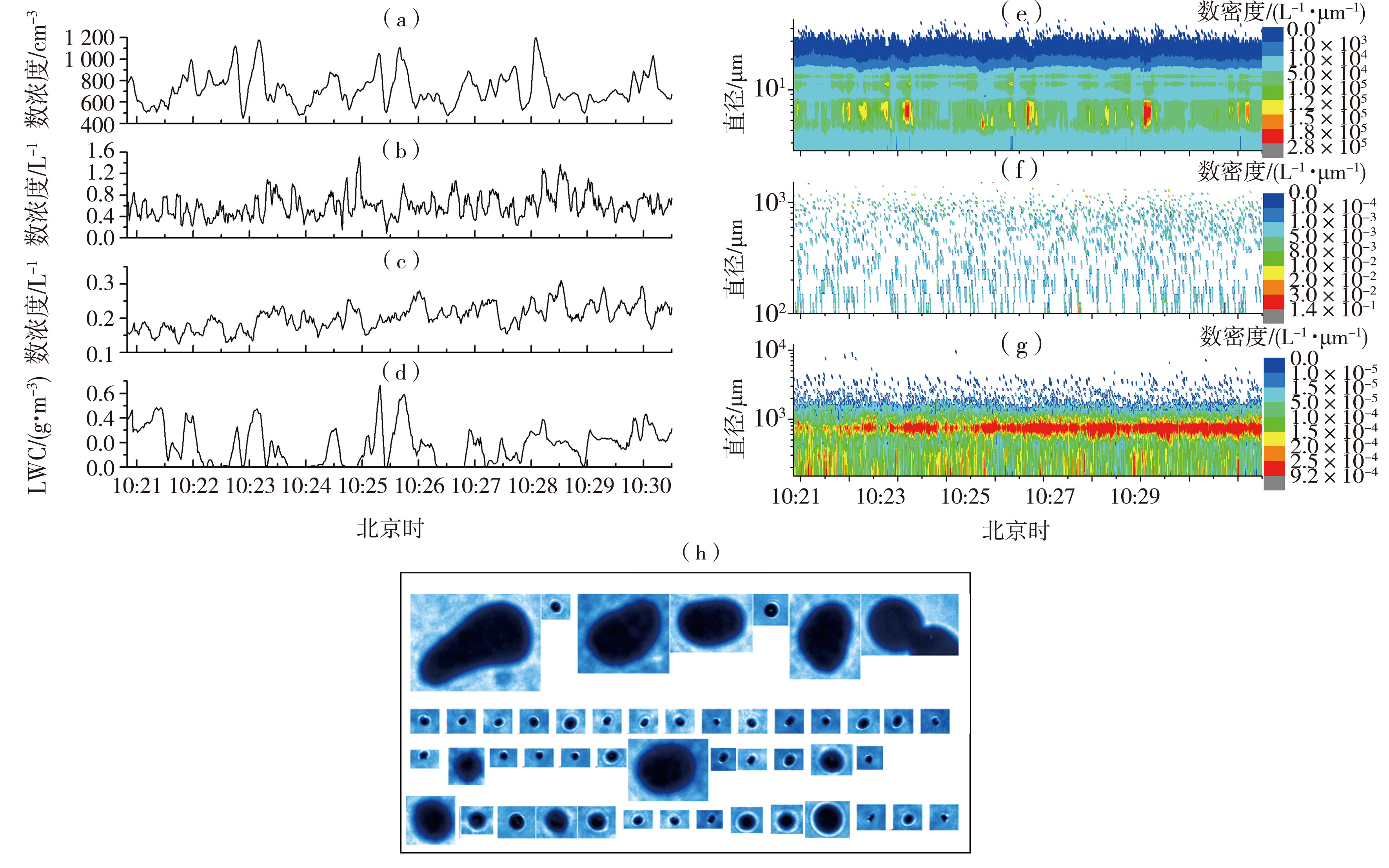
Fig.7 The results detected by the aircraft at flying horizontally stage at a height of 844-866 m (a) particle number concentration detected by CDP, (b) particle number concentration detected by CIP, (c) particle number concentration detected by HVPS, (d) liquid water content, (e) particle spectrum detected by CDP, (f) particle spectrum detected by CIP, (g) particle spectrum detected by HVPS, (h) particle images detected by CPI

