Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (5): 791-803.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-05-0791
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Evapotranspiration-precipitation coupling strength response to hydrothermal factors over northern China
LI Liang( ), YANG Zesu(
), YANG Zesu( ), HE Hang
), HE Hang
- College of Atmospheric Sciences, Chengdu University of Information Technology, Plateau Atmospheric and Environment Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Chengdu 610225, China
-
Received:2022-09-23Revised:2022-10-03Online:2022-10-31Published:2022-11-10 -
Contact:YANG Zesu
中国北方蒸散-降水耦合度时空变化与水热因子的关系
- 成都信息工程大学大气科学学院,高原大气与环境四川省重点实验室,四川 成都 610225
-
通讯作者:杨泽粟 -
作者简介:李梁(2001—),男,学士,主要从事陆面过程研究. E-mail:3011974904@qq.com。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(42205071);国家自然科学基金重点项目(42230611);第二次青藏高原综合科学考察研究项目(2019QZKK0102)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LI Liang, YANG Zesu, HE Hang. Evapotranspiration-precipitation coupling strength response to hydrothermal factors over northern China[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(5): 791-803.
李梁, 杨泽粟, 何杭. 中国北方蒸散-降水耦合度时空变化与水热因子的关系[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(5): 791-803.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-05-0791

Fig.2 Spatial distribution of climate state (a, c) and standard deviation (b, d) of annual precipitation (a, b) and evapotranspiration (c, d) in northern China (Unit: mm)

Fig.3 Spatial distribution of total evapotranspiration-precipitation coupling strength in northern China (the circle dot areas passing α=0.05 significance test. the same as below)

Fig.4 Spatial distribution of evapotranspiration-precipitation coupling strength in northern China in winter (a), spring (b), summer (c) and autumn (d)

Fig.6 The spatial distribution of climate state (a, c) and standard deviation (b, d) of soil moisture (a,b) and air temperature (c, d) (Unit: ℃) in northern China
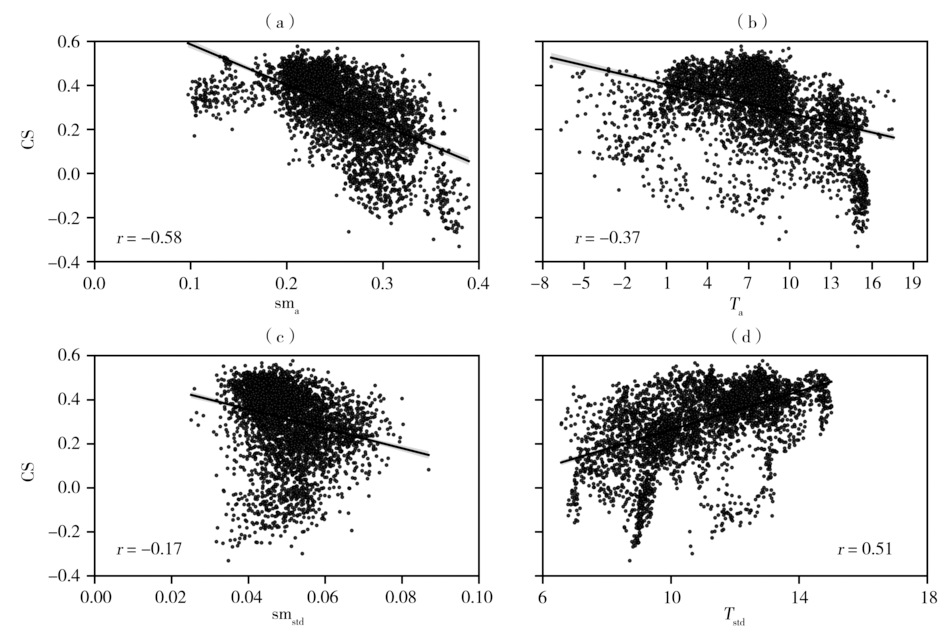
Fig.7 The scatter plots of evapotranspiration-precipitation coupling strength with average soil moisture (a), average temperature (b), soil moisture standard deviation (c) and temperature standard deviation (d)

