Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (1): 156-165.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-01-0156
• Technology and Applications • Previous Articles Next Articles
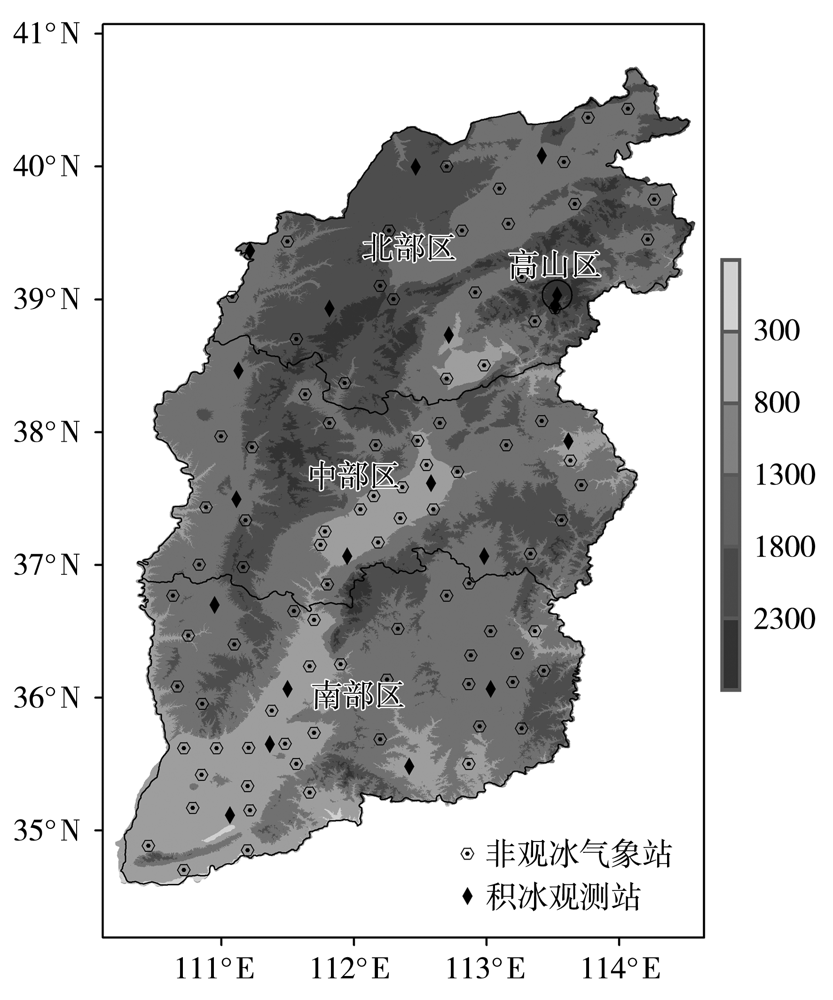
Spatial distribution and division of wire icing thickness under different return periods in Shanxi Province
LI Qinghua1( ), MENG Jie1, LI Jinsong2, LIU Yueli3, CHANG Qing1, JIANG Min2, GUO Dong1
), MENG Jie1, LI Jinsong2, LIU Yueli3, CHANG Qing1, JIANG Min2, GUO Dong1
- 1. Shanxi Meteorological Service Center, Taiyuan 030002, China
2. State Grid Shanxi Electric Power Research Institute, Taiyuan 030001, China
3. Shanxi Climate Center, Taiyuan 030006, China
-
Received:2021-05-18Revised:2021-09-06Online:2022-02-28Published:2022-02-28
山西省不同重现期下电线覆冰厚度空间分布及区划
李清华1( ), 孟洁1, 李劲松2, 刘月丽3, 常清1, 姜敏2, 郭栋1
), 孟洁1, 李劲松2, 刘月丽3, 常清1, 姜敏2, 郭栋1
- 1.山西省气象服务中心,山西 太原 030002
2.国网山西省电力公司电力科学研究院,山西 太原 030001
3.山西省气候中心,山西 太原 030006
-
作者简介:李清华(1975— ),女,高级工程师,主要从事专业气象预报及服务. E-mail: 280327481@qq.com。 -
基金资助:山西省气象局重点科研项目(SXKZDFW20195604);山西省智慧气象服务创新团队共同资助
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LI Qinghua, MENG Jie, LI Jinsong, LIU Yueli, CHANG Qing, JIANG Min, GUO Dong. Spatial distribution and division of wire icing thickness under different return periods in Shanxi Province[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(1): 156-165.
