西北东部半干旱区一次极端特大暴雨的触发和维持机制
Mechanism of trigger and maintenance during an extremely torrential rain in semi-arid region of eastern Northwest China
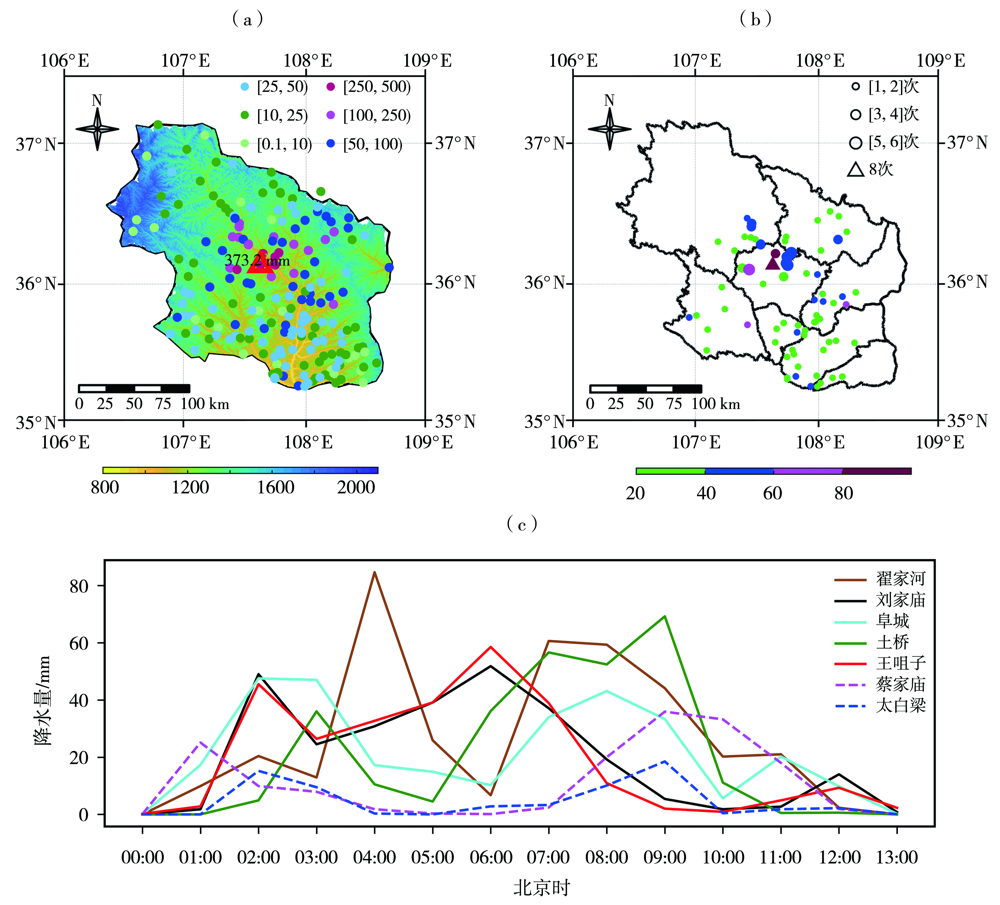
图1. 2022年7月14日20:00至15日20:00庆阳市累积降水量(a,彩色圆点,单位:mm;填色为地形高度,单位:m;红三角为翟家河站)、短时强降水(填色为最大小时雨量,单位:mm;圆圈为发生次数,三角为最大次数)分布(b)及15日00:00—13:00代表站小时降水量演变(c)
Fig.1. The distribution of accumulated precipitation (a, color dots, Unit: mm;the color shaded for the terrain height, Unit: m; the red triangle for Zhaijiahe station) and short-term heavy precipitation (the color shaded for maximum hourly precipitation, Unit: mm; the circles for heavy rainfall frequency, the triangle is the maximum frequency) (b) from 20:00 BST 14 to 20:00 BST 15 July 2022 in Qingyang and the evolution of hourly rainfall at representative stations from 00:00 BST to 13:00 BST 15 July 2022 (c)