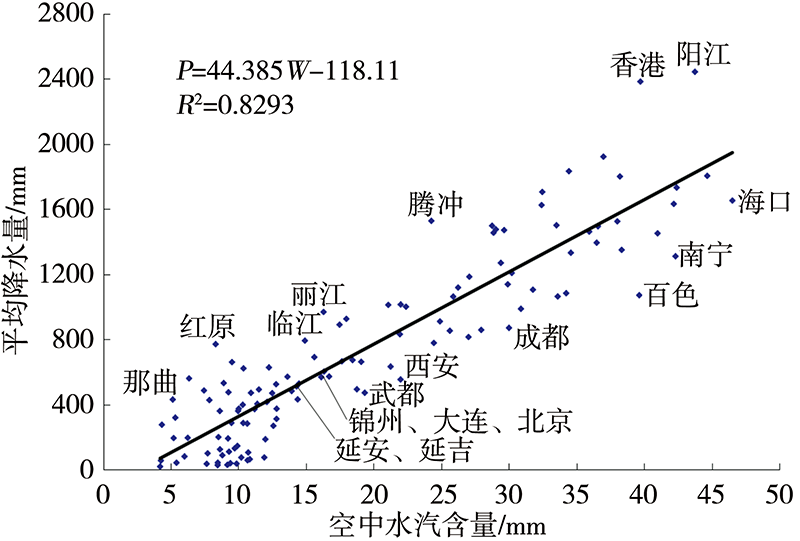
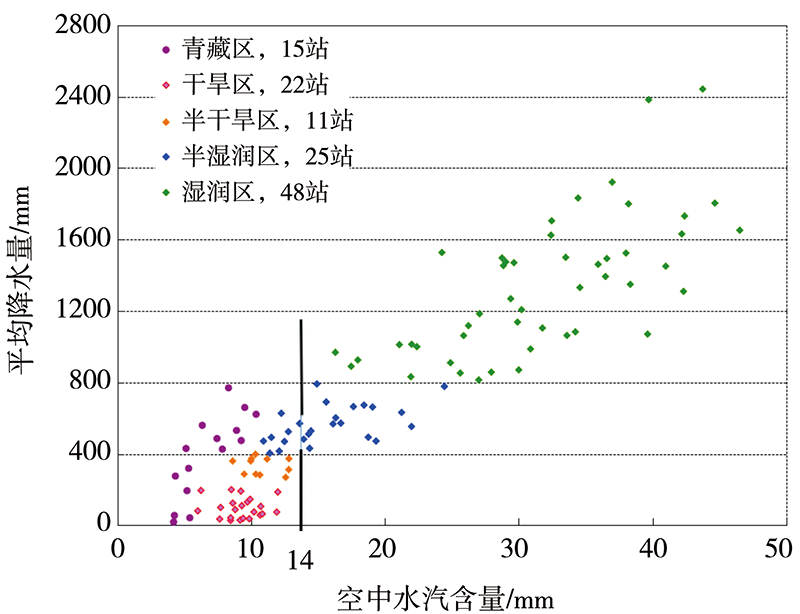
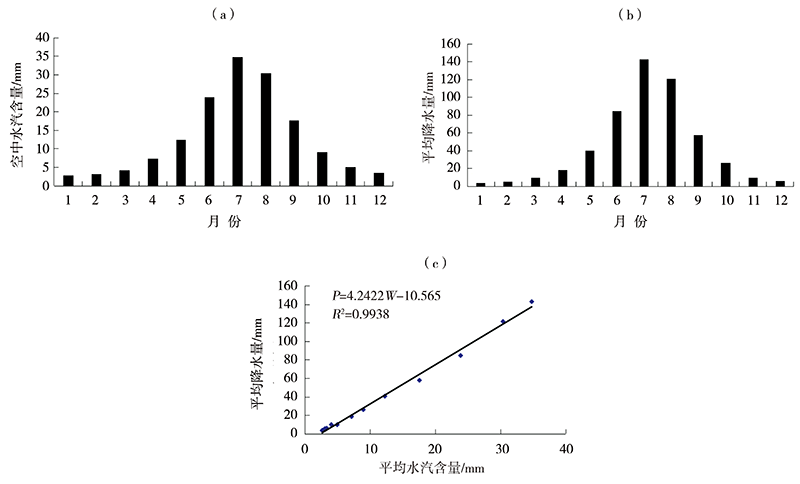
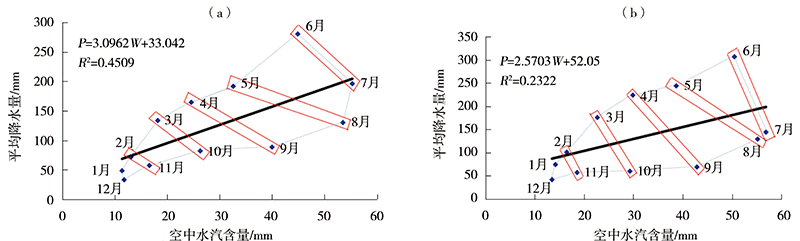
Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (4): 710-719.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-04-0710
• Contention • Previous Articles
Statistical relationship between average precipitation and air water vapor content in China
TAN Chenglong1( ), TAN Jia2
), TAN Jia2
- 1. Zhuhai Public Security Bureau of Guangdong Province,Zhuhai 519070, Guangdong, China
2. Zhuhai Power Supply Bureau of Guangdong Province,Zhuhai 519000, Guangdong, China
-
Received:2022-01-26Revised:2022-04-19Online:2022-08-31Published:2022-09-22
中国陆地平均降水量与空中水汽含量的统计关系分析
- 1. 广东省珠海市公安局,广东 珠海 519070
2. 广东省珠海市供电局,广东 珠海 519000
-
作者简介:檀成龙(1961—),男,工程师,安徽省安庆市人,从事水循环相关研究.E-mail:zhxftcl@sina.com。
CLC Number:
Cite this article
TAN Chenglong, TAN Jia. Statistical relationship between average precipitation and air water vapor content in China[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(4): 710-719.
