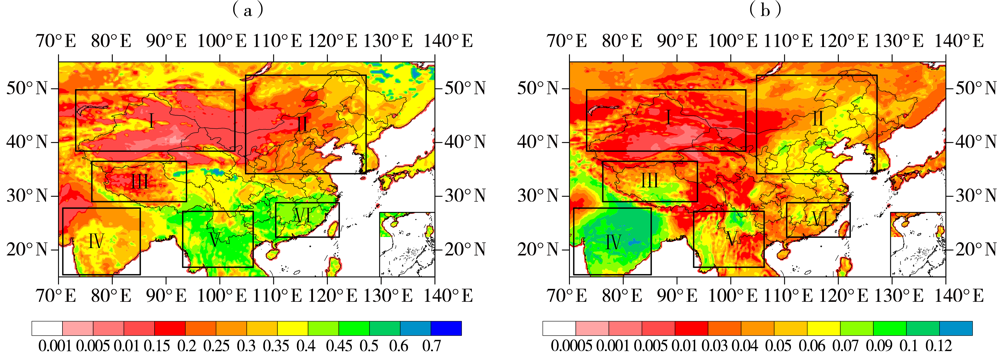
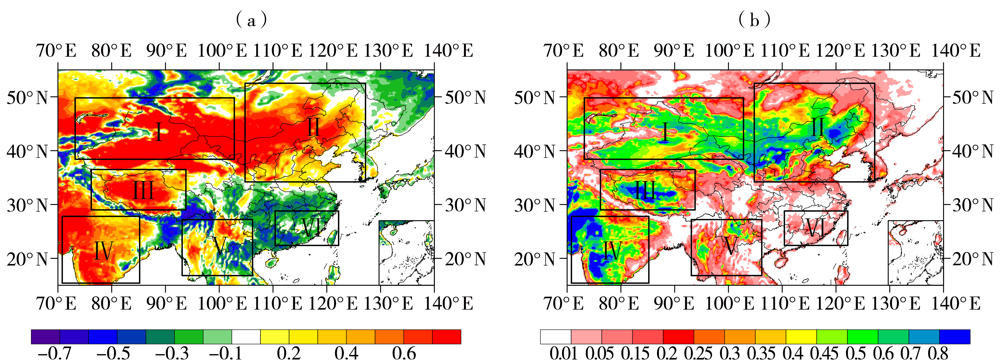
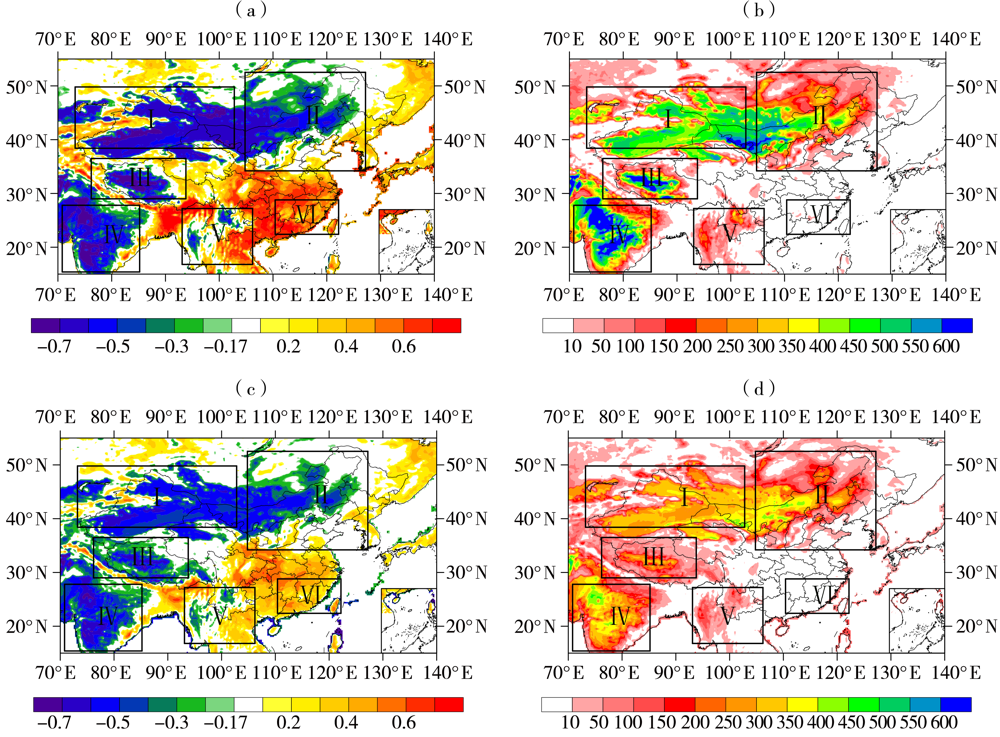
| [1] |
马柱国, 魏和林, 符淙斌. 中国东部区域土壤湿度的变化及其与气候变率的关系[J]. 气象学报: 2000, 58(3): 278-287.
