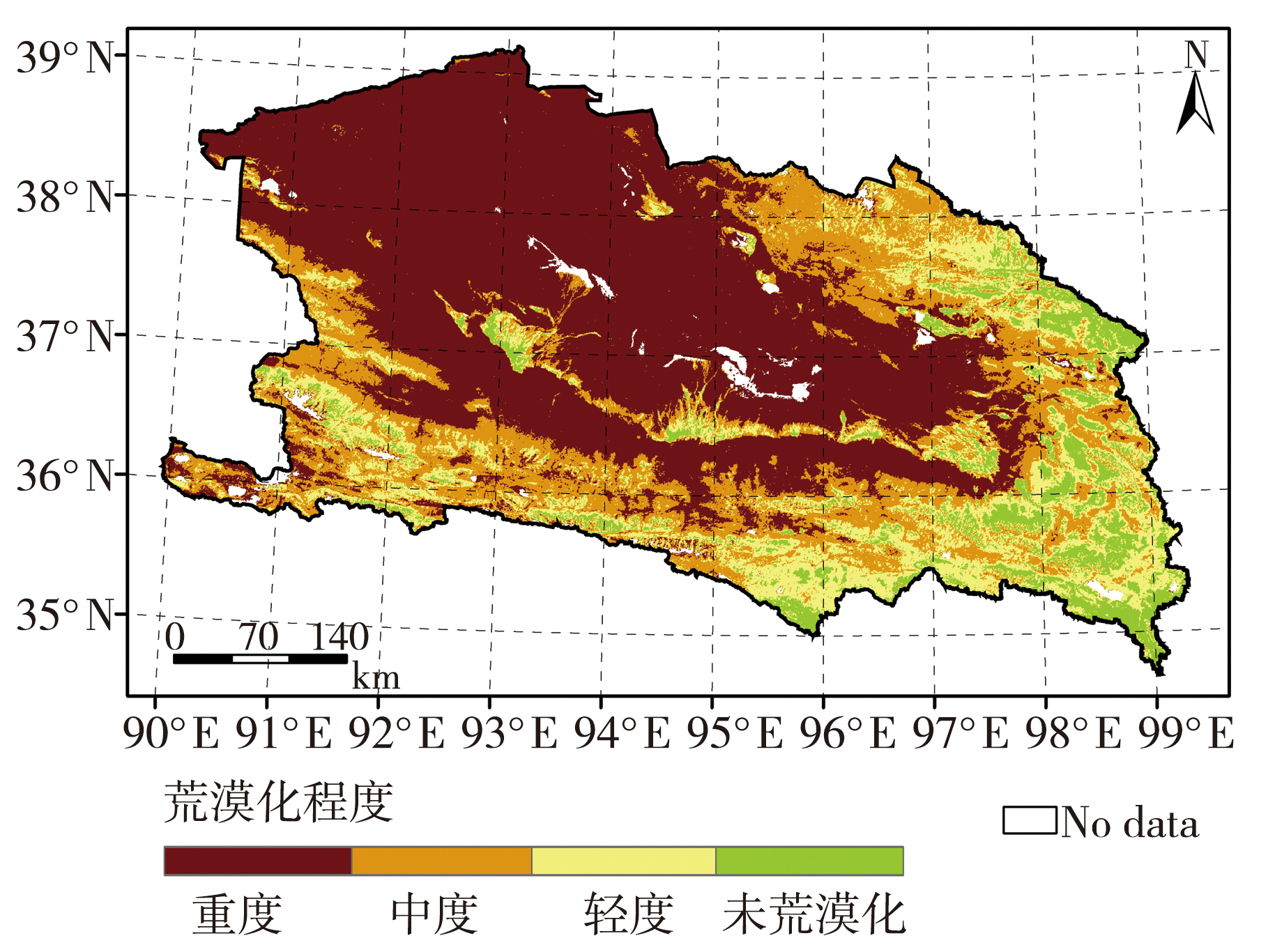
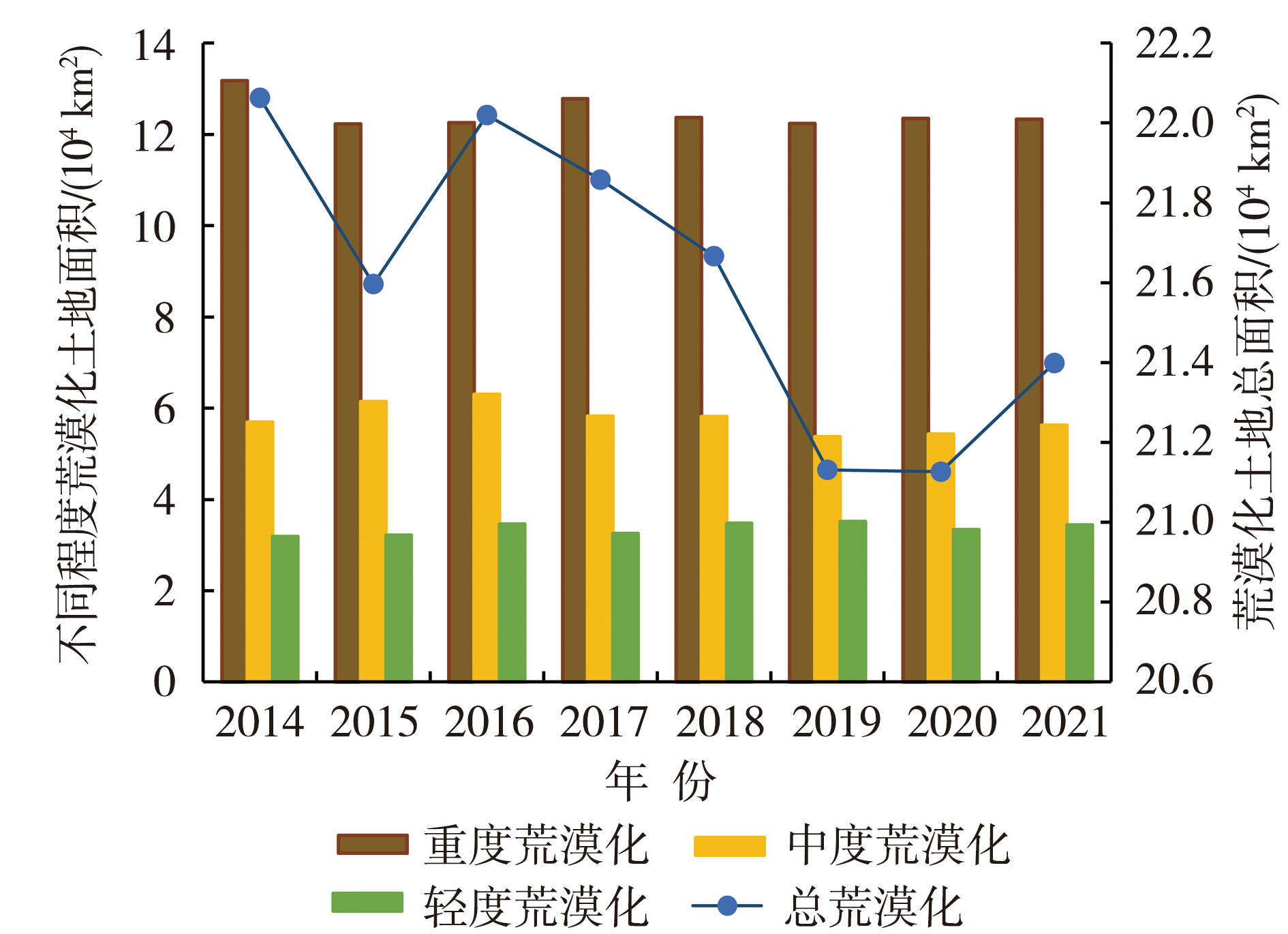
| [1] |
曹晓云, 祝存兄, 陈国茜, 等, 2022. 2000—2021年柴达木盆地地表绿度变化及地形分异研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(6): 1 080-1 090.