檀成龙, 檀佳. 中国陆地平均降水量与空中水汽含量的统计关系分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(4): 710-719.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-04-0710
| 区域 | 降水量P/mm |
|---|---|
| 干旱区 半干旱区 半湿润区 湿润区 | P 200≤P 400≤P P≥800 |
Tab.1 Regional division based on precipitation
| 区域 | 降水量P/mm |
|---|---|
| 干旱区 半干旱区 半湿润区 湿润区 | P 200≤P 400≤P P≥800 |
| 区域 | 序号 | 站名 | 1月水汽含量/mm | 7月水汽含量/mm | 多年平均水汽含量/mm | 多年平均降水量/mm | 逐月降水量与水汽含量的 线性拟合公式 | 相关判定系数R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 半湿润区 | 1 | 伊春 | 2.4 | 33.1 | 12.26 | 627.0 | P=5.0219W-9.3105 | 0.9965 |
| 2 | 哈尔滨 | 2.7 | 34.8 | 12.79 | 524.3 | P=4.2422W-10.565 | 0.9938 | |
| 3 | 延安 | 4.3 | 32.1 | 14.3 | 510.7 | P=4.0302W-15.073 | 0.9924 | |
| 4 | 嫩江 | 2.3 | 31.8 | 11.52 | 492.0 | P=4.5091W-10.929 | 0.9888 | |
| 5 | 张家口 | 2.8 | 30.0 | 11.4 | 403.6 | P=3.9477W-11.371 | 0.9886 | |
| 6 | 延吉 | 3.0 | 37.1 | 14.48 | 528.3 | P=3.5282W-7.0458 | 0.9878 | |
| 7 | 成山头 | 5.3 | 41.3 | 17.65 | 664.7 | P=3.7271W-10.391 | 0.9838 | |
| 8 | 太原 | 3.8 | 34.1 | 14.38 | 431.2 | P=3.3141W-11.716 | 0.9826 | |
| 9 | 平凉 | 4.3 | 28.9 | 13.94 | 482.3 | P=4.0125W-15.749 | 0.9816 | |
| 10 | 沈阳 | 3.4 | 41.0 | 15.62 | 690.3 | P=4.2497W-8.8323 | 0.9806 | |
| 11 | 长春 | 3.0 | 36.3 | 13.63 | 570.4 | P=4.4467W-13.061 | 0.9805 | |
| 12 | 临江 | 3.3 | 38.0 | 14.92 | 791.7 | P=4.9189W-7.3986 | 0.9776 | |
| 13 | 齐齐哈尔 | 2.6 | 33.3 | 12.11 | 415.7 | P=3.7259W-10.514 | 0.9770 | |
| 14 | 青岛 | 5.6 | 45.4 | 19.08 | 662.1 | P=3.4176W-10.045 | 0.9770 | |
| 15 | 锦州 | 3.4 | 41.3 | 16.13 | 567.8 | P=4.0463W-17.964 | 0.9753 | |
| 16 | 大连 | 4.3 | 40.8 | 16.33 | 601.9 | P=3.9509W-14.372 | 0.9731 | |
| 17 | 武都 | 6.8 | 36.2 | 19.34 | 471.9 | P=3.1394W-21.397 | 0.9688 | |
| 18 | 巴塘 | 3.5 | 24.7 | 12.5 | 469.5 | P=5.3258W-27.448 | 0.9518 | |
| 19 | 郑州 | 6.5 | 47.6 | 21.25 | 632.4 | P=3.0117W-11.308 | 0.9443 | |
| 20 | 济南 | 5.1 | 44.8 | 18.44 | 672.7 | P=4.5406W-27.67 | 0.9415 | |
| 21 | 索伦 | 2.3 | 30.0 | 10.93 | 471.4 | P=5.015W-15.548 | 0.9323 | |
| 22 | 北京 | 3.6 | 42.4 | 16.71 | 571.9 | P=4.3912W-25.72 | 0.9299 | |
| 23 | 邢台 | 4.9 | 44.8 | 18.76 | 493.4 | P=3.2789W-20.391 | 0.9284 | |
| 24 | 南阳 | 8.7 | 51.0 | 24.45 | 777.7 | P=3.3177W-16.31 | 0.9214 | |
| 25 | 西安 | 7.5 | 44.1 | 21.99 | 553.3 | P=2.2165W-2.6368 | 0.8380 | |
| 以上25站平均 | 4.2 | 37.8 | 15.80 | 563.1 | 平均斜率3.9750 | 0.9637 | ||
| 青藏高原核心区 | 26 | 那曲 | 1.3 | 11.5 | 5.15 | 430.2 | P=9.7728W-14.48 | 0.9846 |
| 27 | 昌都 | 2.5 | 19.0 | 9.27 | 474.5 | P=6.1027W-17.01 | 0.9914 | |
| 28 | 合作 | 2.5 | 17.9 | 8.92 | 531.4 | P=6.8229W-16.616 | 0.9750 | |
| 29 | 玉树 | 2.2 | 15.4 | 7.46 | 485.8 | P=7.7386W-17.233 | 0.9607 | |
| 30 | 拉萨 | 1.7 | 17.3 | 7.86 | 426.4 | P=7.1666W-20.776 | 0.9381 | |
| 31 | 甘孜 | 2.9 | 18.7 | 9.53 | 659.8 | P=7.7457W-18.794 | 0.9263 | |
| 32 | 格尔木 | 2.4 | 11.9 | 5.43 | 42.2 | P=1.1552W-2.7601 | 0.9037 | |
| 33 | 都兰 | 1.9 | 12.2 | 5.22 | 193.8 | P=3.7764W-3.5503 | 0.8437 | |
| 34 | 德钦 | 3.7 | 19.6 | 10.38 | 621.6 | P=5.5276W-5.5483 | 0.8303 | |