|
| [2] |
SENEVIRATNE S I, LUTHI D, LITSCHI M, et al. Land-atmosphere coupling and climate change in Europe[J]. Nature, 2006, 443(7108): 205-209.
DOI
URL
|
| [3] |
WU L Y, ZHANG J Y. Asymmetric effects of soil moisture on mean daily maximum and minimum temperatures over eastern China[J]. Meteorology and Atmospheric Physics, 2013, 122: 199-213.
DOI
URL
|
| [4] |
张人禾, 刘栗, 左志燕. 中国土壤湿度的变异及其对中国气候的影响[J]. 自然杂志, 2016, 38(5): 313-319.
|
| [5] |
SEGAL M, ARRITT R W. Nonclassical mesoscale circulations caused by surface sensible heat-flux gradients[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 1992, 73(10): 1593-1604.
DOI
URL
|
| [6] |
黄荣辉, 陈文, 张强, 等. 中国西北干旱区陆气相互作用及其对东亚气候变化的影响[M]. 北京: 北京气象出版社, 2011:240-292.
|
| [7] |
詹艳玲, 林朝晖. 6月长江中下游降水和春季东亚季风区土壤湿度的关系[J]. 气象学报, 2012, 70(2): 236-243.
|
| [8] |
ZUO Z Y, ZHANG R H. Influence of soil moisture in eastern China on the East Asian summer monsoon[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2016, 33(2): 151-163.
DOI
URL
|
| [9] |
张强, 岳平, 张良, 等. 夏季风过渡区的陆-气相互作用:评述与展望[J]. 气象学报, 2019, 77(4): 758-773.
|
| [10] |
TEULING A J, VAN LOON A F, SENEVIRATNE S I, et al. Evapotranspiration amplifies European summer drought[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2013, 40(10): 2071-2075.
DOI
URL
|
| [11] |
FISCHER E M, SENEVIRATNE S I, LUTHI D, et al. Contribution of land-atmosphere coupling to recent European summer heat waves[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2007, 34(6),L06707. DOI: 10.1029/2006GL029068.
DOI
|
| [12] |
ZENG D W, YUAN X. Modeling the influence of upstream land-atmosphere coupling on the 2017 persistent droughts over Northeast China[J]. Journal of Climate, 2021, 34: 4971-4988.
|
| [13] |
ZHOU S, PARK WILLIAMS A, BERG A M, et al. Land-atmosphere feedbacks exacerbate concurrent soil drought and atmospheric aridity[J]. Proceedings of The National Academy of Sciences of the United states of America, 2019, 116(38): 18848-18853.
|
| [14] |
WEI J F, DIRMEYER P A. Dissecting soil moisture-precipitation coupling[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2012, 39(19),L19711. DOI: 10.1029/2012GL053038.
DOI
|
| [15] |
周晶, 陈海山. 土壤湿度年际变化对中国区域极端气候事件模拟的影响研究 I.基于CAM3.1的模式评估[J]. 大气科学, 2012, 36(6): 1077-1092.
|
| [16] |
GUO Z C, DIRMEYER P A, DELSOLE T. Land surface impacts on sub seasonal and seasonal predictability[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2011, 38(24): L24812. DOI: 10.1029/2011GL049945.
DOI
|
| [17] |
GUO Z C, DIRMEYER P A. Interannual variability of land-atmosphere coupling strength[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2013, 14(5): 1636-1646.
DOI
URL
|
| [18] |
KOSTER R D, DIRMEYER P A, GUO Z, et al. Regions of strong coupling between soil moisture and precipitation[J]. Science, 2004, 305: 1138-1140.
DOI
URL
|
| [19] |
王胜, 张强, 赵建华, 等. 典型干旱区陆面模式模拟检验[J]. 干旱气象, 2018, 36(6): 921-926.
|
| [20] |
DIRMEYER P A, HALDER S. Application of the land-atmosphere coupling paradigm to the operational Coupled Forecast System (CFSv2)[J]. Journal of Hydrometeor, 2017, 18(1): 85-108.