Fig.8 Multiple linear regression of evapotranspiration-precipitation coupling strength with average soil moisture and average temperature (a), and soil moisture standard deviation and temperature standard deviation (b)

Fig.9 Intra-annual (a) and inter-annual (b) fluctuations of evapotranspiration-precipitation coupling strength in different dry and wet climate background regions
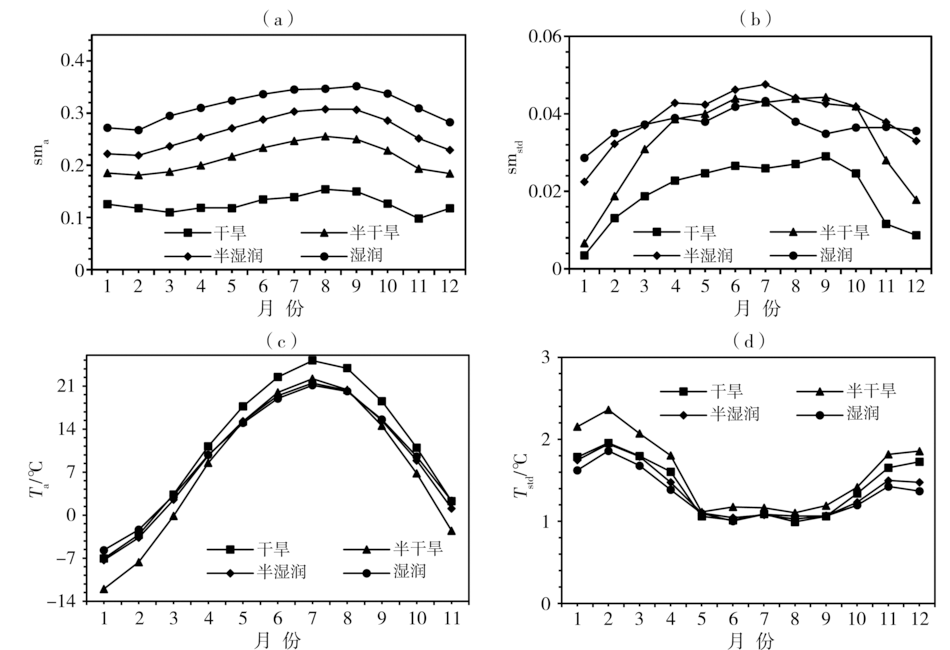
Fig.10 Monthly change of climate state (a, c) and standard deviation (b, d) of soil moisture (a, b), temperature (c, d)in different dry and wet climate background regions
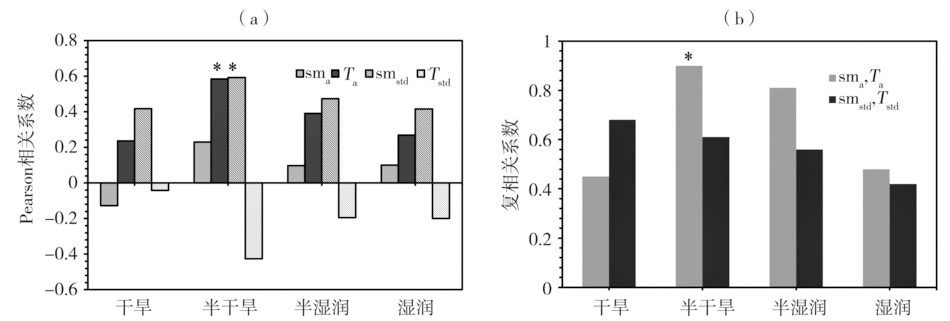
Fig.11 Pearson correlation coefficients of evapotranspiration-precipitation coupling strength with average soil moisture, average temperature, soil moisture standard deviation, temperature standard deviation (a), and complex correlation coefficients of evapotranspiration-precipitation coupling strength with average soil moisture and average temperature, and with soil moisture standard deviation, temperature standard deviation (b)in different dry and wet climate background regions (the asterisk indicates correlation coefficient or multiple correlation coefficient passing α=0.05 significance test. the same as below)

Fig.12 Inter-annual variation of average soil moisture (a) and soil moisture standard deviation (b), average temperature (c) and temperature standard deviation (d) in different dry and wet climate background regions in the northern China

Fig.13 Pearson correlation coefficients of evapotranspiration-precipitation coupling strength with average soil moisture, average temperature, soil moisture standard deviation, temperature standard deviation (a), and complex correlation coefficients of evapotranspiration-precipitation coupling strength with average soil moisture and average temperature, and with soil moisture standard deviation, temperature standard deviation (b) in different dry and wet climate background regions
| [1] |
黄荣辉. 我国重大气候灾害的形成机理和预测理论研究[J]. 地球科学进展, 2006, 21(6): 564-575.
