流感发病对短期天气变化强度的响应及风险预警研究
The response of influenza-like illnesses to short-term weather variability intensity and risk early warning
流感发病对短期天气变化强度的响应及风险预警研究 |
| 赵小芳, 方思达, 雷小妹, 刘敏, 余晓, 徐慧 |
|
The response of influenza-like illnesses to short-term weather variability intensity and risk early warning |
| ZHAO Xiaofang, FANG Sida, LEI Xiaomei, LIU Min, YU Xiao, XU Hui |
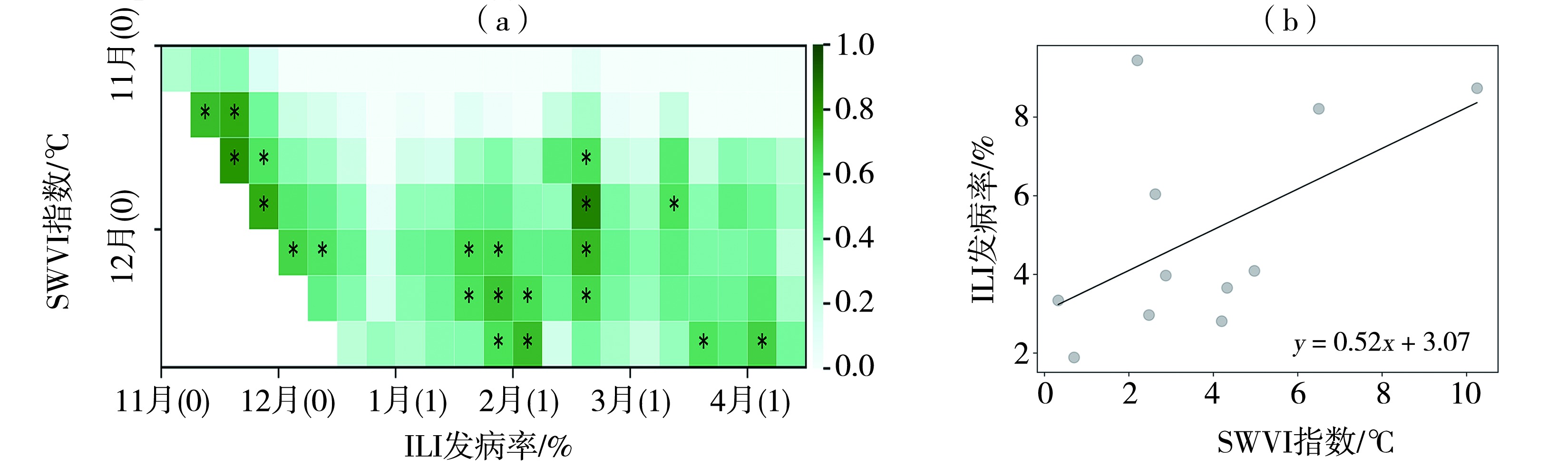
| 图3 2009—2020年武汉市ILI发病率与SWVI指数的滞后相关性(a,0表示当年,1表示次年;*通过α=0.05的显著性检验)与11—12月平均SWVI指数与11月至次年3月ILI发病率最大值的散点图(b) |
| Fig.3 The lag correlation between ILI morbidity and SWVI index (a, 0 represents the current year, 1 represents the next year; the asterisks pass the significant test at α=0.05), and the scatter plot between average SWVI index from November to December and maximum ILI morbidity during November to March of the following year (b) in Wuhan during 2009-2020 |

|