李清华, 孟洁, 李劲松, 刘月丽, 常清, 姜敏, 郭栋. 山西省不同重现期下电线覆冰厚度空间分布及区划[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(1): 156-165.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-01-0156
| 覆冰类型 | 计算值 | 参考范围 |
|---|---|---|
| 雨凇 | 0.80 | 0.70~0.90 |
| 雾凇 | 0.27 | 0.10~0.30 |
| 混合凇 | 0.36 | 0.20~0.60 |
Tab.1 The calculated value of density of wire icing with different types and its reference range
| 覆冰类型 | 计算值 | 参考范围 |
|---|---|---|
| 雨凇 | 0.80 | 0.70~0.90 |
| 雾凇 | 0.27 | 0.10~0.30 |
| 混合凇 | 0.36 | 0.20~0.60 |
| 区 域 | 入选因子 | F值 | 样本量 | 平均偏差/mm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拟合 | 预测 | 拟合 | 预测 | ||||
| 五台山前 | SH,E,RH,Tmax,SH1,RH1,P2 | 50.31 | 1616 | 116 | 1.96 | 1.96 | |
| 五台山后 | SH1,Vave,P1 | 13.263 | 334 | 19 | 0.63 | 0.79 | |
| 北部区 | Tave,Tmin,RH1 | 129.788 | 138 | 60 | 0.89 | 0.71 | |
| 中部区 | E1,RH1,Tave1 | 4.869 74 | 103 | 20 | 0.91 | 1.15 | |
| 南部区 | Tave2,Vave2 | 7.6 | 156 | 45 | 0.67 | 0.73 | |
Tab.2 The regression model of designed wire icing thickness and its error in each region of Shanxi Province
| 区 域 | 入选因子 | F值 | 样本量 | 平均偏差/mm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拟合 | 预测 | 拟合 | 预测 | ||||
| 五台山前 | SH,E,RH,Tmax,SH1,RH1,P2 | 50.31 | 1616 | 116 | 1.96 | 1.96 | |
| 五台山后 | SH1,Vave,P1 | 13.263 | 334 | 19 | 0.63 | 0.79 | |
| 北部区 | Tave,Tmin,RH1 | 129.788 | 138 | 60 | 0.89 | 0.71 | |
| 中部区 | E1,RH1,Tave1 | 4.869 74 | 103 | 20 | 0.91 | 1.15 | |
| 南部区 | Tave2,Vave2 | 7.6 | 156 | 45 | 0.67 | 0.73 | |
| 区 域 | 实测冰厚/ mm | 计算冰厚/ mm | 偏差/ mm | 相对偏差/ % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 北部区 | 1.21 | 1.08 | 0.13 | 10.7 |
| 中部区 | 1.06 | 0.92 | 0.14 | 13.2 |
