2025年1月美国洛杉矶破纪录山火事件的干旱气象条件归因
Attribution of drought-related meteorological conditions for the record-breaking wildfire event in Los Angeles in January 2025
[
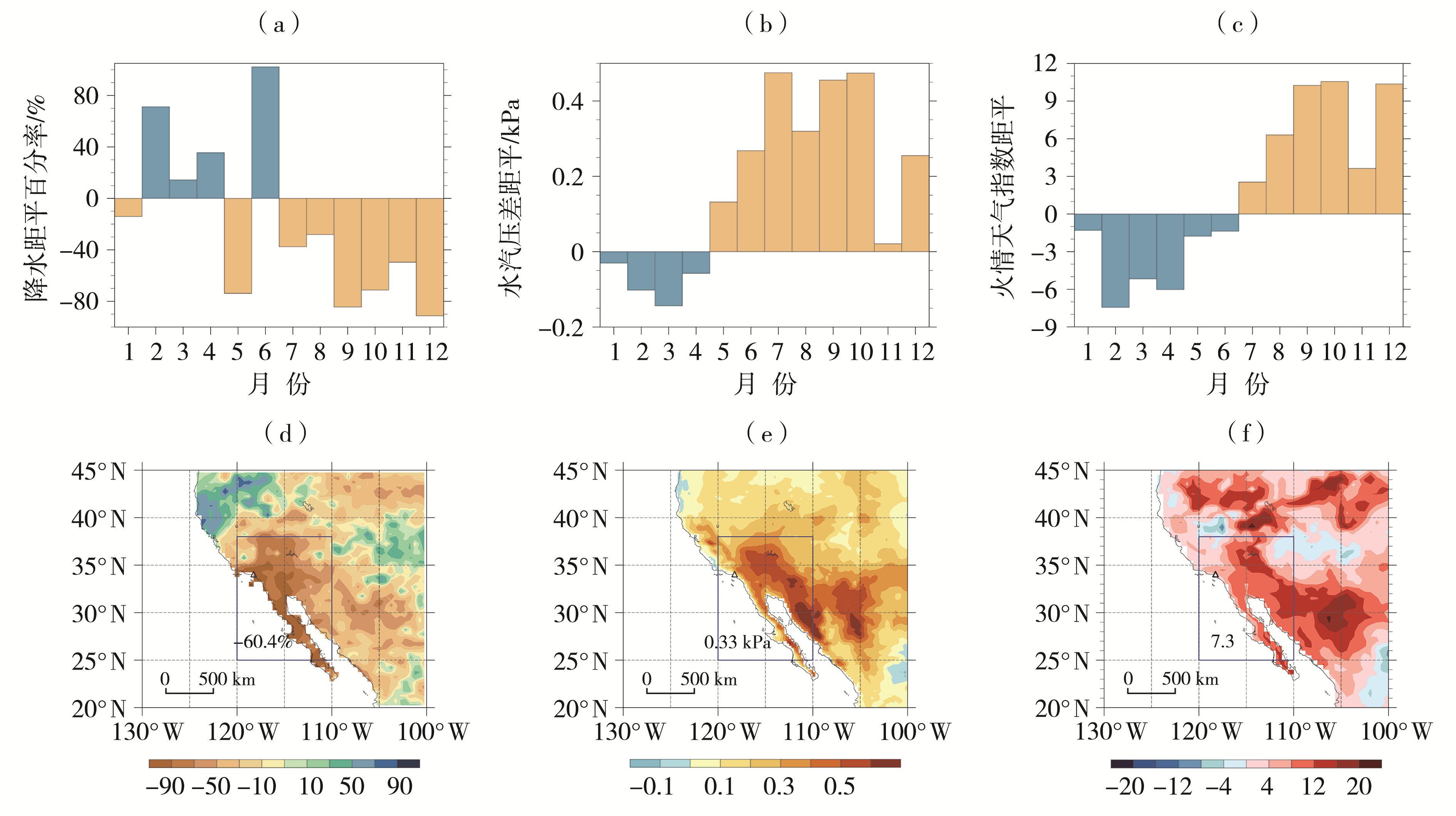
(The blue boxed area (25°N-38°N, 120°W-110°W) in
2025年1月美国洛杉矶破纪录山火事件的干旱气象条件归因 |
| 于晓晶, 张丽霞, 于志翔, 杨可儿 |
|
Attribution of drought-related meteorological conditions for the record-breaking wildfire event in Los Angeles in January 2025 |
| YU Xiaojing, ZHANG Lixia, YU Zhixiang, YANG Ke’er |
| 图4 2024年(a、b、c)及2024年7—12月(d、e、f)美国西部地区降水距平百分率(a、d)(单位:%)、VPD距平(b、e)(单位:kPa)和FWI距平(c、f)的逐月变化(a、b、c)及空间分布(d、e、f) [ |
| Fig.4 The monthly variations (a, b, c) and spatial distributions (d, e, f) of precipitation anomaly percentage (a, d) (Unit: %), VPD anomaly (b, e) (Unit: kPa) and FWI anomaly (c, f) in the western United States in 2024 (a, b, c) and from July to December 2024 (d, e, f) (The blue boxed area (25°N-38°N, 120°W-110°W) in |

|