Fig.8 The results detected by the aircraft at flying horizontally stage at a height of 557-575 m (a) particle number concentration detected by CDP, (b) particle number concentration detected by CIP, (c) particle number concentration detected by HVPS, (d) liquid water content, (e) particle spectrum detected by CDP, (f) particle spectrum detected by CIP, (g) particle spectrum detected by HVPS, (h) particle images detected by CPI

Fig.9 The results detected by the aircraft at flying horizontally stage at a height of 3 603-3 617 m (a) particle number concentration detected by CDP, (b) particle number concentration detected by CIP, (c) particle number concentration detected by HVPS, (d) liquid water content, (e) particle spectrum detected by CDP, (f) particle spectrum detected by CIP, (g) particle spectrum detected by HVPS, (h) particle images detected by CPI

Fig.10 The results detected by the aircraft at flying horizontally stage at a height of 5 445-5 542 m (a) particle number concentration detected by CDP, (b) particle number concentration detected by CIP, (c) particle number concentration detected by HVPS, (d) liquid water content, (e) particle spectrum detected by CDP, (f) particle spectrum detected by CIP, (g) particle spectrum detected by HVPS, (h) particle images detected by CPI

Fig.11 The results detected by the aircraft at flying horizontally stage at a height of 5 705-5 847 m (a) particle number concentration detected by CDP, (b) particle number concentration detected by CIP, (c) particle number concentration detected by HVPS, (d) liquid water content, (e) particle spectrum detected by CDP, (f) particle spectrum detected by CIP, (g) particle spectrum detected by HVPS, (h) particle images detected by CPI
| [1] |
康增妹, 孙玉稳, 董晓波, 等, 2020. 一次冬季层状云的人工催化效果响应分析[J]. 高原气象, 39(3): 620-627.
DOI |
| [2] | 雷恒池, 洪延超, 赵震, 等, 2008. 近年来云降水物理和人工影响天气研究进展[J]. 大气科学, 32(4): 967-974. |
| [3] |
李宝东, 孙玉稳, 孙霞, 2014. 河北春季一次飞机人工增雪的综合分析[J]. 干旱气象, 32(5): 819-829.
DOI |
| [4] | 李义宇, 李培仁, 封秋娟, 2011. 一次层状云降水过程云粒子的特征分析[J]. 山西气象, 96(3): 34-46. |
| [5] | 刘伟, 孙玉稳, 谢祥永, 等, 2021. 河北省冬季低槽冷锋层状云结构特征和可播性分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 37(3): 110-116. |
| [6] | 庞朝云, 张丰伟, 张建辉, 2013. 西北干旱地区一次降水性层状云的飞机观测分析[J]. 干旱气象, 31(2): 272-277. |
| [7] | 彭冲, 周毓荃, 蔡兆鑫, 等, 2016. 一次基于飞机观测的低槽冷锋云系微物理结构的综合分析[J]. 大气科学学报, 39(5): 620-632. |
| [8] | 彭亮, 姚展予, 戴进, 2007. 河南春季一次云降水过程的宏微观物理特征分析[J]. 气象, 33(5): 3-11. |
| [9] |
秦彦硕, 刘世玺, 范根昌, 等, 2015. 华北地区春季一次层状云的微物理特征及可播性分析[J]. 干旱气象, 33(3): 481-489.
DOI |
| [10] | 石爱丽, 2005. 层状云降水微物理特征及降水机制研究概述[J]. 气象科技, 33( 2): 104-108. |
| [11] | 孙霞, 银燕, 韩洋, 等, 2012. 石家庄地区雾霾天气下云滴和云凝结核的分布特征[J]. 中国环境科学, 32(7): 1 165-1 170. |
| [12] |
孙玉稳, 李宝东, 刘伟, 等, 2015. 河北秋季层状云物理结构及适播性分析[J]. 高原气象, 34(1): 237-250.
DOI |
| [13] | 陶树旺, 刘卫国, 李念童, 等, 2001. 层状冷云人工增雨可播性实时识别技术研究[J]. 应用气象学报, 12(增刊1): 14-22. |
| [14] | 张景红, 孟辉, 于翠红, 等, 2020. 人工增雨催化响应试验分析[J]. 干旱气象, 38(6): 1 043-1 051. |
| [15] |
RANGNO A L, HOBBS P V, 2005. Microstructures and precipitation development in cumulus and small cumulonimbus clouds over the warm pool of the tropical Pacific Ocean[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 131: 639-673.
DOI URL |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