| 南部区 | 0.74 | 0.62 | 0.12 | 16.2 |
Tab.3 Comparison of calculated value of designed wire icing thickness at non-icing stations with observed mean value at icing stations in different regions of Shanxi Province
| 区 域 | 实测冰厚/ mm | 计算冰厚/ mm | 偏差/ mm | 相对偏差/ % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 北部区 | 1.21 | 1.08 | 0.13 | 10.7 |
| 中部区 | 1.06 | 0.92 | 0.14 | 13.2 |
| 南部区 | 0.74 | 0.62 | 0.12 | 16.2 |
| 站点 | 设计冰厚/mm | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 a重现期 | 50 a重现期 | 100 a重现期 | |
| 大同 | 1.66 | 1.87 | 2.16 |
| 右玉 | 7.04 | 7.94 | 9.16 |
| 原平 | 5.18 | 5.89 | 6.84 |
| 河曲 | 4.45 | 5.02 | 5.80 |
| 五寨 | 10.24 | 11.75 | 13.79 |
| 五台山前 | 28.56 | 31.08 | 34.48 |
| 五台山后 | 7.04 | 7.83 | 8.90 |
| 太原 | 4.48 | 5.07 | 5.87 |
| 阳泉 | 2.07 | 2.28 | 2.56 |
| 榆社 | 5.85 | 6.66 | 7.77 |
| 介休 | 10.13 | 11.59 | 13.55 |
| 临汾 | 2.04 | 2.25 | 2.54 |
| 隰县 | 2.29 | 2.54 | 2.89 |
| 侯马 | 1.10 | 1.20 | 1.34 |
| 运城 | 0.96 | 1.03 | 1.13 |
| 长治 | 6.24 | 7.11 | 8.30 |
| 阳城 | 2.71 | 2.99 | 3.37 |
Tab.4 The designed wire icing thickness under different return periods at icing stations of Shanxi Province
| 站点 | 设计冰厚/mm | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 a重现期 | 50 a重现期 | 100 a重现期 | |
| 大同 | 1.66 | 1.87 | 2.16 |
| 右玉 | 7.04 | 7.94 | 9.16 |
| 原平 | 5.18 | 5.89 | 6.84 |
| 河曲 | 4.45 | 5.02 | 5.80 |
| 五寨 | 10.24 | 11.75 | 13.79 |
| 五台山前 | 28.56 | 31.08 | 34.48 |
| 五台山后 | 7.04 | 7.83 | 8.90 |
| 太原 | 4.48 | 5.07 | 5.87 |
| 阳泉 | 2.07 | 2.28 | 2.56 |
| 榆社 | 5.85 | 6.66 | 7.77 |
| 介休 | 10.13 | 11.59 | 13.55 |
| 临汾 | 2.04 | 2.25 | 2.54 |
| 隰县 | 2.29 | 2.54 | 2.89 |
| 侯马 | 1.10 | 1.20 | 1.34 |
| 运城 | 0.96 | 1.03 | 1.13 |
