川渝地区夏季气象干旱差异及大气环流成因分析
Analysis on differences of characteristics and atmospheric circulation causes of meteorological drought during summer in Sichuan-Chongqing region
川渝地区夏季气象干旱差异及大气环流成因分析 |
| 何慧根, 张驰, 成青燕, 李永华, 甘薇薇, 金燕 |
|
Analysis on differences of characteristics and atmospheric circulation causes of meteorological drought during summer in Sichuan-Chongqing region |
| HE Huigen, ZHANG Chi, CHENG Qingyan, LI Yonghua, GAN Weiwei, JIN Yan |
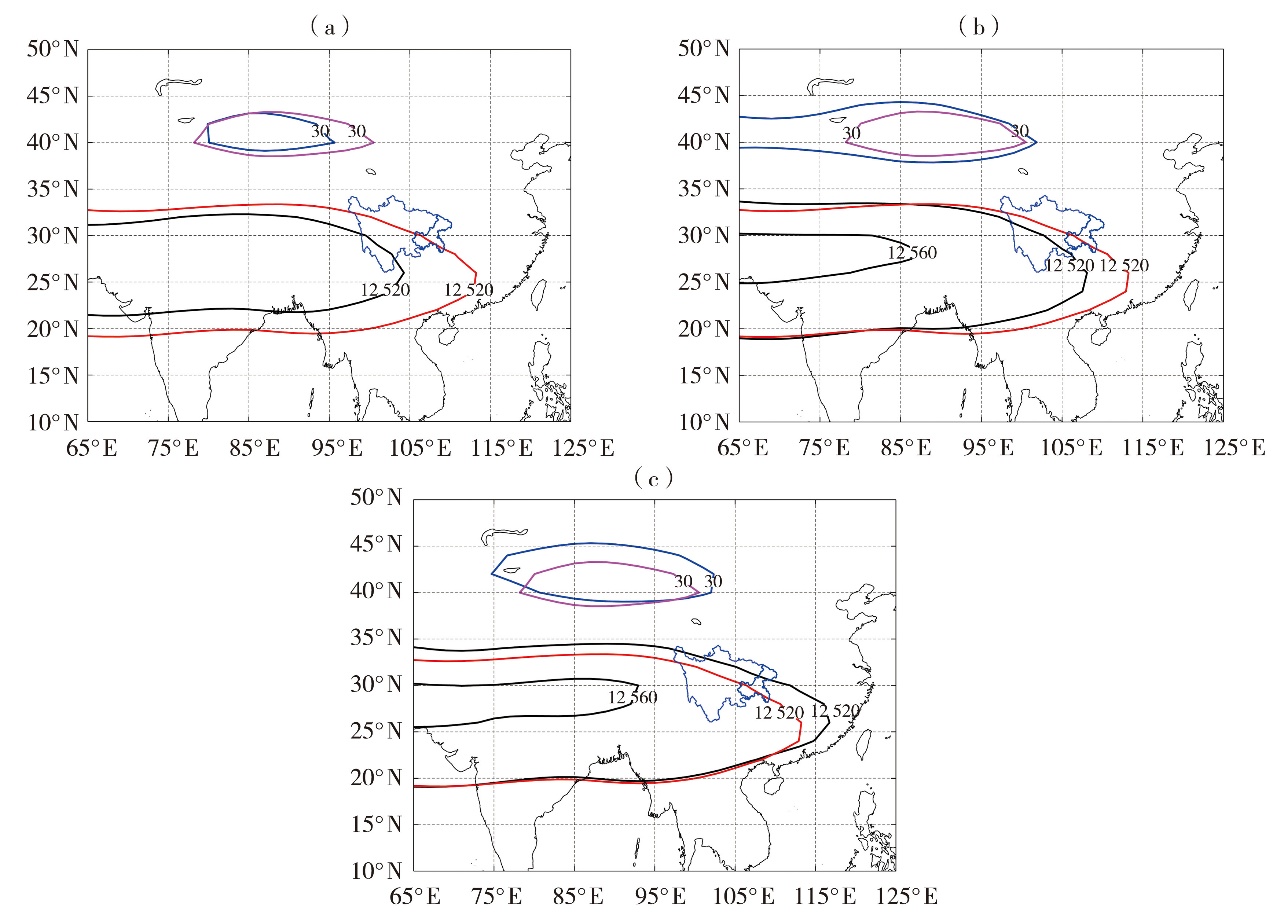
| 图8 四川干旱重年(a)、重庆干旱重年(b)及川渝干旱均重年(c)夏季200 hPa位势高度场大于12 520 gpm等位势高度线(黑色线)及12 520 gpm气候态平均(红色线)(单位:gpm)、200 hPa纬向风速大于30 m·s-1(蓝色粗线)及30 m·s-1风速气候态平均(粉色线)(单位: m·s-1) |
| Fig.8 The composited 200 hPa geopotential height contours greater than 12 520 gpm (black lines) and the climatological mean of 12 520 gpm (red line) (Unit: gpm), zonal wind speed exceeding 30 m·s-1 (blue thick line) and the climatological mean of zonal wind speed at 30 m·s-1 (pink line) (Unit: m·s-1) at 200 hPa in summer in years with severe drought in Sichuan (a), years with severe drought in Chongqing (b), and years with severe drought both in Sichuan and Chongqing (c) |

|