| 35 | 茫崖 | 1.7 | 10.0 | 4.28 | 55.4 | P=1.7705W-2.9523 | 0.6632 | |
| 以上10站平均 | 2.3 | 15.4 | 8.35 | 392.1 | 平均斜率5.7579 | 0.9017 | ||
Tab.2 The fitting relationships of monthly average precipitation and water vapor content in half humid zones and the key areas of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau
| 区域 | 序号 | 站名 | 1月水汽含量/mm | 7月水汽含量/mm | 多年平均水汽含量/mm | 多年平均降水量/mm | 逐月降水量与水汽含量的 线性拟合公式 | 相关判定系数R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 半湿润区 | 1 | 伊春 | 2.4 | 33.1 | 12.26 | 627.0 | P=5.0219W-9.3105 | 0.9965 |
| 2 | 哈尔滨 | 2.7 | 34.8 | 12.79 | 524.3 | P=4.2422W-10.565 | 0.9938 | |
| 3 | 延安 | 4.3 | 32.1 | 14.3 | 510.7 | P=4.0302W-15.073 | 0.9924 | |
| 4 | 嫩江 | 2.3 | 31.8 | 11.52 | 492.0 | P=4.5091W-10.929 | 0.9888 | |
| 5 | 张家口 | 2.8 | 30.0 | 11.4 | 403.6 | P=3.9477W-11.371 | 0.9886 | |
| 6 | 延吉 | 3.0 | 37.1 | 14.48 | 528.3 | P=3.5282W-7.0458 | 0.9878 | |
| 7 | 成山头 | 5.3 | 41.3 | 17.65 | 664.7 | P=3.7271W-10.391 | 0.9838 | |
| 8 | 太原 | 3.8 | 34.1 | 14.38 | 431.2 | P=3.3141W-11.716 | 0.9826 | |
| 9 | 平凉 | 4.3 | 28.9 | 13.94 | 482.3 | P=4.0125W-15.749 | 0.9816 | |
| 10 | 沈阳 | 3.4 | 41.0 | 15.62 | 690.3 | P=4.2497W-8.8323 | 0.9806 | |
| 11 | 长春 | 3.0 | 36.3 | 13.63 | 570.4 | P=4.4467W-13.061 | 0.9805 | |
| 12 | 临江 | 3.3 | 38.0 | 14.92 | 791.7 | P=4.9189W-7.3986 | 0.9776 | |
| 13 | 齐齐哈尔 | 2.6 | 33.3 | 12.11 | 415.7 | P=3.7259W-10.514 | 0.9770 | |
| 14 | 青岛 | 5.6 | 45.4 | 19.08 | 662.1 | P=3.4176W-10.045 | 0.9770 | |
| 15 | 锦州 | 3.4 | 41.3 | 16.13 | 567.8 | P=4.0463W-17.964 | 0.9753 | |
| 16 | 大连 | 4.3 | 40.8 | 16.33 | 601.9 | P=3.9509W-14.372 | 0.9731 | |
| 17 | 武都 | 6.8 | 36.2 | 19.34 | 471.9 | P=3.1394W-21.397 | 0.9688 | |
| 18 | 巴塘 | 3.5 | 24.7 | 12.5 | 469.5 | P=5.3258W-27.448 | 0.9518 | |
| 19 | 郑州 | 6.5 | 47.6 | 21.25 | 632.4 | P=3.0117W-11.308 | 0.9443 | |
| 20 | 济南 | 5.1 | 44.8 | 18.44 | 672.7 | P=4.5406W-27.67 | 0.9415 | |
| 21 | 索伦 | 2.3 | 30.0 | 10.93 | 471.4 | P=5.015W-15.548 | 0.9323 | |
| 22 | 北京 | 3.6 | 42.4 | 16.71 | 571.9 | P=4.3912W-25.72 | 0.9299 | |
| 23 | 邢台 | 4.9 | 44.8 | 18.76 | 493.4 | P=3.2789W-20.391 | 0.9284 | |
| 24 | 南阳 | 8.7 | 51.0 | 24.45 | 777.7 | P=3.3177W-16.31 | 0.9214 | |
| 25 | 西安 | 7.5 | 44.1 | 21.99 | 553.3 | P=2.2165W-2.6368 | 0.8380 | |
| 以上25站平均 | 4.2 | 37.8 | 15.80 | 563.1 | 平均斜率3.9750 | 0.9637 | ||
| 青藏高原核心区 | 26 | 那曲 | 1.3 | 11.5 | 5.15 | 430.2 | P=9.7728W-14.48 | 0.9846 |
| 27 | 昌都 | 2.5 | 19.0 | 9.27 | 474.5 | P=6.1027W-17.01 | 0.9914 | |
| 28 | 合作 | 2.5 | 17.9 | 8.92 | 531.4 | P=6.8229W-16.616 | 0.9750 | |
| 29 | 玉树 | 2.2 | 15.4 | 7.46 | 485.8 | P=7.7386W-17.233 | 0.9607 | |
| 30 | 拉萨 | 1.7 | 17.3 | 7.86 | 426.4 | P=7.1666W-20.776 | 0.9381 | |
| 31 | 甘孜 | 2.9 | 18.7 | 9.53 | 659.8 | P=7.7457W-18.794 | 0.9263 | |
| 32 | 格尔木 | 2.4 | 11.9 | 5.43 | 42.2 | P=1.1552W-2.7601 | 0.9037 | |
| 33 | 都兰 | 1.9 | 12.2 | 5.22 | 193.8 | P=3.7764W-3.5503 | 0.8437 | |
| 34 | 德钦 | 3.7 | 19.6 | 10.38 | 621.6 | P=5.5276W-5.5483 | 0.8303 | |
