东北地区低温春涝事件形成机制及其影响
|
|
张丽, 沈柏竹, 李天宇, 金赫, 王凌
|
Formation mechanism and impacts of low-temperature and spring flood events in Northeast China
|
|
ZHANG Li, SHEN Baizhu, LI Tianyu, JIN He, WANG Ling
|
|
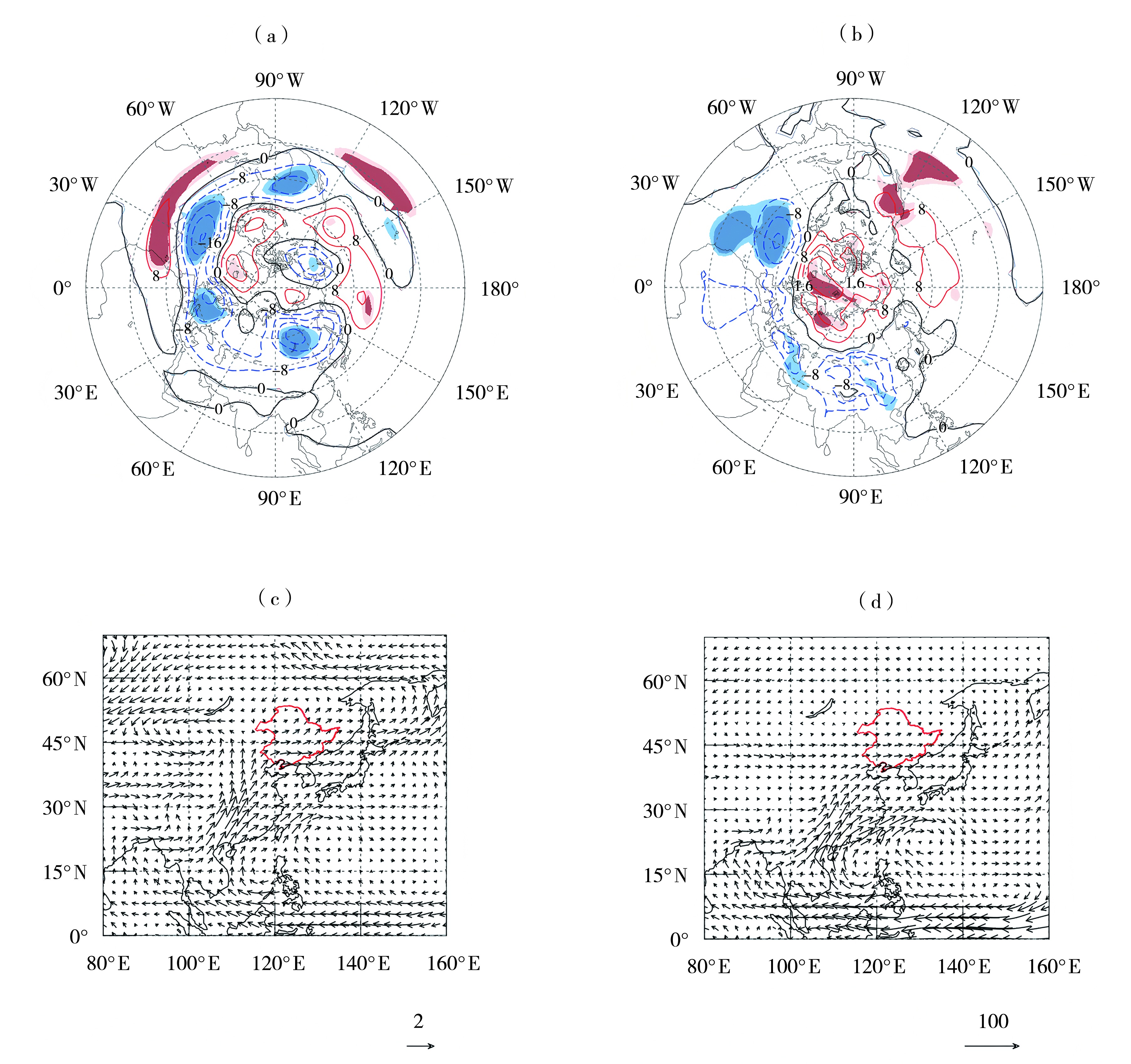
图2 东北地区严重低温春涝典型年春季500 hPa位势高度距平(等值线,单位:gpm)(a)、海平面气压距平(等值线,单位: hPa)(b)、850 hPa风场距平(箭矢,单位:m·s-1)(c)和整层水汽输送通量距平(箭矢,单位:kg·m-1·s-1)(d)合成场
(红色实线为正值,蓝色虚线为负值;红色和蓝色深、浅阴影分别表示通过置信水平为95%、99%的显著性检验;红色线包围区域表示东北地区,下同)
|
Fig.2 The composite field of 500 hPa geopotential height anomaly (contours, Unit: gpm) (a), sea level pressure anomaly (contours, Unit: hPa) (b), 850 hPa wind field anomaly (arrow vectors, Unit: m·s-1) (c) and the whole layer water vapor transport flux anomaly (arrow vectors, Unit: kg·m-1·s-1) (d) in typical years of severity low-temperature and spring flooding in Northeast China
(The red solid lines represent positive values, and the blue dashed lines represent negative values; The deep and light shadows of red and blue indicate passing the significance test at the 95% and 99% confidence levels, respectively; The area surrounded by the red line indicates the Northeast China)
|
|
|
|
|