DOI |
| [2] |
SENEVIRATNE S I, LüTHI D, LITSCHI M, et al. Land-atmosphere coupling and climate change in Europe[J]. Nature, 2006, 443(7108): 205-209.
DOI URL |
| [3] | 张井勇, 吴凌云. 陆-气耦合增加中国的高温热浪[J]. 科学通报, 2011, 56(23): 1905-1909. |
| [4] | ZHOU S, WILLIAMS A P, BERG A M, et al. Land-atmosphere feedbacks exacerbate concurrent soil drought and atmospheric aridity[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2019, 116(38): 18 848-18 853. |
| [5] |
KOSTER R D. Regions of strong coupling between soil moisture and precipitation[J]. Science, 2004, 305(5687): 1138-1140.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
ZENG X, BARLAGE M, CASTRO C, et al. Comparison of land-precipitation coupling strength using observations and models[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2010, 11(4): 979-994.
DOI URL |
| [7] | DIRMEYER P A. The terrestrial segment of soil moisture-climate coupling[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2011, 38(16): L16702. |
| [8] |
KOSTER R D, SUAREZ M J, LIU P, et al. Realistic Initialization of land surface states: impacts on subseasonal forecast skill[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2004, 5(6): 1049-1063.
DOI URL |
| [9] | 陈海山, 周晶. 土壤湿度年际变化对中国区域极端气候事件模拟的影响研究Ⅱ.敏感性试验分析[J]. 大气科学, 2013, 37(1): 1-13. |
| [10] | 单机坤, 沈学顺, 李维京. 陆气相互作用对中尺度对流系统影响的研究进展[J]. 气象, 2013, 39(11): 1413-1421. |
| [11] | 岳平, 张强, 赵文, 等. 黄土高原半干旱草地生长季干湿时段环境因子对陆面水、热交换的影响[J]. 中国科学:D辑地球科学, 2015, 45(8): 1229-1242. |
| [12] | 郭维栋, 马柱国, 姚永红. 近50年中国北方土壤湿度的区域演变特征[J]. 地理学报, 2003, 58(增刊1): 83-90. |
| [13] |
WILLIAMS I N, TORN M S. Vegetation controls on surface heat flux partitioning, and land-atmosphere coupling[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2015, 42(21): 9416-9424.
DOI URL |
| [14] | 曾毓金, 谢正辉. 基于CMIP5模拟的中国区域陆气耦合强度评估及未来情景预估[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2015, 20(3): 337-346. |
| [15] | 张述文, 刘源, 曹帮军, 等. GLDAS和CMIP5产品的中国土壤湿度-降水耦合分析及变化趋势[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2016, 21(2): 188-196. |
| [16] |
SENEVIRATNE S I, CORTI T, DAVIN E L, et al. Investigating soil moisture-climate interactions in a changing climate: a review[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2010, 99(3): 125-161.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
ELTAHIR E A B, BRAS R L. Precipitation recycling[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1996, 34(3): 367-378.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
WEI J, DIRMEYER P A. Toward understanding the large-scale land-atmosphere coupling in the models: roles of different processes[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2010, 37, L19707. DOI:10.1029/2010GL044769.