| 35 | 茫崖 | 1.7 | 10.0 | 4.28 | 55.4 | P=1.7705W-2.9523 | 0.6632 | |
| 以上10站平均 | 2.3 | 15.4 | 8.35 | 392.1 | 平均斜率5.7579 | 0.9017 | ||
| 区域 | 序号 | 站名 | 1月水汽含量/mm | 7月水汽含量/mm | 年平均水汽 含量/mm | 多年平均 降水量/mm | 逐月平均降水量与水汽含量的线性拟合公式 | 相关判定系数R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干旱区 | 1 | 张掖 | 3.2 | 21.5 | 9.73 | 130.4 | P=1.639W-5.0723 | 0.9777 |
| 2 | 二连浩特 | 2.9 | 21.5 | 8.64 | 142.3 | P=2.0706W-6.035 | 0.9762 | |
| 3 | 额济纳旗 | 3.0 | 18.0 | 7.66 | 35.3 | P=0.6308W-1.8891 | 0.9647 | |
| 4 | 乌拉特中 | 2.8 | 20.6 | 8.53 | 199.8 | P=3.2722W-11.273 | 0.9610 | |
| 5 | 酒泉 | 3.2 | 20.3 | 8.82 | 87.8 | P=1.1547W-2.8638 | 0.9493 | |
| 6 | 库尔勒 | 4.7 | 21.0 | 10.68 | 57.4 | P=0.6532W-2.195 | 0.9264 | |
| 7 | 银川 | 3.9 | 26.7 | 12.00 | 186.3 | P=1.882W-7.0588 | 0.9184 | |
| 8 | 临河 | 3.2 | 23.1 | 9.93 | 145.7 | P=1.944W-7.1691 | 0.9157 | |
| 9 | 哈密 | 4.2 | 19.7 | 9.41 | 39.0 | P=0.3651W-0.185 | 0.9150 | |
| 10 | 阿克苏 | 5.2 | 22.8 | 11.92 | 74.4 | P=0.8168W-3.5333 | 0.8754 | |
| 11 | 克拉玛依 | 5.1 | 20.6 | 10.73 | 105.6 | P=0.9766W-1.6745 | 0.8061 | |
| 12 | 库车 | 4.6 | 19.4 | 10.22 | 74.6 | P=0.8947W-2.9245 | 0.7788 | |
| 13 | 若羌 | 4.7 | 19.1 | 9.19 | 29.0 | P=0.5778W-2.894 | 0.7619 | |
| 14 | 安得河 | 4.0 | 17.9 | 8.47 | 27.3 | P=0.5857W-.6837 | 0.7438 | |
| 15 | 敦煌 | 3.7 | 18.6 | 8.48 | 42.2 | P=0.7021W-2.4169 | 0.7414 | |
| 16 | 和田 | 4.4 | 20.1 | 9.87 | 36.4 | P=0.3268W-0.1908 | 0.5475 | |
| 17 | 喀什 | 5.1 | 19.1 | 10.85 | 64.0 | P=0.3756W+1.2585 | 0.4976 | |
| 18 | 阿勒泰 | 3.7 | 20.0 | 9.24 | 191.3 | P=0.4554W+11.733 | 0.2527 | |
| 以上18站平均 | 4.0 | 20.6 | 9.69 | 92.7 | 平均斜率1.0735 | 0.8061 | ||
| 半干旱区 | 19 | 西宁 | 3.0 | 21.1 | 10.03 | 373.6 | P=4.595W-14.953 | 0.9817 |
| 20 | 呼和浩特 | 3.1 | 25.3 | 10.33 | 397.9 | P=4.7363W-15.775 | 0.9719 | |
| 21 | 通辽 | 2.8 | 35.2 | 12.83 | 373.4 | P=3.065W-8.2174 | 0.9697 | |
| 22 | 兰州 | 4.2 | 25.9 | 12.82 | 311.7 | P=3.0984W-13.745 | 0.9689 | |
| 23 | 锡林浩特 | 2.6 | 24.4 | 9.49 | 286.6 | P=3.7514W-11.723 | 0.9664 | |
| 24 | 赤峰 | 2.4 | 30.4 | 11.20 | 371.1 | P=3.4706W-7.9452 | 0.9510 | |
| 25 | 乌鲁木齐 | 4.6 | 19.8 | 10.36 | 286.3 | P=1.2813W+10.577 | 0.4755 | |
| 26 | 塔城 | 4.7 | 21.0 | 10.66 | 282.3 | P=0.264W+20.711 | 0.0370 | |
| 27 | 伊宁 | 5.6 | 22.8 | 12.59 | 268.8 | P=-0.0564W+23.111 | 0.0041 | |
| 以上9站平均 | 3.7 | 25.1 | 11.15 | 328.0 | 平均斜率2.6895 | 0.7029 | ||
Tab.3 The fitting relationships of monthly average precipitation and water vapor content in arid and semiarid areas
| 区域 | 序号 | 站名 | 1月水汽含量/mm | 7月水汽含量/mm | 年平均水汽 含量/mm | 多年平均 降水量/mm | 逐月平均降水量与水汽含量的线性拟合公式 | 相关判定系数R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干旱区 | 1 | 张掖 | 3.2 | 21.5 | 9.73 | 130.4 | P=1.639W-5.0723 | 0.9777 |
| 2 | 二连浩特 | 2.9 | 21.5 | 8.64 | 142.3 | P=2.0706W-6.035 | 0.9762 | |
| 3 | 额济纳旗 | 3.0 | 18.0 | 7.66 | 35.3 | P=0.6308W-1.8891 | 0.9647 | |
| 4 | 乌拉特中 | 2.8 | 20.6 | 8.53 | 199.8 | P=3.2722W-11.273 | 0.9610 | |
| 5 | 酒泉 | 3.2 | 20.3 | 8.82 | 87.8 | P=1.1547W-2.8638 | 0.9493 | |
| 6 | 库尔勒 | 4.7 | 21.0 | 10.68 | 57.4 | P=0.6532W-2.195 | 0.9264 | |