| 长治 | 6.24 | 7.11 | 8.30 |
| 阳城 | 2.71 | 2.99 | 3.37 |
| 冰 区 | 等级 | 设计冰厚/mm |
|---|---|---|
| 轻冰区 | 1 | 0<bt≤5 |
| 2 | 5<bt≤10 | |
| 中冰区 | 3 | 10<bt≤15 |
| 4 | 15<bt≤20 | |
| 重冰区 | 5 | 20≤bt≤30 |
| 6 | 30<bt≤40 | |
| 7 | 40<bt≤50 | |
| 8 | bt≥50 |
Tab.5 The classification standard of icing area
| 冰 区 | 等级 | 设计冰厚/mm |
|---|---|---|
| 轻冰区 | 1 | 0<bt≤5 |
| 2 | 5<bt≤10 | |
| 中冰区 | 3 | 10<bt≤15 |
| 4 | 15<bt≤20 | |
| 重冰区 | 5 | 20≤bt≤30 |
| 6 | 30<bt≤40 | |
| 7 | 40<bt≤50 | |
| 8 | bt≥50 |
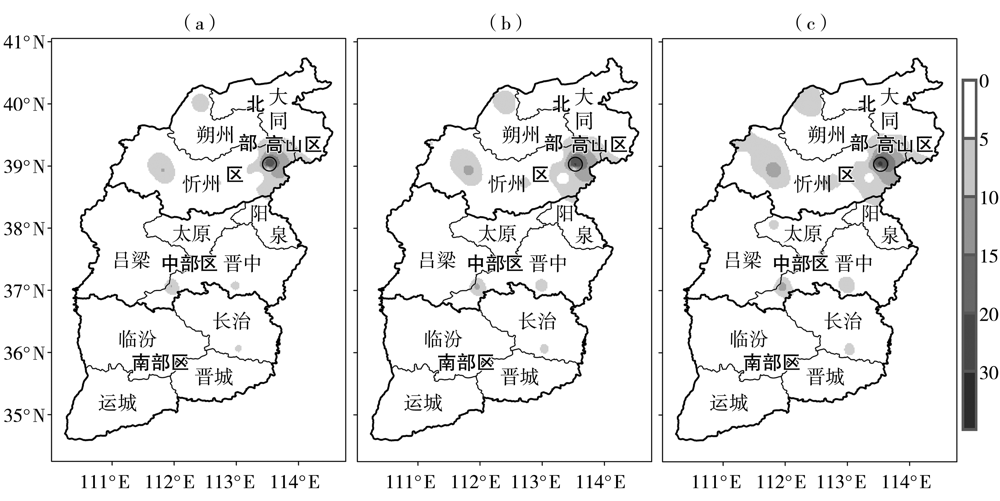
Fig.2 Spatial distribution of designed wire icing thickness under 30-year (a), 50-year (b) and 100-year (c) return periods in Shanxi Province (Unit: mm)
| 地形因子 | 相关系数 | 地形因子 | 相关系数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔高度 | 0.828** | 坡向 | 0.273 |
| 坡度 | 0.452 | 坡向变率 | 0.103 |
| 坡度变率 | -0.379 | 粗糙度 | 0.116 |
| 起伏度 | 0.719** |
Tab.6 The correlation coefficients between designed wire icing thickness under 30-year return period and topography factors at icing stations of Shanxi Province
| 地形因子 | 相关系数 | 地形因子 | 相关系数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔高度 | 0.828** | 坡向 | 0.273 |
| 坡度 | 0.452 | 坡向变率 | 0.103 |
| 坡度变率 | -0.379 | 粗糙度 | 0.116 |
| 起伏度 | 0.719** |

Fig.3 The fitting relationship between designed wire icing thickness under 30-year (a), 50-year (b) and 100-year (c) return periods and elevation at icing stations of Shanxi Province
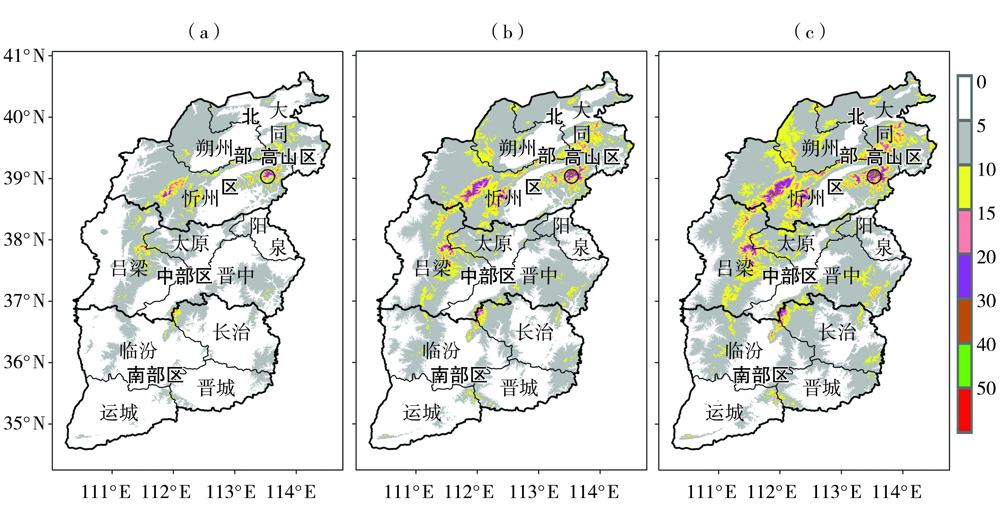
Fig.4 Spatial distribution of designed wire icing thickness under 30-year (a), 50-year (b) and 100-year (c) return periods after the correction of elevation in Shanxi Province (Unit: mm)