DOI |
| [19] |
GOESSLING H F, REICK C H. What do moisture recycling estimates tell us? Exploring the extreme case of non-evaporating continents[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2011, 15(10): 3217-3235.
DOI URL |
| [20] | 左志燕, 张人禾. 中国东部夏季降水与春季土壤湿度的联系[J]. 科学通报, 2007, 54(14): 1722-1724. |
| [21] |
GAO C, CHEN H, LI G, et al. Land-atmosphere interaction over the Indo-China Peninsula during spring and its effect on the following summer climate over the Yangtze River basin[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2019, 53(9/10): 6181-6198.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
FINDELL K L, ELTAHIR E A B. Atmospheric controls on soil moisture-boundary layerinteractions. part I: framework development[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2003, 4(3): 552-569.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
BERG A, FINDELL K, LINTNER B R, et al. Precipitation sensitivity to surface heat fluxes over North America in reanalysis and model data[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2013, 14(3): 722-743.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
SANTANELLO J A, DIRMEYER P A, FERGUSON C R, et al. Land-atmosphere interactions: the LoCo perspective[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2018, 99(6): 1253-1272.
DOI URL |
| [25] | 张宏升, 刘新建, 朱好, 等. 北京北郊冬季大风过程湍流通量演变特征的分析研究[J]. 大气科学, 2010, 34(3): 661-668. |
| [26] |
DIRMEYER P A, CHEN L, WU J, et al. Verification of land-atmosphere coupling in forecast models, reanalyses and land surface models using flux site observations[J]. Journal of hydrometeorology, 2018, 19(2): 375-392.
DOI URL |
| [27] | WEI J, DIRMEYER P A. Dissecting soil moisture-precipitation coupling[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2012, 39(19): 1-6. |
| [28] |
GUO Z, DIRMEYER P A. Interannual variability of land-atmosphere coupling strength[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2013, 14(5): 1636-1646.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
PHILLIPS T J, KLEIN S A. Land-atmosphere coupling manifested in warm-season observations on the U.S. southern great plains[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2014, 119(2): 509-528.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
RUSCICA R C, SöRENSSON A A, MENéNDEZ C G. Pathways between soil moisture and precipitation in southeastern South America[J]. Atmospheric Science Letters, 2015, 16(3): 267-272.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
RUSCICA R C, MENéNDEZ C G, SöRENSSON A A. Land surface-atmosphere interaction in future South American climate using a multi-model ensemble[J]. Atmospheric Science Letters, 2016, 17(2): 141-147.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
PETROVA I Y, VAN HEERWAARDEN C C, HOHENE-GGER C, et al. Regional co-variability of spatial and temporal soil moisture-precipitation coupling in North Africa: an observational perspective[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2018, 22(6): 3275-3294.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
LI M, MA Z, GU H, et al. Production of a combined land surface data set and its use to assess land-atmosphere coupling in China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2017, 122(2): 948-965.
DOI URL |
| [34] | 杨扬, 杨启东, 王芝兰, 等. 中国区域陆气耦合强度的时空分布特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(3): 374-385. |
| [35] |
GAO C, CHEN H, SUN S, et al. Regional features and seasonality of land-atmosphere coupling over eastern China[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2018, 35(6): 689-701.
DOI URL |
| [36] | 赵靖川, 刘树华. 植被变化对西北地区陆气耦合强度的影响[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(1): 47-62. |
| [37] | 张强, 杨泽粟, 郝小翠, 等. 北方蒸散对气候变暖响应随降水类型转换特征[J]. 科学通报, 2018, 63(11): 1035-1049. |
| [38] | HOBEICHI S, ABRAMOWITZ G, EVANS J, et al. Derived Optimal Linear Combination Evapotranspiration (DOLCE): a global gridded synthesis ET estimate[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences (Online), 2018, 22(2): 1317-1336 |
| [39] |
HE J, YANG K, TANG w, et al. The first high-resolution meteorological forcing dataset for land process studies over China[J]. Scientific Data, 2020, 7(5): 1-15.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
GRUBER A, SCANLON T, VAN DER SCHALIE R, et al. Evolution of the ESA CCI Soil Moisture climate data records and their underlying merging methodology[J]. Earth System Science Data, 2019, 11(2): 717-739.