| 7 | 银川 | 3.9 | 26.7 | 12.00 | 186.3 | P=1.882W-7.0588 | 0.9184 | |
| 8 | 临河 | 3.2 | 23.1 | 9.93 | 145.7 | P=1.944W-7.1691 | 0.9157 | |
| 9 | 哈密 | 4.2 | 19.7 | 9.41 | 39.0 | P=0.3651W-0.185 | 0.9150 | |
| 10 | 阿克苏 | 5.2 | 22.8 | 11.92 | 74.4 | P=0.8168W-3.5333 | 0.8754 | |
| 11 | 克拉玛依 | 5.1 | 20.6 | 10.73 | 105.6 | P=0.9766W-1.6745 | 0.8061 | |
| 12 | 库车 | 4.6 | 19.4 | 10.22 | 74.6 | P=0.8947W-2.9245 | 0.7788 | |
| 13 | 若羌 | 4.7 | 19.1 | 9.19 | 29.0 | P=0.5778W-2.894 | 0.7619 | |
| 14 | 安得河 | 4.0 | 17.9 | 8.47 | 27.3 | P=0.5857W-.6837 | 0.7438 | |
| 15 | 敦煌 | 3.7 | 18.6 | 8.48 | 42.2 | P=0.7021W-2.4169 | 0.7414 | |
| 16 | 和田 | 4.4 | 20.1 | 9.87 | 36.4 | P=0.3268W-0.1908 | 0.5475 | |
| 17 | 喀什 | 5.1 | 19.1 | 10.85 | 64.0 | P=0.3756W+1.2585 | 0.4976 | |
| 18 | 阿勒泰 | 3.7 | 20.0 | 9.24 | 191.3 | P=0.4554W+11.733 | 0.2527 | |
| 以上18站平均 | 4.0 | 20.6 | 9.69 | 92.7 | 平均斜率1.0735 | 0.8061 | ||
| 半干旱区 | 19 | 西宁 | 3.0 | 21.1 | 10.03 | 373.6 | P=4.595W-14.953 | 0.9817 |
| 20 | 呼和浩特 | 3.1 | 25.3 | 10.33 | 397.9 | P=4.7363W-15.775 | 0.9719 | |
| 21 | 通辽 | 2.8 | 35.2 | 12.83 | 373.4 | P=3.065W-8.2174 | 0.9697 | |
| 22 | 兰州 | 4.2 | 25.9 | 12.82 | 311.7 | P=3.0984W-13.745 | 0.9689 | |
| 23 | 锡林浩特 | 2.6 | 24.4 | 9.49 | 286.6 | P=3.7514W-11.723 | 0.9664 | |
| 24 | 赤峰 | 2.4 | 30.4 | 11.20 | 371.1 | P=3.4706W-7.9452 | 0.9510 | |
| 25 | 乌鲁木齐 | 4.6 | 19.8 | 10.36 | 286.3 | P=1.2813W+10.577 | 0.4755 | |
| 26 | 塔城 | 4.7 | 21.0 | 10.66 | 282.3 | P=0.264W+20.711 | 0.0370 | |
| 27 | 伊宁 | 5.6 | 22.8 | 12.59 | 268.8 | P=-0.0564W+23.111 | 0.0041 | |
| 以上9站平均 | 3.7 | 25.1 | 11.15 | 328.0 | 平均斜率2.6895 | 0.7029 | ||
| 序号 | 站名 | 年平均水汽 含量/mm | 多年平均 降水量/mm | 月平均降水量与水汽含量的线性拟合方程 | 相关判定 系数R2 | 分组及其 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 宜昌 | 29.91 | 1138.9 | P=4.0855W-27.365 | 0.9716 | 梅雨及其南部相邻的外围地区:两广南部、海南、香港、云贵川、重庆、湖北西部和陕西南部及淮河以北的徐州和丹东。一般来说宜昌以东才是梅雨区,徐州地处梅雨区的北边界,全部不在梅雨中心区 |
| 2 | 腾冲 | 24.26 | 1527.3 | P=9.0159W-91.437 | 0.9677 | |
| 3 | 丹东 | 17.98 | 930.6 | P=5.6286W-24.042 | 0.9643 | |
| 4 | 威宁 | 17.48 | 890.1 | P=8.2309W-69.728 | 0.9625 | |
| 5 | 安康 | 27.01 | 814.3 | P=3.5123W-27.002 | 0.959 | |
| 6 | 西昌 | 22.00 | 1013.6 | P=7.8743W-88.767 | 0.9497 | |
| 7 | 丽江 | 16.30 | 960.9 | P=9.3218W-71.278 | 0.9466 | |
| 8 | 南充 | 30.88 | 987.1 | P=4.1781W-46.777 | 0.9435 | |
| 9 | 昆明 | 21.08 | 1011.3 | P=7.9021W-82.269 | 0.9434 | |
| 10 | 达县(达州) | 30.21 | 1207.4 | P=4.8642W-46.322 | 0.9426 | |
| 11 | 宜宾 | 33.60 | 1063.1 | P=4.8717W-75.097 | 0.9405 | |
| 12 | 百色 | 39.63 | 1070.6 | P=4.7556W-99.222 | 0.9398 | |
| 13 | 香港 | 39.71 | 2127.0 | P=12.117W-282.57 | 0.938 | |
| 14 | 汉中 | 25.63 | 893.0 | P=3.9937W-31.281 | 0.9353 | |
| 15 | 射阳 | 22.39 | 1000.0 | P=4.6734W-20.311 | 0.9294 | |
| 16 | 南宁 | 42.31 | 1309.7 | P=5.0871W-106.08 | 0.9175 | |
| 17 | 思茅 | 28.75 | 1517.8 | P=9.5592W-150.06 | 0.9057 | |
| 18 | 重庆 | 31.77 | 1104.5 | P=4.1902W-41.074 | 0.9048 | |
| 19 | 成都 | 30.00 | 870.2 | P=5.1395W-81.668 | 0.8934 | |
