贺兰山东麓暴雨天气分型及气象要素演变特征研究
Classification and meteorological element evolution of rainstorm in the eastern Helan Mountain foothills
贺兰山东麓暴雨天气分型及气象要素演变特征研究 |
| 陈敏, 陈豫英, 陈荣, 陈宇曦, 杨苑媛 |
|
Classification and meteorological element evolution of rainstorm in the eastern Helan Mountain foothills |
| CHEN Min, CHEN Yuying, CHEN Rong, CHEN Yuxi, YANG Yuanyuan |
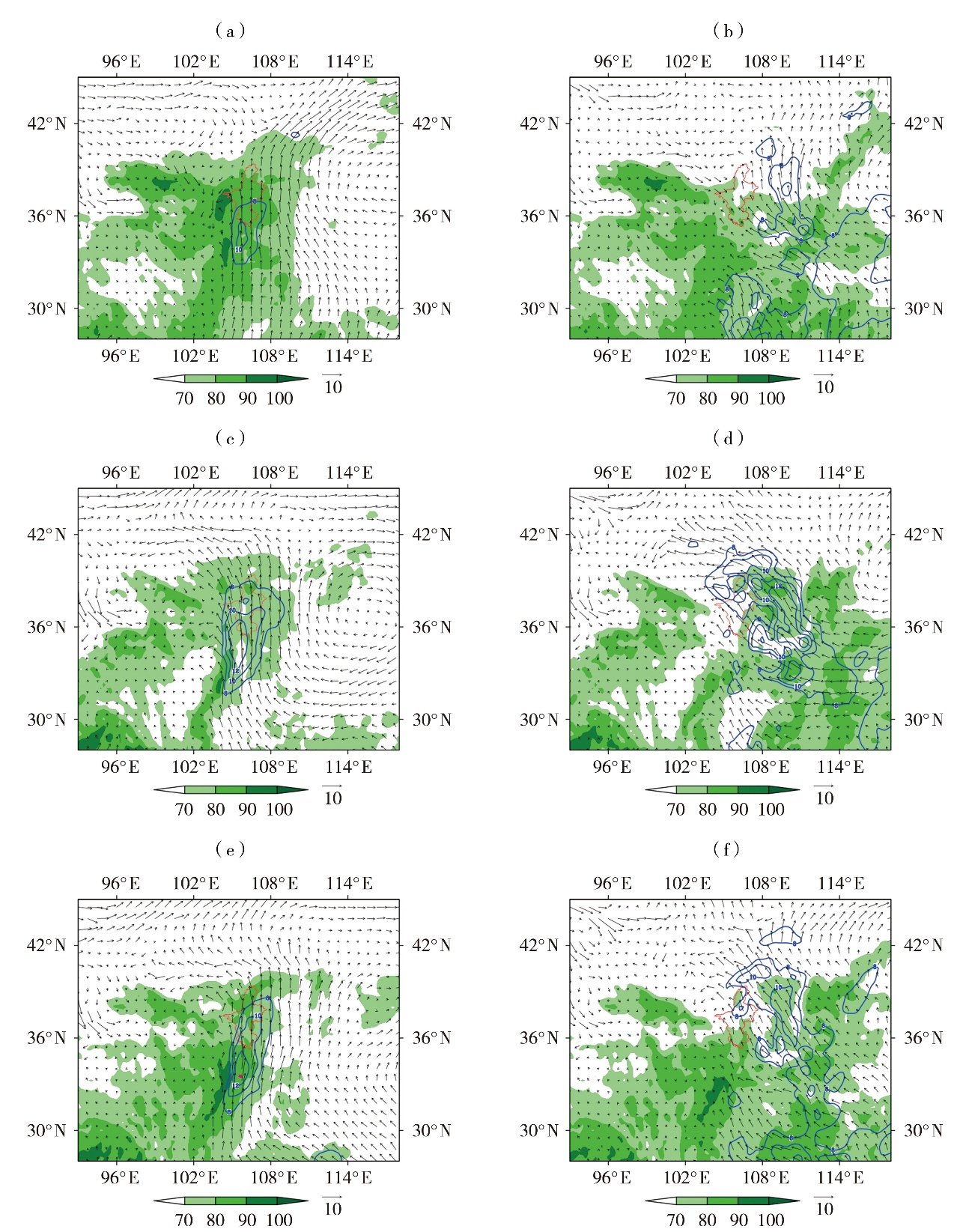
| 图4 冷暖交汇型(a、b)、暖区型(c、d)及弱冷空气入侵型(e、f)暴雨700 hPa(a、c、e)、850 hPa(b、d、f)合成风场(箭矢,单位:m·s-1)、相对湿度场(绿色阴影,单位:%)和大于8×105 g·hPa·cm-1·s-1的水汽通量(蓝色等值线,单位:105 g·hPa·cm-1·s-1) |
| Fig.4 The composite wind field (vector arrows, Unit: m·s-1), relative humidity field (the green shadow, Unit: %) and water vapor flux greater than 8×105 g·hPa·cm-1·s-1 (blue isolines, Unit: 105 g·hPa·cm-1·s-1) at 700 hPa (a, c, e) and 850 hPa (b, d, f) of rainstorm for cold-warm convergence type (a, b), warm-sector type (c, d), and weak cold air intrusion type (e, f) |

|