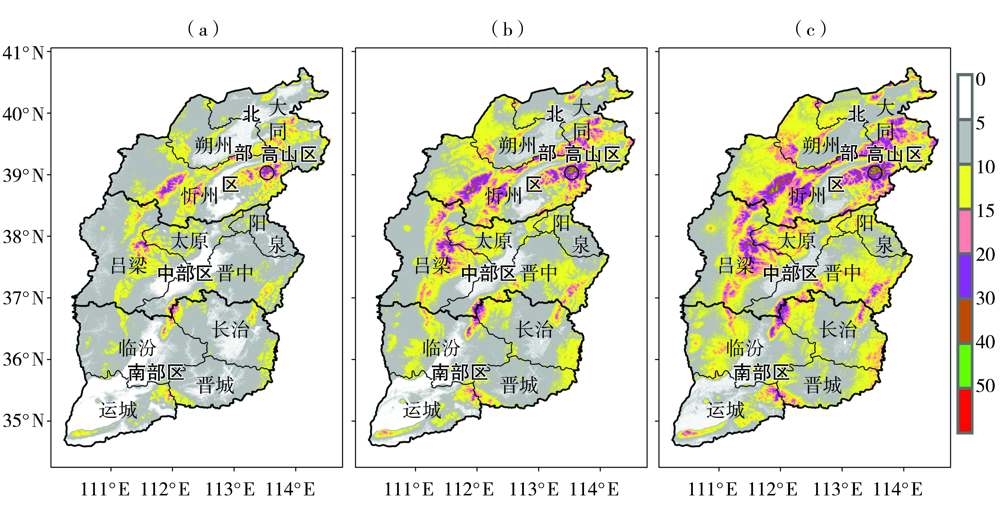
Fig.5 Spatial distribution of designed wire icing thickness under 30-year (a), 50-year (b) and 100-year (c) return periods after the correction of terrain factors in Shanxi Province (Unit: mm)
| 编号 | 覆 冰 区 域 | 地形订正后冰厚值 | 运行经验值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 朔州平鲁虎头山 | 10~15 | 15~20 |
| 2 | 朔城区西北黑驼山 | 10~15 | 15~20 |
| 3 | 忻州宁武县盘道梁 | 10~15 | 20~30(30~40) |
| 10~15 | |||
| 15~20 | |||
| 5~10 | |||
| 4 | 忻州市宁武县摩天岭 | 15~20 | 20~30 |
| 15~20 | |||
| 5 | 忻州 | 5~10 | 15~20 |
| 6 | 吕梁岚县 | 15~20 | 20~30 |
| 7 | 吕梁中阳县车鸣峪地区 | 10~15 | 15~20 |
| 8 | 晋中寿阳县松塔镇上龙泉村 | 5~10 | 20~30 |
| 5~10 | |||
| 9 | 晋中左权 | 5~10 | 20~30 |
| 10~15 | |||
| 10 | 运城芮城中条山 | 5~10 | 20~30 |
| 11 | 运城盐湖区 | 5~10 | 15~20 |
| 12 | 运城平陆 | 5~10 | 15~20 |
Tab.7 The designed wire icing thickness after the terrain correction and operating experience value of icing thickness in wire icing high-risk areas of electric power grid of Shanxi Province from 2011 to 2020
| 编号 | 覆 冰 区 域 | 地形订正后冰厚值 | 运行经验值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 朔州平鲁虎头山 | 10~15 | 15~20 |
| 2 | 朔城区西北黑驼山 | 10~15 | 15~20 |
| 3 | 忻州宁武县盘道梁 | 10~15 | 20~30(30~40) |
| 10~15 | |||
| 15~20 | |||
| 5~10 | |||
| 4 | 忻州市宁武县摩天岭 | 15~20 | 20~30 |
| 15~20 | |||
| 5 | 忻州 | 5~10 | 15~20 |
| 6 | 吕梁岚县 | 15~20 | 20~30 |
| 7 | 吕梁中阳县车鸣峪地区 | 10~15 | 15~20 |
| 8 | 晋中寿阳县松塔镇上龙泉村 | 5~10 | 20~30 |
| 5~10 | |||
| 9 | 晋中左权 | 5~10 | 20~30 |
| 10~15 | |||
| 10 | 运城芮城中条山 | 5~10 | 20~30 |
| 11 | 运城盐湖区 | 5~10 | 15~20 |
| 12 | 运城平陆 | 5~10 | 15~20 |
| 地形起伏度/m | 修正范围/m |
|---|---|
| 500 | 2000 |
| 501~1000 | 1500 |
| 1001~1500 | 1000 |