| 20 | 蒙自 | 27.95 | 857.7 | P=5.1763W-73.202 | 0.8928 | |
| 21 | 恩施 | 29.64 | 1470.4 | P=5.4777W-39.834 | 0.8817 | |
| 22 | 徐州 | 21.94 | 831.6 | P=2.1804W-19.575 | 0.8639 | |
| 23 | 广州 | 42.39 | 1731.6 | P=6.1603W-116.47 | 0.8622 | |
| 24 | 海口 | 46.51 | 1651.9 | P=4.595W-185.67 | 0.8606 | |
| 25 | 贵阳 | 26.24 | 1117.7 | P=6.0934W-66.759 | 0.8488 | |
| 26 | 阳江 | 43.74 | 2338.0 | P=10.719W-265.31 | 0.8473 | |
| 27 | 河池 | 38.01 | 1522.4 | P=6.0304W-102.19 | 0.8296 | |
| 28 | 汕头 | 42.18 | 1631.4 | P=6.2984W-129.69 | 0.7997 | |
| 29 | 北海 | 44.65 | 1532.9 | P=8.8404W-244.41 | 0.7975 | |
| 以上29站平均 | 30.83 | 1245.6 | 0.9083 | |||
| 30 | 阜阳 | 24.90 | 910 | P=2.9788W+1.6619 | 0.7708 | 梅雨及其南部相邻地区:除属于两广北部的梧州、桂林、连平外,其他14站都在梅雨区 |
| 31 | 南京 | 25.88 | 1062.4 | P=2.94W+12.428 | 0.7069 | |
| 32 | 厦门 | 38.33 | 1349.1 | P=4.0053W-41.08 | 0.6556 | |
| 33 | 连平 | 38.20 | 1800 | P=5.4407W-60.666 | 0.6051 | |
| 34 | 杭州 | 28.86 | 1454.6 | P=2.5776W+46.822 | 0.6036 | |
| 35 | 梧州 | 40.98 | 1503.6 | P=4.3387W-56.907 | 0.5973 | |
| 36 | 龙华 | 27.07 | 1184.4 | P=3.1513W+13.405 | 0.5782 | |
| 37 | 武汉 | 29.40 | 1269 | P=2.8657W+21.491 | 0.5605 | |
| 38 | 桂林 | 36.98 | 1921.3 | P=5.2202W-32.908 | 0.4949 | |
| 39 | 福州 | 36.48 | 1393.6 | P=3.178W+0.1985 | 0.4787 | |
| 40 | 安庆 | 29.03 | 1474.9 | P=3.0962W+33.042 | 0.4509 | |
| 41 | 郴州 | 36.58 | 1493.9 | P=2.1804W+44.743 | 0.3183 | |
| 42 | 赣州 | 35.93 | 1461.2 | P=2.1947W+42.903 | 0.2508 | |
| 43 | 邵武 | 34.43 | 1832.5 | P=3.2632W+40.372 | 0.2343 | |
| 44 | 南昌 | 32.41 | 1624.4 | P=2.5703W+52.05 | 0.2322 | |
| 45 | 衢州 | 32.46 | 1705.0 | P=2.1361W+72.749 | 0.1637 | |
| 46 | 长沙 | 34.57 | 1546.4 | P=1.2801W+66.692 | 0.127 | |
| 以上17站平均 | 33.09 | 1468.8 | 0.4605 | |||
| 全部46站平均 | 31.67 | 1328.5 | 0.7428 |
Tab.4 Fitting relationships of monthly average precipitation and water vapor content in humid areas
| 序号 | 站名 | 年平均水汽 含量/mm | 多年平均 降水量/mm | 月平均降水量与水汽含量的线性拟合方程 | 相关判定 系数R2 | 分组及其 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 宜昌 | 29.91 | 1138.9 | P=4.0855W-27.365 | 0.9716 | 梅雨及其南部相邻的外围地区:两广南部、海南、香港、云贵川、重庆、湖北西部和陕西南部及淮河以北的徐州和丹东。一般来说宜昌以东才是梅雨区,徐州地处梅雨区的北边界,全部不在梅雨中心区 |
| 2 | 腾冲 | 24.26 | 1527.3 | P=9.0159W-91.437 | 0.9677 | |
| 3 | 丹东 | 17.98 | 930.6 | P=5.6286W-24.042 | 0.9643 | |
| 4 | 威宁 | 17.48 | 890.1 | P=8.2309W-69.728 | 0.9625 | |
| 5 | 安康 | 27.01 | 814.3 | P=3.5123W-27.002 | 0.959 | |
| 6 | 西昌 | 22.00 | 1013.6 | P=7.8743W-88.767 | 0.9497 | |
| 7 | 丽江 | 16.30 | 960.9 | P=9.3218W-71.278 | 0.9466 | |
| 8 | 南充 | 30.88 | 987.1 | P=4.1781W-46.777 | 0.9435 | |
| 9 | 昆明 | 21.08 | 1011.3 | P=7.9021W-82.269 | 0.9434 | |
| 10 | 达县(达州) | 30.21 | 1207.4 | P=4.8642W-46.322 | 0.9426 | |
| 11 | 宜宾 | 33.60 | 1063.1 | P=4.8717W-75.097 | 0.9405 | |
| 12 | 百色 | 39.63 | 1070.6 | P=4.7556W-99.222 | 0.9398 | |
| 13 | 香港 | 39.71 | 2127.0 | P=12.117W-282.57 | 0.938 | |
| 14 | 汉中 | 25.63 | 893.0 | P=3.9937W-31.281 | 0.9353 | |
| 15 | 射阳 | 22.39 | 1000.0 | P=4.6734W-20.311 | 0.9294 | |
| 16 | 南宁 | 42.31 | 1309.7 | P=5.0871W-106.08 | 0.9175 | |