DOI URL |
| [41] | ALLEN R, PEREIRA L, RAES D, et al. Crop evapotranspiration, Guidelines for computing crop water requirements-FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56[R]. Rome: FAO, 1998. |
| [1] | WANG Xiaochen, MA Xueqing, HE Huayun, REN Siqi, TANG Shuyue, ZHAO Jinyuan, PAN Zhihua, WANG Jing, PAN Xuebiao, HU Qi, . Characteristics of dry and wet changes in sunflower growing areas in northern China and their causes from 1961 to 2020 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 1033-1041. |
| [2] | CHEN Yanli, TANG Meirong, ZHANG Hui, MO Jianfei, QIAN Shuan. Response difference of fractional vegetation cover and net primary productivity to SPEI drought index in karst areas of Guangxi [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 1042-1050. |
| [3] | DU Haolin, WANG Sheng, QIAO Liang, SUN Xuying. Analysis of instrument accuracy and observation error of land surface process observation experiment in semi-arid area [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(3): 364-374. |
| [4] | AN Linli, HUANG Jianping, REN Yu, ZHANG Guolong. Characteristic and cause analysis of terrestrial water storage change in drylands of northern China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(2): 169-178. |
| [5] | YU Jing,WANG Ying,GAO Yamin,QI Jiahui,FU Ming. Spatio-temporal Variation Characteristics of Surface Evapotranspiration in the Korqin Grassland Based on MOD16 Products [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(5): 831-837. |
| [6] | ZHANG Yachun, MA Yaoming, MA Weiqiang, WANG Binbin, WANG Yuyang, . Evapotranspiration Variation and Its Correlation with Meteorological Factors on Different Underlying Surfaces of the Tibetan Plateau [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(3): 366-373. |
| [7] | HOU Qiong, MIAO Bailing, WANG Yingshun, DONG Chunli. Effects of Water Stress on Soil Moisture in Semiarid Typical Steppe [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(6): 987-993. |
| [8] | TAN Yanjing, HU Chengda, SHI Guifen. Spatio-temporal Variation Characteristics of Reference Crop Evapotranspiration and Its Influencing Factors in Huang-Huai-Hai Region [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(5): 794-803. |
| [9] | HUANG Shan, YANG Yang, WANG Hanjia, YANG Qidong. Spatio-temporal Characteristics of Sensible and Latent Heat Flux in Southwest China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(4): 601-611. |
| [10] | SHI Shangyu, WANG Fei, JIN Kai, DING Wenbin. Response of Vegetation Index to Meteorological Drought over Loess Plateau [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(1): 1-13. |
| [11] | WANG Long, GONG Huili, PAN Yun, MIAO Bailing, YANG Jingjing, CUI Xintong. Retrieval of Soil Moisture in Typical Steppe of Xilinhot Based on Sentinel-1 SAR Data [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(6): 979-986. |
| [12] | JIN Hongmei, QIAO Liang, YAN Pengcheng, ZHANG Wei, GAO Shiyu, ZHANG Jin. Nonlinear Characteristics of Drought in Northwest China Based on Approximate Entropy [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(5): 713-721. |
| [13] | HU Die, SHA Sha, WANG Lijuan, WANG Wei. Drought Monitoring Applications of the European Space Agency Climate Change Initiative Soil Moisture Combined Product in Gansu Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(4): 517-528. |
| [14] | JING Hua, KANG Xiuli, MA Aiping, WANG Yuzhi, CUI Huanhu, ZHANG Jiancheng. Effect of Different Altitudes on Characteristics of Soil Water and Water Use Efficiency in Wheat Fields [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(4): 656-662. |
| [15] | CHEN Yanli, MENG Liangli, HUANG Xiaohan, MO Jianfei, WANG Ying, MO Weihua. Temporal and Spatial Distributions of Drought in Guangxi Karst Area During 1971-2017 Based on Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(3): 353-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