| ≥1501 | 500 |
Tab.8 The relief of terrain and its modification range
| 地形起伏度/m | 修正范围/m |
|---|---|
| 500 | 2000 |
| 501~1000 | 1500 |
| 1001~1500 | 1000 |
| ≥1501 | 500 |
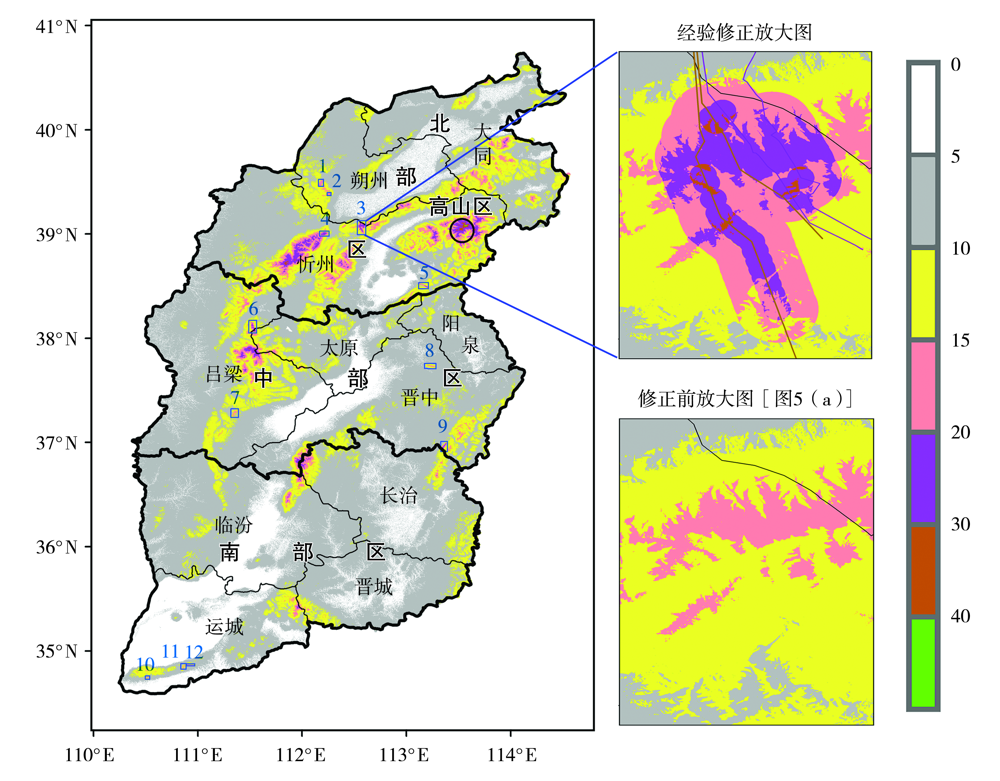
Fig.6 Spatial distribution of designed wire icing thickness after operating empirical modification under 30-year return period in Shanxi Province and enlarged comparison draw in typical area (Unit: mm) (The boxes and interior numbers are the easily icing areas monitored by power grid)
| [1] | 庄文兵, 张海斌, 赵宏宇, 等. 电线覆冰预报模型研究综述[J]. 气象科技进展, 2017, 7(2):6-12. |
| [2] | IMAI I. Studies on ice accretion[J]. Researches on Snow and Ice, 1953, 3(1):35-44. |
| [3] |
LENHARD R W. An indirect method for estimating the weight of glaze on wires[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 1955, 36(3):1-5.
DOI URL |
| [4] | CHAÎNÉ P M, CASTONGUAY G. New approach to radial ice thickness concept applied to bundle-like conductors[R]. Industrial Meteorology Study Ⅳ Environment Canada, Toronto, 1974. |
| [5] | GOODWIN Ⅲ E J, MOZER J D, DIGIOIA JR A M, et al. Predicting ice and snow loads for transmission line design Proceedings of the First IWAIS, 1983:267-273. |
| [6] |
MAKKONEN L. Modeling of ice accretion on wires[J]. Journal of Climate and Applied Meteorology, 1984, 23(6):929-939.
DOI URL |
| [7] | MCCOMBER P, GOVONI J W. An analysis of selected ice accretion measurements on a wire at Mount Washington[C]// Proceedings of the Forty-second Annual Eastern Snow Conference, Montreal, Canada, 1985. |
| [8] |
MAKKONEN L. Modeling power line icing in freezing precipitation[J]. Atmospheric Research, 1998, 46(1/2):131-142.