| 17 | 思茅 | 28.75 | 1517.8 | P=9.5592W-150.06 | 0.9057 | |
| 18 | 重庆 | 31.77 | 1104.5 | P=4.1902W-41.074 | 0.9048 | |
| 19 | 成都 | 30.00 | 870.2 | P=5.1395W-81.668 | 0.8934 | |
| 20 | 蒙自 | 27.95 | 857.7 | P=5.1763W-73.202 | 0.8928 | |
| 21 | 恩施 | 29.64 | 1470.4 | P=5.4777W-39.834 | 0.8817 | |
| 22 | 徐州 | 21.94 | 831.6 | P=2.1804W-19.575 | 0.8639 | |
| 23 | 广州 | 42.39 | 1731.6 | P=6.1603W-116.47 | 0.8622 | |
| 24 | 海口 | 46.51 | 1651.9 | P=4.595W-185.67 | 0.8606 | |
| 25 | 贵阳 | 26.24 | 1117.7 | P=6.0934W-66.759 | 0.8488 | |
| 26 | 阳江 | 43.74 | 2338.0 | P=10.719W-265.31 | 0.8473 | |
| 27 | 河池 | 38.01 | 1522.4 | P=6.0304W-102.19 | 0.8296 | |
| 28 | 汕头 | 42.18 | 1631.4 | P=6.2984W-129.69 | 0.7997 | |
| 29 | 北海 | 44.65 | 1532.9 | P=8.8404W-244.41 | 0.7975 | |
| 以上29站平均 | 30.83 | 1245.6 | 0.9083 | |||
| 30 | 阜阳 | 24.90 | 910 | P=2.9788W+1.6619 | 0.7708 | 梅雨及其南部相邻地区:除属于两广北部的梧州、桂林、连平外,其他14站都在梅雨区 |
| 31 | 南京 | 25.88 | 1062.4 | P=2.94W+12.428 | 0.7069 | |
| 32 | 厦门 | 38.33 | 1349.1 | P=4.0053W-41.08 | 0.6556 | |
| 33 | 连平 | 38.20 | 1800 | P=5.4407W-60.666 | 0.6051 | |
| 34 | 杭州 | 28.86 | 1454.6 | P=2.5776W+46.822 | 0.6036 | |
| 35 | 梧州 | 40.98 | 1503.6 | P=4.3387W-56.907 | 0.5973 | |
| 36 | 龙华 | 27.07 | 1184.4 | P=3.1513W+13.405 | 0.5782 | |
| 37 | 武汉 | 29.40 | 1269 | P=2.8657W+21.491 | 0.5605 | |
| 38 | 桂林 | 36.98 | 1921.3 | P=5.2202W-32.908 | 0.4949 | |
| 39 | 福州 | 36.48 | 1393.6 | P=3.178W+0.1985 | 0.4787 | |
| 40 | 安庆 | 29.03 | 1474.9 | P=3.0962W+33.042 | 0.4509 | |
| 41 | 郴州 | 36.58 | 1493.9 | P=2.1804W+44.743 | 0.3183 | |
| 42 | 赣州 | 35.93 | 1461.2 | P=2.1947W+42.903 | 0.2508 | |
| 43 | 邵武 | 34.43 | 1832.5 | P=3.2632W+40.372 | 0.2343 | |
| 44 | 南昌 | 32.41 | 1624.4 | P=2.5703W+52.05 | 0.2322 | |
| 45 | 衢州 | 32.46 | 1705.0 | P=2.1361W+72.749 | 0.1637 | |
| 46 | 长沙 | 34.57 | 1546.4 | P=1.2801W+66.692 | 0.127 | |
| 以上17站平均 | 33.09 | 1468.8 | 0.4605 | |||
| 全部46站平均 | 31.67 | 1328.5 | 0.7428 |
| 区域 | 统计样 本数 | 1月水汽含量均值/mm | 7月水汽含量均值/mm | 多年平均水汽含量/mm | 多年平均降水量/mm | 拟合公式的 平均斜率 | R2 | R2不同区间站点数/个 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [0.25,0.5) | [0.5,0.8) | ≥0.8 | |||||||||
| 青藏高原 | 10 | 2.3 | 15.4 | 8.35 | 387.0 | 5.7579 | 0.9017 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 9 |
| 干旱区 | 18 | 4.0 | 20.6 | 9.69 | 89.1 | 1.0735 | 0.8061 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 11 |
| 半干旱区 | 9 | 3.7 | 25.1 | 11.15 | 328.0 | 2.6895 | 0.7029 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 6 |
| 半湿润区 | 25 | 4.2 | 37.8 | 15.80 | 560.4 | 3.9750 | 0.9637 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 25 |
| 湿润区 | 46 | 15.3 | 51.8 | 31.67 | 1328.5 | 5.1786 | 0.7428 | 4 | 5 | 10 | 27 |
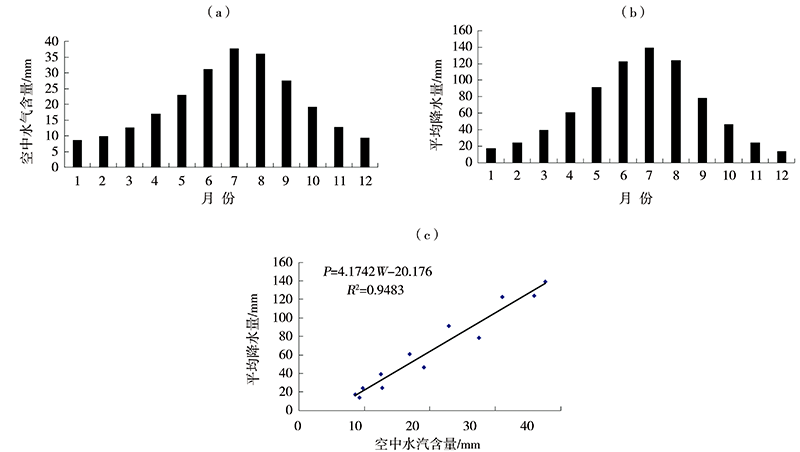
| 中国陆地 | 108 | 8.7 | 37.7 | 20.37 | 778.1 | 4.1742 | 0.8159 | 6 | 8 | 16 | 78 |
Tab.5 The comparison of relative research results about main climatic parameters in different regions and monthly average precipitation and water vapor content