DOI
URL
|
| [21] |
马柱国, 符淙斌. 1951—2004年中国北方干旱化的基本事实[J]. 科学通报, 2006, 51(20): 2429-2439.
|
| [22] |
张强, 张红丽, 张良, 等. 论我国夏季风影响过渡区及其陆气相互作用问题[J]. 地球科学进展, 2017, 32(10): 1009-1019.
|
| [23] |
YUAN X, ROUNDY J K, WOOD E F, et al. Seasonal forecasting of global hydrologic extremes: system development and evaluation over GEWEX basins[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2015, 96(11): 1895-1912.
DOI
URL
|
| [24] |
KOSTER R D, SUAREZ M J, HEISER M. Variance and predictability of precipitation at seasonal-to-interannual timescales[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2000, 1(1): 26-46.
DOI
URL
|
| [25] |
YAMADA T J, KANAE S, OKI T, et al. Seasonal variation of land-atmosphere coupling strength over the West African monsoon region in an atmospheric general circulation model[J]. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 2013, 58(6): 1276-1286.
DOI
URL
|
| [26] |
杨扬, 杨启东, 王芝兰, 等. 中国区域陆气耦合强度的时空分布特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(3): 374-385.
|
| [27] |
王映思, 肖天贵, 董雪峰, 等. 东亚和南亚季风协同作用对西南地区夏季降水的影响[J]. 气象学报, 2021, 79(4): 541-557.
|
| [28] |
DING Y H, SUN Y, WANG Z Y, et al. Inter-decadal variation of the summer precipitation in China and its association with decreasing Asian summer monsoon Part II: possible causes[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2009, 29(13): 1926-1944.
DOI
URL
|
| [29] |
吴国雄, 刘屹岷, 何编, 等. 青藏高原感热气泵影响亚洲夏季风的机制[J]. 大气科学, 2018, 42(3): 488-504.
|
| [30] |
ZHANG J Y, WU L Y. Land-atmosphere coupling amplifies hot extremes over China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2011, 56(31): 3328-3332.
DOI
URL
|
| [31] |
BERG A, LINTNER B, FINDELL K, et al. Soil moisture influence on seasonality and large-scale circulation in simulations of the West African monsoon[J]. Journal of Climate, 2017, 30(7): 2295-2317.
DOI
URL
|
| [32] |
ZENG D W, YUAN X. Multi-scale land-atmosphere coupling and its application in assessing sub seasonal forecasts over East Asia[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2018, 19(5): 745-760.
DOI
URL
|
| [33] |
HERSBACH H, BELL B, BERRISFORD P, et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 2020, 146:1999-2049.
DOI
URL
|
| [34] |
ROUNDY, J K,FERGUSON C R, WOOD E F. Temporal variability of land-atmosphere coupling and its implications for drought over the southeast United States[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2013, 14, 622-635.
DOI
URL
|
| [35] |
LIU L, ZHANG R, ZUO Z. Intercomparison of spring soil moisture among multiple reanalysis data sets over eastern China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2014, 119(1): 54-64.
DOI
URL
|
| [36] |
宋海清, 孙小龙, 李云鹏. 欧洲中期天气预报中心第五代全球再分析土壤湿度资料在内蒙古的适用性评估[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2020, 20(6):2161-2168.
|
| [37] |
陈鑫涛, 邓超. 多种蒸散发产品在黄河流域的评估和融合[J]. 水电能源科学, 2021, 39(5):5-8.
|
| [38] |
SHIN C S, HUANG B H. Slow and fast annual cycles of the Asian summer monsoon in the NCEP CFSv2[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2016, 47(1/2): 529-553.
DOI
URL
|
 ), ZENG Dingwen2(
), ZENG Dingwen2( ), ZHANG Wenbo1, YAN Xiaomin1, AN Xiaodong3, CHEN Cheng1, HAN Wenting4, LIU Yuanpu2
), ZHANG Wenbo1, YAN Xiaomin1, AN Xiaodong3, CHEN Cheng1, HAN Wenting4, LIU Yuanpu2
 ), 曾鼎文2(
), 曾鼎文2( ), 张文波1, 闫晓敏1, 安晓东3, 陈诚1, 韩雯婷4, 柳媛普2
), 张文波1, 闫晓敏1, 安晓东3, 陈诚1, 韩雯婷4, 柳媛普2