印度双低涡对青藏高原西部一次典型暴雪过程的影响
|
|
张入财, 王君, 陈超辉, 付伟基, 魏璐璐
|
Influence of Indian double vortexes on a typical snowstorm event in the west of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau
|
|
ZHANG Rucai, WANG Jun, CHEN Chaohui, FU Weiji, WEI Lulu
|
|
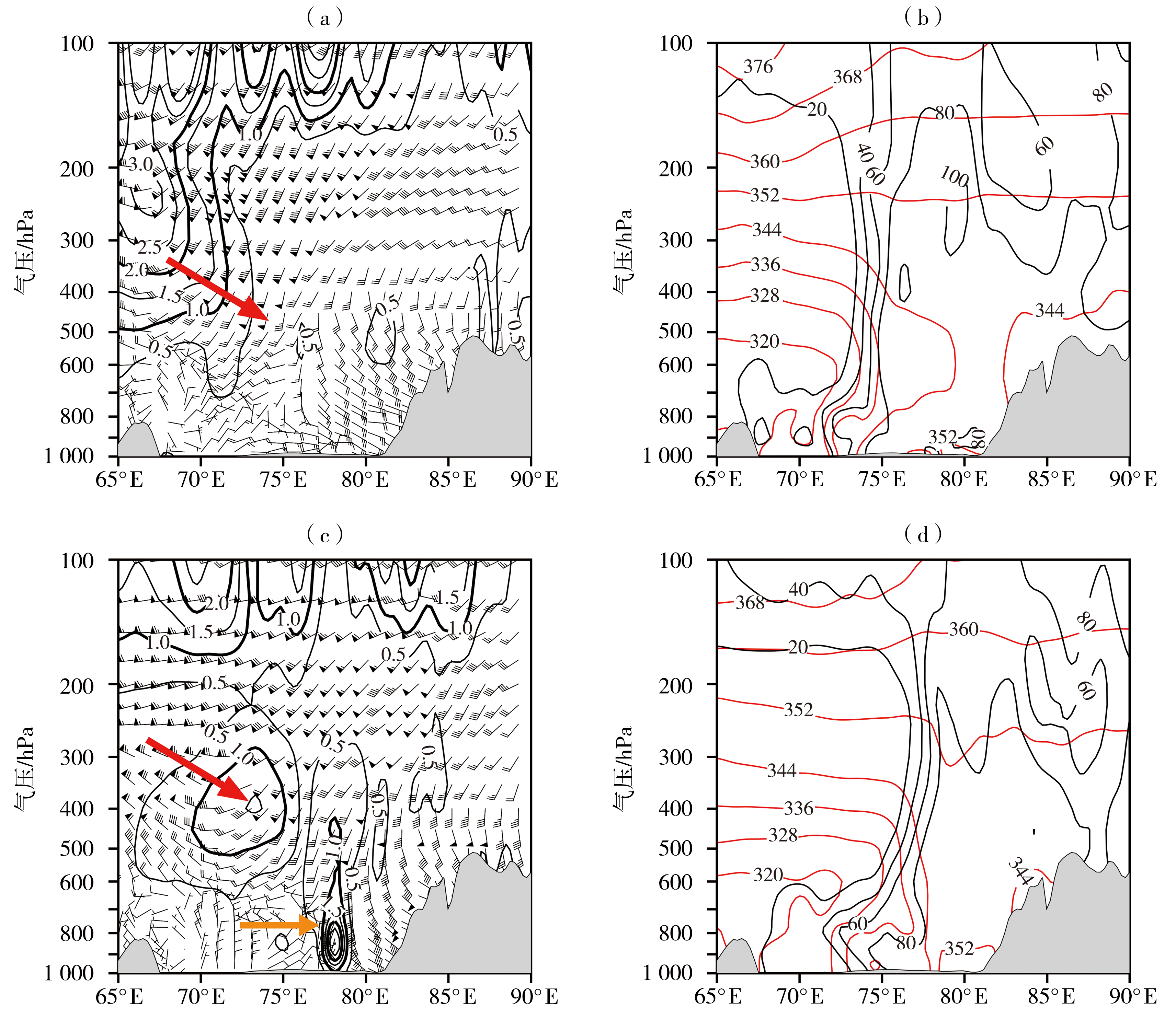
图6 2021年10月18日02:00(a、b)、18:00(c、d)位涡(黑色等值线,单位:10-6 m2·K·s-1·kg-1)和u、v水平风(风矢,单位:m·s-1)(a、c),相当位温(红色等值线,单位:K)和相对湿度(黑色等值线,单位:%)(b、d)沿28°N的纬向剖面
(灰色阴影区为地形;红色箭头指示位涡传播方向,橙色箭头指示低涡位置)
|
Fig.6 The zonal profiles of potential vorticity (black isolines, Unit: 10-6 m2·K·s-1·kg-1) and u,v wind (wind vectors, Unit: m·s-1) (a, c), equivalent potential temperature (red isolines, Unit: K) and relative humidity (black isolines, Unit: %) (b, d) along 28°N at 02:00 (a, b) and 18:00 (c, d) on 18 October 2021
(The gray shaded is terrain, and the red arrow indicates the direction of potential vortex propagation, while the orange arrow indicates the position of the low vortex)
|
|
|
|
|