|
| [2] |
邓梅, 2018. 柴达木地区生态综合治理和绿色产业发展对策研究[J]. 林业经济, (1): 61-65.
|
| [3] |
丁国栋, 2004. 区域荒漠化评价中植被的指示性及盖度分级标准研究——以毛乌素沙区为例[J]. 水土保持学报, 18(1): 158-160.
|
| [4] |
冯娴慧, 曾芝琳, 2022. 粤港澳大湾区植被覆盖特征与变化趋势的自然驱动力研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(9): 1 713-1 724.
|
| [5] |
郭瑞霞, 管晓丹, 张艳婷, 2015. 我国荒漠化主要研究进展[J]. 干旱气象, 33(3): 505-514.
DOI
|
| [6] |
贺鹏, 郑新倩, 徐立帅, 等, 2021. 基于结构相似度的巴丹吉林沙漠地表反照率时空分布特征[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 15(1): 111-118.
|
| [7] |
胡云锋, 张云芝, 韩月琪, 2018. 2000—2015年中国荒漠化土地识别和监测[J]. 干旱区地理, 41(6): 1 321-1 332.
|
| [8] |
李红梅, 2018. 柴达木盆地气候变化对植被的影响分析[J]. 草业学报, 27(3): 13-23.
DOI
|
| [9] |
李三旦, 2015. 青海省防沙治沙生态建设对策研究[J]. 青海农林科技, (1): 31-35.
|
| [10] |
李燕, 2014. 荒漠化动态变化及驱动机制对比研究——以张家口坝上和都阳山山区为例[D]. 桂林: 广西师范学院.
|
| [11] |
刘建宇, 聂洪峰, 肖春蕾, 等, 2021. 2010—2018年中国北方沙质荒漠化变化分析[J]. 中国地质调查, 8(6): 25-34.
|
| [12] |
刘英, 李遥, 鲁杨, 等, 2019. 2000—2016年黄土高原地区荒漠化遥感分析[J]. 遥感信息, 34(2): 30-35.
|
| [13] |
刘晓茜, 2020. 腾格里沙漠东南缘荒漠-绿洲过渡带土地沙化动态变化研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古师范大学.
|
| [14] |
潘竟虎, 李天宇, 2010. 基于光谱混合分析和反照率-植被盖度特征空间的土地荒漠化遥感评价[J]. 自然资源学报, 25(11): 1 960-1 969.
|
| [15] |
任艳群, 刘海隆, 唐立新, 等, 2014. 基于NDVI-Albedo特征空间的沙漠化动态变化研究——以准格尔盆地南缘为例[J]. 水土保持通报, 34(2): 267-271.
|
| [16] |
史尚渝, 王飞, 金凯, 等, 2020. 黄土高原地区植被指数对干旱变化的响应[J]. 干旱气象, 38(1): 1-13.
|
| [17] |
田广庆, 2011. 青海柴达木地区荒漠化现状及防治对策研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学.
|
| [18] |
屠志方, 李梦先, 孙涛, 2016. 第五次全国荒漠化和沙化监测结果及分析[J]. 林业资源管理, (1): 1-5.
|
| [19] |
王林林, 刘普幸, 王允, 2015. 近14年来柴达木盆地NDVI时空变化及其影响因素[J]. 生态学杂志, 34(6): 1 713-1 722.
|
| [20] |
王玲玲, 何巍, 罗米娜, 等, 2021. 基于归一化旱情综合指数的川西高原草地伏旱监测分析[J]. 干旱气象, 39(6): 884-893.
|
| [21] |
王维坤, 胡月宏, 田松妮, 等, 2022. 内蒙古西部沙区气候变化及其植被响应[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 16(3): 112-118.
|
| [22] |
王旭, 刁兆岩, 郑志荣, 等, 2021. 中蒙毗邻草原区荒漠化时空动态研究[J]. 环境科学研究, 34(12): 2 935-2 944.
|
| [23] |
汪震, 姜勇彪, 岳兵, 2021. 江西吉泰盆地荒漠化时空变化特征及影响因素分析[J]. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 44(2): 150-155.
|
| [24] |
魏伟, 俞啸, 张梦真, 等, 2021. 1995—2018年石羊河流域下游荒漠化动态变化[J]. 应用生态学报, 32(6): 2 098-2 106.
|
| [25] |
徐浩杰, 杨太保, 2014. 柴达木盆地植被生长时空变化特征及其对气候要素的响应[J]. 自然资源学报, 29(3): 398-409.