| 区域 | 统计样 本数 | 1月水汽含量均值/mm | 7月水汽含量均值/mm | 多年平均水汽含量/mm | 多年平均降水量/mm | 拟合公式的 平均斜率 | R2 | R2不同区间站点数/个 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [0.25,0.5) | [0.5,0.8) | ≥0.8 | |||||||||
| 青藏高原 | 10 | 2.3 | 15.4 | 8.35 | 387.0 | 5.7579 | 0.9017 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 9 |
| 干旱区 | 18 | 4.0 | 20.6 | 9.69 | 89.1 | 1.0735 | 0.8061 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 11 |
| 半干旱区 | 9 | 3.7 | 25.1 | 11.15 | 328.0 | 2.6895 | 0.7029 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 6 |
| 半湿润区 | 25 | 4.2 | 37.8 | 15.80 | 560.4 | 3.9750 | 0.9637 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 25 |
| 湿润区 | 46 | 15.3 | 51.8 | 31.67 | 1328.5 | 5.1786 | 0.7428 | 4 | 5 | 10 | 27 |
| 中国陆地 | 108 | 8.7 | 37.7 | 20.37 | 778.1 | 4.1742 | 0.8159 | 6 | 8 | 16 | 78 |
| [1] | 张秉祥, 韩军彩, 陈静, 等. 华北地区空中水汽含量与降水量的关系[J]. 干旱气象, 2012, 30(2): 207-214. |
| [2] | 周顺武, 吴萍, 王传辉, 等. 青藏高原夏季上空水汽含量演变特征及其与降水的关系[J]. 地理学报, 2011, 66(11):1466-1478. |
| [3] | 赵玲, 安沙舟, 杨莲梅, 等. 1976-2007年乌鲁木齐可降水量及其降水转化率[J]. 干旱区研究, 2010, 27(3): 433-437. |
| [4] | 王炳忠, 申彦波. 我国上空的水汽含量及其气候学估算[J]. 应用气象学报, 2012, 23(6):763-768. |
| [5] | 彭艳秋, 王卫国, 刘煜, 等. 利用不同资料研究我国大陆上空柱水汽含量[J]. 应用气象学报, 2012, 23(1):59-68. |
| [6] | 毛文书, 巩远发, 周强. 青藏高原大气热源与江淮梅雨异常的关系[J]. 高原气象, 2009, 28(6):1291-1298. |
| [7] | 王建. 现代自然地理学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2001: 140-141. |
| [8] | 伍光和、 王乃昂、 胡双熙. 自然地理学第4版[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2008: 129-130. |
| [9] | GILES D C. Advanced research methods in psychology[M]. New York: Routledge, 2002: 57. |
| [1] | XIE Qiyu, GONG Yuanfa, YANG Rong. Water Vapor Budget of High Water Vapor Content Region over Tibet Plateau in Winter and Its Relationship with Precipitation of China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(5): 732-739. |
| [2] | DANG Zhangli, ZHANG Jingpeng, QU Zongxi, ZHAO Hui, ZHANG Beidou, ZHANG Wenyu. The Application of Microwave Radiometer Observation Data on Precipitation Forecast [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(2): 340-343. |
| [3] | . Analysis of Correlation Between Water Vapor Content and Precipitation over North China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2012, 30(2): 207-214. |
| [4] | CUI Li-Na, SHI Yu-Guang, CUI Cai-Xia, DIAO Ling, LI Yan-Yong. Diurnal Variation of Atmospheric Water Vapor Content in 2009 over Taklimakan Desert [J]. J4, 2010, 28(4): 407-410. |
| [5] | BA Jin- , WANG Xiu-Qin. Analysis of Climate Character in Dunhuang in Recent 56 Years [J]. J4, 2010, 28(3): 304-308. |
| [6] |
DONG An-Xiang, BAI Hu-Zhi- , LEI Xiao-Bin.
New Development of Arid Climate Research in |
| [7] | LIU Shi-Xiang, WANG Sui-Chan- , LIU Bi- , HUANG Yu-Xia- , WANG Wei-Sheng- , BO Su. Trend Analysis of the Water Vapor Content and Its Transport over Lanzhou City [J]. J4, 2006, 24(1): 18-22. |
| [8] | BI Xiao-Dong, ZHANG Jiang, HU Wen-Chao. Arid Climate Observing System [J]. J4, 2005, 23(1): 78-83. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||