DOI URL |
| [9] | 蒋兴良, 孙才新, 顾乐观, 等. 三峡地区导线覆冰的特性及雾凇覆冰模型[J]. 重庆大学学报(自然科学版), 1998, 21(2):16-19. |
| [10] | 刘和云, 周迪, 付俊萍, 等. 导线雨淞覆冰预测简单模型的研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2001, 21(4):44-47. |
| [11] | 覃武, 罗小莉, 郑凤琴, 等. 广西输电线路覆冰典型年份的环流特征分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 2019, 13(1):110-116. |
| [12] | 王如荣, 解朝真, 张树林. 南岭覆冰气象站观测资料分析与高压输电线路建设的探讨[J]. 山西气象, 1997(4):16-18. |
| [13] | 刘军臣, 郭二凤, 康雯瑛. 河南电线积冰气候特征及对架空线路的影响[J]. 河南气象, 1999(1):27-28. |
| [14] | 刘赫男, 张洪玲, 朱红蕊, 等. 黑龙江省电线积冰的气候特征及电网冰区划分[J]. 冰川冻土, 2014, 36(3):555-562. |
| [15] | 顾光芹, 田国强, 周须文. 河北省电线积冰的气候特征及一次电线积冰天气过程分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 2012, 35(1):8-13. |
| [16] | 张婷. 吉林省电线积冰的特征分析及气象条件初探[J]. 气象灾害防御, 2015(3):44-48. |
| [17] | 吴素良, 范建勋, 姜创业, 等. 兰州至关中电线积冰与导线线径及高度关系[J]. 应用气象学报, 2010, 21(1):63-69. |
| [18] | 龚强, 汪宏宇, 蔺娜, 等. 辽宁省电线积冰特征与电网冰区划分研究[J]. 冰川冻土, 2010, 32(3):549-556. |
| [19] | 武辉芹, 张金满, 赵增保. 河北省输电线路冰害的气象要素时空分布特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2017, 35(6):991-997. |
| [20] | 王馨, 卢毅, 张旭, 等. 冀北地区输电线路覆冰风险预报研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(1):164-168. |
| [21] | 殷水清, 赵珊珊, 王遵娅, 等. 全国电线结冰厚度分布及等级预报模型[J]. 应用气象学报, 2009, 20(6):722-728. |
| [22] | 温华洋, 田红, 唐为安, 等. 安徽省电线积冰标准冰厚的气象估算模型[J]. 应用气象学报, 2011, 22(6):747-752. |
| [23] | 廖玉芳, 段丽洁. 湖南电线覆冰厚度估算模型研究[J]. 大气科学学报, 2010, 33(4):395-400. |
| [24] | 庞文保, 白光弼, 李建科, 等. 陕西省电线积冰区划[J]. 气象, 2012, 38(6):733-739. |
| [25] | 张小军, 庄文兵, 肯巴提·波拉提. 北疆电线积冰的分布及区划[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 2021, 15(3):117-121. |
| [26] | 吴素良, 范建勋, 宋丽莉, 等. 陕西省冰区划分[J]. 电网技术, 2010, 34(4):152-157. |
| [27] | 王传辉, 姚叶青, 苗开超, 等. 安徽省电线覆冰厚度推算初探[J]. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(3):500-507. |
| [28] | 唐亚平, 张凯, 李岚, 等. 辽宁省电线覆冰特征及冰区重现期标准冰厚分布[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2015, 31(4):58-64. |
| [29] | 张弦. 输电线路中微地形和微气象的覆冰机制及相应措施[J]. 电网技术, 2007, 31(增刊2):87-89. |
| [30] | 国网湖南省电力公司防灾减灾中心, 国网湖南省电力公司, 中国电力科学研究院, 等. 电网冰区分布图绘制技术导则: GB/T 35706—2017[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018. |
| [31] | 蒋兴良, 易辉. 输电线路覆冰及防护[M]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2002. |
| [32] | 蒋兴良, 杜珍, 莫文强, 等. 重庆地区电网覆冰的海拔高度特性[J]. 高电压技术, 2011, 37(6):1336-1342. |
| [33] | 黄俊杰, 周悦, 阮羚. 湖北省地形因子对电线覆冰的影响研究[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2015, 34(3):254-259. |
| [34] | 黄俊杰, 吴边, 阮羚, 等. 一种基于微地形的电网冰区分布图局部订正方法: 201410397252.2[P]. 2014-11-05. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||