DOI
|
| [26] |
徐新良, 刘纪远, 张树文, 等, 2018. 中国多时期土地利用土地覆被遥感监测数据集(CNLUCC)[Z]. 中国科学院资源环境科学数据中心数据注册与出版系统. (http://www.resdc.cn/DOD).DOI:10.12078/2018070201.
DOI
URL
|
| [27] |
许学莲, 雷玉红, 曹雪枫, 等, 2021. 1981—2018年柴达木盆地作物生长季气象要素时空变化特征分析[J]. 湖北农业科学, 60(18): 42-49.
|
| [28] |
游宇驰, 李志威, 黄草, 等, 2017. 1990—2016年若尔盖高原荒漠化时空变化分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 26(10): 1 671-1 680.
|
| [29] |
于志翔, 2023. 基于MODIS数据的新疆大气气溶胶光学厚度时空变化分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 17(2): 128-136.
|
| [30] |
曾永年, 向南平, 冯兆东, 等, 2006. Albedo-NDVI特征空间及沙漠化遥感监测指数研究[J]. 地理科学, 26(1): 75-81.
|
| [31] |
张钛仁, 张玉峰, 柴秀梅, 等, 2010. 人类活动对我国西北地区沙质荒漠化影响与对策研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 30(2): 228-234.
|
| [32] |
张登山, 高尚玉, 2007. 青海高原沙漠化研究进展[J]. 中国沙漠, 27(3): 367-372.
|
| [33] |
张国龙, 2020. 人类活动与气候变化影响下全球荒漠化风险研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学.
|
| [34] |
郑春燕, 梁俊红, 王建, 2022. 中巴经济走廊归一化植被指数(NDVI)时空变化及影响因素分析[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 38(9): 1 147-1 156.
|
| [35] |
朱震达, 1988. 中国沙漠化的现状及其研究的若干问题[J]. 地球科学信息, 4: 20-24.
|
| [36] |
邹明亮, 韩雅敏, 曾建军, 等, 2019. 基于Albedo-NDVI特征空间的玛曲县荒漠化时空动态监测[J]. 冰川冻土, 41(1): 45-53.
|
| [37] |
HUANG J P, YU H P, GUAN X D, et al, 2015. Accelerated dryland expansion under climate change[J]. Nature Climate Change, 6(2): 166-171.
DOI
|
| [38] |
LI S G, HARAZONO Y, OIKAWA T, et al, 2000. Grassland desertification by grazing and the resulting micrometeorological changes in Inner Mongolia[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 102(2/3): 125-137.
DOI
URL
|
| [39] |
VERSTRAETE M, PINTY B, 1996. Designing optimal spectral indexes for remote sensing applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 34(5): 1 254-1 265.
DOI
URL
|
| [40] |
WU Z H, LEI S G, BIAN Z F, et al, 2019. Study of the desertification index based on the Albedo-MSAVI feature space for semi-arid steppe region[J]. Environmental Earth Science, 78(6): 1-13.
DOI
|
| [41] |
ZHOU Y Q, HU Z W, GENG Q Q, et al, 2023. Monitoring and analysis of desertifcation surrounding Qinghai Lake (China) using remote sensing big data[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30(7): 17 420-17 436.
DOI
|
 ), 曹晓云1,2, 肖建设1,2, 孙玮婕1,2, 祝存兄1,2(
), 曹晓云1,2, 肖建设1,2, 孙玮婕1,2, 祝存兄1,2( )
)
 ), CAO Xiaoyun1,2, XIAO Jianshe1,2, SUN Weijie1,2, ZHU Cunxiong1,2(
), CAO Xiaoyun1,2, XIAO Jianshe1,2, SUN Weijie1,2, ZHU Cunxiong1,2( )
)