贺兰山东麓暴雨天气分型及气象要素演变特征研究
Classification and meteorological element evolution of rainstorm in the eastern Helan Mountain foothills
(红色线范围为宁夏,下同)
(The red line range indicates Ningxia, the same as below)
贺兰山东麓暴雨天气分型及气象要素演变特征研究 |
| 陈敏, 陈豫英, 陈荣, 陈宇曦, 杨苑媛 |
|
Classification and meteorological element evolution of rainstorm in the eastern Helan Mountain foothills |
| CHEN Min, CHEN Yuying, CHEN Rong, CHEN Yuxi, YANG Yuanyuan |
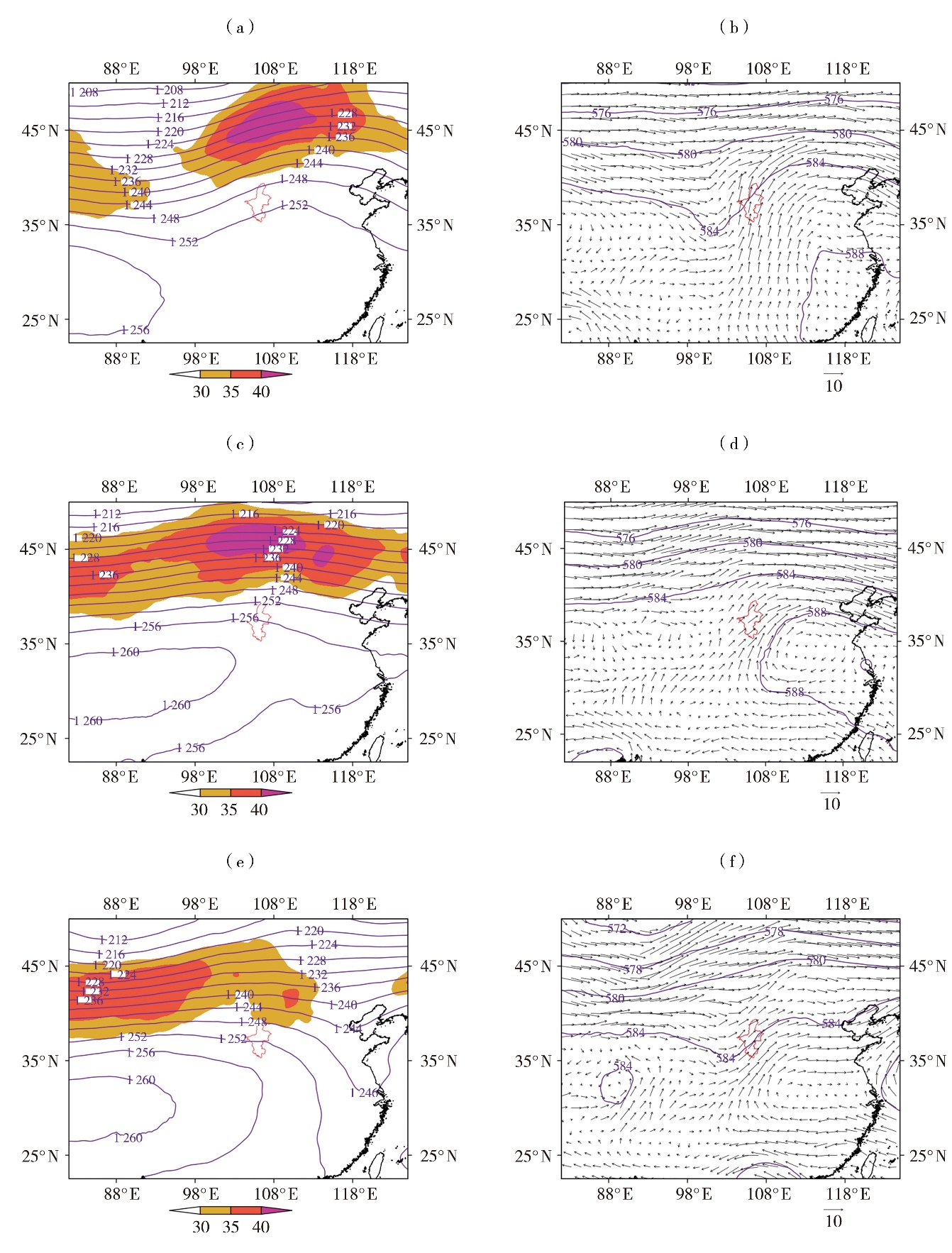
| 图3 冷暖交汇型(a、b)、暖区型(c、d)及弱冷空气入侵型(e、f)暴雨200 hPa平均位势高度场(等值线,单位:dagpm)及风速≥30 m·s-1的高空急流区(阴影)(a、c、e)、500 hPa平均位势高度场(等值线,单位:dagpm)及风场(风矢,单位:m·s-1)(b、d、f) (红色线范围为宁夏,下同) |
| Fig.3 The average geopotential height field (contours, Unit: dagpm) and jet flow area with wind speed greater than or equal to 30 m·s-1 (the color shaded) at 200 hPa (a, c, e) and the average geopotential height field (contours, Unit: dagpm) and wind field (wind vectors, Unit: m·s-1) at 500 hPa (b, d, f) of rainstorm for cold-warm convergence type (a, b), warm-sector type (c, d), and weak cold air intrusion type (e, f) (The red line range indicates Ningxia, the same as below) |

|